Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(7):388-396
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000700003
PURPOSE: to generate knowledge in order to allow of the determination the factors affecting the high incidence of caesarean section and its relation to sterilization. METHODS: the multicentric study on reproductive health in Brazil, carried out from 1998 to 2000, included the States of Rio Grande do Norte, Minas Gerais, São Paulo, and Rio Grande do Sul. It was characterized as a longitudinal study, where the women, proceeding from public as well as private health services, were interviewed at three moments: at the beginning of pregnancy (until the 22nd week of gestation), at the end of pregnancy (between 30 and 40 days before the probable date of childbirth) and after delivery (between 15 and 45 days after childbirth). The interviewed women complied with the following eligibility criteria: to have 18 to 40 years of age, to live in Natal and plan to deliver the baby in Natal. At the first moment, 433 women were interviewed, 380 at the second moment and 269 at the third moment. The data were submitted to the chi-square test, with the level of significance set at 0.05, just to assure the relation between the variable years of schooling (0 to 8 and 9 or +) and the representative variables for reproductive health. RESULTS: the result disclosed a statistically significant relationship (p<0.05) between the variables: years of schooling, parity, type of service used, social class, job status, and prenatal consultations. It was found that a higher educational level is predominant among those women who searched for private services, coming from higher social classes and large number of prenatal visits. Although without statistical significance, having a for the women coming from this type of service, a higher number of caesarean section5 was observed, probably due to an easy doctor-patient interaction, while the planned caesarean section was frustrated for 43% of those women coming from public health services, as well as the wish to have a tubal ligation at childbirth (57%). CONCLUSIONS: These results show up the great differentials between the private and public services, with a clear favoritism for the private sector, demonstrating clearly that the practical obstetrics in Brazil needs a change and an improvement both for those women with access to the private service, who obtain the accomplishment of the caesarean section without consistent medical indications, and those with access to the public service, who face difficulties in accomplishing this procedure, even with consistent medical indications, in order to provide equality in the reproductive rights of those women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(7):397-402
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000700004
PURPOSE: to compare the uterine cervix measurements and funneling obtained by two- and three-dimensional transvaginal sonography during pregnancy. METHODS: a prospective, descriptive study, with group comparison, was carried out between April 2004 and February 2005 in 74 pregnant women, who were between the 19th and 24th week of pregnancy, regardless of risk factors for premature delivery. The ultrasound examination of the cervix was carried out only once in the same patient and by only one observer. The measurements of the cervix by two-dimensional ultrasound were made at the time of the test and by three-dimensional ultrasound at intervals of 7 to 15 days after the two-dimensional ultrasound. The measurements of cervical length, funnel width and length were taken by two-dimensional ultrasound in the sagittal plane and by three-dimensional in the sagittal plane as well as in coronal plane. RESULTS: there was no significant difference between the averages of the measurements of the cervix obtained by two- and three-dimensional ultrasound in the sagittal plane (p=0.23); however, there was a difference in the averages of the measurements of the cervix obtained by two-dimensional ultrasound in sagittal plane and three-dimensional ultrasound in the coronal plane (p=0.009) and between three-dimensional ultrasound in the sagittal and coronal planes (p=0.001). The kappa test (0.86) showed no superiority of either the two-dimensional and three-dimensional ultrasound in the visualization of the cervical funnel. No statistically significant difference was observed between the methods when the average of the measurements of funneling was compared (p>0.05). CONCLUSION: there were differences between two-dimensional and three-dimensional ultrasound of cervical length, only using the coronal plane of the three-dimensional ultrasound.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(7):403-409
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000700005
PURPOSE: to compare in a retrospective way, 51 women who underwent tubal ligation, 30 through microlaparoascopy (Gmicrol) and 21 through minilaparotomy (Gminil). METHODS: the analyzed parameters were: total time for accomplishment of the procedure and the surgical technique, time of hospital stay and return to the habitual activities after the surgery, postoperative pain, morbidity, satisfaction degree and esthetic effect, considering values of p<0,05 as significant, and also standard cost. RESULTS: Gmicrol took less time to accomplish the surgery than the Gminil (43 against 57 minutes respectively, p<0,05), less time to accomplish the surgical technique (6.48 against 30.32 minutes respectively, p<0,05), and lower hospital stay (9,90 hours as against 41,7 hours respectively, p <0,05). There was no significant difference between the two groups regarding time to return to the habitual activities after surgery. To evaluate postoperative pain, a scale of 0-10 it was applied. Gmicrol present a lower pain score on the 1st and 2nd postoperative days (1.13 and 0.26 to Gmicrol and 4.52 and 1.14 to Gminil, respectively, p<0,05). There was no significant difference between immediate postoperative the most common complaint being pain at the site of pain and that on the 3rd postoperative day. Gminil presented a higher morbidity rate incision. To evaluate the satisfaction degree and esthetic effect, numeric values were attributed to as good, regular, poor and very bad as answered by the patiets. Gmicrol presented a higher satisfaction degree (p<0,05) and better esthetic effect as compared to Gminil (p <0,05). The microlaparoscopy standard cost was R$ 109.30 being lower than that of minilaparotomy. CONCLUSIONS: tubal ligation by microlaparoscopy, under local anesthesia and conscious sedation presented some advantages compared to minilaparotomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(7):410-415
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000700006
PURPOSE: to verify, through pelvic ultrasound, the existence of changes in the internal genitalia of girls with central precocious puberty, submitted to treatment with gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analogs. METHODS: pelvic ultrasound was performed in 18 girls with idiopathic central precocious puberty, before and after three months of onset of the treatment with GnRH analogs, to investigate the impact of the therapy on the internal genitalia. Ovarian and uterine volumes, uterine longitudinal length, relation between the longitudinal diameter of the uterine corpus and the uterine cervix, the relation between the anterior-posterior diameter of the uterine corpus and the uterine cervix, and endometrial echogenicity were evaluated. Statistical analysis was performed through Shapiro-Willkis's test, to assess data normality. When normality was present, Student's test t was applied. For data without normality, a non-parametric test (the signal test) was used. RESULTS: after therapy, statistically significant decline of the mean uterine volume (from 5.4 cm³ to 3.0 cm³, p<0.001), of the mean ovarian volume (from 2.2 cm³ to 1.1 cm³, p= 0.004), of the mean uterine longitudinal length (from 4.2cm to 3.4 cm, p=0.001), and of the mean endometrial echogenicity (from 1.8 mm to 0.6 mm, p=0.018) occurred. CONCLUSION: In girls with idiopathic central precocious puberty, pelvic ultrasound is a valid method to assess the efficacy of treatment with GnRH analogs. The main parameters of the therapeutic response were the decrease of uterine and ovarian volume, of uterine longitudinal length, and atrophy or absence of endometrial echogenicity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(7):416-423
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000700007
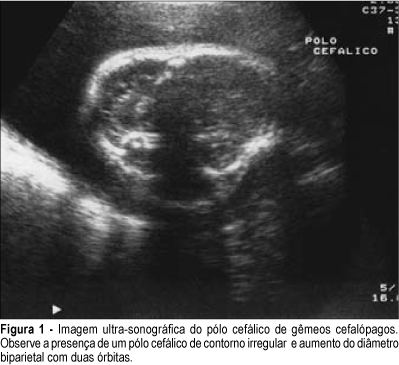
Conjoined twins have a rare prevalence and special curiosity among physicians and the general population. The reported frequency varies from 1:50,000 to 1:200,000 pregnancies. Its early diagnosis becomes very important when we think about pregnancy management, method of delivery and neonatal care. We describe two cases of conjoined twins diagnosed by ultrasound and magnetic resonance during prenatal care with the aim to better studying the fetus anatomy. The first conjoined twins were cephalopagus sharing head, thorax and abdominal wall and with two pelvis and four arms and four legs. The second were thoracopagus, united by thorax and part of abdomen. Magnetic resonance imaging contribution was not important to diagnose conjoined twins. However, it was useful to describe the shared organs, contributing to define fetal outcome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):446-452
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800002
PURPOSE: to describe the obstetric outcomes in pregnant adolescents at a tertiary hospital and to compare the maternal and labor outcomes between precocious and late adolescents. METHODS: in a transversal analytical study, 2058 cases were evaluated, considering 322 (15.65%) from the precocious group and 1736 (84.35%) from the late group that delivered at the "Maternidade Escola Assis Chateaubriand/UFC" from January 1, 2000 to December 31, 2000. The clinical complications in the prenatal period, kind of delivery, indications for cesarean section, birth gestational age at birth, birth weight, comparison of birth weight and gestational age, Apgar score at the first and fifth minute, presence of malformations, and neonatal death were analyzed. The exact Fisher and the chi2 tests were used to compare both groups. The prevalence ratio was calculated. RESULTS: from of total of deliveries, 25.95% belonged to adolescents. The average age was 17.19 years. Prenatal visits were made by 88% of the patients, but 60% had an insufficient number of visits. The most frequent clinical situations were preeclampsia (14.72%), anemia (12.97%) and urinary tract infections (6.37%), with no statistical difference between the groups. Thirty-one and three percent of the births were by cesarean section, preeclampsia being the main indication in the two age groups (25 and 23%, respectively). The frequency of an Apgar score less than 7 at the first minute was 19,9% in the precocious adolescent group and 14,2% in the late adolescent group (x²=6,96, p=0.008). There was no statistical difference regarding prematurity rate (20.2 vs 16.1%), low-birth weight infants (12.4 vs 10.4%), low Apgar score at the fifth minute (5.3 vs 3.3%), congenital malformations (3.1 vs 2.7%), and neonatal death (5.3 vs 3.3%). CONCLUSIONS: the precocious and late pregnant adolescents presented similar pregnancy evolution and obstetric outcomes, except for the differences of the first minute Apgar scores.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(8):453-459
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000800003
PURPOSE: to analyze the fetal heart rate (FHR) and umbilical artery Dopplervelocimetry between 18th and 20th weeks of gestation in pregnant women complicated by pregestational diabetes mellitus. METHODS: twenty-eight pregnancies with pregestational diabetes and 27 normal pregnant women were analyzed prospectively, in a cross-sectional and case-control study. The inclusion criteria were the following: singleton pregnancy between 18 and 29 weeks, no other associated maternal diseases and no fetal abnormality. Ultrasonography was performed and FHR was calculated by the interval between the beginnings of two consecutive cardiac cycles, in the three umbilical artery Doppler sonograms, obtained in the umbilical cord near to the placental insertion, using color Doppler. Five consecutive FHR cycles from each sonogram were measured, to analyze mean FHR and its variation. The following Doppler indices were studied: systolic/diastolic ratio, pulsatility index (PI) and resistance index (RI). Student's t test and Mann-Whitney Utest were applied to comparative study. p values were considered significant when p<0.05. Results: no significant difference was observed in mean FHR between the studied groups (diabetic group: 149.2 bpm, control group: 147.2 bpm; p = 0.12). FHR variation revealed similar results between the groups (diabetic group: 5.3 bpm; control group: 5.3 bpm; p=0.50). No significant difference was found in the Doppler indices S/D (p=0.79), PI (p=0.25) and RI (p=0.71) between the groups. CONCLUSIONS: the absence of differences in FHR characteristics between the 18th and 20th gestational weeks indicates similar neurological maturation of FHR regulatory systems in this period, between fetuses of diabetic mothers and controls. Abnormalities in the uteroplacental resistance were not identified in the studied period, in pregnancies complicated by pregestational diabetes.