-
Original Article
Depression, anxiety, sexual function and quality of life in women with hyperprolactinemia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo7
04-30-2025
Summary
Original ArticleDepression, anxiety, sexual function and quality of life in women with hyperprolactinemia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo7
04-30-2025Views26Abstract
Objective:
To evaluate anxiety, depression, sexual function and quality of life in women with hyperprolactinemia.
Methods:
Cross-sectional study with 80 women divided into two groups: 30 women with hyperprolactinemia (Study Group) followed and treated at the endocrine gynecology outpatient clinic and 50 women without hyperprolactinemia, with regular menstrual cycles (Control Group) followed at the family planning outpatient clinic of the State University of Campinas from June 2021 to October 2022. Sociodemographic characteristics, quality of life (SF-36 Questionnaire), sexual function (Female Sexual Function Index Questionnaire), depression (Beck Depression Inventory) and anxiety (Beck Anxiety Scale) were evaluated in both groups. Categorical variables were described as absolute frequency and percentage; numerical variables as mean and standard deviation. Comparison of numerical variables between two groups was performed by Mann-Whitney test, while categorical were compared by Chi-Square or Fisher's exact tests.
Results:
The mean age of women with hyperprolactinemia was 39.6±8.1 years and the Control Group was 31.2±9.5 years (p<0.001). There was no difference in anxiety scores (p=0.66), depression (p=0.08) and general sexual function (p=0.08) in both groups. However, women with hyperprolactinemia had lower scores in the domains of pain and arousal and worse functional capacity than Control Group (p<0.05).
Conclusion:
Women with hyperprolactinemia under treatment do not show any impairment in their anxiety, depression and sexual function when compared to women without hyperprolactinemia. However, analysis of quality of life showed that women with hyperprolactinemia have poor functional capacity.
Key-words AnxietyDepressionHyperpituitarismHyperprolactinemiaQuality of lifesexual functionsurveys and questionnairesSee more -
Original Article
Evaluation of pathological complete response rates in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo13
04-30-2025
Summary
Original ArticleEvaluation of pathological complete response rates in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo13
04-30-2025Views23See moreAbstract
Objective:
This study aims to assess the rate of pathological complete response (pCR) in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy and to explore its correlation with clinical, molecular, and prognostic factors.
Methods:
We conducted this retrospective observational study at Liga Contra o Câncer, a major public oncology reference center in Northeast Brazil. We included patients diagnosed with breast cancer who initiated neoadjuvant therapy between June 2018 and June 2019. Patients with a history of recurrent breast cancer or those who did not undergo surgery were excluded. The primary outcome was the pCR rate, with secondary outcomes including Overall Survival (OS), Disease-Free Survival (DFS), mortality, and disease recurrence. Follow-up extended until August 2022. We performed multivariate Cox regression analysis to correlate outcomes with predetermined variables.
Results:
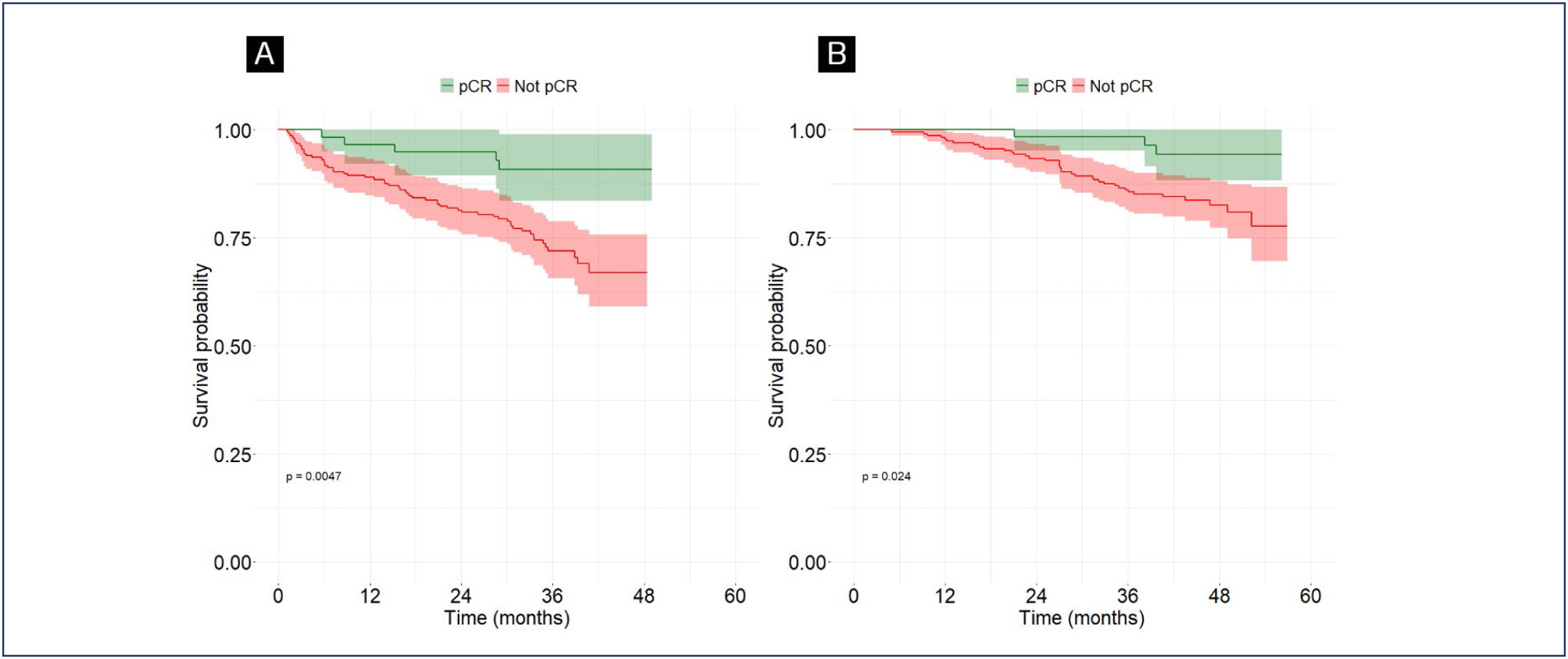
Of the 292 included patients, 63 (21.6%) achieved pCR. The mean follow-up duration was 42.8 months. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed an association between pCR and the AC-TH regimen [OR = 2.4; 95%CI = 1.13 - 5.24; p=0.023], as well as between pCR and HER2-positive tumors [OR 2.49; 95% CI = 1.14 - 5.86; p=0.028]. Complete pathological response was associated with higher DFS [HR 0.33; 95%CI 0.13-0.86; p=0.024].
Conclusion:
Neoadjuvant therapy demonstrated significant efficacy in achieving pathological response in breast cancer patients. We observed a strong association between the AC-TH regimen, HER2-positive status, and pCR.
-
Original Article
Clinical and epidemiological profile of pregnant and postpartum women affected by COVID-19 who required respiratory support
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo14
04-30-2025
Summary
Original ArticleClinical and epidemiological profile of pregnant and postpartum women affected by COVID-19 who required respiratory support
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo14
04-30-2025Views20Abstract
Objective:
This study described the clinical and epidemiological profile and the management provided to pregnant and postpartum women with COVID-19 who required respiratory support.
Methods:
A descriptive study was conducted with pregnant and postpartum women with confirmed COVID-19 who received care between April 2020 and December 2021 in eight referral centers in northeastern Brazil. Statistical analysis was conducted using Epi-Info 7.2.5 and Medcalc, version 20.112.
Results:
Of the 720 patients admitted, 208 (32.7%) required respiratory support. Mean age of the participants was 28.9±7.1 years. Most (52.8%) were brown-skinned; 31.3% had little formal schooling; 41.1% had a personal income and 23.1% were married. Around half were referred from another hospital. Overall, 36.8% were obese and 36.9% were hypertensive. Criteria for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) were present in 80.7% of cases. Overall, 151 patients (74.7%) required corticoids, and 150 (76.1%) were admitted to an intensive care unit. Non-invasive ventilation was needed in 89.4% of cases, with nasal catheters being the most common type (55.3% of cases). Invasive mechanical ventilation was necessary in 35.5% of cases and 91.6% had a cesarean section. Maternal near miss and death occurred in 24% and 12.9% of cases, respectively.
Conclusion:
Pregnant and postpartum women with COVID-19 who required respiratory support were predominantly brown-skinned, in the third trimester of pregnancy and had been referred from another hospital. The cesarean section rate was high; the presence of criteria for SARS was common and the rates of COVID-19-related maternal near miss and death were high.
Clinical Trials registry:
NCT04462367
Key-words Cesarian sectionCOVID-19Intensive care unitsNear miss, healthcareNoninvasive ventilationObesityPostpartum periodPregnancyPregnancy trimester, thirdRespiration, artificialSARS-CoV-2severe acute respiratory syndromeSee more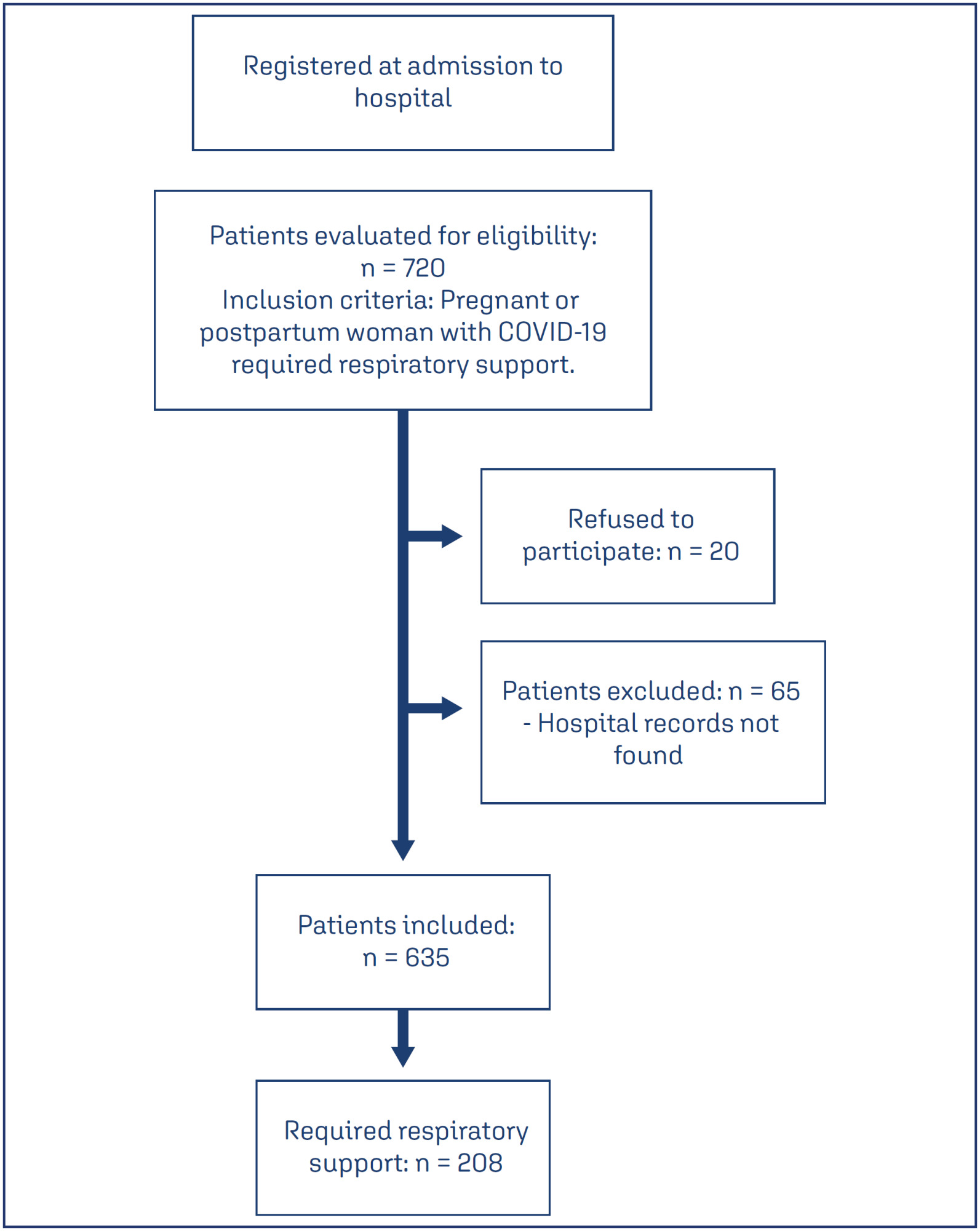
-
Original Article
The ımpact of demographic and obstetric factors on perception of traumatic birth and breastfeeding attitudes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo15
04-30-2025
Summary
Original ArticleThe ımpact of demographic and obstetric factors on perception of traumatic birth and breastfeeding attitudes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo15
04-30-2025Views23Abstract
Objective:
This study aims to examine the effects of sociodemographic and obstetric factors on traumatic birth perception and breastfeeding attitudes in primiparous mothers who have had a vaginal birth in the early postpartum period.
Methods:
The sample of the research, developed with a cross-sectional and correlational design, consisted of 252 women residing in a province in the Western Black Sea region of Türkiye. The data were obtained by employing a Personal Information Form, Traumatic Childbirth Perception Scale, and Breastfeeding Attitudes of The Evaluation Scale. Data analysis was conducted using the statistical programming language R (R version 4.3.3).
Results:
Women who were not employed, had a planned pregnancy, and did not experience health problems during pregnancy had higher mean breastfeeding attitude scores, and this difference was statistically significant. It was determined that a one-unit increase in gestational week led to an average increase of 1.926 units in breastfeeding attitude score, and a one-unit increase in Traumatic Childbirth Perception Scale score led to an average decrease of 0.110 units in breastfeeding attitude score. The mean traumatic childbirth perception scores of women living in urban areas were found to be lower than those living in villages or towns, and the difference was statistically significant.
Conclusion:
The research findings indicate that gestational age, perception of traumatic childbirth, and certain sociodemographic factors significantly affect breastfeeding attitudes. Additionally, mothers living in urban areas have a lower perception of traumatic childbirth. Therefore, individualized approaches to childbirth and breastfeeding support are crucial.
Key-words Breast feedingDelivery, obstetricParturitionperceptionPostpartum periodSociodemographic factorsStress disorders, post-traumaticSee more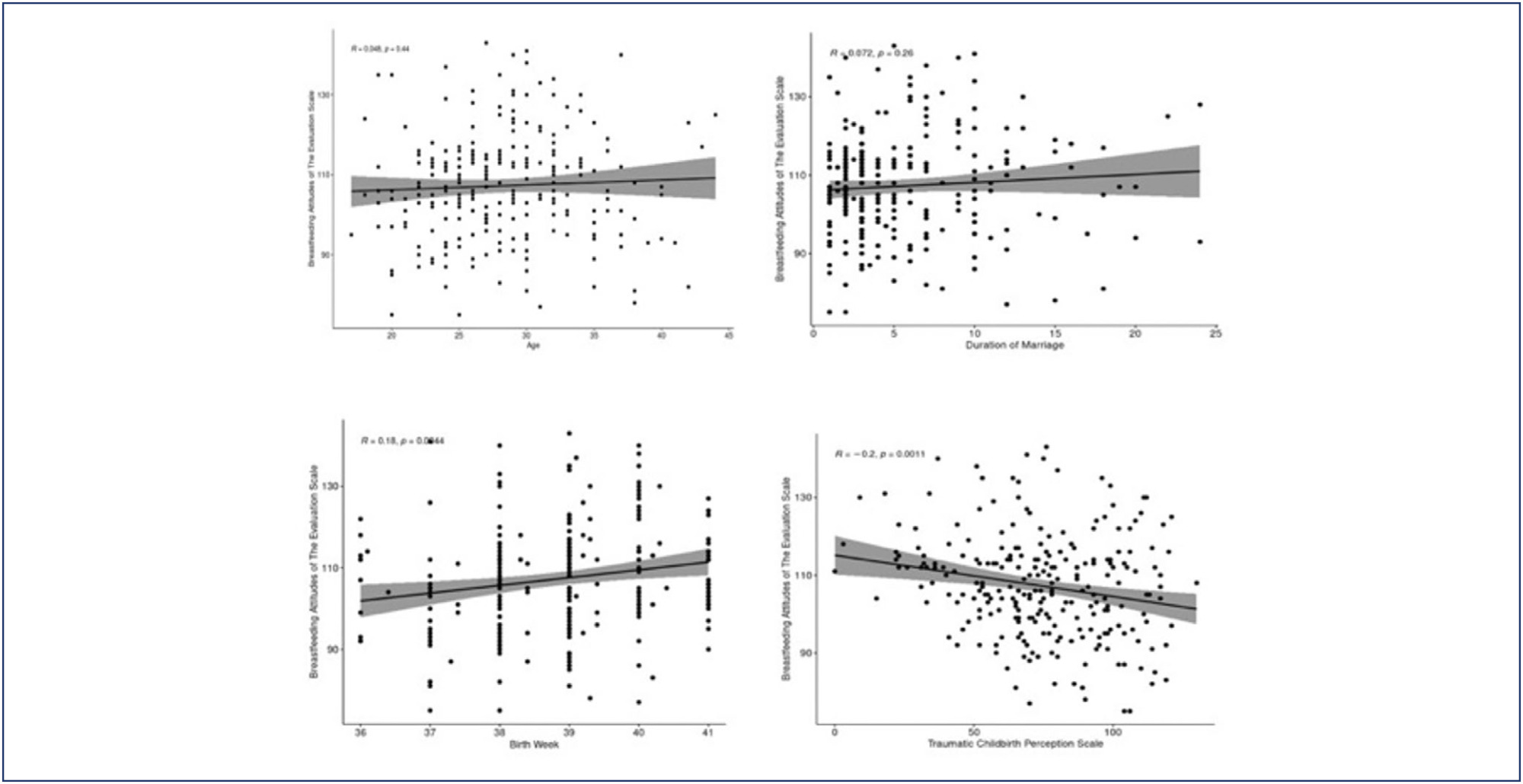
-
Original Article
Effects of domestic violence on menopausal symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo16
04-30-2025
Summary
Original ArticleEffects of domestic violence on menopausal symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo16
04-30-2025Views48Abstract
Objective:
To investigate the association between lifetime experience of domestic violence and climacteric symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life in climacteric women in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted with 700 pre-, peri-, and postmenopausal women, recruited online via an anonymous questionnaire (REDCap platform). Women aged 40 to 65 years, residing in Rio Grande do Sul, and classified by the STRAW+10 criteria were included. Climacteric symptoms and sexual function were assessed using the 10-item Cervantes Scale (CS-10) and the 6-item Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI-6). Data were analyzed using SPSS version 18.0; quantitative data as median [IQR], qualitative as frequencies. Group comparisons used Kruskal-Wallis, Chi-Square, and Spearman's correlation between violence against women (VAW) and/or climacteric groups on CS-10 or FSFI-6. Significance was set at 5%.
Results:
The median [IQR] age of pre- (46 [43 - 50] years), peri- (50 [47 – 52] years), and postmenopausal (55 [51 – 58] years) were different among groups. Prevalence rates of psychological (38.8%), sexual (34.9%), and physical (21.3%) violence were observed. Postmenopausal women showed the poorest outcomes. Premenopausal women experiencing violence had severe anxiety, while postmenopausal women reported feeling worthless. Various sexual dysfunctions were associated with violence, including low desire, lubrication issues, and sexual pain.
Conclusions:
Domestic violence was linked to worse climacteric symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life, particularly in postmenopausal women. These findings underscore the need for improved care and public policies to enhance safety and well-being among women of all ages.
Key-words AnxietyClimactericDomestic violenceMenopausePostmenopauseQuality of lifeSexualitysurveys and questionnairesViolence against womenSee more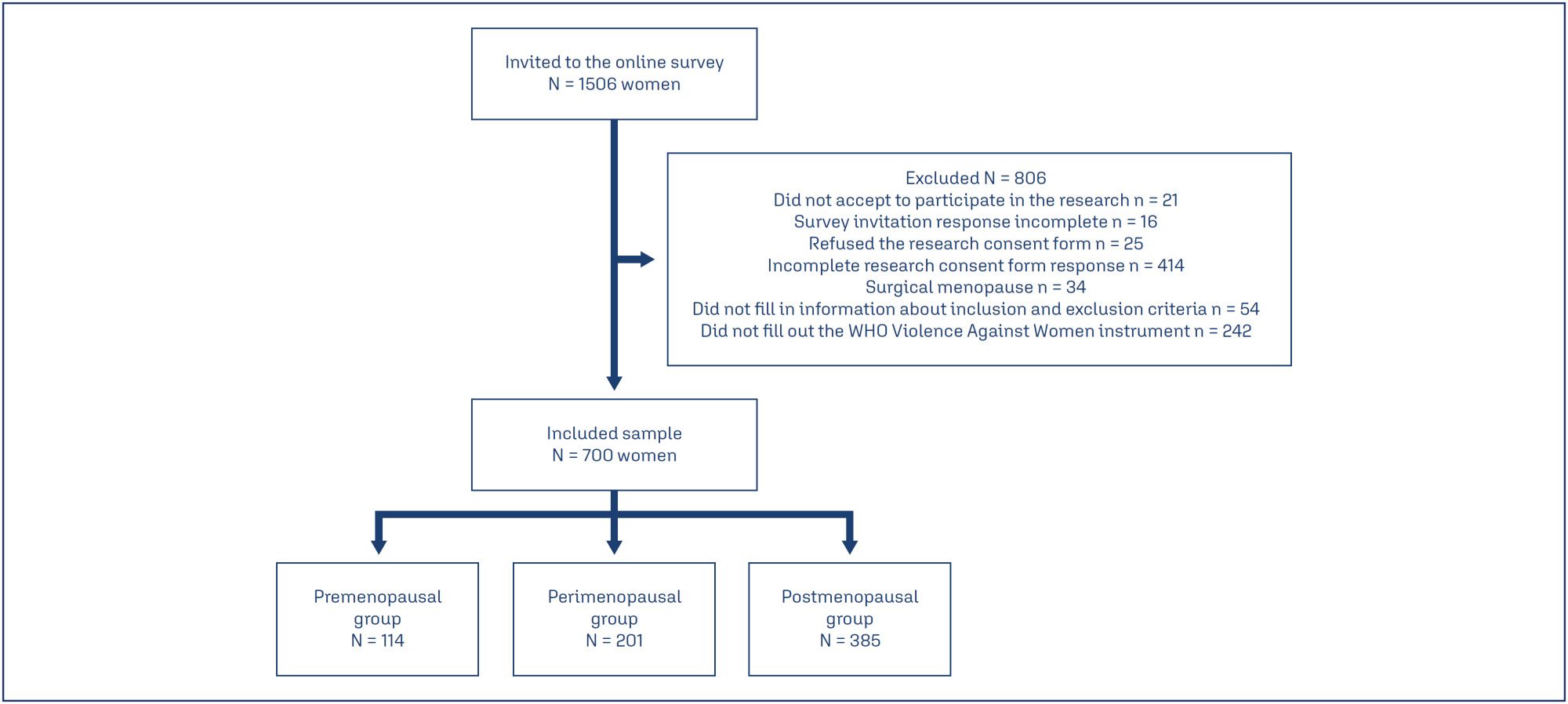
-
Original Article
Assessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo17
04-30-2025
Summary
Original ArticleAssessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo17
04-30-2025Views40Abstract
Objective:
This retrospective study aimed to investigate blood-based immune-inflammatory biomarkers (IIBs) in predicting neonatal outcomes in pregnancies with pregestational diabetes mellitus (PGDM).PIV[(neutrophil×platelet×monocyte)/lymphocyte)], SII (neutrophil×platelet/lymphocyte), and NLR neutrophil/lymphocyte) values were evaluated in all three trimesters, and their correlation with neonatal outcomes was examined.
Methods:
We included 82 cases of PGDM pregnancies delivered after 32 weeks. Maternal age, gravidity, parity, types of diabetes, and route of delivery were noted. For neonatal outcomes, we recorded gestational age at birth, birth weight percentile, existence of fetal growth restriction, LGA, neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) requirement, Apgar Score <7 at 1, 5, or 10 minutes, need for positive pressure ventilation (PPV), need for mechanical ventilation, hypoglycaemia, hyperbilirubinemia and the need for phototherapy. PIV, SII and NLR values were calculated in each trimester and their association with adverse neonatal outcomes was analyzed.
Results:
We could not detect any consistent and significant correlation between SII and PIV values and adverse neonatal outcomes for each trimester. There was a correlation between 3rd trimester NLR and adverse neonatal outcomes, including APGAR <7, the requirement for PPV and mechanical ventilation (p=0.056, 0.013 and 0.060, respectively).
Conclusion:
While SII and PIV values did not consistently correlate with adverse neonatal outcomes throughout each trimester in PGDM pregnancies, 3rd-trimester NLR showed a notable association with the requirement for PPV with statistical significance and with Apgar Score <7 and the requirement for mechanical ventilation without statistical significance. NLR in the third trimester may hold potential as a predictive marker for specific adverse neonatal outcomes in PGDM pregnancies, warranting further investigation.
Key-words biomarkersDiabetes mellitusGestational ageHypoglycemiaInfant, newbornIntensive care units, neonatalLymphocytesMaternal ageMonocytesNeuthrophilsPregancyPregnancy in diabetesRespiration, artificialSee more -
Original Article
Incidence of small-for-gestational-age newborns in pregnant women with COVID-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo20
04-30-2025
Summary
Original ArticleIncidence of small-for-gestational-age newborns in pregnant women with COVID-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo20
04-30-2025Views41Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to assess the incidence of small for gestational age (SGA) newborns in pregnant women infected with COVID-19 and examine the associated neonatal outcomes.
Methods:
This study involved a secondary analysis of the REBRACO Network, a prospective cohort study conducted in 15 maternity hospitals in Brazil before the introduction of COVID-19 vaccination (February 2020 to February 2021). Demographic data of pregnant women tested for COVID-19 were analyzed, and fetal outcomes were compared between women with positive and negative COVID-19 results who had SGA fetuses.
Results:
A total of 729 symptomatic pregnant women with COVID-19 were included in the study. However, there were 248 participants with missing information regarding childbirth or loss of follow-up, and 107 participants without confirmatory tests for COVID-19. Among the remaining participants, 198 had confirmed COVID-19 and 176 tested negative. The incidence of SGA among women with COVID-19 was 22.4%, whereas the incidence among women who tested negative for COVID-19 was 14.8%. SGA newborns born to COVID-19 positive pregnant women were 1.6 times more likely to experience adverse outcomes (such as prematurity, stillbirth, neonatal death, and admission to a neonatal ICU) compared to non-SGA newborns [OR = 1.655 (1.145 – 2.394); P=0.017]. In SGA newborns of pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection, mechanical ventilation use was found to be associated with the infection [OR = 0.692 (0.562 – 0.853); P=0.002].
Conclusion:
The higher incidence of SGA newborns and its stronger association with prematurity in pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection suggest that COVID-19 infection is a significant factor contributing to neonatal morbidity and mortality.
Key-words coronavirus infectionsCOVID-19Infant, newbornInfant, small for gestational agematernal healthPregnancy complicationsSee more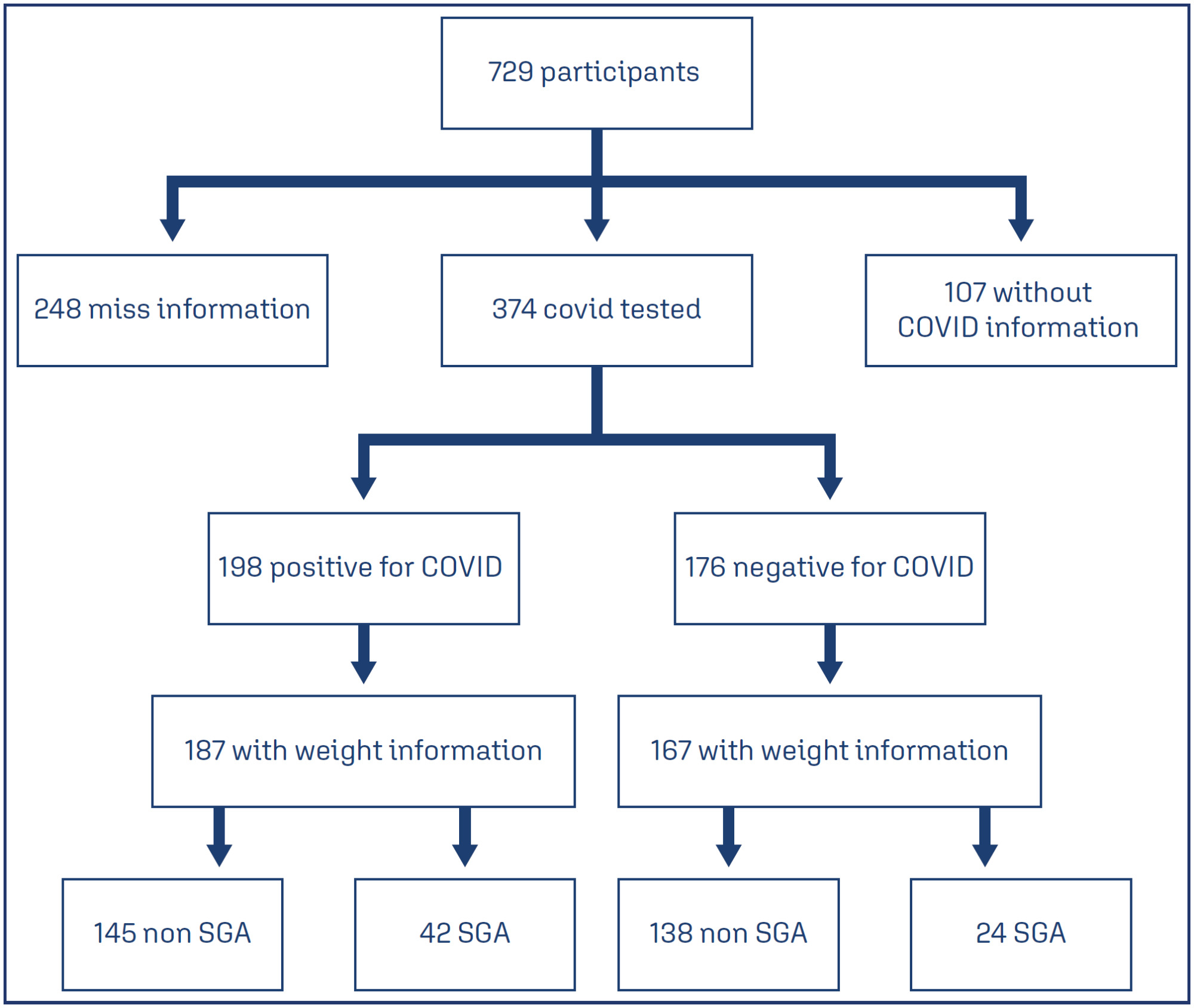
-
Original Article
An assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
04-30-2025
Summary
Original ArticleAn assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
04-30-2025Views47Abstract
Objective:
In vitro, fertilization is the primary treatment method for infertility. Follicular fluid analysis is an approach used to optimize the results of assisted reproductive techniques. Oxidative stress represents the imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and their detoxification. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative Stress Index levels are the main oxidative stress markers. This study investigated the effects of oxidative stress markers on infertility etiology, embryo quality, and success of In vitro fertilization.
Methods:
Before enrolling in the ICSI-ET cycle, participants had their FSH and LH levels assessed on the second day of the cycle. The ovarian degrees of the participants were evaluated by transvaginal ultrasonography. Participants underwent controlled ovarian stimulation using the GnRH antagonist protocol. TV-USG and serial E2 measurements were performed at appropriate intervals to follow follicular development. Follicle sizes, quantity, and endometrial thickness were recorded. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative analyses were conducted using Rel Assay Diagnostics Assay Kits.
Results:
The average number of total oocytes in the participants was 10.25±6.66, and the average of mature M2 stage oocytes was 6.71±3.72. The average number of fertilized oocytes was 4.65±2.81. Fertilization rates were calculated as approximately 54.75±25.58%. A statistically significant positive correlation was found between embryo quality and serum Total Antioxidant Status levels (p=0.004). Similarly, a significant positive correlation was observed between embryo quality and follicular Total Antioxidant Status values (r = 0.42, p = 0.01).
Conclusion:
This study concluded that oxidative stress markers affect certain stages of the IVF treatment process.
Key-words AntioxidantsFertilization in vitroFollicular fluidInfertilityOocytesOxidantsOxidative stressSee more