Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(3):139-143
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000300007
PURPOSE: to identify if there is a difference in the prevalence of sexual dysfunction and in the sexual domain scores between a group of women attended at a public service and a group attended at a private service, and to investigate if there is an association between sexual dysfunction, family income and educational status. METHODS: transversal study including 201 sexually active women aged from 18 to 45 years, 90 of them from a public service and 111 from private services. We evaluated age, marital status, use of hormonal contraception, income and educational status, and all women were submitted to the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), an instrument for the evaluation of their sexuality. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences, version 15.0, was used for statistical analysis. The χ2 test was applied for categorical variables and the Student's t-test to independent samples. RESULTS: there was no significant difference regarding the prevalence of sexual dysfunction between groups (public versus private) (20 and 23.4%, p=0.5), or concerning the domain scores, desire (3.9±1.3 and 3.8±1.0, p=0.6), sexual arousal (4.5±0.8 and 4.4±0.9, p=0.5), lubrication (5.2±1.2 and 5.0±0.9, p=0.1), orgasm (5.0±1.2 and 4.9±1.1, p=0.5), satisfaction (5.2±1.2 and 5.1±1.0, p=0.9), and pain (5.3±1.1 and 5.2±1.0, p=0.8). Sexual dysfunction was detected in 28% of the women with income between two and four minimum wages, in 17.5% of those with an income of five wages or more, and in 14.3% among those with an income of one wage or less (p=0,1). The dysfunction occurred in 30.2% of women with elementary education, in 24.2% of those with high school education and in 13.4% of those with higher education (p=0.09). CONCLUSIONS: There was no significant difference in the prevalence of sexual dysfunction or in the sexual domain scores between groups, nor was there an association with income or education status.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(2):88-93
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000200007
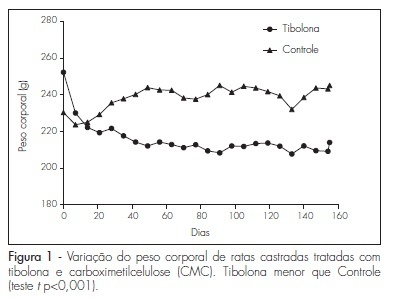
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of the prolonged use of a high dose of tibolone on the body weight variation and lipid profile of oophorectomized female rats. METHODS: 15 Wistar rats weighing 250 g were randomly divided into two groups. The Experimental Group (n=9) received 1 mg/day of oral tibolone. The Control Group (n=6) received daily 0.5 mL of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose by gavage. Bilateral oophorectomy was performed 30 days before the beginning of the experiment. On day 0 of the experiment, the animals began to receive the respective treatment for 20 weeks. Body weight was controlled every seven days and food consumption was measured every three to four days along the experiment, in order to establish the daily mean consumption per animal. The results were compared by the Student's t-test, with the significance level set at p<0.05. RESULTS: the daily food consumption of the Tibolone Group was significantly lower (12.7±1.2 g, p<0.001) compared to the Control Group (14.5±1.4 g). This difference was also significant when the body weight was compared between the Tibolone and Control Groups (p<0.001), with the Tibolone Group having lower weight along the experiment. At the end of the experiment, the mean body weight was 215.6±9.3 g in the Tibolone Group and 243.6±6.4 g in the Control Group. Regarding the lipid profile, the Tibolone Group had significantly (p<0.001) lower total cholesterol compared to the Control Group (30.3 versus 78.6 mg/dL). The level of HDL-c was also significantly different (p<0.001), with the Tibolone Group showing lower levels than the Control Group (9.0 versus 52.0 mg/dL). No significant difference between the groups was registered in the other biochemical parameters examined (LDL-c, VLDL-c and triglycerides). CONCLUSIONS: tibolone causes a significant reduction of HDL-c and total cholesterol and has a deleterious effect on the body weight of oophorectomized rats, which may be related to the lower food ingestion by these animals.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(2):82-87
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000200006
PURPOSE: to study the clinical and microbiological profile of women with bacterial vaginosis participating in a randomized, double-blind clinical trial, which compared the vaginal use of preparations from red pepper tree and metronidazole for the treatment of genital discharge. METHODS: the study was conducted on a series of 277 women with bacterial vaginosis concomitantly diagnosed by the criteria of Amsel and Nugent, selected from a total of 462 recruited patients using the information obtained before intervention. Data were analyzed with the Epi-Info 3.32 software. In order to compare the outcomes frequencies between the intervention groups, the χ2 test was used and the risk ratio and 95% confidence interval were calculated. The intention to treat analysis was performed. In addition to the determination of diagnostic parameters, the culture of vaginal content and a Papanicolaou cytology test were also performed. RESULTS: the most frequent clinical complaints were genital discharge, observed in 206 participants (74.4%) and the fish odor of the vaginal secretion, which occurred in 68.6% of the cases (190 patients). Among the diagnostic clinical criteria, the presence of clue-cells was positive in 275 women (99.3%), the Whiff test, in 266 (96.0%), followed by pH >4.5, which occurred in 92.8% of the cases, and by the presence of fluid grayish discharge reported by 206 participants (74.4%). Regarding the Nugent criterion, the median score was 8.0. Culture of the vaginal content permitted the identification of Gardnerella vaginalis in 96.8% of cases and of Mobiluncus in 53.1%. Only one third of the exams showed the presence of Lactobacillus (89 women - 32.1%). Fungal growth occurred in the cultures of 14 participants (5.1%). In most cases, culture revealed the presence of Corynebacterium (94.2%), Gram-positive cocci (98.2%), as well as Gram-positive (99.3%) and Gram-negative (91.0%) bacilli. Oncotic colposcopy revealed a very scarce presence of lactobacilli, which were present in only 8 cytological exams (2.9%) out of the total of 273 exams performed. CONCLUSIONS: the results of the present study did not differ from the literature regarding the symptoms reported by the women, the clinical criteria most frequently observed in the diagnosis, or the bacterial species detected in cultures of vaginal content. These findings indicate the need for further studies that might better elucidate the interrelations between the microbiological findings and the clinical expression of bacterial vaginosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(2):72-76
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000200004
PURPOSE: to translate into Brazilian Portuguese and culturally adapt the Short Personal Experiences Questionnaire (SPEQ) to climacteric women. METHODS: the original English version from the University of Melbourne, Australia, was initially translated into Portuguese and back-translated into English. A sociocultural adaptation of vocabulary and linguistic constructions was performed to facilitate comprehension. The questionnaire was then pretested in successive stages in 50 women, until no doubts remained. The final version of the adapted instrument was self-responded by 378 Brazilian-born women, between 40 to 65 years old, with 11 years or more of schooling in a population-based study. The reliability (internal consistency as measured by Cronbach's alpha), the construct validity (correlation coefficients between the items comprising the SPEQ and selected variables) and the criterion validity (correlation coefficient between sexual dysfunction score and overall score of sexual life classification) were analyzed. RESULTS: one hundred and eight women answered all the questions of the SPEQ and were included in the study. Internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha) for all the nine SPEQ items ranged from 0.55 to 0.77 and the general alpha was 0.68. In the construct validity analysis, most of the correlation coefficients were significant (p<0.005). The criterion validity analysis showed significant correlation coefficients in most cases. CONCLUSIONS: following the adaptation process, the Portuguese version of the SPEQ was deemed useful and appropriate for collecting data on sexual function and dyspareunia in Brazilian women, aged 45 to 65 years, with at least 11 years of schooling.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(2):66-71
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000200003
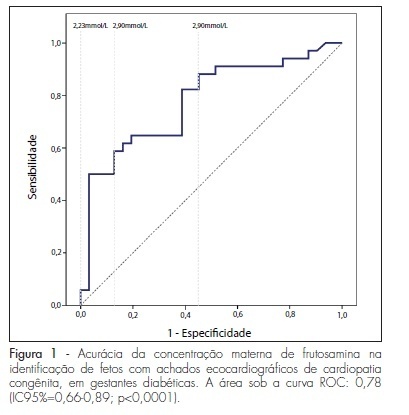
PURPOSE: to evaluate the importance of maternal plasma concentration of fructosamine as an indicator of fetal congenital cardiopathies in pregnancies complicated by diabetes mellitus. METHODS: this was a retrospective study conducted on 91 pregnant women with diabetes mellitus who underwent routine fetal echocardiography at a university reference center in fetal medicine. Sixty-five patientes who presented pre-gestational diabetes mellitus and plasma fructosamine level were registered in the medical records prior to the ultrasound exam. The first measurement recorded was compared with the result of routine fetal echocardiography, carried out by a specialist physician of the service. The presence or absence of echocardiographic findings of congenital cardiopathies (EFCC) was related to plasma levels of fructosamine by the mean t-test and its accuracy for EFCC was verified by the ROC curve. Plsama fructosamine concentrations of 2.68, 2.9 and 2.23 mmol/L, which are, respectively, the local reference laboratory values, the value of the kit employed for measurement and the one of highest overall accuracy, were discussed as the cut-off values. RESULTS: EFCC was found in 52.3% of the fetuses. The first measurement of fructosamine, during the prenatal care period, was performed, on average, at 20.4±8.0 weeks of pregnancy. The maternal concentration ability of the fructosamine to identify fetuses with EFCC was significant (p<0.0001) and had an area under the ROC curve of 0.78 (95%CI=0.66-0.89). The 2.9 mmol/L plasma concentration of fructosamine revealed EFCC with better specificity, but with a higher percentage of false-negative results (96.8 and 55.9%). Values above 2.68 mmol/L were associated with a probability of 4.6 to identify fetuses with EFCC compared with lower values, with 58.8% of sensitivity and 87.1%, specificity. The value of 2.23 mmol/L proved to be the most overall accurate of the three values suggested, with a sensitivity of 88.2% in the identification of fetuses with echocardiographic abnormalities. CONCLUSIONS: it is possible to use a second trimester plasma fructosamine level to refer high risk pregnant women to a reference center of fetal echocardiography. These findings are important for the management of women with diabetes mellitus who initiate late prenatal care.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(2):61-65
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000200002
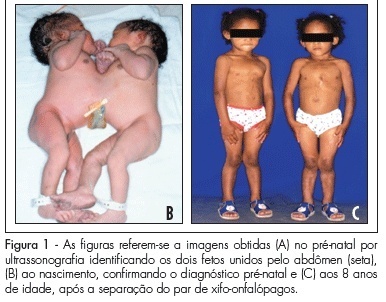
PURPOSE: to analyze the occurrence of conjoined twins at a tertiary perinatology reference university hospital over a period of 25 years (January 1982 to January 2007) and to describe the successful separation of one of the pairs. METHODS: we consulted retrospectively the database of the University Hospital of the Medical School of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo, Brazil, in order to determine the number of pairs of conjoined twins, their frequency, classification, gender, type of pregnancy resolution, attempted surgical separation, prenatal diagnosis and survival. RESULTS: we detected 14 pairs of conjoined twins (1/22,284 live births and 1/90 pairs of twin live births) born during this period (six males, seven females and one of indeterminate sex). The prenatal diagnosis was performed in all twins and all births were accomplished by cesarean section. The separation was possible in only one pair, which survives in excellent health conditions after eight years. Of the remaining 13, ten died on the day of birth and three survived only a few months (less than one year). CONCLUSION: Although our study revealed an abnormally high number of conjoined twins, this is a rare phenomenon, with a poor perinatal prognosis depending on the organs shared by the twins and associated malformations, especially those related to the fetal heart. Due to the poor prognosis of these pairs and to the maternal reproductive impairment caused by the need to perform body cesareans, we suggest that, based on these numbers, early interruption of these pregnancies be legally granted, as in the case of other diseases incompatible with fetal survival outside the uterus. Thus, the confirmation of a diagnosis of conjoined twins and the resolution of pregnancy should be performed at a tertiary obstetric and perinatal care center, and an authorization for the interruption of pregnancy should be obtained by judicial means.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(1):4-10
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000100002
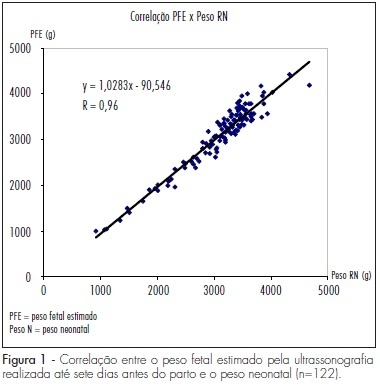
PURPOSE: to evaluate the correlation between the estimated fetal weight (EFW) by ultrasonography and the neonatal weight (NW), as well as the EFW's capacity to predict changes in NW among pregnant women in João Pessoa, Paraíba, Brazil. METHODS: a diagnostic validation study, including 122 pregnant women who have had the EFW calculated by ultrasonography up to seven days before delivery and the NW established immediately after birth, with a specific newborn's scale. The correlation between EFW and NW measurements was assessed by Pearson's correlation coefficient and by the mean difference between them. EFW and NW were classified as: low for the gestational age (LGA), adequate for the gestational age (AGA) and high for the gestational age (HGA), according to the percentiles 10 and 90 of the respective reference curves. The diagnosis of EFW deviation has been validated using the values of the Alexander's NW reference curve as gold-standard, by estimating the sensitivity, specificity, and positive and negative predictive values. RESULTS: there has been a high linear correlation between the EFW and NW (R=0.96), and the difference between them has varied from -474 g to +480 g, with an average of +3 g. Most of the highest percent weight estimate variations were between 10 and 15%. EFW has had 85.7% of sensitivity and 100% of specificity for the detection of LGA, and 100 and 77.2%, respectively, for the detection of HGA. CONCLUSIONS: EFW is able to predict NW adequately, and the reference EFW tested has had a good performance in the screening of fetal growth deviation, in the population studied.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(1):39-46
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000100007
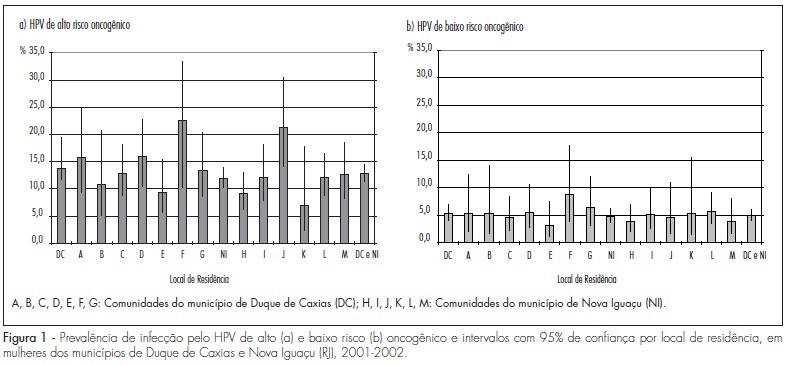
PURPOSE: to evaluate the prevalence of HPV infection and associated factors among women living in the "Baixada Fluminense", state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. METHODS: a cross-sectional study conducted on a sample of 2,056 women aged 25-59 years covered by the Family Health Program in the municipalities of Duque de Caxias and Nova Iguaçu, state of Rio de Janeiro, southeastern Brazil. All women were submitted to the Papanicolaou and HPV detection tests in a single session by second-generation hybrid capture from December 2001 to July 2002. The prevalence of HPV was stratified by age, place of residence, schooling, smoking habit, and sexual and reproductive history. The prevalence rates associated with the studied variables were calculated by Multivariate Poisson regression. RESULTS: the prevalence of HPV was 12.3% and 5.0% for high-risk and low-risk HPV types, respectively. A reduction in high-risk HPV prevalence was observed with aging, with an increase in the 55-59 year age range. After adjusting for age, schooling, smoking, early sexual initiation and parity, high-risk HPV infection was associated with not living with a partner (1.4; 95%CI=1.1-1.8) and having more than one sexual partner (an increase of 1.4%; 95%CI=1.1-1.6, for each lifetime sexual partner). CONCLUSIONS: the prevalence of HPV was lower than that reported in other Brazilians studies, most likely because our sample was population-based. HPV infection was associated only with factors related to sexual behavior, but the potential association between HPV infection and smoking still needs to be better understood. Further studies are needed to explore these issues, as well as postmenopausal increased infection rates, and to identify the most prevalent HPV types in the Brazilian population.