Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):650-655
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100003
PURPOSE: to asses the efficiency of the radioguided localization and removal of occult breast lesions using radiopharmaceuticals injected directly into the lesions or close to them with posterior air injection as a radiological control. METHODS: twenty-nine consecutive patients with thirty-two occult breast lesions detected mammographically or by ultrasound, and categorized 3, 4 and 5 BI-RADS®, were included in this observational study with results expressed in percentages. The radiopharmaceutical used was human serum albumin labeled with 99mTc-HSA injected inside or close to the lesion using mammographic or ultrasonographic guidance. The injection of the radiopharmaceutical was followed immediately by air injection through the needle used for stereotaxis as a radiological control of the radiopharmaceutical placement. The excision biopsy was carried out with the aid of a hand-held gamma-detecting probe and the entire removal of the lesion was verified by X-ray of the surgical specimens or by intraoperative frozen section examination. RESULTS: breast cancer was found in 10.0% (1/10) of the 3 BI-RADS® lesions, in 31.5% (6/19) of the 4 BI-RADS® and in 66.6% (2/3) of the 5 BI-RADS®. The radiotracer was correctly positioned in 96.8% of the specimens (31/32) allowing the removal of also 96.8% of the studied non-palpable breast lesions. To show the entire removal, X-ray was used in 23 cases (71.8%), intraoperative frozen section study in 21.8% (7/32) and both methods in 6.2% (2/32). CONCLUSIONS: radioguided surgery showed to be an important tool in the removal of non-palpable breast lesions, as a simple, fast and feasible method that can be implemented in the clinical routine of these patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):656-660
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100004
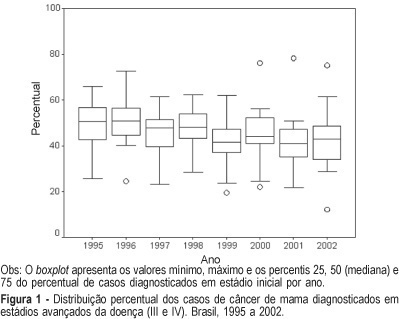
PURPOSE: to analyze time trends in the clinical staging at the moment of diagnosis in patients with breast and cervix cancer based on data produced by the Brazilian Public Health System (SUS). METHODS: in the first part of this study we identified the published documents describing clinical staging of patients at the moment of diagnosis. Considering their scarcity and poor representativity we conducted the second part of this study through an active search for information. A form was sent via regular mail to all cancer centers in the country (n=173) requesting information about the tumor site and stage at diagnosis by year, in the period of 1995-2002. The statistical analysis was performed using the "R" statistical package. The results are reported as percentage and boxplots. RESULTS: in the first part of the study (1990-1994) we described data from 18 hospitals concerning 7,458 patients with breast cancer and 7,216 patients with cervix cancer. The median of the percentage of cancers diagnosed at an advanced stage (stages III or IV) was 52.6 and 56.8%, respectively. In the second part of the study (1995-2002) data were collected from 89 cancer hospitals and 7 chemotherapy or radiotherapy clinics. There was a total of 43,442 cases of breast cancer and 29,263 of cervix cancer. The response rate based on the potential contact list was 55%. The median percentage of patients in advanced stage was 45.3% for breast cancer and 42.5% for cervix cancer. CONCLUSIONS: few studies have examined the time trends in staging of cancer at diagnosis in Brazilian hospitals. Data obtained from Hospital Cancer Registries showed that in the last decade there was a reduction in the percentage of cervix and breast cancer at the advanced stage. This reduction can be due to an improvement in early detection of these cancers.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):661-664
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100005
PURPOSE: to compare the outcome of treatment in patients undergoing assisted reproductive technology (ART) cycles who donated eggs during their own ART treatment with the outcome of patients undergoing ART without egg donation. METHODS: we studied retrospectively the pregnancy and implantation rates of 50 patients who donated eggs during the course of their ART treatment (donor group), and the pregnancy and implantation rates of 50 patients who underwent ART cycles and kept all their eggs (non-donor group). between the years 2001-2003. The inclusion criteria used were as follows: age <35 years old, normal menstrual cycles, FSH<10 mIU/mL, first attempt of ART treatment and more than six mature oocytes retrieved. The results were analyzed statistically using the chi2 test. RESULTS: both groups were comparable in terms of age, indication, and duration of infertility. The mean age was 30.6 years for the donor group and 31.1 years for the non-donor group. All the patients of the donor group produced more than 6 eggs. From the donor group we collected 590 oocytes; 215 eggs were donated to recipients (36.5%) and 152 embryos were transferred. A total of 15 pregnancies were achieved (pregnancy rate per transfer: 30%); the implantation rate was 11.2% and there were 2 miscarriages (miscarriage rate: 13.3%). From the non-donor group, 545 oocytes were collected and 153 embryos were transferred. A total 17 pregnancies were achieved (pregnancy rate per transfer: 34%); the implantation rate was 14.3% and there were 3 miscarriages (miscarriage rate: 17.6%). The pregnancy and implantation rates were similar in both groups, and there were no significant statistical differences regarding the miscarriage rate (p>0.05). CONCLUSION: this study suggests that in patients who produce more than 6 oocytes, egg donation in the treatment cycle does not influence adversely the outcome of ART cycles and does not increase the miscarriage rate.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):665-671
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100006
PURPOSE: to define the characteristics of unviable embryos that may be donated for stem-cell research. METHODS: a retrospective evaluation of in vitro fertilzation cycles between January 1995 and January 2005 was structured. Cycles were chosen in which the embryos transferred to the uterine cavity had the same morphological characteristics. Subsequently, the rates of pregnancy, implantation, and involution of the gestational sacs of the fresh embryos as well as of those cryopreserved were analyzed and distributed into groups according to their morphology. Embryos that were symmetric and with 0% of fragmentation were designated type A; asymmetric with up to 25% of fragmentation were designated type B; between 25 and 50% of volume occupied were designated type C, and those with 50% or more of fragmentation were designated type D. RESULTS: one hundred and seventy-two type D embryos transferred in 87 cycles presented low rates of implantation (11%) with 50% of those implanted persisting in development. Embryos with the same morphology, after cryopreservation and thawing, did not show the capacity to evolve. In 36 cycles, 113 thawed type D embryos were transferred, resulting in only one implantation, presenting a minute 3% pregnancy rate. The implanted gestational sac did not evolve, showing a 100% rate of involution. CONCLUSION: embryos with low morphological scores cannot be considered unviable because they are capable, even though with a very low frequency, of supporting gestation. However, these same embryos, after cryopreservation, thawing and transfer showed an insignificant rate of pregnancy, that did not result in viable pregnancy. Therefore, when in excess to requirements, type D embryos should not be cryopreserved; instead, rather than discarded, they should be donated for embryo stem-cell research.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):672-676
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100007
PURPOSE: to evaluate the influence of vaginal environment of pregnant women on group B streptococcus (GBS) survival after 8, 24 e 48 h in Amies and Stuart transport media. METHODS: Three vaginal samples were collected from 30 pregnant women attending the Prenatal Care Outpatient Clinic of the Centro de Atenção Integral à Saúde da Mulher (CAISM), Universidade Estadual de Campinas (UNICAMP). The first sample was placed directly onto Todd-Hewitt selective medium; the second was used to perform a gram-stained microscopy, and the third swab was placed in 2 mL physiological saline to which 200 µL of a suspension with 1-2 x 10(8) colony-forming units of GBS was added. After homogenization, six swabs were collected from this suspension (3 from Amie medium and 3 from Stuart medium). These six swabs were kept at room temperature for 8, 24 and 48 h and then incubated on blood agar. Bacterial growth at 37ºC was observed after a 24-h incubation period and it was semiquantitatively graded (0-3+) according to the number of colonies. Statistical analysis was performed by the exact Fisher test and the level of significance was set at 0.05. RESULTS: the recovery of GBS after 48-h storage in Amie and Stuart media was 97 e 87%, respectively. In one of the four cases where no GBS recovery was possible after 48 h of storage, vaginal pH was higher than 4.5, and in two of those cases cytolytic vaginosis was found. CONCLUSIONS: both transport media showed to be appropriate for GBS recovery up to 48 h after sampling. Characteristics of the vaginal enviroment did not influence GBS recovery as observed in this study.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):677-682
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100008
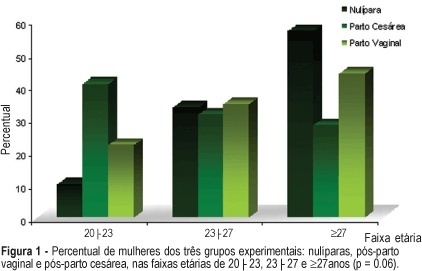
PURPOSE: to evaluate the influence of the delivery route on pelvic floor (PF) muscle strength. METHODS: a cross-sectional study was conducted to evaluate PF muscle strength by the pelvic floor strength evaluation (PFSE) test and perineometer in primiparous patients aged 20 to 30 years 4 to 6 months after delivery. The categorization was: zero lack of muscle contraction; one - weak contraction; two - moderate contraction not sustained for 6 s and three - normal contraction sustained for 6 s. A total of 94 patients were divided into there groups based on prior delivery route. They were: 32 patients with vaginal delivery with singleton cephalic presentation; 32 patients with cesarean delivery, and 30 nulliparous patients as a control group. The independent variable was delivery route and the dependent one was the muscle strength of the PF. Comparison between contraction levels was performed by Kruskal-Wallis and Dunn multiple comparison tests and the influence of delivery method was tested by chi2. Confidence interval of 95% was obtained for relative risk (RR) of Pf muscle strength changes and kappa statistics. RESULTS: the 1st and 3rd quartiles of delivery route regarding PF muscle strength were lower (p=0.01) for vaginal delivery (2.0;1-2) and intermediate for cesarean section (2.0;2-3) compared to the nulliparous (3.0;2-3) by the PFSE test and perineometer. RR of the altered examination was increased after vaginal delivery (RR=2.58; CI 95%: 1.32-5.04, p=0.002); (RR=2.31; CI 95%: 1.24-4.32, p=0.005), and after cesarean section (RR=1.56; CI 95%: 0.94-2.57, p= 0.12); (RR=1.38; CI 95%: 0.85-2.23, p=0.29) by AFA and perineometer, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: vaginal delivery decreased PF muscle strength when compared with cesarean delivery and control groups.