Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(12):554-561
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001200005
PURPOSE: To investigate the etiology and the epidemiological profile of patients with vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC) and predisposing factors. METHODS: Vaginal secretions were streaked in Sabouraud agar and yeast samples were isolated and identified by Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Demographic and clinical data were obtained with a questionnaire. For statistical analysis, the Student's t-test, the χ² and Fischer tests were applied as needed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) software, with the level of significance set at 5%. RESULTS: Sixty-nine patients aged from 15 to 52 years were evaluated. They were predominantly white (79.7%), with higher education (58%), married (56.5%) and sexually active (97.1%). Among them, 34.8% were pregnant, 7.2% diabetic, 1.4% seropositive for AIDS, and 36.2% were using oral contraceptives. Recent antibiotic therapy was mentioned by 13% of the patients, and antifungal or anti-trichomonas therapy was mentioned by 5.8 and 1.4% of the patients, respectively. Corticosteroid use was reported by 2.9% and antineoplastic by 1.4%. Vaginal discharge and itching were the main complaints (97.1 and 73.9%), followed by burning (63.8%) and erythema (63.8%). When present, the vaginal flow was predominantly white (88.1%) or lumpy (86.6%). The diagnosis was confirmed by culture in 55 (79.7%) patients, with mixed infections in 4 patients. The most prevalent species was C. albicans, followed by C. glabrata (one monoinfection and two mixed infections with C. albicans). C. lusitaniae and C. albicans were also identified in mixed infections (two patients). CONCLUSION: Despite the high culture positivity and clinical data characteristic of VVC, the symptoms were not pathognomonic. C. albicans is the most prevalent species, but other species are also involved in VVC etiology, such as the emergence of C. lusitaniae.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(2):50-55
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000200002
To evaluate pregnancy outcome and thrombophilia frequency in women with recurrent
fetal death.
Evaluation of obstetric outcomes in a retrospective cohort of pregnant women with
recurrent stillbirth after the 20th week, from 2001 to 2013.
Antithrombin activity, protein C and S activity, factor V Leiden, prothrombin gene
mutation and antiphospholipid syndrome were analyzed.
We included 20 patients who had recurrent fetal death. Thrombophilia were found
in 11 of them, 7 diagnosed with antiphospholipid syndrome, 3 with protein S
deficiency and 1 with prothrombin gene mutation. All of them were treated with
subcutaneous heparin (unfractionated heparin or enoxaparina) and 14 of them with
acetylsalicylic acid (AAS) during pregnancy. Obstetric complications occurred in
15 patients and included: intrauterine fetal growth restriction (25%), placenta
previa (15%), reduced amniotic fluid index (25%), severe preeclampsia (10%), fetal
distress (5%), and stillbirth (5%). The mean gestational age at delivery was
35.8±3.7 weeks and newborn weight averaged 2,417.3±666.2 g.
Thrombophilia screening should be performed in all pregnant women with recurrent
fetal death after the 20th week as a way to identify possible causal
factors suitable for treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(2):56-64
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000200003
To evaluate the adequacy of the process of prenatal care according to the
parameters of the Program for the Humanization of Prenatal Care (PHPN) and of the
procedures provided by the Stork Network of Unified Health System (SUS) in the
microregion of Espirito Santo state, Brazil.
A cross-sectional study was conducted in 2012-2013 by interviewing and analyzing
the records of 742 women during the postpartum period and of their newborns in 7
hospitals in the region chosen for the research. The information was collected,
processed and analyzed by the χ2 and Fisher's exact test to determine
the difference in proportion between the criteria adopted by the PHPN and the
Stork Network and the place of residence, family income and type of coverage of
prenatal service. The level of significance was set at 5%.
The parameters showing the lowest adequacy rate were quick tests and repeated
exams, with frequencies around 10 and 30%, respectively, in addition to
educational activities (57.9%) and tetanus immunization (58.7%). In contrast, risk
management (92.6%) and the fasting plasma glucose test (91.3%) showed the best
results. Adequacy was 7.4% for the PHPN, 0.4% for the Stork Network, with respect
to the parameters of normal risk pregnancies, and 0 for high risk pregnancies.
There was a significant difference between puerperae according to housing location
regarding the execution of serology for syphilis (VDRL), anti-HIV and repeated
fasting glucose tests, and monthly income influenced the execution of blood
type/Rh factor tests, VDRL, hematocrit and anti-HIV test.
Prenatal care in the SUS proved to be inadequate regarding the procedures
required by the PHPN and Stork Network in the micro-region of a state in
southeastern Brazil, especially for women of lower income, PACS users and
residents of rural areas.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(2):65-71
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000200004
To analyze the relationships among gestational risk, type of delivery and
immediate maternal and neonatal repercussions.
A retrospective cohort study based on secondary data was conducted in a
university maternity hospital. A total of 1606 births were analyzed over a 9-month
period. Epidemiological, clinical, obstetric and neonatal characteristics were
compared according to the route of delivery and the gestational risk characterized
on the basis of the eligibility criteria for high clinical risk. The occurrence of
maternal and neonatal complications during hospitalization was analyzed according
to gestational risk and cesarean section delivery using univariate and
multivariate logistic analysis.
The overall rate of cesarean sections was 38.3%. High gestational risk was
present in 50.2% of births, mainly represented by hypertensive disorders and fetal
malformations. The total incidence of cesarean section, planned cesarean section
or emergency cesarean section was more frequent in pregnant women at gestational
high risk (p<0.001). Cesarean section alone did not influence maternal outcome,
but was associated with poor neonatal outcome (OR 3.4; 95%CI 2.7-4.4). Gestational
high risk was associated with poor maternal and neonatal outcome (OR 3.8; 95%CI
1.3-8.7 and OR 17.5; 95%CI 11.6-26.3, respectively). In multivariate analysis, the
ratios were maintained, although the effect of gestational risk has determined a
reduction in the OR of the type of delivery alone from 3.4 (95%CI 2.7-4.4) to 1.99
(95%CI 1.5-2.6) for adverse neonatal outcome.
Gestational risk was the main factor associated with poor maternal and neonatal
outcome. Cesarean delivery was not directly associated with poor maternal outcome
but increased the chances of unfavorable neonatal outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(2):79-83
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000200006
To investigate the presence of depressive symptoms in women with chronic pelvic
pain.
This descriptive cross-sectional study was performed with women aged 18 years or
older, diagnosed with chronic pelvic pain, with no pregnancy history in the
previous year, and with no cancer history. The sample was established by
calculating the representative sample, estimated as 50 women. All women were
undergoing treatment at a gynecology outpatient clinic, referred by the primary
health care network of the Brazilian national health system. Data collection was
performed from October2009 to May 2010. The women's sociodemographic, economic and
clinical characteristics were analyzed. Pain intensity was evaluated using a
visual analogue scale. The depressive symptoms were investigated using Beck's
Depression Inventory. Statistical analysis was performed using position measures
(mean, median), dispersion (standard deviation) and the χ2 test. Values
of p≤ .05 were considered statistically significant.
The participants' mean age was 41.6±9.4 years. The following features
predominated: secondary education level; pardo (brown) skin color; Catholic
religion; and living with a steady partner. Most (98%) were economically active
and worked with general domestic services. Regarding the participants' subjective
perception of pain, 52% reported experiencing intense pain, while 48% reported
experiencing moderate pain. Most women (52%) had been living with pain for five
years or less, and 30%, for over 11 years. The mean BDI score was 17.4 (±9.4). It
was observed that 58% of the women presented mild, moderate and severe depressive
symptoms according to the BDI. The most frequent depressive symptoms were
fatigability, loss of libido, irritability, difficulty to work, somatic
preoccupations, crying, dissatisfaction, sadness, and insomnia.
Depressive symptoms were frequent among these women suffering with chronic pelvic
pain.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(2):84-89
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000200007
To identify and relate body fat percentage (skin fold measures), body mass index
(BMI) and age at menarcheto aerobic capacity using the indirect VO2
maximum value (VO2 max) of girls in the second cycle of primary school.
A total of 197 girls aged 13.0±1.2 years on average, students from two public
schools in the city of Atibaia in São Paulo, were evaluated. Anthropometric
evaluation of skin folds was performed using the Slaughter protocol for teenage
girls, and BMI (kg/m2) was based on "Z score" (graphic of percentile)
according to WHO recommendations. The Léger protocol was used to determine
VO2 max. Pearson linear regression and the Student t-test were used
for statistical analysis.
22.3% of the girls were overweight and 3.5% were obese according to the
classification proposed by the WHO; 140 (71.1%) girls reported menarche. The
average age at menarche was 12.0±1.0 years and was significantly higher in the
group with normal BMI (12.2±0.9 years) than in the overweight or obese groups
(11.6±1.0 years). The average indirect VO2 max value was 39.6±3.7
mL/kg/min, ranging from 30.3 to 50.5 mL/kg/min. The advance of chronological age
and early age at menarche were positively correlated with lower VO2 max
values.
This study showed that 25.8% of the girls had aBMI value above WHO
recommendations. Girls with higher BMI and higher body fat percentage had lower
VO2 max. The earlier age at menarche and the advance of
chronological age were the most important factors for the reduction of aerobic
capacity. The ageat menarche was higher in girls with adequate BMI compared
tooverweight or obese girls.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(2):90-96
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000200008
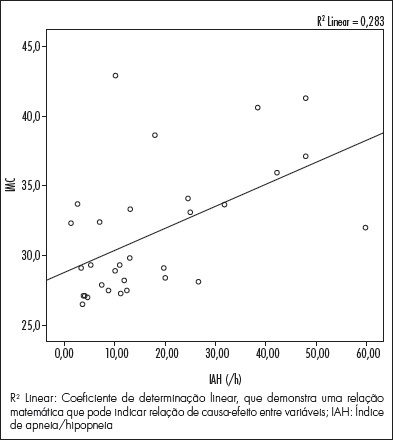
To evaluate the frequency of sleep disorders, such as obstructive sleep apnea,
restless leg syndrome and insomnia in overweight/obese postmenopausal women seen
in a climacteric sleep disorders clinic.
Thirty-four postmenopausal women were selected using the following inclusion
criteria: age between 50 and 70 years; at least 12 months of amenorrhea; body mass
index (BMI) greater than or equal to 25 kg/m2; and sleep-related
complaints with at least one previous polysomnography. Patients provided responses
to 6 questionnaires related to sleep characteristics and menopausal symptoms.
Weight and height were measured using standardized scales, and abdomen and hip
circumferences were also measured. The statistical analyses were performed using
the χ2 test for qualitative variables and using Student's t-test for
quantitative variables.
Patients' characteristics were as follows: mean age of 60.35 years; mean BMI of
31.62; an average of 11.61 postmenopausal years and an average Kupperman Index of
19. A total of 85.2% of the patients had a waist/hip ratio of less than 0.8. The
Epworth Scale score was greater than or equal to 9 in 50% of patients; 68% had
sleep disturbances according to the Pittsburgh Index, and 68% were classified as
high-risk for sleep apnea by the Berlin Questionnaire. On polysomnography, 70.58%
of the patients had a sleep efficiency lower than 85%; 79.41% had a sleep latency
of less than 30 min; 58.82% had a REM sleep latency of less than 90 min, and
44.11% had mild apnea. When the groups were compared, a linear association was
identified between BMI and the AHI average, and a relationship between high BMI
and use of drugs for thyroid treatment was found.
There was a high prevalence of sleep-disordered breathing, initial insomnia,
fragmented sleep, and thyroid disorders in the group with higher BMI.