- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Original Article04-09-1998
Comparison between active management with oxytocin and expectant management for premature rupture of membranes at term
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):495-501
Abstract
Original ArticleComparison between active management with oxytocin and expectant management for premature rupture of membranes at term
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):495-501
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000900002
Views141See moreObjective: to compare the expectant versus active management with oxytocin in a Brazilian population of pregnant women with premature rupture of membranes (PROM) at term. Methods: a prospective, randomized and multicenter clinical trial was performed, evaluating variables concerning the time from PROM until the onset of labor and delivery, and maternal and neonatal hospitalization periods. Two hundred pregnant women with PROM at term were selected from four public hospitals in São Paulo state, from November 1995 to February 1997. They were randomly divided into two groups: active management, with oxytocin induction of labor until 6 h of PROM; and expectant management, waiting for the spontaneous onset of labor up to 24 h. The data were analyzed with the Epi-Info and SPSS-PC+ packages, using the statistical c², Student’s t and log-rank tests. Results: the results indicate that the differences between the two managements concern to the longer time needed for the expectant management group until onset of labor and delivery, besides the higher number of women and neonates who remained in hospital for more than three days. Conclusions: the time between admission and onset of labor and delivery, and also the latent period were longer in the expectant management group.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-09-1998
Ética em pesquisa
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):494-494
Abstract


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-09-1998
Estudo Controlado e Randomizado para Prevenção de Infecção Pós-Cesárea com Penicilina e Cefalotina
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):424-424
Abstract
Estudo Controlado e Randomizado para Prevenção de Infecção Pós-Cesárea com Penicilina e Cefalotina
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):424-424
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700011
Views49Estudo Controlado e Randomizado para Prevenção de Infecção Pós-Cesárea com Penicilina e Cefalotina […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-09-1998
Estudo Morfológico e Morfométrico do Endométrio de Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa Durante Terapêutica Estrogênica Contínua, Associada ao Acetato de Medroxiprogesterona a Cada Dois, Três e Quatro Meses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):423-423
Abstract
Estudo Morfológico e Morfométrico do Endométrio de Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa Durante Terapêutica Estrogênica Contínua, Associada ao Acetato de Medroxiprogesterona a Cada Dois, Três e Quatro Meses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):423-423
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700009
Views45Estudo Morfológico e Morfométrico do Endométrio de Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa Durante Terapêutica Estrogênica Contínua, Associada ao Acetato de Medroxiprogesterona a Cada Dois, Três e Quatro Meses[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-09-1998
Sangramento e Endometrite em Pacientes Portadoras de DIU Pós-Placentário na Maternidade de Encruzilhada – Recife (PE)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):423-424
Abstract
Sangramento e Endometrite em Pacientes Portadoras de DIU Pós-Placentário na Maternidade de Encruzilhada – Recife (PE)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):423-424
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700010
Views49Sangramento e Endometrite em Pacientes Portadoras de DIU Pós-Placentário na Maternidade de Encruzilhada Recife (PE) […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-09-1998
Complete Mole in Twin Pregnancy: a Case Report
- Izildinha Maestá,
- Iracema M.P. Calderon,
- Marilza V.C. Rudge,
- Magaly M. Sales,
- Fabiano P. Saggioro, [ … ],
- José Carlos Peraçoli
Abstract
Case ReportComplete Mole in Twin Pregnancy: a Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):415-419
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700008
- Izildinha Maestá,
- Iracema M.P. Calderon,
- Marilza V.C. Rudge,
- Magaly M. Sales,
- Fabiano P. Saggioro,
- José Carlos Peraçoli
Views90Twin pregnancy in which a normal fetus and a complete mole develop at the same time is a rare event. Clinical complications and malignancy are frequent in this type of disease.This report is about a case of a late diagnosis due to the presence of the fetus. The diagnosis was made when the pregnancy was interrupted and then confirmed by histopathological study and flow cytometry. The pregnancy was terminated transpelvically due to massive uterine hemorrhage. The post-molar follow-up showed the persistence of high levels of bhCG. The patient’s complete recovery was achieved after the administration of methotrexate. The diagnosis, natural history, and procedures for this rare disease are discussed in view of this case.
Key-words ChemotherapyComplete hydatidiform moleGestational trophoblastic diseaseHemorrhagePregnancy complicationsTwin pregnancyUltrasonographySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-09-1998
Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Endocervix in a 7-year-old Child
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):411-414
Views109

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Case ReportClear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Endocervix in a 7-year-old Child
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):411-414
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700007
Views109See moreClear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina and cervix is a rare disease associated commonly with the use of diethylstilbestrol (DES) during pregnancy. The most commom complaint is irregular vaginal bleeding, which could be confused with vaginitis in children and abnormalities in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis in adolescents. We report a case of clear cell adenocarcinoma of the endocervix in a 7-year-old child who was attended at the Children and Adolescent Gynecology Sector, and we call attention to the diagnosis of genital cancer which, in spite of its rarity at this age, must be considered in children with genital bleeding.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Equipments and Methods04-09-1998
Endometrial Resection by Video-Hysteroscopy: experience in a Teaching Hospital
- Caio Parente Barbosa,
- Marcelo Ettruri Santos,
- Ana Cristina Napolitano,
- Paula Harue Tamanaka,
- Emerson Barchi Cordts
Abstract
Equipments and MethodsEndometrial Resection by Video-Hysteroscopy: experience in a Teaching Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):405-410
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700006
- Caio Parente Barbosa,
- Marcelo Ettruri Santos,
- Ana Cristina Napolitano,
- Paula Harue Tamanaka,
- Emerson Barchi Cordts
Views90See moreObjective: to demonstrate the effectiveness of video-hysteroscopic endometrial resection in the treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding. Patients and method: The authors studied 60 records of patients with abnormal uterine bleeding who did not respond to clinical treatment. Results: eighty-eight percent of the patients had adequate response to the treatment (53% oligomenorrhea and 35% amenorrhea). The complication rate was 8.3% (5 uterine perforations). Conclusion: video-hysteroscopic endometrial resection is an effective technique to treat abnormal uterine bleeding which failed to respond to clinical management. The intra and postoperative complication rates are low.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Original Article01-01-2014
Doplervelocimetria da artéria uterina no segundo e terceiro trimestres para predição dos resultados gestacionais
- Maryam Afrakhteh,
- Aida Moeini,
- Morteza Sanei Taheri,
- Hamid Reza Haghighatkhah,
- Mohammad Fakhri, [ … ],
- Nina Masoom
Views392

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleDoplervelocimetria da artéria uterina no segundo e terceiro trimestres para predição dos resultados gestacionais
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(1):35-39
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000100008
- Maryam Afrakhteh,
- Aida Moeini,
- Morteza Sanei Taheri,
- Hamid Reza Haghighatkhah,
- Mohammad Fakhri,
- Nina Masoom
Views392OBJETIVO:
O objetivo do presente estudo longitudinal foi avaliar o valor da ultrassonografia Doppler das artérias uterinas no segundo e terceiro trimestres de gestação para a predição de desfecho adverso da gravidez em mulheres de baixo risco.
MÉTODOS:
De julho de 2011 até agosto de 2012, 205 gestantes de feto único atendidas em nossa clínica de pré-natal foram incluídas no presente estudo prospectivo e avaliadas em termos de dados demográficos e obstétricos. As pacientes foram submetidas à avaliação de ultrassom durante o segundo e terceiro trimestres, incluindo avaliação Doppler das artérias uterinas bilaterais, visando determinar os valores do índice de pulsatilidade (IP) e do índice de resistência (IR), bem como a presença de incisura diastólica precoce. O desfecho do presente estudo foi a avaliação da sensibilidade, especificidade, valor preditivo positivo (VPP) e valor negativo preditivo (VNP) da ultrassonografia Doppler das artérias uterinas para a predição de desfechos adversos da gravidez, incluindo pré-eclâmpsia, natimortalidade, descolamento prematuro da placenta e trabalho de parto prematuro.
RESULTADOS:
A média de idade das gestantes foi de 26,4±5,11 anos. Os valores de IP e IR das artérias uterinas para o primeiro (IP: 1,1±0,42 versus 1,53±0,59, p=0,002; IR: 0,55±0,09 versus 0.72±0.13, p=0,000, respectivamente) e para o terceiro trimestre (IP: 0,77±0,31 versus 1,09±0,46, p=0,000; IR: 0,46±0,10 versus 0,60±0,14, p=0,010, respectivamente) foram significativamente maiores em pacientes com desfecho adverso da gravidez em relação às mulheres com desfecho normal. A combinação de IP e IR > percentil 95 e a presença de incisura bilateral apresentou sensibilidade e especificidade de 36,1 e 97%, respectivamente, no segundo trimestre e de 57,5 e 98,2% no terceiro trimestre.
CONCLUSÕES:
Com base no presente estudo, o Doppler das artérias uterinas parece ser ferramenta valiosa para a predição de uma variedade de desfechos adversos no segundo e terceiro trimestres de gestação.
Key-words Laser-doppler flowmetryPregnancy outcomePregnancy trimester, secondPregnancy trimester, thirdUltrasonography, dopplerUterine artery/ultrasonographySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article12-21-2020
Use of GnRH Analogues in the Reduction of Submucous Fibroid for Surgical Hysteroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Thayane Delazari Corrêa
 ,
, - Isabela Maciel Caetano
 ,
, - Pedro Henrique Tannure Saraiva
 ,
, - Maurício Bechara Noviello,
- Admário Silva Santos Filho

Views291

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleUse of GnRH Analogues in the Reduction of Submucous Fibroid for Surgical Hysteroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):649-658
- Thayane Delazari Corrêa
 ,
, - Isabela Maciel Caetano
 ,
, - Pedro Henrique Tannure Saraiva
 ,
, - Maurício Bechara Noviello,
- Admário Silva Santos Filho

Views291See moreAbstract
Objective
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues (GnRH-a) have been used preoperatively before hysteroscopic myomectomy to decrease the size and vascularization of the myomas, but evidence to support this practice is weak. Our objective was to analyze the use of GnRH-a in the reduction of submucous fibroid as a facilitator for surgical hysteroscopy from published clinical trials.
Data sources
Studies from electronic databases (Pubmed, Scielo, EMBASE, Scopus, PROSPERO), published between 1980 and December 2018. The keywords used were fibroid, GnRH analogue, submucous, histeroscopy, histeroscopic resection and their correspondents in Portuguese.
Study selection
The inclusion criteria were controlled trials that evaluated the GnRH-a treatment before hysteroscopic resection of submucous myomas. Four clinical trials were included in the meta-analysis.
Data collection
Two review authors extracted the data without modification of the original data, using the agreed form. We resolved discrepancies through discussion or, if required, we consulted a third person.
Data synthesis
The present meta-analysis included a total of 213 women and showed no statistically significant differences in the use of GnRH-a compared with the control group for complete resection of submucous myoma (relative risk [RR]: 0.94; 95%; confidence interval [CI]: 0.80-1.11); operative time (mean difference [MD]: – 3.81; 95%;CI : – 3.81-2.13); fluid absorption (MD: – 65.90; 95%;CI: – 9.75-2.13); or complications (RR 0.92; 95%;CI: 0.18-4.82).
Conclusion
The present review did not support the routine preoperative use of GnRH-a prior to hysteroscopic myomectomy. However, it is not possible to determine its inferiority when compared with the other methods due to the heterogeneity of existing studies and the small sample size.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Thayane Delazari Corrêa
-
Review Article04-11-2022
Doppler Ultrasound of the Umbilical Artery: Clinical Application
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):519-531
Views252

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleDoppler Ultrasound of the Umbilical Artery: Clinical Application
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):519-531
Views252See moreAbstract
Objective
To provide a survey of relevant literature on umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound use in clinical practice, technical considerations and limitations, and future perspectives.
Methods
Literature searches were conducted in PubMed and Medline, restricted to articles written in English. Additionally, the references of all analyzed studies were searched to obtain necessary information.
Results
The use of this technique as a routine surveillance method is only recommended for high-risk pregnancies with impaired placentation. Meta-analyses of randomized trials have established that obstetric management guided by umbilical artery Doppler findings can improve perinatal mortality and morbidity. The values of the indices of Umbilical artery Doppler decrease with advancing gestational age; however, a lack of consensus on reference ranges prevails.
Conclusion
Important clinical decisions are based on the information obtained with umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound. Future efforts in research are imperative to overcome the current limitations of the technique.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article03-14-2024
Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
- Vanessa Merjane
 ,
, - Douglas Marcel Puricelli Perin
 ,
, - Patrícia Martins Gomes El Bacha
 ,
, - Beatriz Medicis Maranhão Miranda
 ,
, - Almir Galvão Vieira Bitencourt
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Wagner Iared

Views392

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleBreast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo6
- Vanessa Merjane
 ,
, - Douglas Marcel Puricelli Perin
 ,
, - Patrícia Martins Gomes El Bacha
 ,
, - Beatriz Medicis Maranhão Miranda
 ,
, - Almir Galvão Vieira Bitencourt
 ,
, - Wagner Iared

Views392See moreAbstract
BI-RADS® is a standardization system for breast imaging reports and results created by the American College of Radiology to initially address the lack of uniformity in mammography reporting. The system consists of a lexicon of descriptors, a reporting structure with final categories and recommended management, and a structure for data collection and auditing. It is accepted worldwide by all specialties involved in the care of breast diseases. Its implementation is related to the Mammography Quality Standards Act initiative in the United States (1992) and breast cancer screening. After its initial creation in 1993, four additional editions were published in 1995, 1998, 2003 and 2013. It is adopted in several countries around the world and has been translated into 6 languages. Successful breast cancer screening programs in high-income countries can be attributed in part to the widespread use of BI-RADS®. This success led to the development of similar classification systems for other organs (e.g., lung, liver, thyroid, ovaries, colon). In 1998, the structured report model was adopted in Brazil. This article highlights the pioneering and successful role of BI-RADS®, created by ACR 30 years ago, on the eve of publishing its sixth edition, which has evolved into a comprehensive quality assurance tool for multiple imaging modalities. And, especially, it contextualizes the importance of recognizing how we are using BI-RADS® in Brazil, from its implementation to the present day, with a focus on breast cancer screening.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Vanessa Merjane
-
Review Article10-07-2022
The Effects of Hysterectomy on Urinary and Sexual Functions of Women with Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review
- Mariana Alves Firmeza
 ,
, - Camila Teixeira Moreira Vasconcelos
 ,
, - José Ananias Vasconcelos Neto
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo de Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Flávio Mendes Alves
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Natália Maria de Vasconcelos Oliveira

Views262

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleThe Effects of Hysterectomy on Urinary and Sexual Functions of Women with Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):790-796
- Mariana Alves Firmeza
 ,
, - Camila Teixeira Moreira Vasconcelos
 ,
, - José Ananias Vasconcelos Neto
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo de Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Flávio Mendes Alves
 ,
, - Natália Maria de Vasconcelos Oliveira

Views262See moreAbstract
Objective
This systematic review aims at describing the prevalence of urinary and sexual symptoms among women who underwent a hysterectomy for cervical cancer.
Methods
A systematic search in six electronic databases was performed, in September 2019, by two researchers. The text search was limited to the investigation of prevalence or occurrence of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and sexual dysfunctions in women who underwent a hysterectomy for cervical cancer. For search strategies, specific combinations of terms were used.
Results
A total of 8 studies, published between 2010 and 2018, were included in the sample. The average age of the participants ranged from 40 to 56 years, and the dysfunctions predominantly investigated in the articles were urinary symptoms (n= 8). The rates of urinary incontinence due to radical abdominal hysterectomy ranged from 7 to 31%. The same dysfunction related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy varied from 25 to 35% and to laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy varied from 25 to 47%. Nocturia ranged from 13%, before treatment, to 30%, after radical hysterectomy. The prevalence rates of dyspareunia related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy and laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy ranged from 5 to 16% and 7 to 19% respectively. The difficulty in having orgasm was related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy (10 to 14%) and laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy (9 to 19%).
Conclusion
Urinary and sexual dysfunctions after radical hysterectomy to treat cervical cancer are frequent events. The main reported disorders were urinary incontinence and dyspareunia.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Mariana Alves Firmeza
-
Review Article07-10-2023
Technologies Applied to the Mental Health Care of Pregnant Women: A Systematic Literature Review
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
 ,
, - Júlia Magna da Silva Teixeira
 ,
, - Roberto José Gervásio Unger
 ,
, - Vivian Genaro Motti
 ,
, - Giovanni Marcos Lovisi
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Fabiane Rossi dos Santos Grincenkov

Views262

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleTechnologies Applied to the Mental Health Care of Pregnant Women: A Systematic Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):149-159
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
 ,
, - Júlia Magna da Silva Teixeira
 ,
, - Roberto José Gervásio Unger
 ,
, - Vivian Genaro Motti
 ,
, - Giovanni Marcos Lovisi
 ,
, - Fabiane Rossi dos Santos Grincenkov

Views262See moreAbstract
Objective:
This article aims to review the literature regarding the use of technologies to promote mental health for pregnant women. We seek to: understand the strategies that pregnant women use for mental health care. Also, we investigate the existence of scientific evidence that validates such practices.
Methods:
This study follows the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews. We analyze 27 studies published between 2012 and 2019. We include publications in Portuguese, English, and Spanish.
Results:
The results revealed several different possibilities to use technology, including the use of text messages and mobile applications on smartphones. Mobile applications are the most commonly used approaches (22.5%). Regarding the strategies used, cognitive-behavioral approaches, including mood checks, relaxation exercises, and psychoeducation comprised 44.12% of the content.
Conclusion:
There is a need for further investigation and research and development efforts in this field to better understand the possibilities of intervention in mental health in the digital age.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 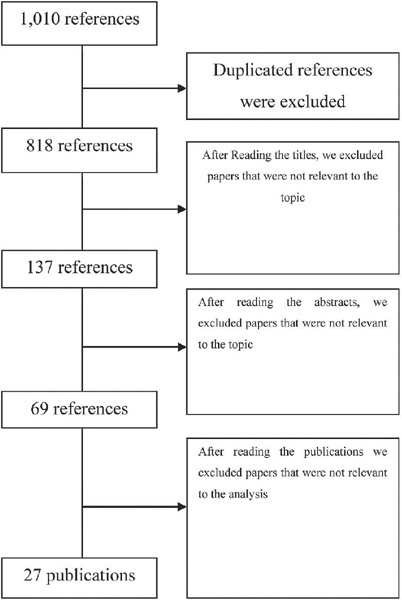
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
-
Letter to the Editor04-09-2024
Letter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
Abstract
Letter to the EditorLetter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
Views392Dear Editor,First and foremost, we express our gratitude towards the authors for their clear and concise description of the positive effects of aerobic and strength training on dynamic stability.() Additionally, their ability to provide a focused and informative introduction section is commendable. The study piqued our interest in further exploring the benefits of aerobic and […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article03-11-2022
Exercise and Physical Activity Levels and Associated Factors Among High-Risk Pregnant Women
- Larissa Antunes Miranda
 ,
, - Anna Caroline Ribeiro de Moura
 ,
, - Karina Tamy Kasawara
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Mayle Andrade Moreira
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Simony Lira do Nascimento

Views271

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleExercise and Physical Activity Levels and Associated Factors Among High-Risk Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):360-368
- Larissa Antunes Miranda
 ,
, - Anna Caroline Ribeiro de Moura
 ,
, - Karina Tamy Kasawara
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Mayle Andrade Moreira
 ,
, - Simony Lira do Nascimento

Views271See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the levels of physical activity and exercise practice, and examine the associated maternal characteristics; as well as the anxiety levels of high-risk pregnant women.
Methods
A cross-sectional study conducted with pregnant women at a High-risk Prenatal Clinic (HRPC) in a tertiary maternity. Pregnant women of 18 to 40-years-old, with a single fetus, and with gestational age up to 38 weeks were included. The level of physical activity and exercise practice of the study’s participants were investigated using the Pregnancy Physical Activity Questionnaire (PPAQ). Maternal sociodemographic, anthropometric, and medical data were investigated using a specific form. For anxiety levels, the short version of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) was applied. We used the Student t-test, chi-square test, odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) and multiple logistic regression. The significance level was 5%.
Results
Among the 109 pregnant women included, 82 (75.2%) were classified as sedentary/little active. The higher energy expenditure were for domestic activities (133.81±81.84 METs), followed by work-related activities (40.77±84.71 METs). Only 19.3% women exercised during pregnancy (4.76±12.47 METs), with slow walking being the most reported exercise. A higher level of education was the most important factor associated with women being moderately or vigorously active (OR=29.8; 95% CI 4.9-117.8). Nulliparity (OR=3.1; 95% CI 1.0-9.1), low levels of anxiety (OR=3.6; 95% CI 1.2-10.7), and unemployment (OR=4.8; 95% CI 1.1-19.6) were associated with the practice of exercise during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Most women with high-risk pregnancies exhibited a sedentary pattern, with low prevalence of physical exercise practice. Recognizing factors that hinder the adoption of a more physically active lifestyle is essential for an individualized guidance regarding exercise during pregnancy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Larissa Antunes Miranda
-
Systematic Review11-01-2017
Management of Axillary Web Syndrome after Breast Cancer: Evidence-Based Practice
- Clarissa Medeiros da Luz,
- Julia Deitos,
- Thais Cristina Siqueira,
- Marina Palú,
- Ailime Perito Feiber Heck
Views216

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Systematic ReviewManagement of Axillary Web Syndrome after Breast Cancer: Evidence-Based Practice
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):632-639
- Clarissa Medeiros da Luz,
- Julia Deitos,
- Thais Cristina Siqueira,
- Marina Palú,
- Ailime Perito Feiber Heck
Views216Abstract
Axillary web syndrome is characterized as a physical-functional complication that impacts the quality of life of women who have undergone treatment for breast cancer. The present study aims to verify the physiotherapy treatment available for axillary web syndrome after surgery for breast cancer in the context of evidence-based practice. The selection criteria included papers discussing treatment protocols used for axillary web syndrome after treatment for breast cancer. The search was performed in the MEDLINE, Scopus, PEDro and LILACS databases using the terms axillary web syndrome, lymphadenectomy and breast cancer, focusing on women with a previous diagnosis of breast cancer who underwent surgery with lymphadenectomy as part of their treatment. From the 262 studies found, 4 articles that used physiotherapy treatment were selected. The physiotherapy treatment was based on lymphatic drainage, tissue mobilization, stretching and strengthening. The four selected articles had the same outcome: improvement in arm pain and shoulder function and/or dissipation of the axillary cord. Although axillary web syndrome seems to be as frequent and detrimental as other morbidities after cancer treatment, there are few studies on this subject. The publications are even scarcer when considering studies with an interventional approach. Randomized controlled trials are necessary to support the rehabilitation resources for axillary web syndrome.
Key-words axillary web syndromeconservative treatmentcordingLymphadenectomyPhysiotherapyRehabilitationSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article03-27-2020
Gestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Views317

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleGestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):12-18
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 ,
, - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Views317See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus and the main associated risk factors in the population served by the Brazilian Unified Health System in the city of Caxias do Sul, state of Rio Grande do Sul.
Materials and Methods
A descriptive, cross-sectional and retrospective study was conducted. Maternal variables were collected from the medical records of all pregnant women treated at the basic health units in 2016. Hyperglycemia during pregnancy (pregestational diabetes, overt diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus) was identified by analyzing the results of a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, as recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. Based on the data, the women were allocated into two groups: the gestational diabetes group and the no gestational diabetes group.
Results
The estimated prevalence of gestational diabetes among 2,313 pregnant women was of 5.4% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 4.56-6.45). Pregnant women with 3 or more pregnancies had twice the odds of having gestational diabetes compared with primiparous women (odds ratio [OR]=2.19; 95%CI: 1.42-3.37; p<0.001). Pregnant women aged 35 years or older had three times the odds of having gestational diabetes when compared with younger women (OR=3.01; 95%CI: 1.97-4.61; p<0.001). Overweight pregnant women were 84% more likely to develop gestational diabetes than those with a body mass index lower than 25 kg/m2 (OR =1.84; 95%CI: 1.25-2.71; p=0.002). A multivariable regression analysis showed that being overweight and being 35 years old or older were independent variables.
Conclusion
In this population, the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus was of 5.4%. Age and being overweight were predictive factors for gestational diabetes.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
-
Original Article09-01-2018
Urinary Incontinence and Quality of Life in Female Patients with Obesity
- Christiana Campani Nygaard,
- Lucas Schreiner,
- Thiago Picolli Morsch,
- Rodrigo Petersen Saadi,
- Marina Faria Figueiredo, [ … ],
- Alexandre Vontobel Padoin
Views184

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleUrinary Incontinence and Quality of Life in Female Patients with Obesity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):534-539
- Christiana Campani Nygaard,
- Lucas Schreiner,
- Thiago Picolli Morsch,
- Rodrigo Petersen Saadi,
- Marina Faria Figueiredo,
- Alexandre Vontobel Padoin
Views184See moreAbstract
Objective
To analyze the prevalence of urinary incontinence (UI) in female patients with an indication for bariatric surgery, to investigate the potential risk factors and the impact on quality of life.
Methods
A cross-sectional study with female patients with obesity. The evaluation consisted of a structured interview, a specific study form and quality of life questionnaires. The Poisson regression was performed to identify independent risk factors related to UI.
Results
A total of 221 patients were enrolled; 118 of the study participants (53.4%) reported UI episodes. Mixed UI (MUI), stress UI (SUI) only, and urgency UI (UUI) only were reported by 52.5% (62), 33.9% (40) , and 13.5% (16) of these patients respectively. The prevalence of UI was increased by 47% among the women who had given birth vaginally and by 34% of the women who had entered menopause. Vaginal delivery and menopause were identified as independent risk factors related to UI. The mean International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire – Short Form (ICIQ-SF) score was 9.36 ± 4.9. The severity of symptoms was considered moderate in 53.3% (63) of the patients with UI.
Conclusion
Urinary incontinence impacts quality of life negatively, and the prevalence of UI is high among obese patients. In the present study, vaginal delivery and menopause were independently associated with UI.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article08-01-2016
Impacts of Preeclampsia on the Brain of the Offspring
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):416-422
Views176

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleImpacts of Preeclampsia on the Brain of the Offspring
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):416-422
Views176See moreAbstract
Preeclampsia (PE) is a significant gestational disorder that causes complications in 3- 5% of all human pregnancies. Apart from the immediate risks and complications for mother and fetus, both additionally carry elevated lifelong risks for specific complications. Offspring of PE pregnancies (PE-F1) have higher risks for hypertension, stroke and cognitive impairment compared with well-matched offspring (F1) fromuncomplicated pregnancies. Prior to the clinical onset of PE, placental angiokines secreted into the maternal plasma are deviated. In many PE patients this includes deficits in placental growth factor (PGF). Our laboratory found that mice genetically-deleted for PGF (PGF – / -) have altered cerebrovascular and brain neurological development detectable from midgestation to adulthood. We hypothesized that the PGF deficits seen in human PE, deviate fetal cerebrovascular and neurological development in a manner that impairs cognitive functions and elevates stroke risk. Here we summarize the initial analytical outcomes from a pilot study of 8-10 year old male and female PE-F1s and matched controls. Our studies were the first to report magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and functional brain region assessment by eyemovement control and clinical psychometric testing in PE-F1s. Further studies in larger cohorts are essential to define whether there are image-based biomarkers that describe unique anatomical features in PE-F1 brains.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 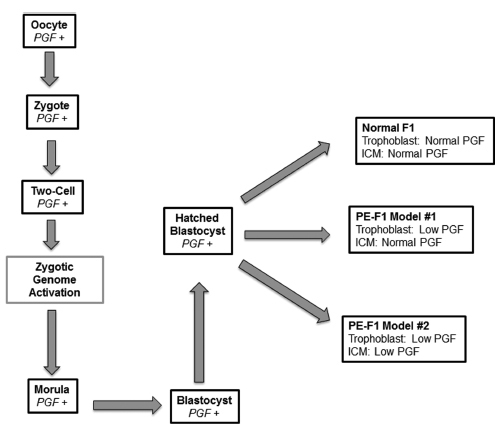
-
Review Article12-01-2018
Female Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder: Review of the Related Factors and Overall Approach
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):787-793
Views288

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleFemale Genito-Pelvic Pain/Penetration Disorder: Review of the Related Factors and Overall Approach
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):787-793
Views288See moreAbstract
Genito-pelvic pain/penetration disorder (GPPPD) can be an extremely bothersome condition for patients, and a tough challenge for professionals regarding its assessment and treatment. The goal of the present paper is to review the etiology, assessment, and treatment of GPPPD, especially focusing on the cognitive aspects of the disease and cognitive-behavioral treatment options, through a non-systematic review of articles indexed to the Medline, Scopus and Web of Science databases, using the following MeSH queries: pelvic pain; dyspareunia; vaginismus; vulvodynia; and cognitive therapy. Altogether, 36 articles discussing the etiology, diagnosis and management of GPPPD were selected. We provide an overview of GPPPD based on biological, psychological and relational factors, emphasizing the last two. We also summarize the available medical treatments and provide strategies to approach the psychological trigger and persisting factors for the patient and the partner. Professionals should be familiarized with the factors underlining the problem, and should be able to provide helpful suggestions to guide the couple out of the GPPPD fear-avoidance circle.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article07-01-2016
Epidemiological Risk Factors and Perinatal Outcomes of Congenital Anomalies
- Lissa Fernandes Garcia Almeida,
- Edward Araujo Júnior,
- Gerson Claudio Crott,
- Marcos Masaru Okido,
- Aderson Tadeu Berezowski, [ … ],
- Alessandra Cristina Marcolin
Views235

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleEpidemiological Risk Factors and Perinatal Outcomes of Congenital Anomalies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(7):348-355
- Lissa Fernandes Garcia Almeida,
- Edward Araujo Júnior,
- Gerson Claudio Crott,
- Marcos Masaru Okido,
- Aderson Tadeu Berezowski,
- Geraldo Duarte,
- Alessandra Cristina Marcolin
Views235See moreAbstract
Objectives
To identify the epidemiological risk factors for congenital anomalies (CAs) and the impact of these fetal malformations on the perinatal outcomes.
Methods
This prospective cohort study comprised 275 women whose fetuses had CAs. Maternal variables to establish potential risk factors for each group of CA and perinatal outcomes were evaluated. The primary outcome was CA. Secondary outcomes included: fetal growth restriction (FGR); fetal distress (FD); premature rupture of membranes (PROM); oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios; preterm delivery (PTD); stillbirth; cesarean section; low birth weight; Apgar score < 7 at the 1st and 5th minutes; need for assisted ventilation at birth; neonatal infection; need for surgical treatment; early neonatal death; and hospitalization time. Chi-square (x2) test and multilevel regression analysis were applied to compare the groups and determine the effects of maternal characteristics on the incidence of CAs.
Results
The general prevalence of CAs was of 2.4%. Several maternal characteristics were associated to CAs, such as: age; skin color; level of education; parity; folic acid supplementation; tobacco use; and history of previous miscarriage. There were no significant differences among the CA groups in relation to FGR, FD, PROM, 1-minute Apgar score > 7, and need for assisted ventilation at birth. On the other hand, the prevalence of the other considered outcomes varied significantly among groups. Preterm delivery was significantly more frequent in gastrointestinal tract/abdominal wall defects. The stillbirth rate was increased in all CAs, mainly in isolated fetal hydrops (odds ratio [OR]: 27.13; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 2.90-253.47). Hospitalization time was higher for the urinary tract and congenital heart disease groups (p < 0.01). Neonatal death was significantly less frequent in the central nervous system anomalies group.
Conclusion
It was possible to identify several risk factors for CAs. Adverse perinatal outcomes were presented in all CA groups, and may differ according to the type of CA considered.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article02-01-2018
Influence of Sexual Function on the Social Relations and Quality of Life of Women with Premature Ovarian Insufficiency
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):66-71
Views186

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleInfluence of Sexual Function on the Social Relations and Quality of Life of Women with Premature Ovarian Insufficiency
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):66-71
Views186See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the impact of sexual function (SF) in the quality of life (QoL) of women with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI).
Methods
Case-control study in which 80women with POIwere evaluated using estrogen plus progestogen therapy, compared with 80 women matched by age (2 years) and presenting preserved gonadal function. Sexual function was evaluated using the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), and the QoL was evaluated using theWorld Health Organization’s (WHO) QoL assessment instrument (WHOQoL-BREF).
Results
The mean age of the women with POI and of the control group was 38.4 ± 7.3 years and 38.1 ± 7.3 years respectively. The QoL, was worse among the POI group, and there were significant differences in the physical (63.4 ± 17.4 and 72.7 ± 15.2 respectively, p = 0.0004) and psychological (63.2 ± 14.6 and 69.3 ± 13.9 respectively, p = 0.0075) domains among this group when compared with the control group. Women with POI presented significantly lower arousal, lubrication, orgasm and satisfaction, more dyspareunia and a worse FSFI scores when compared with the control group. All aspects of SF correlate directly with the worsening of the QoL regarding social relationships.
Conclusion
Women with POI showed worse QoL and SF than the control group. The psychological aspects (desire, excitement, orgasm and sexual satisfaction) of SF had greater influence on the parameters of the QoL, while the physical aspects (pain and lubrication) had a low impact on the QoL. The poor SF in women with POI is directly correlated with a worsening acrossmultiple domains of the QoL; however, the negative impact is particularly important in the social domain. These results suggest that the improvement in sexuality can improve the social interactions of women with POI.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article08-01-2016
HIV Prevalence among Pregnant Women in Brazil: A National Survey
- Gerson Fernando Mendes Pereira,
- Meritxell Sabidó,
- Alessandro Caruso,
- Silvano Barbosa de Oliveira,
- Fábio Mesquita, [ … ],
- Adele Schwartz Benzaken
Views219

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleHIV Prevalence among Pregnant Women in Brazil: A National Survey
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):391-398
- Gerson Fernando Mendes Pereira,
- Meritxell Sabidó,
- Alessandro Caruso,
- Silvano Barbosa de Oliveira,
- Fábio Mesquita,
- Adele Schwartz Benzaken
Views219See moreAbstract
Background
This study was conducted to determine the seroprevalence of HIV among pregnant women in Brazil and to describe HIV testing coverage and the uptake of antenatal care (ANC).
Methods
Between October 2010 and January 2012, a probability sample survey of parturient women aged 15-49 years who visited public hospital delivery services in Brazil was conducted. Data were collected from prenatal reports and hospital records. Dried blood spot (DNS) samples were collected and tested for HIV.We describe the agespecific prevalence of HIV infection and ANC uptake with respect to sociodemographic factors.
Results
Of the 36,713 included women, 35,444 (96.6%) were tested for HIV during delivery admission. The overall HIV prevalence was of 0.38% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.31-0.48), and it was highest in: the 30 to 39 year-old age group (0.60% [0.40- 0.88]), in the Southern region of Brazil (0.79% [0.59-1.04]), among women who had not completed primary (0.63% [0.30-1.31]) or secondary (0.67% [0.49-0.97]) school education, and among women who self-reported as Asian (0.94% [0.28-3.10]). The HIV testing coverage during prenatal care was of 86.6% for one test and of 38.2% for two tests. Overall, 98.5% of women attended at least 1 ANC visit, 90.4% attended at least 4 visits, 71% attended at least 6 visits, and 51.7% received ANC during the 1st trimester. HIV testing coverage and ANC uptake indicators increased with increasing age and education level of education, and were highest in the Southern region.
Conclusions
Brazil presents an HIV prevalence of less than 1% and almost universal coverage of ANC. However, gaps in HIV testing and ANC during the first trimester challenge the prevention of the vertical transmission of HIV. More efforts are needed to address regional and social disparities.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 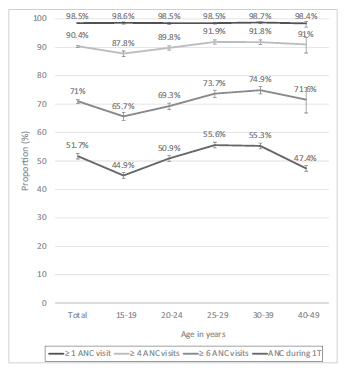
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
