Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(6):365-368
Cellular angiofibroma (CA)is a rare benign mesenchymal tumor. In women, it occurs mainly in the vulvovaginal region, with vulvar location in 70% of the cases. Its clinical presentation is nonspecific and similar to several other vulvar tumors of different cellular origins. Thus, its histological and immunohistochemical features allow distinction fromother tumors. Cellular angiofibromas have good prognosis, despite some risk of relapse. The authors present the case of a 49-year-old woman with a bulky right vulvar lesion, for which the preoperative diagnosis was a Bartholin cyst, but the histological and immunohistochemical evaluation yielded a CA.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):297-302
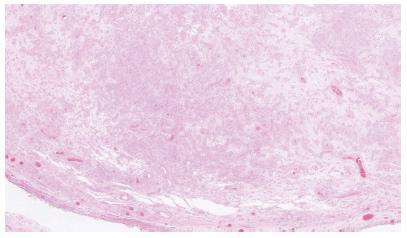
Desmoplastic small round cell tumor (DSRCT) is a rare intraabdominal neoplasm that grows along serosal surfaces and is primarily found in young men. To Keywords date, only 16 cases of ovarian DSRCT have been previously reported in women in the English literature, and no large population-based studies on this topic exist.
We report the case of a 19-year-old virgo with unremarkable past medical history, initially presented with abdominal fullness. After being treated with the optimal treatment modality (primary and secondary surgical debulking, unique chemotherapy, protocol and adjuvant radiotherapy), the patient has remained without tumor disease for 40 months.
Although the best therapy for patients with DSRCT has yet to be determined, combining complete surgical resection, adjuvant chemotherapy, and radiotherapy is required to prolong survival and to achieve proper quality of life.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(4):228-232
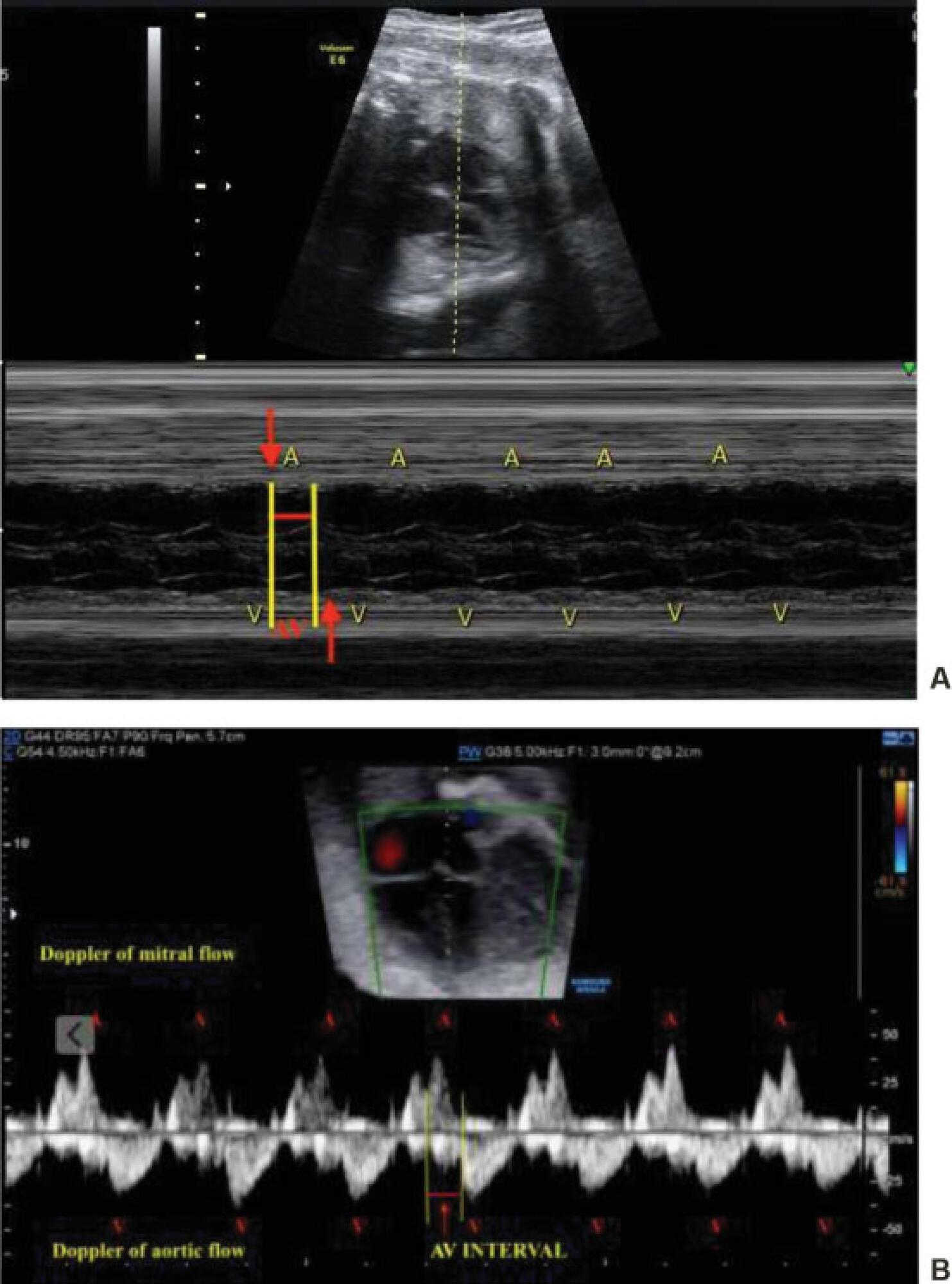
The present report describes a case of complete atrioventricular block (CAVB) diagnosed at 25 weeks of gestation in a pregnant woman with Sjögren's syndrome and positive anti-Ro/SSA antibodies. Fluorinated steroids (dexamethasone and betamethasone) and terbuline were used to increase the fetal heart rate, but the fetal heart block was not reversible, and the administration of drugs was discontinued due to maternal collateral effects. Follow-up fetal echocardiograms were performed, and the fetus evolved with pericardial effusion, presence of fibroelastosis in the right ventricle, and ventricular dysfunction. Interruption of pregnancy by cesarean section was indicated at 34 weeks of gestation, and a cardiac pacemaker was implanted in the male newborn immediately after birth. Therapy for fetuses with CAVB is controversial mainly regarding the use or not of corticosteroids; however, monitoring of the atrioventricular interval by fetal echocardiography should be performed in fetuses from pregnant women with positive autoantibodies anti-Ro/SSA and/or anti-La/SSB to prevent the progression to CAVB.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(3):165-168
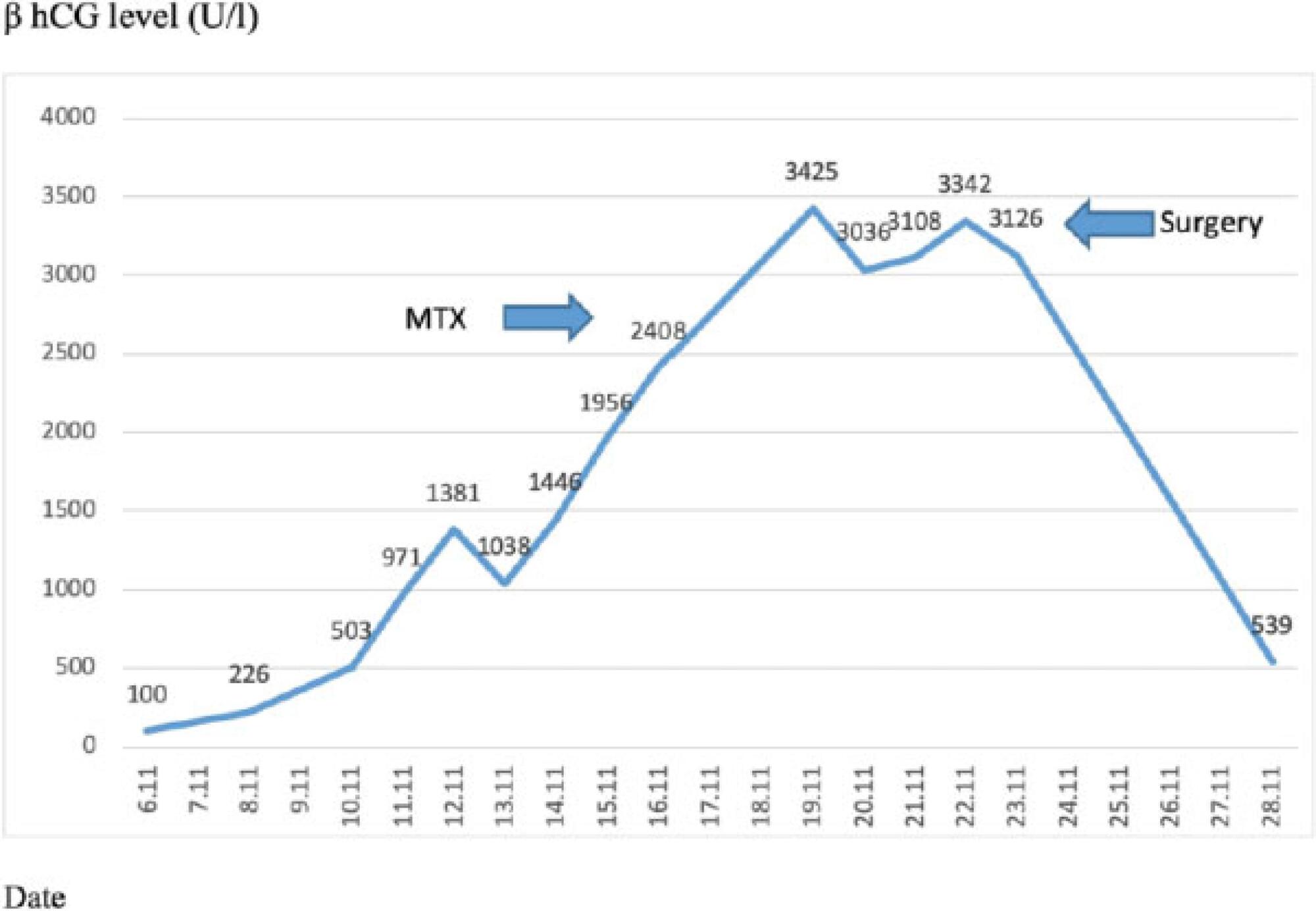
Bilateral tubal ectopic pregnancy is a very rare form of ectopic pregnancy. The incidence is higher in women undergoing assisted reproductive techniques or ovulation induction. We report the case of bilateral tubal ectopic pregnancy. The patient was 30 years old and had a 3-year history of infertility; she was referred to the in-vitro fertilization (IVF) program because of tubal factor infertility. A pregnancy resulted from the transfer of two embryos during an artificial cycle. Despite the increase in β-hCG values during the follow-up, 22 days after the embryo transfer, the β-hCG levels were 2,408 U/L and the serum progesterone (P4) level was 10.53 ng/ml. After application with methotrexate, β-hCG levels did not decrease effectively. Moreover, the sonographic screening revealed a suspicious bilateral tubal focus for ectopic pregnancy. A mini-laparotomy was performed and a bilateral tubal pregnancy was found. In the case of unilateral tubal pregnancy after the transfer of two embryos, the situation of the other tube should be systematically checked and β-hCG levels should be monitored.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):114-119
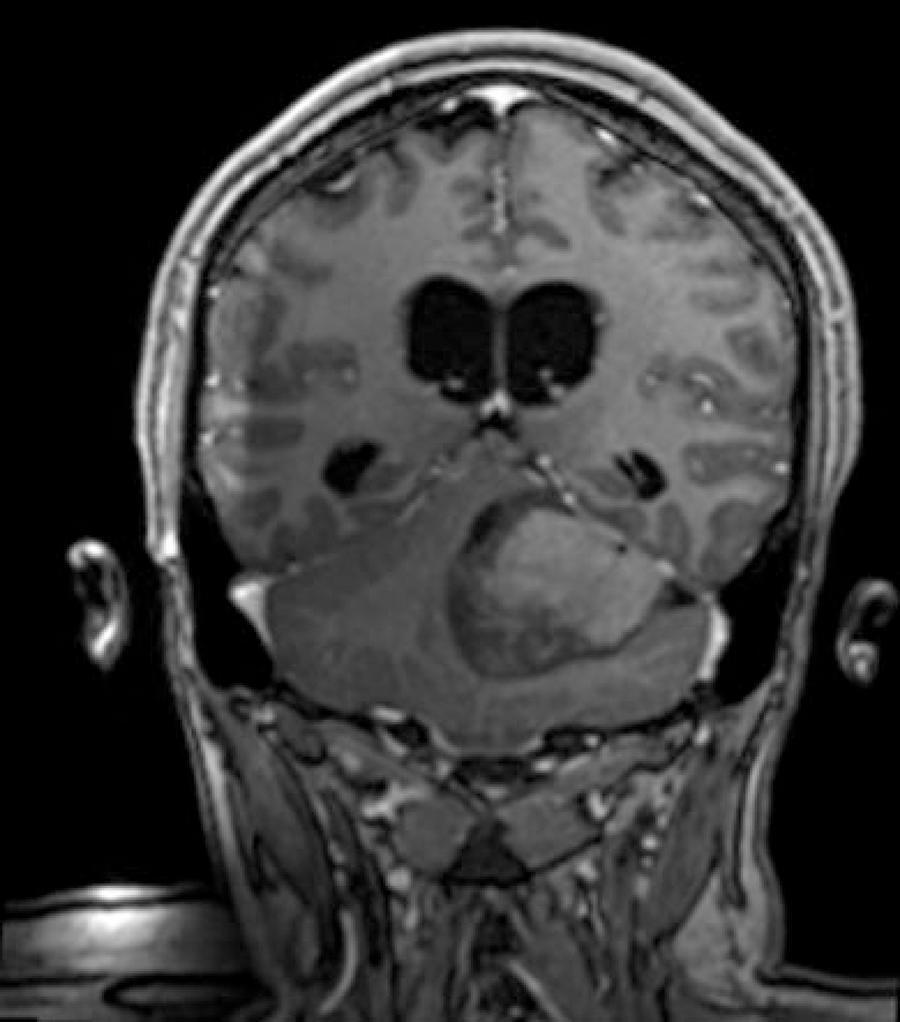
Several factors trigger the development of genetic mutations that are responsible for causing a neoplasm. Medulloblastoma is a malignant and invasive cerebellar neoplasm, that affects children and young adults. Mucinous carcinoma is a special type of breast cancer. Being a special atypical subtype of invasive carcinoma, it most frequently affects women of advanced age and represents 1 to 7% of all breast cancers. The reported case aims to show the rarity of the occurrence of desmoplastic medulloblastoma and mammary mucinous carcinoma in a young patient in a short period of time, in different sites, without direct anatomical attachment and without occurrence of metastasis. Initially, this patient had a desmoplastic medulloblastoma and was treated with lumpectomy and radiotherapy. After 13 months, the patient was diagnosed with a mucinous breast carcinoma, underwent mastectomy, adjuvant chemotherapy and is currently undergoing endocrinotherapy. We conclude, based on the metachronous characteristic of the neoplasia and clinical characteristics, that the patient is likely to have Li-Fraumeni syndrome, an autosomal dominant disease with mutation of the TP53 gene, which is the the main involved. Because the patient does not present all the characteristics of the phenotype of the syndrome, she can thus be classified as having Li-Fraumeni variant or Li-Fraumeni-like syndrome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):61-64
Premature delivery often complicates multifetal pregnancies, placing neonates at risk of seriousmorbidity andmortality. In select cases, pretermbirth of one sibling may not require delivery of the remaining fetus(es), which may remain in utero for a delayedinterval delivery, consequently improving neonatalmorbidity andmortality. Currently, there is no consensus on the best protocol for the optimalmanagement of these cases. We report one case of delayed-interval delivery of a dichorionic pregnancy assisted in our center. In this case, prophylactic cerclage, tocolytic therapy and administration of broad-spectrum prophylactic antibiotics enabled delivery at 37 weeks, corresponding to 154 days of latency, which is, to our knowledge, the longest interval described in the literature. The attempt to defer the delivery of the second fetus in peri-viability is an option that should be offered to parents after counseling, providing that the clinical criteria of eligibility are fulfilled. The correct selection of candidates, combined with the correct performance of procedures, as well as fetal and maternal monitoring and early identification of complications increase the probability of success of this type of delivery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):628-632
Although mature cystic teratoma (MCT) is benign, malignant transformation (MT) occurs in ~ 1% to 2% of all cases, and usually consists of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), which accounts for ~ 80% of the cases. Spindle-cell (sarcomatoid) carcinoma (SCSC) is an uncommon type of SCC, comprising up to 3% of all cases. The lack of characteristic symptoms and specific imaging findings may lead to preoperative misdiagnosis. Moreover, the clinicopathologic characteristics, the treatment, the prognostic factors and the mechanism of MT have not yet been well understood due to the rarity of such tumors, especially in women of reproductive age. The authors present a case of a 34- year-old patient with 14 weeks of gestation who was diagnosed with an adnexal mass suggestive of ovarian teratoma. A laparoscopy salpingo-oophorectomy was performed after 6 months of delivery, and the histological exam revealed a sarcomatoid SCC in the MCT.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):575-578
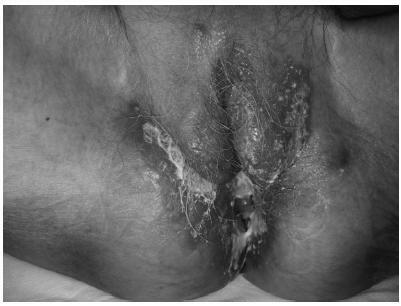
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. According to data from the World Health Organization, this disease remains one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Although it most commonly affects the lungs, tuberculosis can compromise any organ. The present study reports a rare case of vulvar tuberculosis in a postmenopausal woman with a history of asymptomatic pulmonary and pleural tuberculosis, with no prior documented contact with the bacillus. Diagnosis was based on vulvar lesion biopsies, with histological findings suggestive of infection and isolation of M. tuberculosis by microbiological culture and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) essays. The lesions reverted to normal after tuberculostatic therapy.