Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):252-257
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005278
To determine the feasibility of evaluation of the right subclavian artery during
the first trimester ultrasound scan, as well as to describe the technique for its
evaluation and, in case of aberrant right subclavian artery (ARSA) identification,
to determine its association with chromosomal abnormalities and/or cardiac
malformations and its management.
A prospective study for evaluation of the right subclavian artery during the
first trimester ultrasound scan (crown-to-rump length between 45 and 84 mm), in
all consecutive single pregnancies, by a single examiner, using a Voluson E8
system (GE Healthcare, Zipf, Austria) with a 2 to 8 MHz RAB 4-8-D transabdominal
probe, within a short period of time (less than 2 minutes), in a general low risk
population. Color and/or power Doppler flow mapping was used to classify the right
subclavian artery as normal or aberrant. Regression analysis with the IBM SPSS
Statistics software for Windows, version 20.0 was used to determine the
significance of the association between failure to examine/classify the right
subclavian artery and both fetal crown-rump length and maternal body mass index.
Median maternal age was 30 years (range: 17-43 years) and median gestational age
at the time of evaluation of the right subclavian artery was 12 weeks (range:
11-13 weeks). The evaluation of the right subclavian artery was successful in
138/176 (78.4%) of the cases. ARSA was diagnosed in a single case (0.7%). This
fetus with ARSA also presented a hyperechogenic focus on the left cardiac
ventricle. Fetal echocardiography at 16 weeks of gestation was performed and
confirmed ARSA and the hyperechogenic focus. Amniocentesis revealed a normal 46,
XX karyotype.
ARSA can be identified during a routine first trimester ultrasound scan. Our
single ARSA case had a normal karyotype and no associated cardiac
malformations.
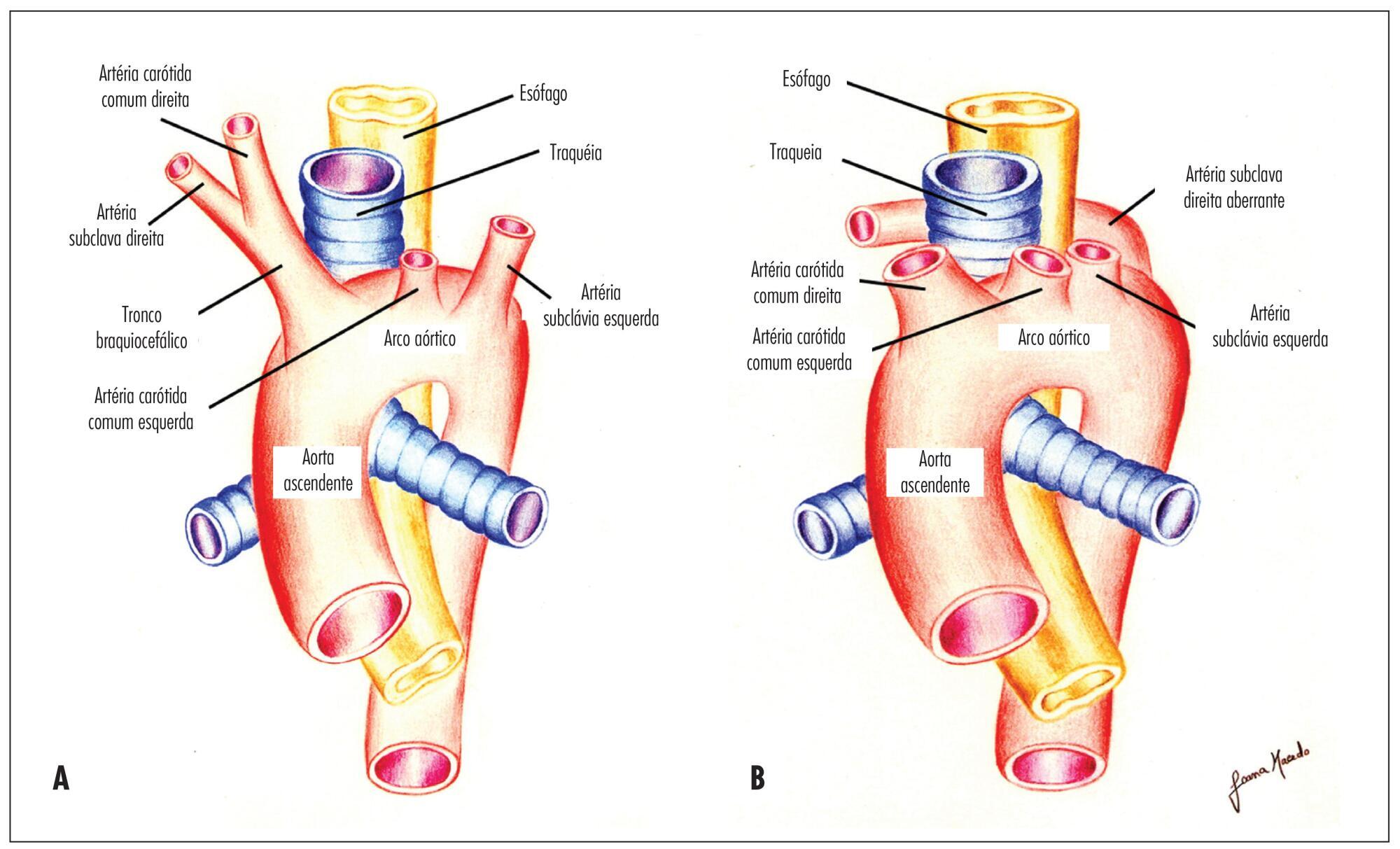
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):266-271
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005254
To investigate the relationship between sexual function and quality of life in
pregnant women living in two cities of Northeastern Brazil.
The sample consisted of 207 pregnant women. The data were collected through a
questionnaire containing questions about socio-demographic, gynecological and
obstetrical data, body and sexual knowledge. Quality of life was assessed by
applying the Ferrans & Powers Quality of Life Index (QLI Ferrans and Power).
Sexual function was assessed using the Female Sexual Function Index (IFSF). Data
were statistically analyzed using the Shapiro-Wilk, Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon
tests.
The pregnant women studied had a median age of 30 years (quartile 26-33 years)
and were approximately at the 26th gestational week. A significant
decrease in the monthly frequency of sexual relations of the couple was observed,
with a median of 12 to 4 times per month (Z=-10.56; p<0.001). Sexual
dysfunction was detected in 35.7% of the pregnant women studied, whose quality of
life was lower when compared to women with unchanged sexual function (Z=-2.9;
p=0.004).
The results of this study show that sexual dysfunction negatively affected the
quality of life of pregnant women, and this should be an important aspect for
review during prenatal consultations.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):272-277
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005301
To evaluate the ovarian response after cyclophosphamide use (CPM) in patients
with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and to correlate the age and cumulative
dose findings with changes in menstrual cycle and/or progression to ovarian
failure (OF).
This was a cross-sectional, retrospective study of 50 patients with a diagnosis
of SLE who used CFM with a clinical follow-up of at least 1 year. Included were
patients aged 12-40 years, who had undergone chemotherapy for SLE control and who
had regular menstrual cycles before the beginning of CPM treatment. Patients who
discontinued follow-up, who were followed up for less than one year or who had
irregular/absent menses before the beginning of CPM treatment were excluded. All
women studied were submitted to an interview and a questionnaire containing
questions about the pattern of the menstrual cycle before and after therapy, and
about the gestational periods and contraception. We asked if the patients had been
instructed about the side effects and consequences of CFM. Statistical analysis
was performed using the Student t-test and the Mann Whitney, χ2 and
nonparametric Kolmogorov-Smirnov tests.
The mean age of the patients included in the study was 30.8 years and the mean
age at the time of use of CPM was 25.3 years. After CFM, 24% of patients stopped
menstruating, 28% returned to regular cycles and 48% continued to have irregular
cycles. It was found that the patients who developed OF had longer disease
duration (12.3 years) than those who did not develop it (8.9 years). Thirteen
patients became spontaneously pregnant after CFM; however, 66% progressed to
abortion. The mean age of the patients who used CFM and developed OF was 28.1
years. Amenorrhea occurred in 50% of those aged 31-40 years, in 22.2% of those
aged 21-30 years and in 7.7% of those aged 12-20 years. Our study showed no
statistical correlation between cumulative dose and OF, although cumulative doses
greater than 11grams tended to promote some type of menstrual irregularity.
SLE disease duration, age at the time of treatment and the highest cumulative
doses are important predictors of OF after therapy with CFM. Pregnancy in lupus
patients is more likely to evolve with abortion after the use of chemotherapy. It
was seen that a small proportion of patients were aware of all the implications of
the drug. Therefore, additional studies should be conducted for further knowledge
and awareness of the importance of contraception and the preservation of ovarian
tissue on the part of the medical community.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):278-282
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005326
to analize the level of functional fitness of a group of postmenopausal women in
the city of Presidente Prudente using the set of functional fitness tests of the
American Alliance for Health, Physical Education, Recreation and Dance and to
check whether there are differences between groups of women in the fifth and sixth
decade of life.
This was a cross-sectional study conducted on 175 postmenopausal women (follicle
stimulating hormone level>26.72 mIU/L) in the city of Presidente Prudente in
2013. The inclusion criteria were not being part of any type of systematic motor
intervention for at least six months before the collection of research data;
absence of motor or cognitive impairment that would prevent the evaluation
protocols, and absence of chronic or degenerative disease, musculoskeletal injury
or comorbidity that could prevent or limit the evaluations. The women were
evaluated by the same trained examiners. The 50 to 59 year group showed a mean age
of 55.3±4.5 years, mean FSH values of 53.5±21.1 mIU/mL, mean coordination of
11.4±2.2 seconds, mean strength of 20.1±3.9 repetitions, mean flexibility of
51.7±11.8 cm, mean 23.2±2.8 seconds agility and mean aerobic resistance of
500±43/2 . The 60 to 69 year group had a mean age of 65.1±4.1 years with FSH
54.9±15.9, 11.6±2.6 seconds coordination, strength 20.3±4.7 repetitions, 54.6±11.2
cm flexibility, agility 24.7±4.3 seconds, and aerobic resistance of 508±51
seconds.
It was possible to analyze the functional fitness of postmenopausal women through
the set of the American Alliance testing for Health, Physical Education,
Recreation and Dance with no significant differences between groups for the
variables strength, flexibility, aerobic capacity and coordination, and with only
the speed variable showing significant differences. We recommend further studies
seeking to formulate normative values for the population in question.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):203-207
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005293
To determine the frequency of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) in the placenta, in the
colostrum and in the umbilical cord blood of parturient women and their newborns
assisted at the Clinic of Gynecology and Obstetrics of the University Hospital of
Rio Grande (RS), Brazil.
Biopsies were collected from 150 placentas on the maternal side, 150 on the fetal
side, 138 samples of umbilical cord blood and 118 of the colostrum. The placenta
biopsies were collected from the central and peripheral portions. DNA was
extracted according to the manufacturer's protocol and to a reference found in the
literature. HPV was detected by the nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR-Nested)
using primers MY09/11 and GP5/GP6. Genotyping was performed by direct sequencing.
The participants responded to a self-applied questionnaire with demographic and
clinical data, in order to characterize the sample.
HPV was detected in 4% (6/150) of cases on the mother's side of the placentas, in
3.3% (5/150) on the fetal side, in 2.2% (3/138) in umbilical cord blood and in
0.84% (1/118) in colostrum samples. The vertical transmission rate was 50%. HPV-6
was the low-risk genotype found (60%) and the high-risk genotypes were HPV-16 and
HPV-18 (20% each).
These results suggest that HPV can infect the placenta, the colostrum and the
umbilical cord blood.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):208-215
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005321
To describe the evolution of the prevalence of anemia in pregnant adolescents
attended at a public maternity in the city of Rio de Janeiro from 2004 to 2013.
A retrospective cross-sectional study with 628 pregnant/postpartum women divided
into 3 groups: Group A (2004-2006), Group B (2007-2010) and Group C (2013).
Information about anthropometric, clinical, sociodemographic data and obstetric
and prenatal care of adolescents was obtained from medical records of the pregnant
women. A hemoglobin concentration n<11 g/dL was considered to be anemia. Data
were analyzed statistically by the chi-square test, Student's t-test and ANOVA,
and the post hoc Tukey test.
The prevalence of gestational anemia over the years was 43% (GA=138), 36% (GB=80)
and 47.1% (GC=40) and the overall prevalence for the 2004-2013 period was 41.1%
(n=258). The occurrence of anemic pregnant women increased with the progression of
pregnancy; however, in the 3rd quarter there was a decrease in the prevalence of
anemia in GB (29.3%) compared to GA (38.7%; p=0.04). Factors associated with
anemia were number of prenatal visits and prenatal nutritional assistance, place
of residence, pre-pregnancy BMI, and gestational weight gain.
The results showed that the prevalence of anemia among pregnant adolescents seen
at a public maternity is high. There was no reduction of anemia during the study
period and other factors in addition to iron deficiency were involved in the
genesis of anemia in this population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):216-221
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005272
To compare obstetric outcomes of induced preterm twin births (under 32 weeks gestation) with those spontaneously conceived.
Prospective study of twin pregnancies (25 induced and 157 spontaneously conceived) developed over a period of 16 years in a tertiary obstetric center. Demographic factors, obstetric complications, gestational age at delivery, mode of delivery, birth weight and immediate newborn outcome were compared.
The analysis of obstetrical complications concerning urinary or other infections, hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, gestational diabetes, fetal malformations, intrauterine fetal death, intrauterine growth restriction and intrauterine discordant growth reveal no significant statistical differences between the two groups. First trimester bleeding was higher in the induced group (24 versus 8.3%, p=0.029). The cesarean delivery rate was 52.2% in spontaneous gestations and 64% in induced gestations. Gestational age at delivery, birth weight, Apgar scores at first and fifth minutes, admissions to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit and puerperal complications show no statistically significant differences between the two groups. These results were independent of chorionicity and induction method.
The mode of conception did not influence obstetric and neonatal outcomes. Although induced pregnancies have higher risk of first trimester bleeding, significant differences were not observed regarding other obstetric and puerperal complications and neonatal results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(5):222-228
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005183
To estimate the prevalence of bacterial vaginosis (BV), candidiasis and
trichomoniasis and compare the findings of physical examination of the vaginal
secretion with the microbiological diagnosis obtained by cytology study of a
vaginal smear using the Papanicolaou method.
A cross-sectional study of 302 women aged 20 to 87 years, interviewed and
submitted to a gynecology test for the evaluation of vaginal secretion and
collection of a cytology smear, from June 2012 to May 2013. Sensitivity analyses
were carried out and specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative
predictive value (NPV) with their respective 95%CI were determined to assess the
accuracy of the characteristics of vaginal secretion in relation to the
microbiological diagnosis of the cytology smear . The kappa index (k) was used to
assess the degree of agreement between the clinical features of vaginal secretion
and the microbiological findings obtained by cytology.
The prevalence of BV, candidiasis and trichomoniasis was 25.5, 9.3 and 2.0%,
respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of the clinical
characteristics of vaginal secretion for the cytological diagnosis of BV were 74,
78.6, 54.3 and 89.9%, respectively. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV and the NPV
of the clinical characteristics of vaginal secretion for the cytological diagnosis
of candidiasis were 46.4, 86.2, 25.5 and 94%, respectively. The correlation
between the clinical evaluation of vaginal secretion and the microbiological
diagnosis of BV, candidiasis and trichomoniasis, assessed by the kappa index, was
0.47, 0.23 and 0.28, respectively.
The most common cause of abnormal vaginal secretion was BV. The clinical
evaluation of vaginal secretion presented amoderate to weak agreement with the
microbiological diagnosis, indicating the need for complementary investigation of
the clinical findings of abnormal vaginal secretion.