Summary
. 2022;44(2):169-177
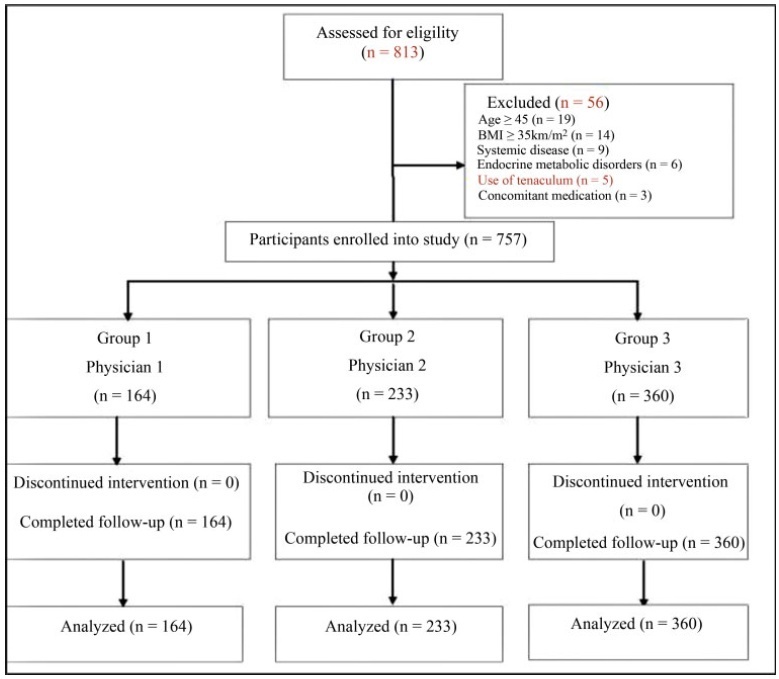
To evaluate genital hygiene among women with and without bacterial vaginosis (BV) and/or vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC).
A cross-sectional study of reproductive-aged women who underwent gynecological and laboratory tests and fulfilled a genital hygiene questionnaire.
This study evaluated 166 healthy controls and 141 women diagnosed with either BV (n=72), VVC (n=61), or both (n=8). The use of intimate soap and moist wipes after urination was more frequent among healthy women (p=0.042 and 0.032, respectively). Compared to controls, bactericidal soap was more used by women with BV (p=0.05).
Some hygiene habits were associated to BV and/or VVC. Clinical trials should address this important issue in women’s health.
Summary
. 2022;44(2):178-186
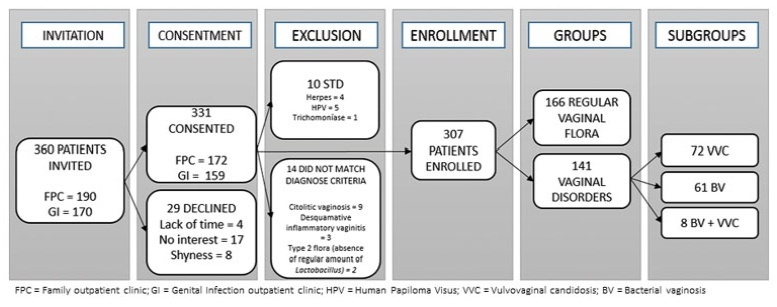
To determine the accuracy of colposcopy findings in diagnosing cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) in women with an atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (ASC-H) pap smear result and analyze whether the prevalence of HSIL and cancer correlates with sociodemographic risk factors and specific colposcopic findings.
Colposcopic findings and sociodemographic risk factors were analyzed as possible predictors of a CIN 2 or worse diagnosis in women with an ASC-H pap smear result.
Accuracy of the colposcopic impression was 92%, sensitivity was 91.6%, and specificity was 93.1%, with a positive predictive value of 96.4% and negative predictive value of 84.3%. Diagnosis of CIN 2 or worse was more frequent in patients with a previous history of cervical dysplasia and pre-menopausal patients. Identification of major colposcopic findings, dense acetowhite epithelium, coarse mosaicism, and punctuation correlated significantly with CIN 2 or worse.
Colposcopy performed by an experienced examiner can accurately differentiate patients with CIN 1 or less from patients with CIN 2 or worse. Diagnosis of CIN 2 or worse was more frequent in patients with a previous history of cervical dysplasia and pre-menopausal patients. The degree of acetowhite changes was the best colposcopic feature to predict CIN2 or worse.
Summary
. 2022;44(2):91-99
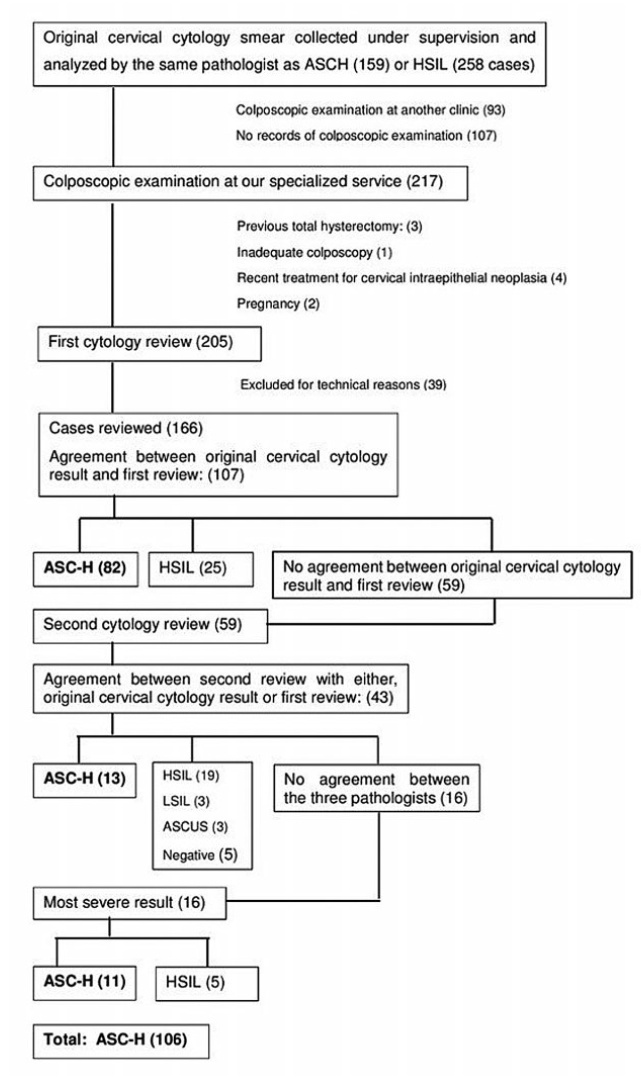
To investigate the dietary total antioxidant capacity (DTAC) of pregnant women, and associated factors.
Cross-sectional study conducted with 785 pregnant adult women attended in primary health care centers of Ribeirão Preto, state of São Paulo, Brazil. Two 24-hour dietary recalls were obtained, and the usual intake was estimated through the Multiple Source Method. The DTAC was estimated using the ferric reducing antioxidant power assay. The relationship between the higher DTAC estimate (≥ median of 4.3 mmol/day) and associated factorswas investigated usingadjusted logisticmodels with backward selection.
In total, 25% of the pregnant women were classified as overweight, and 32% as obese. Themedian (P25, P75)DTAC was 4.3 (3.3-5.6)mmol/day. Through adjusted logistic regression models with backward selection, a higher chance of DTAC estimates above the median among pregnant womenaged ≥ 35 years old (2.01 [1.24-3.27])was verified when compared with younger pregnant women. Women with prepregnancy overweight (0.63 [0.45-0.89]) and obesity (0.59 [0.40-0.88]) presented a lower chance of DTAC estimates above the median when compared with eutrophic pregnant women. A higher DTAC estimate was positively associated with the use of dietary supplements (1.39 [1.03-1.88]), and negatively associated with total dietary energy (0.59 [0.42-0.85]).
The DTAC estimate over the median was associated with greater age, adequate body weight, use of dietary supplements, and lower energy intake.
Summary
. 2022;44(4):360-368
To assess the levels of physical activity and exercise practice, and examine the associated maternal characteristics; as well as the anxiety levels of high-risk pregnant women.
A cross-sectional study conducted with pregnant women at a High-risk Prenatal Clinic (HRPC) in a tertiary maternity. Pregnant women of 18 to 40-years-old, with a single fetus, and with gestational age up to 38 weeks were included. The level of physical activity and exercise practice of the study’s participants were investigated using the Pregnancy Physical Activity Questionnaire (PPAQ). Maternal sociodemographic, anthropometric, and medical data were investigated using a specific form. For anxiety levels, the short version of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) was applied. We used the Student t-test, chi-square test, odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) and multiple logistic regression. The significance level was 5%.
Among the 109 pregnant women included, 82 (75.2%) were classified as sedentary/little active. The higher energy expenditure were for domestic activities (133.81±81.84 METs), followed by work-related activities (40.77±84.71 METs). Only 19.3% women exercised during pregnancy (4.76±12.47 METs), with slow walking being the most reported exercise. A higher level of education was the most important factor associated with women being moderately or vigorously active (OR=29.8; 95% CI 4.9-117.8). Nulliparity (OR=3.1; 95% CI 1.0-9.1), low levels of anxiety (OR=3.6; 95% CI 1.2-10.7), and unemployment (OR=4.8; 95% CI 1.1-19.6) were associated with the practice of exercise during pregnancy.
Most women with high-risk pregnancies exhibited a sedentary pattern, with low prevalence of physical exercise practice. Recognizing factors that hinder the adoption of a more physically active lifestyle is essential for an individualized guidance regarding exercise during pregnancy.
Summary
. 2022;44(4):385-390
To evaluate the role of cervical cytology (Pap smear) in the diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2 or greater (CIN2+), presented exclusively in the endocervical canal, the clinical-epidemiological characteristics of this lesion, the necessary length of canal to be removed to treat, and the rate of invasive lesion hidden in the endocervical canal.
Cross-sectional study, by database analysis, of patients with abnormal cytology (high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion [HSIL]), without visible colposcopy lesion, submitted to loop electrosurgical procedure (LEEP) to evaluate the association of cytology results with the histological product of the conization, to identify the epidemiological characteristics of endocervical lesion and clinical evolution, using a pvalue< 0.05 and 95% CI.
In 444 cases, the Pap smear sensitivity for CIN2+ diagnosis was 75% (95% CI: 69.8-79.7), specificity was 40% (95% CI: 30.2-49.5), and the prevalence rate of histological lesion was 73% (95% CI: 70.1-78.7). There was a higher prevalence of CIN2+ in women over 42 years old and invasive cancer in those over 56 years old (p<0.001), and it was necessary to remove 2.6 cm in length of the canal to reduce the chance of recurrence (p<0.006). The rate of invasive cancer was 2.7%.
Cytology was related to a high prevalence to histological lesion (73%) in the diagnosis of CIN2+ in the endocervical disease; older patients presented a higher relationship with histological lesions in the canal disease, and it was necessary to remove an average of 2.6 cm in length of the endocervical canal to avoid the persistence and progression of CIN. The rate of occult neoplasia in the endocervical canal was 2.7%.
Summary
. 2022;44(5):452-457
To detect depression during pregnancy and in the immediate postpartum period using the Edinburgh postpartum depression scale (EPDS).
Cross sectional study of 315 women, aged between 14 and 44 years, who received perinatal care at the Leonor Mendes de Barros Hospital, in São Paulo, between July 1st, 2019 and October 30th, 2020. The cutoff point suggesting depression was ≥ 12.
The screening indicated 62 (19.7%) patients experiencing depression. Low family income, multiparity, fewer prenatal appointments, antecedents of emotional disorders, dissatisfaction with the pregnancy, poor relationship with the partner, and psychological aggression were all risk factors associated with depression in pregnancy or in the immediate postpartum period. Antecedents of depression and psychology aggression during pregnancy were significant variables for predicting perinatal depression in the multivariate analysis.
There is a significant association between the occurrence of perinatal depression and the aforementioned psychosocial factors. Screening patients with the EPDS during perinatal and postpartum care could facilitate establishing a line of care to improve the wellbeing of mother and infant.
Summary
. 2022;44(1):10-18
To characterize and compare the outcomes of omphalocele and gastroschisis from birth to 2 years of follow-up in a recent cohort at a tertiary center.
This is a retrospective clinical record review of all patients with gastroschisis and omphalocele admitted to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit between January 2009 and December 2019.
There were 38 patients, 13 of whom had omphalocele, and 25 of whom had gastroschisis. Associated anomalies were present in 6 patients (46.2%) with omphalocele and in 10 (41.7%) patients with gastroschisis. Compared with patients with omphalocele, those with gastroschisis had younger mothers (24.7 versus 29.6 years; p=0.033), were born earlier (36 versus 37 weeks, p=0.006), had lower birth weight (2365±430.4 versus 2944.2±571.9 g; p=0.001), and had a longer hospital stay (24 versus 9 days, p=0.001). The neonatal survival rate was 92.3% for omphalocele and 91.7% for gastroschisis. Thirty-four patients were followed-up over a median of 24 months; 13 patients with gastroschisis (59.1%) and 8 patients with omphalocele (66.7%) had at least one adverse event, mainly umbilical hernia (27.3% vs 41.7%), intestinal obstruction (31.8% vs 8.3%), or additional surgical interventions (27.3% vs 33.3%).
Despite the high proportion of prematurity, low birth weight, and protracted recovery, gastroschisis and omphalocele (without chromosomal abnormalities) may achieve very high survival rates; on the other hand, complications may develop in the first years of life. Thus, a very positive perspective in terms of survival should be transmitted to future parents, but they should also be informed that substantial morbidity may occur in the medium term.
Summary
. 2022;44(1):19-24
To evaluate whether there is an effect of the physician who transfers the embryos on pregnancy rates in in vitro fertilization-intracytoplasmic sperm injection (IVF-ICSI) treatment.
A total of 757 participants were analyzed between 2012 and 2017. Participants were classified according to 3 physicians who transferred the embryos: ([group 1=164 patients]; [group 2=233 patients]; [group 3=360 patients]). Baseline parameters and IVF-ICSI outcomes were compared between the groups.
No differences were determined between the groups regarding the baseline parameters (age, age subgroups [20-29, 30-39, and ≥ 40 years old)], body mass index (BMI), smoking status, infertility period, cause of infertility, baseline follicle stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone, estradiol (E2), thyroid stimulating hormone, prolactin levels, antral follicle count, duration of stimulation, stimulation protocol, gonadotropin dose required, maximum E2 levels, progesterone levels, endometrial thickness on human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) administration and transfer days (p>0.05). The numbers of oocytes retrieved,metaphase II (MII), 2 pronucleus (2PN), transferred embryo, fertilization rate, day ofembryo transfer, the catheter effect and embryo transfer technique, and clinical pregnancy rates (CPRs) were also comparable between the groups (p>0.05).
Our data suggests that the physician who transfers the embryos has no impact on CPRs in patients who have undergone IVF-ICSI, but further studies with more participants are required to elucidate this situation.