Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(4):205-210
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000400007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the experience of an assisted reproduction center that uses depot administration of half-dose of GnRH agonist for pituitary suppression in assisted reproductive cycles. METHODS: prospective study that evaluated in vitro fertilization or intracytoplasmatic sperm injection (IVF/ICSI) cycles utilizing half-dose of leuprolide acetate between August 2005 and March 2006. Recombinant FSH was administered for controlled ovarian induction based on the protocol. hCG was administered when at least one follicle reached 19 mm in diameter. IVF or ICSI was performed according to infertility factor. Up to four embryos were transferred on the second or third day after oocyte retrieval. Progesterone supplementation was initiated on the same day of oocyte retrieval, and after 14 days beta-hCG was measured. The following parameters were evaluated: number of aspirated cycles, cancelled cycles, transferred cycles, total dose of FSH employed, number of mature oocytes retrieved, fertilization rate, number of transferred embryos, embryo implantation rate, and pregnancy rate. RESULTS: A hundred and nine IVF/ICSI cycles were initiated. The mean age of the patients was 34.9 years. We observed 1.8% of cancellation rate. The mean total dose of gonadotrophins employed was 1,905 IU per cycle. We obtained 86.5% of mature oocytes and the fertilization rate was 76.3%. The mean number of embryos transferred was 2.7. Pregnancy rates per aspiration and per transfer were 25.2 and 25.7%, respectively. Of those who reached pregnancy, 26.3% were twins and 5.3% were triplets. CONCLUSIONS: the half-dose of GnRH depot employed for pituitary suppression was a useful alternative for ovarian stimulation in IVF cycles because it is comfortable and practical for the patient, besides its low cost.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):120-125
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000300002
PURPOSE: to present a surgical technique for patients submitted to caesarean section, which evolves to medicine refractory hemorrhage. METHODS: a case report study, of which the including criteria were failure in the pharmacological treatment to control post-partum hemorrhage, and the patients' request to preserve their uterus. Four patients submitted to caesarean section which evolved to immediate post-partum hemorrhage, refractory to the use of ocytocin, ergometrine and misoprostol, were treated with the suture technique described by B-Lynch, without modification. The uterus was transfixed in six points according to the standard procedure, with chrome catgut-2 or polyglactine-1thread. After the assistant's manual compression of the uterus, the thread was pulled by its extremities by the surgeon, and a double knot followed by two simple knots were applied before performing the hysterorraphy. RESULTS: needled chrome catgut-2 thread was used in three cases and needled poluglactine-1 in one case. In the four cases there was immediate discontinuity of the vaginal bleeding, after the suture. The four patients did not present any complication during the procedure or along the immediate and late puerperal period. CONCLUSION: this technique represents a surgical alternative to deal with post-partum hemorrhage and may represent a reduction in the maternal morbidity and mortality in our country.
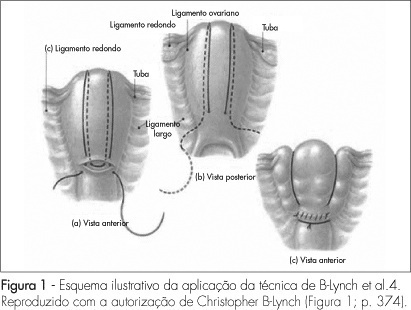
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):126-133
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000300003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the impact of the nutritional status of pregnant adolescents on the birth weight. METHODS: a cohort study including 97 adolescents and their respective newborns, evaluated from May to June, 2004. Pregnant women from 10 to 19 years old in labor were included in the study, and those with multiple pregnancies, complications, less than 37 weeks gestation, and incomplete data records were excluded. Maternal nutritional status evaluation included height, body mass index (BMI) before pregnancy, gestational weight gain (GWG) and caloric-proteic intake, obtained by habitual food intake recordatory by the end of the third gestational trimester. The association between maternal variables (height, pre-gestational BMI, GWG and intake) and the newborn weight was analyzed by Spearman's correlation test. Statistical significance was assumed when p<0.05. RESULTS: the mean age was 17.8±1.12 years old. Most adolescents (66%) started pregnancy with adequate weight, 29% had low weight and 5% overweight. Most adolescents showed inadequate GWG, caloric and proteic intake. Low birth weight was recorded in 7% of the newborns and insufficient weight was recorded in 37% of them. Maternal height and GWG showed positive and significant BW relation. Pre-gestational BMI and protein intake showed statistically significant inverse correlation with birth weight. No correlation between caloric intake and BW was demonstrated. CONCLUSION: maternal height and GWG influence the newborn nutritional status.
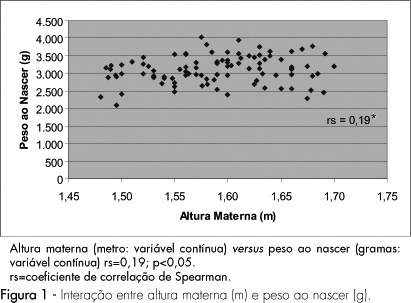
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):134-140
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000300004
PURPOSE: to compare women's quality of life (QoL) before and after physical therapy treatment for stress urinary incontinence (SUI). METHODS: an uncontrolled clinical trial of 26 women, who had mainly complaints of SUI. Post-menopausal women with overactive bladder, cystocele >grade II and previous surgical/conservative treatments were excluded from the study. The physiotherapy treatment relied on 12 individual pelvic floor exercises assisted by electromyographyc-biofeedback sessions. A total of 200 contractions were carried out, divided in phasic (quick) and tonic (slow). The tool used to evaluate QoL was the King's Health Questionnaire (KHQ), before and after the treatment. RESULTS: there was a decrease in the urinary symptoms, particularly in urinary frequency, nocturia, urgency and urinary incontinence. Regarding the QoL, there was a significant improvement in the following domain scores: general health perception (49.0±24.0 versus 26.9±15.7; p=0.0015), incontinence impact (78.2±28.2 versus 32.1±30.5; p=0.001), activity limitation (75.0±28.2 versus 13.5±22.6; p<0.001), physical limitation (72.4±29.4 versus 15.4±24.5; p<0.001), social limitations (38.3±28.6 versus 6.4±14.5; p<0.001), emotions (59.0±33.8 versus 14.1±24.7; p=0.0001, sleep/energy (34.0±23.8 versus 6.4±16.4; p=0.001) and severity measures (66.9±19.6 versus 22.3±24.2; p<0.001), except for personal relationships (60.5±33.9 versus 41.7±16.7; p=0.0679). CONCLUSIONS: there was an improvement in several aspects of women's QoL treated by physiotherapy, when evaluated with a specific tool, the KHQ.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):141-146
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000300005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of obesity on beta-cell function in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). METHODS: this cross-section study evaluated 82 patients with PCOS selected consecutively, at the moment of the diagnosis. We compared 31 PCOS obese women (BMI >30 kg/m²) to 51 age-matched PCOS nonobese patients (BMI <30 kg/m²). Using fasting glucose and insulin levels, homeostatic model assessment values for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR and QUICKI) and percent beta-cell function (HOMA-%beta-cell) were calculated. As secondary variables, the age at PCOS diagnosis, age of menarche, hormonal levels (testosterone, prolactin, FSH and LH), total cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol and LDL cholesterol were also analyzed. RESULTS: menarche was significantly earlier in obese PCOS patients (11.7±1.8 years) than in nonobese patients (12.67±1.86 years) (p<0.05). Obese patients presented lower LH levels (7.9±5 mIU/mL) than did nonobese patients (10.6±6 mIU/mL) (p<0.05). Both groups presented mean HDL cholesterol levels below 50 mg/dL. Obese patients presented significantly higher baseline insulin levels (32.5±25.2 mIU/mL) and fasting blood glucose levels (115.9±40.7 mg/dL) than did nonobese patients (8.8±6.6 mIU/mL and 90.2±8.9 mg/dL, respectively) (p<0.01). Of the obese PCOS patients, 93% presented insulin resistance versus 25% of nonobese PCOS patients (p<0.01). Eighty-six perecent of the obese women had hyperfunction of beta-cell versus 41% of nonobese with PCOS (p<0.0001). CONCLUSIONS: obese PCOS patients presented higher prevalence of insulin resistance and hyperfunction of beta-cell than did nonobese PCOS patients.
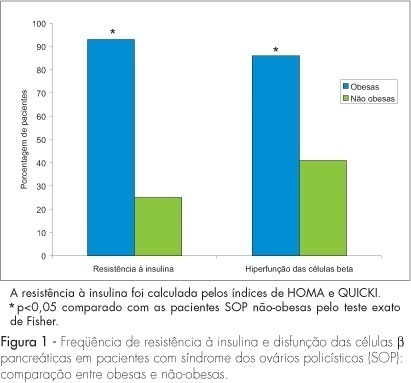
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(3):147-152
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000300006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the vascular blood flow of the central retinal arteries using dopplervelocimetry in the different phases of the ovulatory menstrual cycle. METHODS: we performed an observational, longitudinal and prospective study evaluating 34 healthy and ovulatory women. All women were submitted to Doppler scan of the eye to evaluate the vascular resistance of the central retinal arteries, either lying down or on a seated position, during four phases of the menstrual cycle. Confirmation of ovulation was performed by measuring serum progesterone during the luteal phase. We analyzed the pulsatility and resistance index and the maximum, minimum and mean velocity. RESULTS: mean age was 29.7 years. No differences were observed between the indexes obtained in both eyes, therefore a mean index was used for comparisons. As the comparison between the positions used for the exams showed a higher PI for the seated position, the analyses were performed separately. The pulsatility index in the lying position was different among the different phases of the menstrual cycle. The arterial resistance was significantly lower during the intermediate follicular and the periovulatory phases, as compared to the early follicular and luteal phases. When the comparison was performed with the patient in the seated position, no differences were observed. CONCLUSIONS: Our results demonstrate a reduction in the vascular resistance of the cerebral microcirculation and a posterior reversal, as shown by changes in the PI.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(2):67-73
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000200002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the teaching and the practice of hysterectomy in the Brazilian regions and to compare them with data of international literature. METHODS: questionnaires about nine issues on benign hysterectomy indications, surgical procedures, use of antibiotic prophylaxis, suture of the vaginal vault and complications were sent to the 132 Gynecological and Obstetrics Residency Services of Brazil, registered by the Ministry of the Education and Culture in 2003. Data were computed and statically analyzed, with the use of the Friedman's, Kruskal-Wallis's and chi2 tests, according to the characteristics of the variables. RESULTS: 48.5% of the questionnaires were answered or justified when there were no answers, mainly in the Southeastern region (62%). The main surgical hysterectomy procedure was the abdominal, varying from 60 to 100% (p<0.001), followed by the vaginal (10 to 40%) and the laparoscopy (6%). In 94% of the cases, laparoscopy was not employed. The main indication for hysterectomy was myomatosis (60.4%; p<0.001), followed by adenomiosis (8.3%) and abnormal uterine bleeding (7.5%). First generation cephalosporin was used for antibiotic prophylaxis in 94% of the cases. There was no significant statistical difference among the threads (simple Catgut®, chrome Catgut® or Vicryl®) used for the suture of the vaginal vault and the development of granuloma in this region, which was the main complication of the procedure (p=0,002). CONCLUSIONS: the surgical procedures, the hysterectomy indications, the threads used to suture the vaginal vault and the complications were similar in the different regions of Brazil and they agreed with the evidence reported in the international literature.
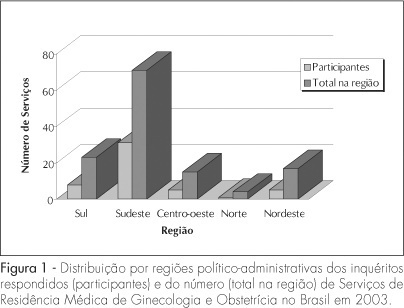
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(2):74-79
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000200003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the association between women's menstrual experience and preferred changes in their menstrual cycles. METHODS: a cross-sectional study design was used. A total of 420 women were interviewed. Participants complied with the following criteria: age (18 to 20, 25 to 34 and 45 to 49 years); schooling (<8 years and >12 years); having menstruated during the three months previous to the study. Subjects were selected in the city of Campinas (SP), in nine private and seven public health services. For data collection, a questionnaire was prepared on the basis of the results of a previous pilot study that consisted of small groups. A data bank was prepared with the information registered in the questionnaires and the analysis was carried out with SAS, version 8.2. For the statistical analysis, the Pearson chi2 test and the Fisher exact test were used to evaluate the association between variables (p<0.05). RESULTS: most subjects preferred greater than once a month intervals between menstruations. There was an association of the typical menstrual intervals experienced by women (p=0.0248) and the degree of interference of menstruation with daily activities (p=0.048) with the preferred interval between menses. However, there was no association between preferred intervals by women and the following characteristics of pain: duration, intensity and use of medication. CONCLUSIONS: the results suggest that women would like intervals longer than one month or to never menstruate.