Summary
. 2020;42(12):793-799
To find out which was the opinion of residents in obstetrics and gynecology about the advantages and disadvantages of medical abortion as compared with surgical procedures.
Cross-sectional multicenter study among residents in obstetrics and gynecology from 21 maternity hospitals located in 4 different geographical regions of Brazil, using a self-responded questionnaire with 31 questions related to their opinion and experience on providing abortion services.
Most residents agreed that “being less invasive” (94.7%), “does not require anesthesia” (89.7%), “can be accompanied during the process” (89.1%), “prevents physical trauma” (84.4%) were the main advantages of medical abortion.
Residents perceived both clinical and personal issues as advantages of medical abortion.
Summary
. 2020;42(12):800-804
In recent years, there has been an increase in the incidence of ectopic pregnancies; therefore, it is important for tertiary centers to report their approaches and outcomes to expand and improve treatment modalities. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the general characteristics, treatment and outcomes of cases diagnosed with ectopic pregnancy.
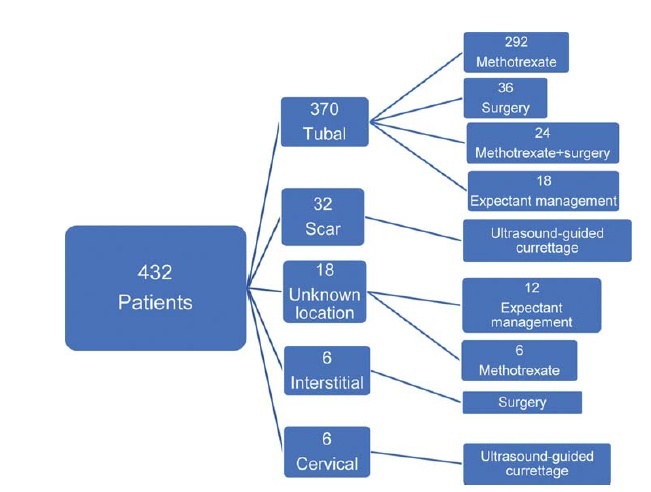
In total, 432 patients treated for ectopic pregnancy between February 2016 and June 2019 were retrospectively evaluated.
Overall, 370 patients had tubal pregnancy, 32 had cesarean scar pregnancy, 18 had pregnancy of unknown location, 6 had cervical pregnancy, and 6 had interstitial pregnancy. The most important risk factors were advanced age (> 35 years; prevalence: 31.2%) and smoking (prevalence: 27.1%). Thirty patients who did not have any symptoms of rupture and whose human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) levels were ≤ 200 mIU/ml were followed-up with expectant management, while 316 patients whose β-hCG levels were between 1,500 mIU/ml and 5,000 mIU/ml did not have an intrauterine gestational sac on the transvaginal or abdominal ultrasound, did not demonstrate findings of rupture, and were treated with a systemic multi-dose methotrexate treatment protocol. In total, 24 patients who did not respond to the medical treatment, 20 patients whose β-hCG levels were > 5,000 mIU/ml, 16 patients who had shown symptoms of rupture at the initial presentation, and 6 patients diagnosed with interstitial pregnancy underwent surgery. Patients with cervical and scar pregnancies underwent ultrasound-guided curettage, and no additional treatment was needed.
The fertility status of the patients, the clinical and laboratory findings, and the levels of β-hCG are the factors that must be considered in planning the appropriate treatment.
Summary
. 2020;42(12):805-810
To analyze the most frequent referrals for fetal echocardiography, including advanced maternal age and its association with abnormal results.
We included all pregnant women referred to perform fetal echocardiography (gestational age 22-32 weeks) in 2 health centers in Rio de Janeiro, from June 2015 to June 2016. Advanced maternal age was considered when age was > 35 years at the time of delivery). Referral reasons and results were recorded, according to the Brazilian Fetal Cardiology Statement. Crude and adjusted prevalence ratios were calculated (Poisson regression). We considered p < 0.05 as significant.
A total of 1,221 tests were analyzed. Abnormal fetal echocardiography was observed in 14.82% of the cases. The most frequent abnormalities were interventricular septal defect (6.39%), septal hypertrophy (3.35%) and atrioventricular septal defect (1.14%). Routine exams were performed in 559 women, 289 were referred for advanced maternal age and 373 were referred according to the Brazilian FetalCardiology Statement criteria. An obstetric ultrasound suggesting fetal cardiacabnormality, maternal diabetes, increased nuchal translucency, and obstetric ultrasound suggesting a noncardiac abnormality were strongly associated with an abnormal fetal echocardiography. Abnormal results were not more frequent in women with advanced maternal age when compared with the rest of the study group.
It was observed that routine exams and advancedmaternal age referrals were very frequent. Those exams were not associated to fetal echocardiography abnormalities. In this scenario, when the obstetric ultrasound suggests a fetal cardiac
Summary
. 2020;42(12):820-828
To evaluate the distribution of the main sociodemographic and clinicalpathological characteristics in women with breast cancer according to the molecular profile by immunohistochemistry.
A cross-sectional, retrospective, analytical and quantitative study was performed, with an analysis of 137 medical records from January 2015 to December 2018 of women attending the High Complexity in Oncology Unit of the city of Imperatriz, state of Maranhão, Brazil. The immunohistochemical profile of tumors based on the estrogen and progesterone receptor, Human Epidermal growth factor Receptor-type 2 (HER2) overexpression and Ki67 cell proliferation indexwas defined, fromwhich six molecular subtypes were determined: luminal A, luminal B-HER2 negative, luminal B-HER2 positive, triple negative, overexpression of HER2 and inconclusive.
A total of 52.6% of the patients were postmenopausal, mean age 52.1 years old, brown (56.2%), had a schooling level < 9 years (40%), staging > IIB (52.6%) and 23.4% hadmetastasis. Invasive ductal carcinoma accounted for 84.7%, tumor size was 2 to 5 cm (48.9%), with lymph node involvement (56.2%), axillary lymphadenectomy in 67.2%, andmastectomy in 73.7% of the patients. Themost frequentmolecular subtype was the luminal B-HER2 negative (36.5%), and the luminal A subtype showed characteristics of better prognosis when compared with the others.
It was concluded that in the association of molecular subtypes with sociodemographic and clinical-pathological characteristics, there were no statistically significant results obtained, except for complementary therapy, referring to hormone therapy, and there was a high index of metastasis at diagnosis, which was a worrying factor and indicative of failures in the screening and early diagnosis of this population.
Summary
. 2020;42(12):811-819
The present study aimed to investigate the physical performance of handgrip strength (HGS) in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
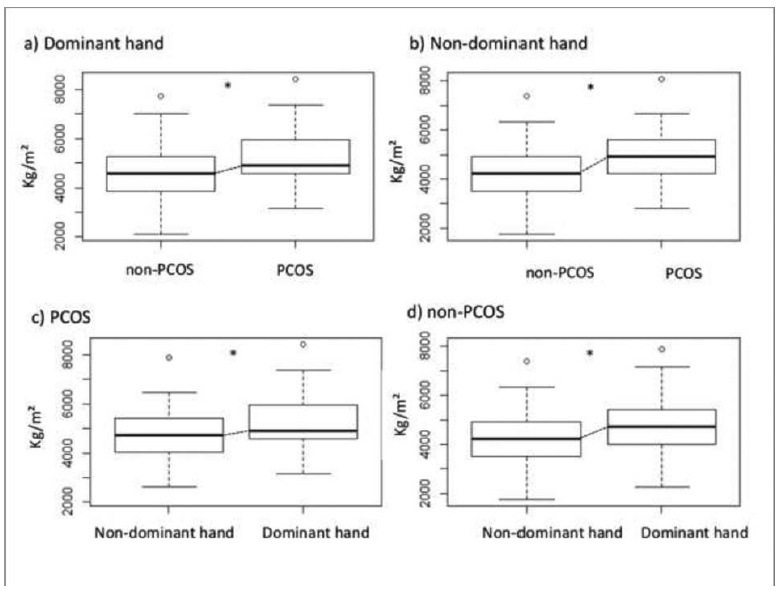
A case-control study that included 70 women with PCOS and 93 agematched healthy women aged between 18 and 47 years with body mass index (BMI) between 18 Kg/m2-39.9 Kg/m2. The serum levels of total testosterone, androstenedione, insulin, estradiol, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), prolactin, sex hormonebinding globulin (SHBG), and 17-hydroxyprogesterone (17-OHP) were measured. The free androgen index (FAI) and the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) were calculated. The body composition regions of interest (ROIs) were assessed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), and the handgrip strength (HGS) was evaluated for both the dominant and the non-dominant hands with a manual Sammons Preston (Bolingbrook, IL, US) bulb dynamometer.
Women with PCOS had high serum levels of total testosterone (p < 0.01), androstenedione (p = 0.03), and insulin (p < 0.01), as well as high FAI (p < 0.01) and HOMA-IR (p = 0.01) scores. Compared with the non-PCOS group, the PCOS group had greater total lean mass in the dominant hand (p < 0.03) and greater HGS in both the dominant and the non-dominant hands (p < 0.01). The HGS was correlated with lean mass (p < 0.01).
Women with PCOS have greater HGS. This may be associated with age and BMI, and it may be related to lean mass. In addition, the dominance effect on muscle mass may influence the physical performance regarding HGS in women with PCOS.
Summary
. 2020;42(10):597-606
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the quality of mother-child bonding in three different contexts related to the labor, that is, vaginal delivery, elective cesarean section, and intrapartum cesarean section.
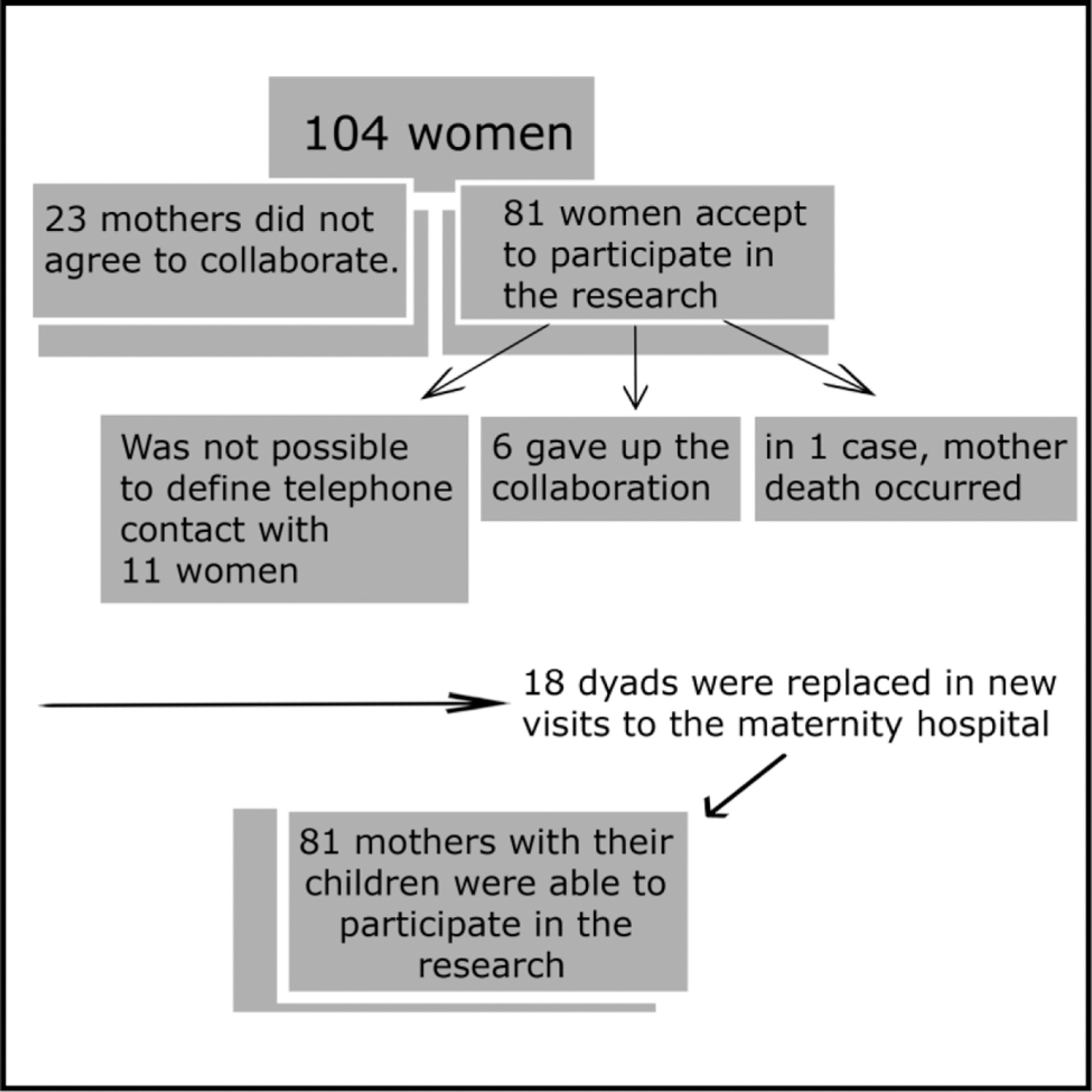
This was an observational, cross-sectional clinical study conducted in two cities within the state of São Paulo, Brazil. The study sample consisted of 81 babies born without any major complications during pregnancy and labor, aged 3 to 4 months, and their respective mothers, aged between 20 and 35 years old, primiparous, living in the cities of Palmital and Ourinhos, state of São Paulo, Brazil. The evaluation of the quality of the maternal-filial interaction was performed through video-image analysis, using the Mother-baby Interaction Observation Protocol from 0 to 6 months (POIMB 0-6, in the Portuguese acronym).
Mothers who had vaginal delivery had higher amount of visual contact or attempted visual contact (p = 0.034), better response to the social behavior of the child (p = 0.001) and greater sensitivity (p = 0.007) than the others. Their children also showed more interaction with them, as they looked more frequently at the mother's face (p ≤ 0.008) and responded more frequently to the mother's communicative stimulus (p < 0.001).
Considering the occurrence of vaginal delivery, it is concluded that the interaction between the mother-child dyad is quantitatively larger and qualitatively better when compared with intrapartum or elective cesarean section.
Summary
. 2020;42(10):607-613
The present study aims to analyze adverse fetal or neonatal outcomes in women with gestational diabetes, including fetal death, preterm deliveries, birthweight, neonatal morbidity and mortality, as well as the synergic effect of concomitant pregnancy risk factors and poor obstetric outcomes, as advanced maternal age, maternal obesity and pre-eclampsia in their worsening.
The present cohort retrospective study included all pregnant women with gestational diabetes, with surveillance and childbirth at the Hospital da Senhora da Oliveira during the years of 2017 and 2018. The data were collected from the medical electronic records registered in health informatic programs Sclinico and Obscare, and statistical simple and multivariate analysis was done using IBM SPSS Statistics.
The study participants included 301 pregnant women that contributed to 7.36% of the total institution childbirths of the same years, in a total of 300 live births. It was analyzed the influence of pre-eclampsia coexistence in neonatal morbidity (p = 0.004), in the occurrence of newborns of low and very low birthweight (p < 0.01) and in preterm deliveries (p < 0.01). The influence of maternal obesity (p = 0.270; p = 0.992; p = 0.684) and of advanced maternal age in these 3 outcomes was also analyzed (p = 0,806; p = 0.879; p = 0.985).Using a multivariate analysis, the only models with statistic significance to predict the three neonatal outcomes included only pre-eclampsia (p = 0.04; p < 0.01; p < 0.01).
Only coexistence of pre-eclampsia showed an association with adverse neonatal outcomes (neonatal morbidity, newborns of low and very low birthweight and preterm deliveries) and can be used as a predictor of them in women with gestational diabetes.
Summary
. 2020;42(10):614-620
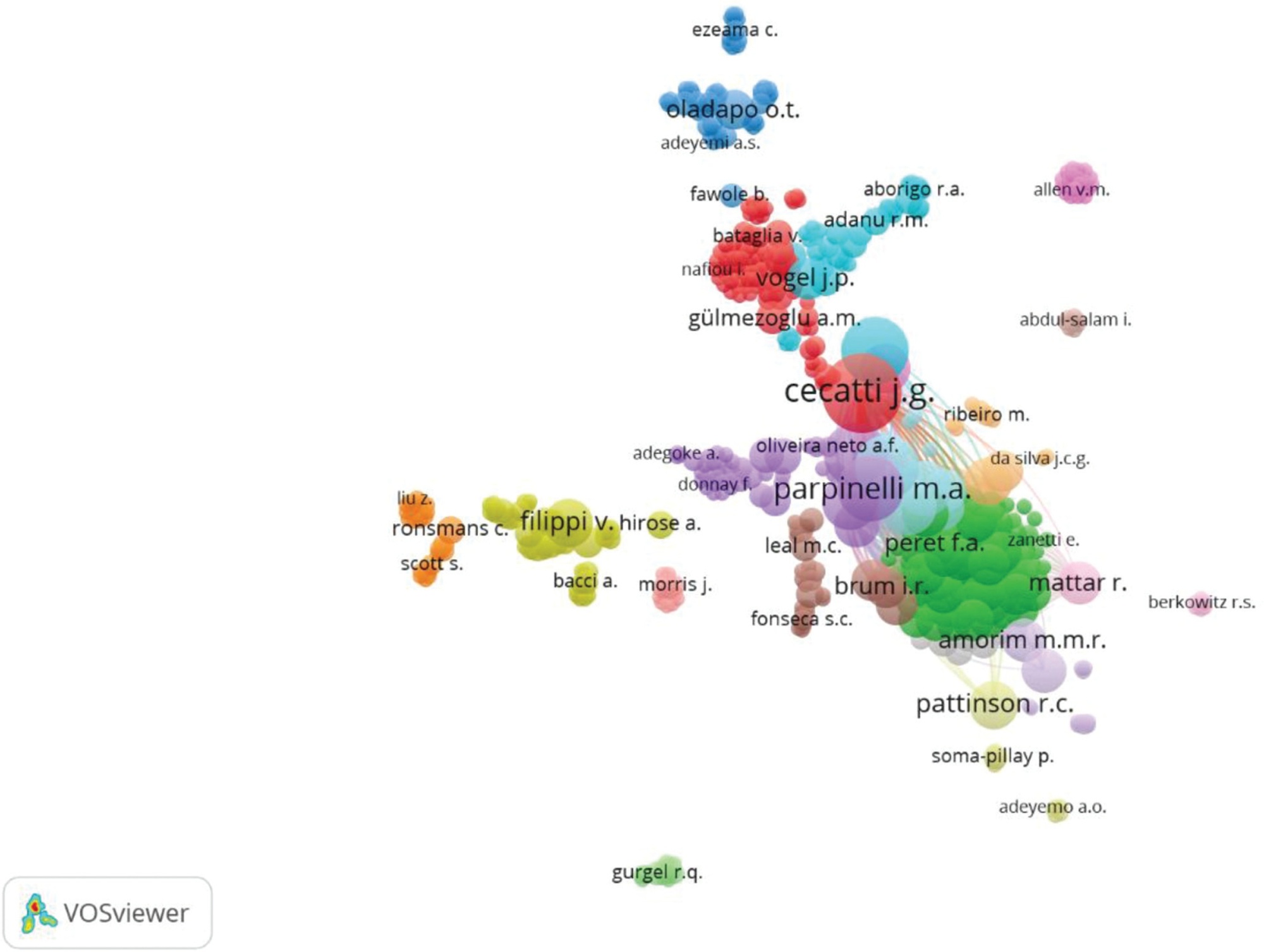
To evaluate the global productivity regarding original articles on maternal near-miss (MNM).
We conducted a bibliometric analysis of original articles published from 2008 to November 2019 in the journals indexed in the Scopus database. The averages of the number of articles by author, of the number of authors by article, of the number of citations by article, and the total number of documents with one or more authors were obtained. An analysis of the co-citation of authors and a co-occurrence analysis of the terms included in the titles and abstracts were performed and were presented as network visualization maps.
A total of 326 original articles were analyzed. There was an increase in the number of articles (p < 0.001; average annual growth rate = 12.54%;). A total of 1,399 authors, an average number of articles per author of 4.29, with an index of authors per document of 0.23, and an index of co-authors per document of 8.16 were identified. A total of 85 countries contributed with original articles on MNM. Among the top ten countries regarding the contribution of articles, five were low and middle-income countries (LMICs). Brazil had the highest volume of production (31.1%;), followed by the US (11.5%;). Terms related to countries and the measurement of the rates and cases of MNM and the associated factors were found in recent years in the analysis of the co-occurrence of terms.
There was an increase in the production of original articles on MNM, with a significant participation of authors and institutions from LMICs, which reveals a growing interest in the use of MNM indicators to improve the quality of maternal health care.