Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):229-232
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005295
To compare the frequency of an ASCUS Pap Smear result in pregnant and
non-pregnant women, stratified by age group.
We analyzed the results of 1,336,180 cytopathologyc exams of Pap smears performed
between 2000 and 2009 (ten years) with the purpose of screening for cervical
carcinoma. Comparisons were made between pregnant and non-pregnant women, and the
sample was stratified into three age groups (20-24, 25-29 and 30-34 years). The
χ2 test was used and the magnitude of association was determined by
the by Odds Ratio (OR) with the 95% confidence interval (95%CI).
A Total of 447,489 samples were excluded on the basis of the criteria adopted,
for a total final sample of 37,137 pregnant women and 851,554 non-pregnant women.
An ASCUS result was detected in 1.2% of cases, with a significant difference
between pregnant and non-pregnant women in the age groups of 20-24 years (OR=0.85;
95%CI 0.75-0.97) and 25-29 years (OR=0.78; 95%CI 0.63-0.96). There was no
difference in the group between 30-34 years (OR=0.76; 95%CI 0.57-1.03).
This study suggested that non-pregnant women have a higher frequency of ASCUS,
most evident in the age group of 20 to 29 years. The collection of cervical cancer
screening should not be a compulsory part of the prenatal routine.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):233-240
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005333
To assess the effect of tibolone on mammary tissue of castrated rats over 3
different periods of time.
Sixty virgin female Wistar rats were submitted to oophorectomy. Twenty-one days
after surgery, with hypoestrogenism confirmed, the experimental rats were randomly
assigned to six groups: Tibolone 1 (n=10) received tibolone 1 mg/day for 23 days,
tibolone 2 (n=10) for 59 days and tibolone 3 (n=10) for 118 days. The groups
control 1 (n=8), control 2 (n=7) and control 2 (n=10) received distilled water for
23, 59 and 118 days, respectively. After treatment, all six pairs of mammary
glands were removed and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) for histological
analysis after euthanasia. The histological parameters evaluated were: epithelial
cell proliferation and secretory activity. The variables were analyzed
statistically, with the level of significance set at 0.05.
Histological changes were observed in 20/55 rats, mild epithelial hyperplasia in
7/55, moderate epithelial hyperplasia in 5/55, alveolar-nodular hyperplasia in
7/55, atypia without epithelial proliferation in 1/55, and no cases of severe
epithelial hyperplasia were found. Secretory activity was observed in 31/55 rats.
The secretory activity was significantly higher in the tibolone groups compared to
control at all the time points assessed (p=0,001). The histological changes were
did not show significance when the control and tibolone groups were compared. The
time of exposure to tibolone did not show significance when the three different
periods of evaluation were compared.
No relation between histological modification and tibolone treatment was verified
after short-, medium- and long-term treatment.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):241-246
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005304
It was to analyse the most critical areas in Obstetrics and to suggest measures to reduce or avoid the situations most often involved in these disputes.
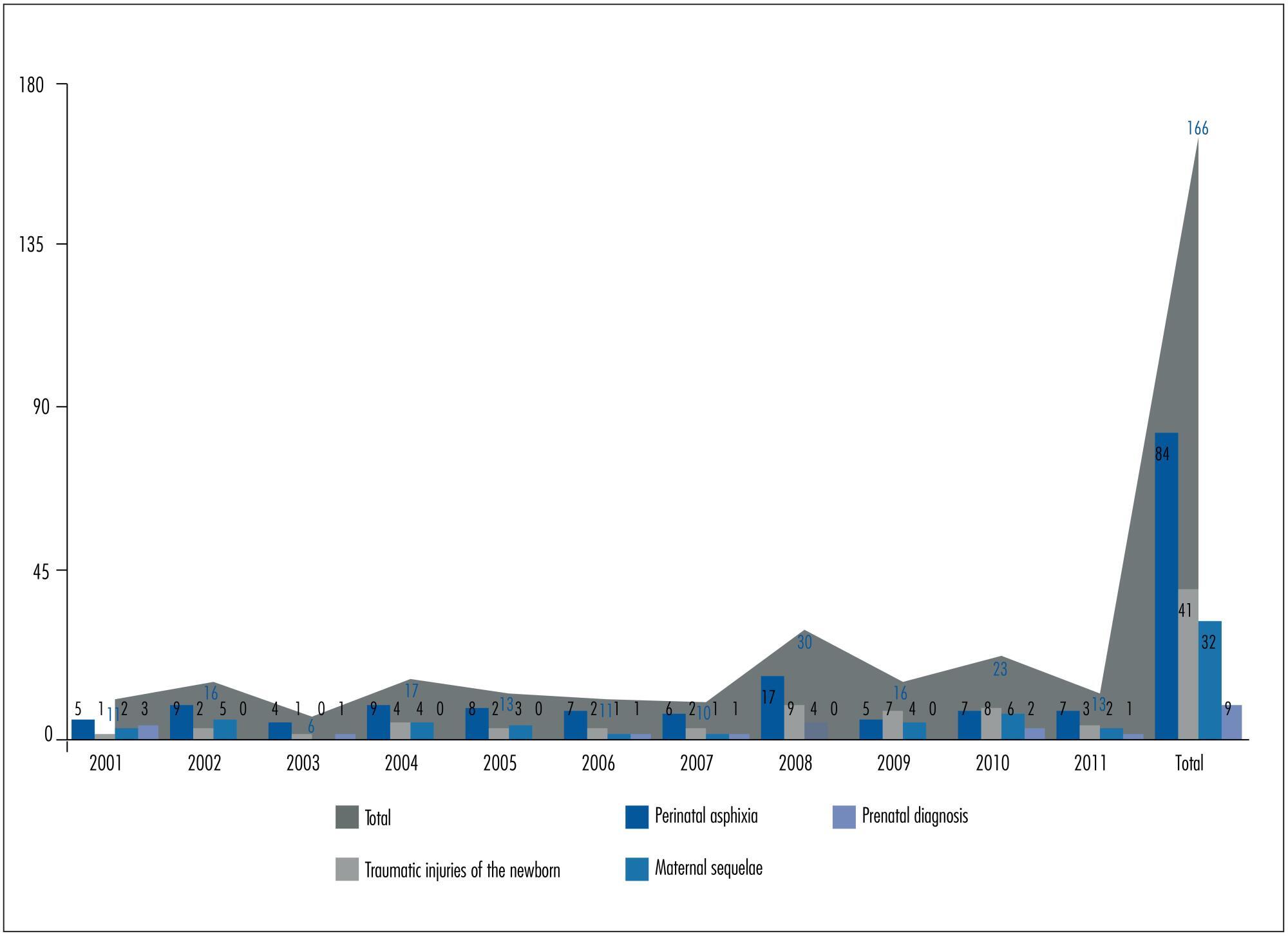
Obstetrics cases submitted to the Medico-legal Council since the creation of the National Institute of Legal Medicine and Forensic Sciences in 2001 until 2011 were evaluated. A comprehensive characterization, determination of absolute/relative frequencies, hypothesis of a linear trend over the years and the association between each parameter was done.
The analysis has shown no significantly linear trend. The most common reasons for disputes were perinatal asphyxia (50%), traumatic injuries of the newborn (24%), maternal sequelae (19%) and issues related to prenatal diagnosis and/or obstetric ultrasound (5.4%). Perinatal asphyxia showed no significantly linear trend (p=0.58) and was usually related to perinatal deaths or permanent neurologic sequelae in newborn children. Traumatic injuries of the newborn, mostly related to instrumented deliveries, shoulder dystocia or vaginal delivery in breech presentation, has shown a significantly increased linear trend (p<0.001), especially related to instrumented deliveries. The delay/absence of cesarean section was the clinical procedure questioned in a significantly higher number of cases of perinatal asphyxia (68.7%) and of traumatic lesions of the newborn due to instrumented deliveries (20.5%).
It is important to improve and correct theoretical/practical daily clinical performance in these highlighted areas, in order to reduce or even avoid situations that could end up in medico-legal litigations.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):152-158
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005282
To determine the average age at the onset of menopause and to investigate menopausal symptoms in women in a metropolitan region in Southeastern Brazil.
A descriptive, exploratory, cross-sectional study was conducted with 749 women (a population-based household survey). The dependent variable was the intensity of menopausal symptoms assessed by th Menopause Rating Scale (MRS). The independent variables were sociodemographic data, health-related habits and problems, self-perception of health, and gynecological background. Statistical analysis was carried out by the χ2 test and Poisson regression using the backward selection criteria.
The mean age of the women was 52.5 (±4.4) years. With regard to menopausal status, 16% were premenopausal, 16% perimenopausal and 68% postmenopausal. The mean age at the onset of menopause was 46.5 (±5.8) years. The intensity of menopausal symptoms was defined according to the median MRS score and was considered severe for values above 8. Depression/anxiety (PR=1.8; 95%CI 1.5-2.2; p<0.01), rheumatic diseases (PR 1.5; 95%CI 1.2-1.7; p<0.01), self-perception of health as fair/poor/very poor (PR 1.4; 95% CI 1.2-1.7; p<0.01), history of abortion (PR 1.3; 95%CI 1.1-1.4; p<0.01), current or previous treatment for menopausal symptoms (PR 1.2; 95%CI 1.1-1.4; p<0.01), peri- or postmenopausal status (PR 1.4; 95%CI 1.1-1.7; p<0.01), number of normal deliveries >1 (PR 1.2; 95%CI 1.02-1.4; p<0.01) and asthma (PR 1.2; 95%CI 1.01-1.4; p<0.01) were associated with more severe menopausal symptoms. Older age (PR 0.96; 95%CI 0.96-0.97; p<0.01) was associated with less severe symptoms.
The severity of menopausal symptoms was related to a wild range of factors, especially presence of chronic diseases, a larger number of pregnancies, use of hormone therapy, and worse self-rated health. A better understanding of these factors can help to reduce the impact of symptoms on quality of life, and to identify groups of women who are likely to need more care during and beyond menopause.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):159-163
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150004973
To analyze the relationship between route of delivery and other aspects of pregnancy and the occurrence of intracranial hemorrhage in newborns of very low weight at a teaching hospital in South Brazil.
A case-control study was conducted. Medical records of all patients who were born weighing ≤1,500 g and who were submitted to transfontanellar ultrasonography were analyzed from January 2011 to September 2014. The cases were newborns with diagnosis of intracranial hemorrhage, while newborns with regular exams were used as controls. Differences between groups were analyzed by the Student t test and by χ2 or Fisher exact tests, and association was determined using the odds ratio with a 95% confidence interval and α=5%.
A total of 222 newborns with birth weight ≤1,500 g were recorded; of these, 113 were submitted to transfontanellar ultrasonography and were included in the study. Sixty-nine (61.1%) newborns were diagnosed with intracranial hemorrhage (cases) and 44 (38.9%) showed no abnormal results (controls). Most cases had grade I hemorrhage (96.8%) originating from the germinative matrix (95.7%). The predominant route of delivery was caesarean section (81.2% of the cases and 72.7% of the controls). Five deaths were recorded (3 cases and 2 controls). Gestational age ranged from 24 to 37 weeks. Median birth weight was 1,205 g (range: 675-1,500 g). The median time of hospitalization was 52 days, ranging from 5 to 163 days.
Grade I intracranial hemorrhage from the germinative matrix was the most frequent. No differences were found between cases and controls for the variables studied. The small number of infants submitted to transfontanellar ultrasonography limited the sample size and the results of the study.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):164-171
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005186
To identify the factors associated with weight retention after pregnancy.
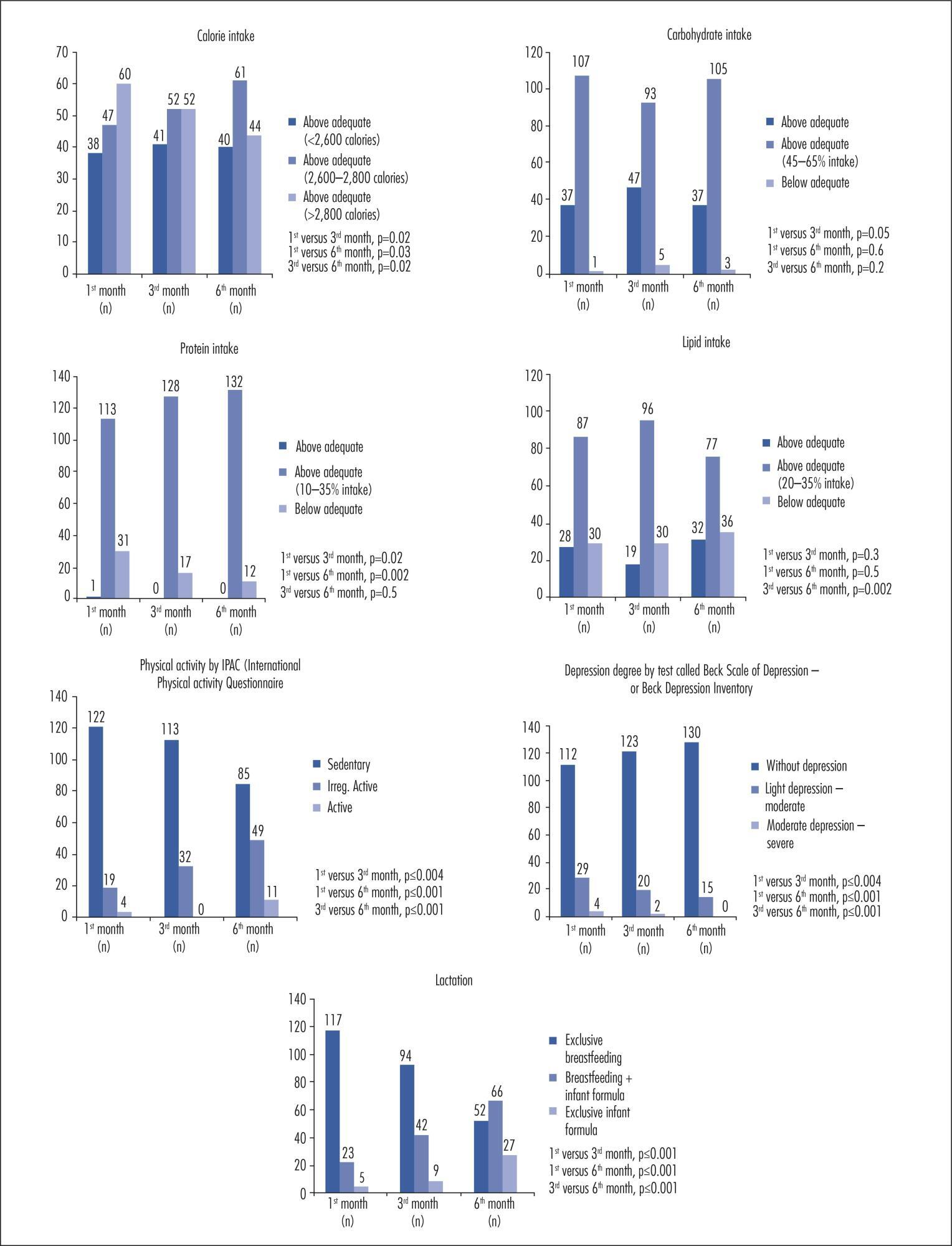
A cohort study was performed with 145 women receiving maternity care at a hospital in Caxias do Sul, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, aged 19 to 45 years, between weeks 38 and 42 of pregnancy. The patients were evaluated at one month, three months, and six months after delivery. Student's t-test or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to compare groups, as indicated; correlations were assessed with Pearson's and Spearman's tests, as indicated; to identify and evaluate confounders independently associated with total weight loss, a multivariate linear regression analysis was performed and statistical significance was set at p≤0.05.
There was a significant positive association between total weight gain - and a negative association with physical exercise during pregnancy - with total weight loss. Higher parity, inter-pregnancy interval, calorie intake, pre-pregnancy body mass index (BMI), weight gain related to pre-pregnancy BMI, presence and severity of depression, and lack of exclusive breastfeeding were directly associated with lower weight loss. Among nominal variables, level of education and marital status were significantly associated with total weight loss.
In the present study, lower weight retention in the postpartum period was associated with higher educational attainment and with being married. Normal or below-normal pre-pregnancy BMI, physical activity and adequate weight gain during pregnancy, lower parity, exclusive breastfeeding for a longer period, appropriate or low calorie intake, and absence of depression were also determinants of reduced weight retention.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):172-177
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005238
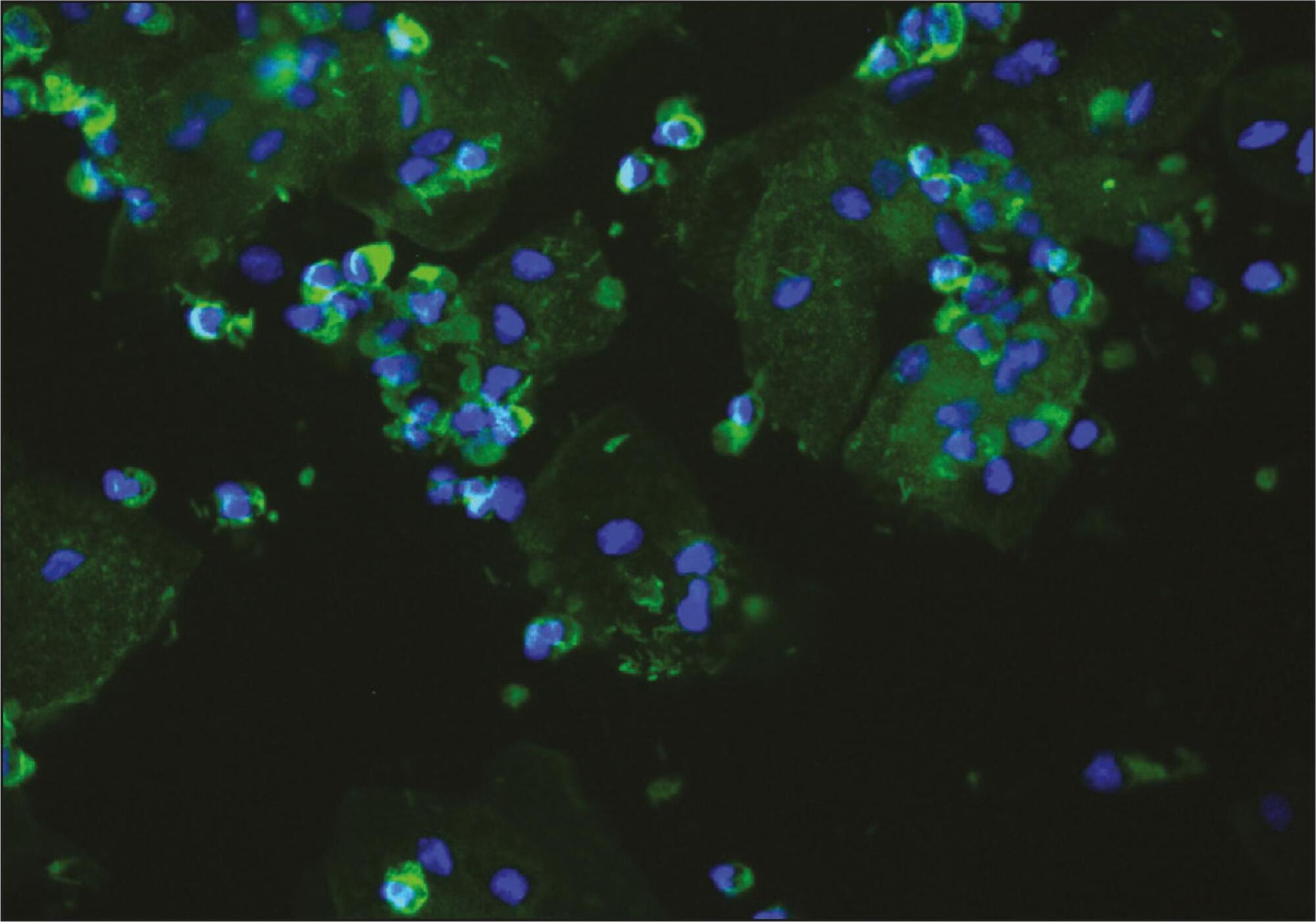
To evaluate the presence of podocyturia in chronic hypertensive pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy and its possible association with renal disease.
This was an observational study of a convenience sample of 38 chronic hypertensive pregnant women. The podocytes were labeled by the indirect immunofluorescence technique with anti-podocin and diamidino-phenylindole (DAPI). The count was made on 30 random fields analyzed and corrected according to urinary creatinine (podocytes/mg creatinine). The patients were assigned to two groups: NG (normal glomerular function), up to 100 podocytes, and GP (probable glomerulopathy), more than 100 podocytes. Urinary creatinine was measured by the alkaline picrate method. The variables analyzed were body mass index, gestational age, and systolic and diastolic blood pressure at the time of sample collection. Data were analyzed using the SPSS - version 16.0 (IBM - USA). Statistical analysis was performed by the χ2 test, and significant differences were considered when p<0.05.
The median podocyte count was 20.3 (0.0-98.1) for group GN, and 176.9 (109.1-490.6) for GP. The mean body mass index was 30.2 kg/m2 (SD=5.6), mean gestational age was 35.1 weeks (SD=2.5), median systolic blood pressure was 130.0 mmHg (100.0-160.0) and median diastolic blood pressure was 80.0 mmHg (60.0-110.0). There was no significant correlation between podocyturia and body mass index (p=0.305), gestational age (p=0.392), systolic blood pressure (p=0.540) or diastolic blood pressure (p=0.540).
In this study, there was no podocyturia pattern consistent with the presence of active renal disease, although some of the women studied (15.8%) exhibited a significant loss. We believe that it is premature to recommend the inclusion of the determination of podocyturia in routine prenatal clinical practice in chronically hypertensive pregnant women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):178-185
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005184
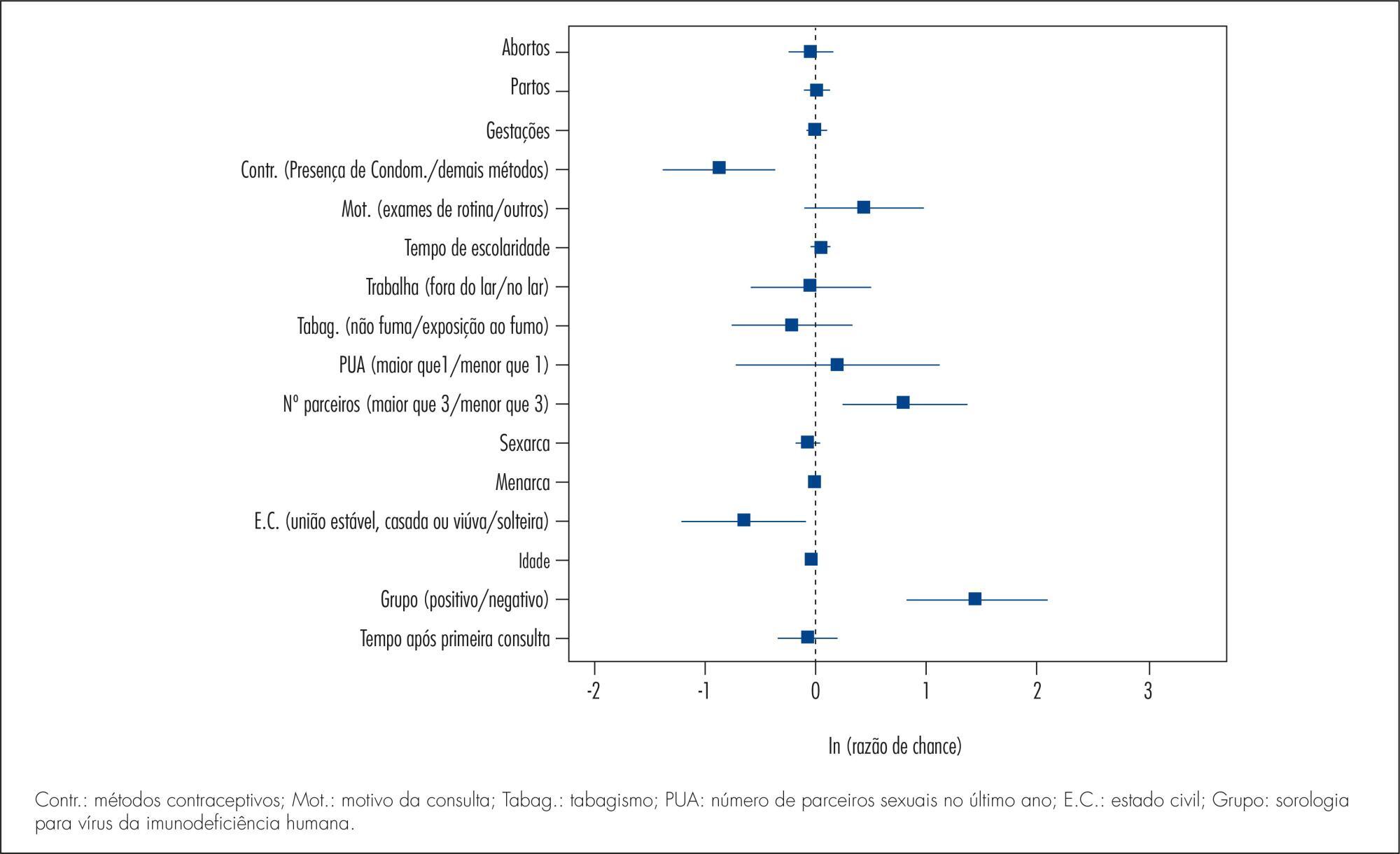
To conduct a comparative study between two groups of women (HIV positive and negative) analyzing: the prevalence of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical HPV infection; viral risk and relationship with development of CIN; and sociodemographic and behavioral parameters that influence cervical HPV infection and the development of CIN.
A cross-sectional study in which 202 HIV-positive women and 164 HIV-negative women were analyzed to assess the prevalence of CIN and 171 HIV-positive women and 160 HIV-negative women were analyzed to assess the prevalence of cervical HPV infection. The following procedures were performed on the occasion of each medical visit: collection of cervical samples for cytology and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to detect HPV DNA; colposcopy; standardized questionnaire to collect demographic and behavioral data; and biopsy of all colposcopic changes. Histopathology was the gold standard for the diagnosis of CIN.
The prevalence of CIN was 2.4 and 15.3% (p<0.001) and the prevalence of cervical HPV infection was 37.1 and 55.5% (p=0.002), respectively, among HIV-negative and -positive women. HIV-positive women had a higher risk of HPV infection (35.7 and 23.6%) (p=0.02). HPV 16 was the most prevalent virus type, occurring in 11.3 and 10.2% of HIV-positive and negative women and was also more prevalent among women presenting CIN in both groups. Factors associated fwith the development of CIN were: HIV infection (HT=4.64; 95%CI 2.23-9.65), age (HT=0.95; 95%CI 0.93-0.98 for each year of life) and marital status(HT=0.49; 95%CI 0.30-0.80). Associated factors for HPV infection were: HIV presence (HT=2.72; 95%CI 1.77-4.17), greater number of sexual partners (HT=1.87; 95%CI 1.23-2.84), age (HT=0.97; 95%CI 0.95-0.99 for each year of life) and marital status (HT=0.65; 95%CI 0.42-1.0 for stable union/widows).
The prevalence of CIN and cervical HPV infection was higher in HIV-positive women, who also presented a higher risk of HPV infections and multiple viral types. Type 16 was predominant in both groups and in women with CIN. Older women and women with stable union/widows were less likely to acquire cervical HPV infection and CIN.