Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(11):683-690
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001100009
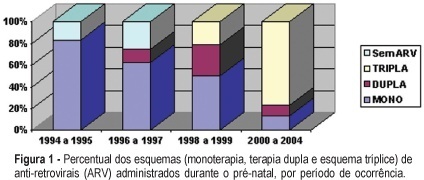
PURPOSE: to evaluate human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) vertical transmission and risk factors related to perinatal infection. METHODS: descriptive study of 170 HIV-infected pregnant women and their 188 neonates, admitted from June 1994 to September 2004 at the "Maternidade do Hospital das Clínicas da UFMG". Demographic characteristics, mother's serologic state, mode of delivery and perinatal results were analyzed. Children were followed for 18 months after birth. Data were stored and analyzed by Epi-Info, version 6.0. Confidence interval was established at 95% (p<0.05). RESULTS: HIV infection was confirmed in 84 (45.4%) patients during gestation. Viral load was below 1,000 copies/mL in 60.4% patients. Highly active antiretroviral therapy was the predominant antiretroviral regimen (65.5%). C-section rate was high: 79.5%. Prematurity rate was 18.2%. There were 184 (97.8%) live births and four (2.2%) perinatal deaths among 188 neonates. Among live neonates 97.8% received zidovudine after birth. Global mother-to-child transmission rate was 3.8%. Virus vertical transmission rates for each period were: 60%, until 1996; 28% between 1996 and 1998; 0.68%, between 1999 and 2004. Significant risk factors were not found related to perinatal HIV-infection because there was a small number of infected neonates (n=6). CONCLUSION: there was a great reduction of HIV vertical transmission during the analyzed period. Current transmission rate is zero. This confirms that by adopting adequate measures perinatal virus transmission can be prevented.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(3):112-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000300003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the influence of previous hormonal therapy (HT) on breast cancer prognostic markers in postmenopausal women. Methods: a cross-sectional study was carried out, applying questionnaires and medical record surveys of 157 postmenopausal patients with breast cancer diagnosis. Clinical data, personal and familiar history, HT use, and mammograms were investigated. The medical record surveys yielded information about tumor size, imunohistochemical data, and type of surgery. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA and the chi2 test. RESULTS: 38.2% of the patients were HT ex-users and 61.8% were non-users. Mean time of HT use was 3.7±3.6 years. HT ex-users were younger and with a shorter menopause time than non-users (p<0.05). 26.8% of the patients reported previous cases of breast cancer in their families, with no difference between the groups. Of the HT ex-users, 43.3% had previous mammograms, while of the non-users, only 11.3% (p<0.001). Mean tumor size was smaller in HT ex-users (2.3±1.1 cm) than in non-users (3.3±1.5cm) (p<0.001). The conservative surgeries (quadrantectomies) were predominant in HT ex-users (60%) when compared to non-users (32%) (p<0.001). The immunohistochemical study showed, a positive correlation between the presence of positive estrogen and progesterone receptors and the HT use (p<0.001). There was no correlation between HT and c-erbB-2 and p53. CONCLUSION: postmenopausal women who used hormonal therapy previously to breast cancer diagnosis presented indication of a better prognosis when compared to non-users.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(3):118-124
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000300004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of the association of estrogen and androgen on the quality of life and sexuality of women during climacterium. METHODS: ninety-six postmenopausal women with vasomotor symptoms and sexual dysfunction were included. The participants were randomly divided into three treatment groups with 32 pacients each: placebo, conjugated equine estrogens (CEE) (0.625 mg per day) and CEE (0.625 mg per day) associated with methyltestosterone (2.5 mg per day). The length of the treatment period was three months. The Women Health Questionnaire (WHQ) and the Modified Sexuality Questionnaire were applied to evaluate the quality of life and sexuality before and after the treatment. Some parameters of cardiovascular risk, endometrial echo and hepatic toxicity were evaluated. ANOVA was used for data analysis followed by the Fisher test and the Shapiro-Wilk post hoc test. RESULTS: the improvement in WHQ parameters was significant in the hormonal treatment groups (CEE and CEE + methyltestosterone) compared to the placebo group. However, there were no differences in somatic symptoms among the three groups. The association of estrogen with androgen significantly improved sexual function (score (mean): 64 vs 67, p<0.05) and depressive humor (score (mean): 75 vs 80, p<0.05) compared to estrogen alone. This therapy also presented a large number of WHQ questions with a high score (p<0.05). The use of CEE associated with methyltestosterone decreased the total cholesterol (212±42 and 194±43, before and after the treatment, respectively) and HDL colesterol (56±16 and 48±14, before and after the treatment, respectively), and slightly increased the endometrial echo (4.7±2.3 and 5.5±2.3, before and after the treatment, respectively). No signifcant changes in liver enzymes during the treatment period was detected. CONCLUSIONS: estrogen associated with methyltestosterone resulted in significant improvement in the quality of life and sexuality of postmenopausal women. This effect was superior to estrogen alone and placebo. The effect of treatment with the estrogen-androgen association was evident regarding depressive humor and sexual function questions of the WHQ.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(3):125-129
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000300005
BACKGROUND: patients with primary amenorrhea and gonadal dysgenesia have higher serum gonadotrophins and should be submitted to chromosome studies. Karyotype studies may be performed in gonadal tissue or peripheral blood however, it is not yet established if cases of primary amenorrhea without signs of virilization need additional investigation of gonadal karyotype. PURPOSE: to analize the gonadal karyotypes (ovaries) from patients with primary amenorrhea and compare them to their respective peripheral blood karyotypes. METHODS: clinical and karyotype data of 12 patients were retrospectively analyzed from January 1997 to December 2003. RESULTS: when the investigation was indicated for primary amenorrhea without signs of virilization, the gonadal and peripheral blood karyotypes were concordant in 8 cases (7 cases 46XX and 1 case 46XY). One patient with virilization signs was the only case of discordant karyotype. CONCLUSION: the present study suggests that the gonadal karyotype does not bring additional information to peripheral blood karyotype in patients with amenorrhea and no signs of virilization. Although all previous studies had a small number of patients, it seems advisable to investigate the gonadal karyotype in patients with signs of virilization. The cost-benefit analysis could allow cost and stress reduction for patients, family and institutions.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(3):130-136
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000300006
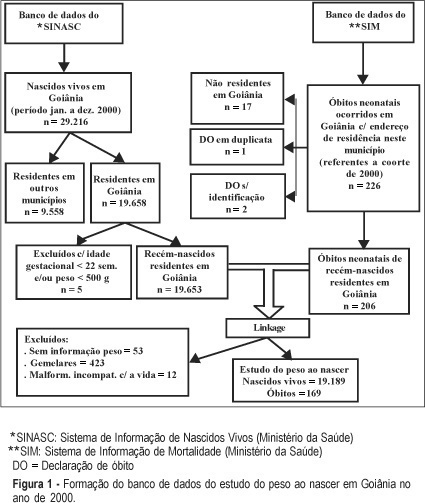
PURPOSE: to analyze birth weight in a cohort of newborns for the year 2000, in Goiânia, by determining the coefficient of mortality and neonatal survival probability, stratified by categories of birth weight, and also, through the identification of factors associated with low birth weight (LBW). METHODS: a retrospective cohort study, made possible by the linkage of data from the ISM (Information System on Mortality) and ISLB (Information System on Live Births) files. Coefficients of neonatal mortality were calculated for the categories of birth weight and a neonatal survival probability chart was constructed with the help of linear regression analysis. Risk factors for LBW were identified by univariate analysis (RR) and logistic regression analysis, and the level of significance was set at 5%. RESULTS: the incidence of LBW was 6.9% and 140 (66.8%) neonatal deaths took place in this group. Thirty percent of these deaths occurred in the 1,500-2,500 g weight bracket. The following risk factors were identified for LBW: preterm pregnancy, presence of congenital malformations, mothers at the extreme ages for reproduction, mothers living in the northwestern region of the city, insufficient prenatal appointments with the doctor, delivery in a public hospital, and female babies. CONCLUSION: Goiânia had an incidence of LBW which is comparable to that of developed countries and coefficients of neonatal mortality by category of weight were below those found for those countries. These results recommend that we pay attention to: prematurity, public hospitals, and the northwestern region of Goiânia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(3):137-142
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000300007
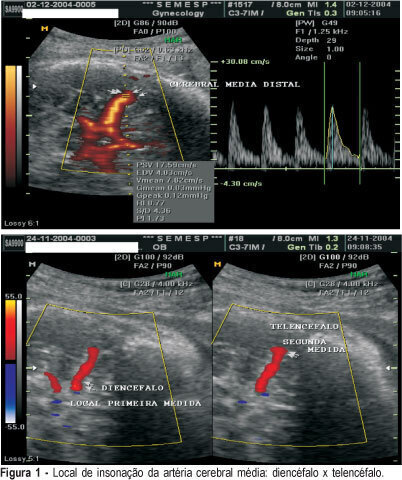
PURPOSE: to evaluate if there is any difference between Doppler indexes in the middle cerebral artery in two different sites of insonation in healthy patients and in patients with diseases. METHODS: a random prospective survey, in the period from June 2003 to March 2004 that analyzed the Doppler indexes of 100 patients: patient group (n = 50) included patients admitted to Clemente Farias University Hospital, which is part of UNIMONTES-MG, havinfg as inclusion criteria: to be in the 28th to 34th gestational week, diagnosis of chronic arterial hypertension, pre-eclampsia, intrauterine growth restriction. As control group, 50 healthy pregnant patients between the 28th and the 34th week, originary from SEMESP's clinic. The Doppler variables were the resistance index (RI), the pulsatility index (PI) and the relation systole/diastole (SD). All three Doppler indexes were assessed at two different sites of the cerebral artery: the first measurement in the diencephalons region, soon after the beginning of the middle cerebral artery and the second on a distal location in the telencephalon. The median Doppler indexes in the patient group in the first and second measurements were 1.55 and 1.69 for the PI, 0.77 and 0.79 for RI and 4.29 and 4.86 for SD, respectively. In the control group, the values were 1.73 and 1.86 for the PI; 0.83 and 0.79 for RI and 5.83 and 5.46 for SD. There were no differences between sites with a p value of 0.38, 0.29 and 0.39 for PI, RI and SD, respectively. In 15t fetuses with centralization (brain sparing effects), in the diencephalon the median indexes were 1.02 for PI, 0.63 for RI and 2.68 for SD. In the epencephalon the median indexes were 0.95 for IP, 0.62 for RI and 2.44 for SD. There were no differences between sites, with a p value of 0.53 for PI; 0.56 for IR and 0.31 for SD. The Doppler index site of assessment in the middle cerebral arteries does not interfere with the results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(3):143-148
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000300008
PURPOSE: to describe etiology, evolution and prevalence of hydrops fetalis in a cohort of pregnant women during a period of ten years (1992 to 2002) in a tertiary maternity. METHODS: a retrospective study was carried out in patients referred to the maternity of the Fernandes Figueira Institute, with diagnosis of hydrops fetalis, detected by ultrasonography, during the period from 1992 to 2002. The cases were selected according to etiology (immune or nonimmune) and evolution, performed invasive procedures and survival were compared between both groups. Analysis of variables was performed by Epi-Info 6.0 and a p value less than 0.05 was considered to be statistical significant. RESULTS: in ten years of follow-up, 80 patients with an initial diagnosis of hydrops were attended. The frequency of hydrops in this population was 1 in 157 live births. Rh immunization (immune group) was detected in 13 cases (16.2%), and for 67 cases (83.8%) nonimmune causes (nonimmune group) were considered. Major causes of nonimmune hydrops fetalis were idiopathic (40.2%), genetic (20.8%), infectious diseases (20.7%), and cardiopathy (7.4%). A difference was found in relation to maternal age in the immune group (mean = 32.8 years) when compared with the nonimmune group (mean = 28.7 years) (p=0.03), but gestational age at delivery was similar in both groups (mean = 33.6 weeks in the immune group and 33.1 weeks in the nonimmune group) (p=0.66). Amniocentesis and blood transfusion in utero were carried out more frequently in the immune group (p<0.001) and perinatal mortality was 53.8% in the immune group and 68.6% in the nonimmune group (p=0.47). Complementary research of IgG anti-parvovirus B19 antibodies was carried out in 41 of 67 cases of nonimmune hydrops, with 16 being positive for the presence of anti-B19 IgG antibodies. CONCLUSION: nonimmune etiology was the most common form of presentation of hydrops fetalis in our study. Perinatal mortality of this entity is still high and a substantial number of cases had no identified cause. Characterization of fetal karyotype and performance of specific parvovirus B19 serology could increase causal identification of nonimmune hydrops classified as idiopathic.