- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
10-03-2000
Estudo de Fatores Relacionados com a Violência Sexual contra Crianças, Adolescentes e Mulheres Adultas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):459-459
Abstract
Estudo de Fatores Relacionados com a Violência Sexual contra Crianças, Adolescentes e Mulheres Adultas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):459-459
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700011
Views52Estudo de Fatores Relacionados com a Violência Sexual contra Crianças, Adolescentes e Mulheres Adultas […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
10-03-2000
Avaliação do Tratamento Não-Medicamentoso (Orientação Verbal) das Mastalgias Cíclicas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):459-459
Abstract
Avaliação do Tratamento Não-Medicamentoso (Orientação Verbal) das Mastalgias Cíclicas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):459-459
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700010
Views54Avaliação do Tratamento Não-Medicamentoso (Orientação Verbal) das Mastalgias Cíclicas[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report10-03-2000
Angiosarcoma of the Breast: Case Report
- Renata Silva de Oliveira Viviani,
- Luiz Henrique Gebrim,
- Afonso Celso Pinto Nazário,
- Cláudio Kemp,
- Geraldo Rodrigues Lima
Abstract
Case ReportAngiosarcoma of the Breast: Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):455-458
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700009
- Renata Silva de Oliveira Viviani,
- Luiz Henrique Gebrim,
- Afonso Celso Pinto Nazário,
- Cláudio Kemp,
- Geraldo Rodrigues Lima
Views111Primary angiosarcoma of the breast is a rare tumor, which appears between 14 and 82 years, with an average of 35 years of age. Its predominant clinical aspect is a painful mass with diffuse increase in the breast and violet or blackened color. Equally to other cases of sarcoma, the medium size of the lesion is approximately 5 cm at the diagnosis. Histologically, it is characterized by the proliferation of endothelial cells that form vascular channels linked to each other infiltrating glandular structures and fatty tissue. Its histological diagnosis is difficult and not always the right diagnosis is immediately established, mainly in the cases of a low malignancy degree, due to limited biopsy material. Because of the difficult diagnosis and aggressivity, it is a neoplasia with ominous prognosis, due to frequent metastasis. In our service, a 18-year-old patient presented with a painful lump which grew quickly. It was biopsied and a hemangioma was diagnosed, a wide excision being indicated. Three months later, she suffered a tumoral relapse, that was biopsied again and mastectomy was indicated, because it was an angiosarcoma with low degree of malignancy. After other relapses, chemotherapy was indicated and later, radiotherapy. During radiotherapy she developed new metastases, and died of pulmonary metastasis.
Key-words Breast neoplasmsSarcomaSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article10-03-2000
Prognostic Indicators In Lymph Node-Negative Breast Cancer: Estrogen Receptor and P53 and c-erbB-2 Protein Expression
- Adriana Harter Teixeira Bolaséll,
- Cláudio Galleano Zettler,
- Jeferson Vinholes,
- Simone Márcia Machado,
- Cláudia Kliemann
Abstract
Original ArticlePrognostic Indicators In Lymph Node-Negative Breast Cancer: Estrogen Receptor and P53 and c-erbB-2 Protein Expression
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):449-454
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700008
- Adriana Harter Teixeira Bolaséll,
- Cláudio Galleano Zettler,
- Jeferson Vinholes,
- Simone Márcia Machado,
- Cláudia Kliemann
Views126See morePurpose: to evaluate the prognostic value of estrogen receptor and p53 and c-erbB-2 proteins in lymph node-negative breast cancer. Methods: an immunohistochemical study was made in paraffin-embedded tissues from the file of the Instituto de Pesquisas Cito-Oncológicas of the Fundação Faculdade Federal de Ciências Médicas de Porto Alegre of fifty cases of postmenopausal women, who were treated at the Irmandade da Santa Casa de Misericórdia de Porto Alegre and at the Santa Rita Hospital from 1990 to 1994. For statistical analysis c² with Yates correction, as well as exact Fisher tests were used and Kaplan Meier curves compared with log-rank test. The mean follow-up of the patients was 3.6 years (3.1-4.5). Of the 50 cases, 14 showed recurrence during the period of follow-up. Results: the mean age was 61 years (46-78). Modified radical mastectomy was performed in 35 patients (70%) and 15 (30%) were submitted to lumpectomy/axillary dissection and postoperative radiation therapy. Fifty percent of the patients who showed recurrence did it in the first three years after the diagnosis. The mean size of the tumor was 2.8 cm (1.98-3.13) and the most frequent histological type was invasive ductal carcinoma of no special type (92%), according to the Bloom and Richardson graduation, 3 being stage I (6.6%), 35 stage II (76%) and 8 stage III (17.4%). In the tumors with recurrence, there was no grade I, 9 stage II (25.7%) and 3 stage III (37.5%). In relation to the prognosis, the disease-free interval was less when there was association of a poorly differentiated tumor with negative estrogen receptor (p = 0.006), positive p53 (p = 0.006) and positive c-erbB-2 (p = 0.001). Conclusion: postmenopausal women with lymph node-negative breast cancer showed worse prognosis in relation to disease-free interval when they presented poorly differentiated tumor associated with negative estrogen receptor, positive p53 and positive c-erbB-2.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article10-03-2000
Factors Related to Obesity and Android Pattern of Body Fat Distribution in Climacteric Women
- Diana Beatriz Filip Raskin,
- Aarão Mendes Pinto-Neto,
- Lúcia Helena Simões Costa Paiva,
- Analisa Raskin,
- Edson Zangiacomi Martinez
Views118

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleFactors Related to Obesity and Android Pattern of Body Fat Distribution in Climacteric Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):435-441
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700006
- Diana Beatriz Filip Raskin,
- Aarão Mendes Pinto-Neto,
- Lúcia Helena Simões Costa Paiva,
- Analisa Raskin,
- Edson Zangiacomi Martinez
Views118See morePurpose: to describe sociodemographic characteristics of a group of climacteric women in order to discover the frequency and the variables associated with obesity and android profile of body fat distribution. Methods: an observational study was carried out in 518 patients aged 45 to 65 years, in a climacterium outpatient clinic. Age, color, menopausal status, duration of menopause, physical activity, smoking status, diet, alcohol intake, personal and family antecedents of arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, dyslipidemia and obesity were considered. Body mass index and the waist/hip ratio were the dependent variables. For the statistical analysis Wilcoxon test, Pearson’s correlation coefficient, with a 5% level of significance, and multivariate analysis using regression model were used. Results: more than two thirds of the participants were nonobese with an android profile and postmenopausal. One fourth had physical activity and were smokers; half reported an inadequate diet and one fifth were alcoholics. Patients with an android profile presented higher mean age than women with gynecoid pattern. Personal antecedents of obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes and family history of diabetes were related to obesity and android pattern. Postmenopausal status was significantly associated with the android profile. Conclusions: the majority of the participants were nonobese with an android profile, white, postmenopausal, sedentary, neither smokers nor alcoholics. The main factors related to obesity and android pattern were personal antecedents of obesity, arterial hypertension, diabetes, family history of diabetes and particularly, postmenopausal status with android profile.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article10-03-2000
Gastroschisis: Prenatal Evaluation of Prognostic Factors for Postnatal Outcome
- Liliana Patroni,
- Maria de Lourdes Brizot,
- Samir A. Mustafá,
- Mário H.B. Carvalho,
- Marcos Marquês Silva, [ … ],
- Marcelo Zugaib
Views84

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleGastroschisis: Prenatal Evaluation of Prognostic Factors for Postnatal Outcome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):421-428
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000700004
- Liliana Patroni,
- Maria de Lourdes Brizot,
- Samir A. Mustafá,
- Mário H.B. Carvalho,
- Marcos Marquês Silva,
- Seyzo Miyadahira,
- Marcelo Zugaib
Views84See morePurpose: to evaluate 24 cases of gastroschisis, in relation to the prognostic factors that interfered with postnatal outcome. Patients and Method: twenty-four pregnancies with fetal prenatal ultrasound diagnosis of gastroschisis, during an 8-year period, were analyzed. Gastroschisis was classified into isolated, when there were no other structural abnormalities, or associated, when other abnormalities were present. For both groups the following parameters were examined: ultrasound bowel dilatation (>18 mm), obstetric complications and postnatal outcome. Nonparametric Mann-Whitney and exact Fisher’s tests were used for statistical analyses. Results: in 9 cases (37.5%) gastroschisis was associated with other abnormalities, and in 15 cases it was isolated (62.5%). All cases of associated gastroschisis had a letal prognosis, therefore the overall mortality rate was 60.8%. In the group of isolated gastroschisis, all were born alive and were submitted to surgery, but the survival rate after surgical correction was 60%. The median gestational age at birth was 35 weeks and birth weight 2,365 grams. Premature delivery was observed in 10 cases, mainly as a consequence of obstetric complication. Two newborns were small for gestational age, and only 3 had birth weight >2,500 grams. Oligohydramnios was found in 46.6% and it was more frequent in the group of postnatal death (66.7%). Ultrasound assessment of bowel showed bowel dilatation in 86.6%, however, without relation to the prognosis and postnatal bowel findings. There was no significant difference between gestational age at birth and birth weight comparing the survivor and postnatal death groups. Conclusions: isolated gastroschisis had a better prognosis when compared to associated, therefore this prenatal differentiation is important. Isolated gastroschisis was often associated with prematurity, small birth weight and obstetric complications. Prenatal diagnosis allows better monitoring of fetal and obstetric conditions. Delivery should be at term, unless presenting with obstetric complications.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
10-03-2000
MAIS UMA META ATINGIDA
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(7):399-399
Abstract


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
07-23-2000
Isoformas de Prolactina no Fluido Folicular de Pacientes Submetidas a FIV
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(10):658-658
Abstract


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Original Article11-28-2005
Cardiofemoral index for the evaluation of fetal anemia in isoimmunized pregnancies
- Antônio Carlos Vieira Cabral,
- Thales Bittencourt de Barcelos,
- Isabela Gomes Melo Apocalipse,
- Henrique Vitor Leite,
- Zilma Silveira Nogueira Reis
Views130

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleCardiofemoral index for the evaluation of fetal anemia in isoimmunized pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):450-455
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800003
- Antônio Carlos Vieira Cabral,
- Thales Bittencourt de Barcelos,
- Isabela Gomes Melo Apocalipse,
- Henrique Vitor Leite,
- Zilma Silveira Nogueira Reis
Views130See morePURPOSE: to test a new, noninvasive method for the diagnosis of fetal anemia in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. METHODS: the index obtained by the ratio between the ultrasonographic measurement of the biventricular outer dimension (BVOD) and femur length (both in centimeters) was correlated with fetal hemoglobin values in a cross-sectional study. Fifty-nine fetuses of isoimmunized pregnancies selected for invasive treatment and submitted to 130 cordocenteses for the diagnosis and treatment of anemia were included in the study. The cardiofemoral index was obtained immediately before the cordocentesis and the fetal hemoglobin index was obtained from fetal blood samples. Linear regression was carried out to assess the correlation between the index and fetal hemoglobin; ROC curve was applied to determine the most accurate cutoff for the diagnosis of the fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl. RESULTS: BVOD measurement varied from 1.6 to 4.7 cm (average 2.5±1.3cm), and length of the femur, from 3.0 to 6.9 cm (average 4.3±0.9 cm). The cardiofemoral index varied from 0.4 to 1.0 (average 0.6±0.1). A significant inverse correlation between the cardiofemoral index and fetal hemoglobin (R²=0.37 and p<0.0001) was observed. The cutoff of 0.60 was the best to predict a level of fetal hemoglobin below or equal to 10.0g/dl: 80.85% sensitivity, 83.13% specificity, 73.8% positive predictive value, and 88.46% negative predictive value, in the diagnosis of fetuses anemia. CONCLUSION: the cardiofemoral index allows for good accuracy in the prediction of fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. It may thus be applied as a noninvasive method to the diagnosis of this pathology.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article01-30-2005
Fetal macrosomia risk factors in pregnancies complicated by diabetes or daily hyperglycemia
- Luciane Teresa Rodrigues Lima Kerche,
- Joelcio Francisco Abbade,
- Roberto Antonio Araújo Costa,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge,
- Iracema de Mattos Paranhos Calderon
Views110

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleFetal macrosomia risk factors in pregnancies complicated by diabetes or daily hyperglycemia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(10):580-587
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001000003
- Luciane Teresa Rodrigues Lima Kerche,
- Joelcio Francisco Abbade,
- Roberto Antonio Araújo Costa,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge,
- Iracema de Mattos Paranhos Calderon
Views110See morePURPOSE: to identify risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia. METHODS: retrospective study, control-case, including 803 pairs of mothers and newborns belonging to this specific population, divided into two groups – macrosomic (cases, n=242) and non-macrosomic (controls, n=561). Variables regarding age, parity, weight and body mass index (BMI), weight gain (WG), diabetes history, high blood pressure and tabagism, diabetes type and classification, and glycemic control indicators in the third trimester were compared. The means were evaluated by the F test and the categorized variables were submitted to univariate analysis using the chi² test. The significative results were included in the multiple regression model for the identification of macrosomia independent risk considering OR, 95% CI and p value. The statistical significance limit of 5% was established for all analyses. RESULTS: there was a significative association between macrosomia and WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², personal, obstetric and macrosomic history, classification in the Rudge groups (IB and IIA + IIB), glycemic mean (GM) >120 mg/dL and postprandial glycemic mean >130 mg/dL in the third trimester. In the multiple regression analysis, WG >16 kg (OR=1,79; 95% CI: 1,23-1.60), BMI >25 kg/m² (OR=1.83; 95% CI: 1.27-2.64), personal history of diabetes (OR=1.56; 95% CI: 1.05-2.31) and of macrosomia (OR=2.37; 95% CI: 1.60-3.50) and GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester (OR=1.78; 95% CI: 1.13-2.80) confirmed to be independent risk factors for macrosomia in these pregnancies. CONCLUSION: WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester and personal history of macrosomia and diabetes were identified as risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article01-12-2008
Tibolone’s effect on retinal and ophthalmic arteries flowmetry
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):537-543
Views118

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleTibolone’s effect on retinal and ophthalmic arteries flowmetry
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):537-543
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001100002
Views118PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of tibolone use on dopplervelocimetric parameters of ophthalmic and retinal arteries. METHODS: clinical, prospective, longitudinal, randomized, placebo-controlled, triple-blind study, in which among 100 menopausal women, 50 have used 2.5 mg of the active principle tibolone (Tib Group) and 50, placebo as a means to form the control-group (Plac Group). In the Tib Group, 44 of the 50 women returned after 84 days to finish the exams, and in the Plac Group, 47. The ophthalmic and retinal arteries were studied to determine the resistance index (RI), the pulsatility index (PI) and the systole/diastole ratio (S/D). Assessments have been done before and 84 days after medication. The t-Student test has been used for the comparison of means between the groups in independent samples, as well as for within-group comparisons in dependent samples. RESULTS: in both groups, the women’s characteristics were similar in age, menopause duration, body mass index, arterial blood pressure, deliveries and cardiac rate. The Tib Group presented the following values in the ophthalmic artery: RI(pre)=0.71±0.05, RI(post)0.72±0.08 (p=0.43); PI(pre)=1.29±0.22, PI(post)=1.30±0.25 (p=0.4) and S/D(pre)=3.49±0.77, SD(post)=3.65±0.94 (p=0.32). In the retinal artery, the following values have been found: RI(pre)=0.67±0.09, RI(post)=0.69±0.10 (p=0.7); PI(pre)=1.20±0.29, PI(post)=1.22±0.3 (p=0.2) and SD(pre)=3.29±0.95, SD(post)=3.30±1.07 (p=0.3). Also, the tibolone and control groups did not show any significant difference in regard to the above indexes in the end of the study. CONCLUSIONS: the 2.5 mg dose of tibolone had no effect on the Doppler velocimetry indexes of the ophthalmic and retinal arteries.
Key-words Laser-doppler flowmetryNorpregnanesOphthalmic arteryPlacebosRandomized controlled trialsRetinal arteryUltrasonographySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article07-02-2010
Myomectomy in the second trimester of pregnancy: case report
- Guilherme Karam Corrêa Leite,
- Henri Augusto Korkes,
- Arildo de Toledo Viana,
- Alexandre Pitorri,
- Grecy Kenj, [ … ],
- Nelson Sass
Views109

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleMyomectomy in the second trimester of pregnancy: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(4):198-201
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000400008
- Guilherme Karam Corrêa Leite,
- Henri Augusto Korkes,
- Arildo de Toledo Viana,
- Alexandre Pitorri,
- Grecy Kenj,
- Nelson Sass
Views109See moreUterine leiomyomas are characterized as a benign disease and are observed in 2 to 3% of all normal pregnancies. Out of these, about 10% may present complications during pregnancy. We present a case of a pregnant patient sought emergency obstetric care at the 17th week, complaining of severe pain, presenting with painful abdominal palpation and sudden positive decompression. Ultrasonography revealed a myoma nodule measuring 9.1 x 7.7 cm; the patient was hospitalized and medicated, being also submitted to laparotomy and myomectomy due to worsening of her condition. Prenatal care revealed no further abnormalities, with resolution of gestation at 39 weeks. The newborn weighed 3,315 g, with Apgar scores of 9 and 10. In such cases, clinical treatment should always be attempted and surgery should be considered only in selected cases, mainly in the impossibility of conservative treatment or when the patient’s clinical features require immediate intervention. In this case, myomectomy was effective against maternal-fetal obstetric complications.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article01-06-2011
Assessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by maternal moderate to severe thrombocytopenia
- Roseli Mieko Yamamoto Nomura,
- Ana Maria Kondo Igai,
- Verbênia Nunes Costa,
- Seizo Miyadahira,
- Marcelo Zugaib
Views117

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleAssessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by maternal moderate to severe thrombocytopenia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(10):280-285
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001000002
- Roseli Mieko Yamamoto Nomura,
- Ana Maria Kondo Igai,
- Verbênia Nunes Costa,
- Seizo Miyadahira,
- Marcelo Zugaib
Views117See morePURPOSE: To analyze the results of assessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by moderate or severe maternal thrombocytopenia. METHODS: Data from April 2001 to July 2011 of 96 women with a diagnosis of thrombocytopenia in pregnancy were retrospectively analyzed. We analyzed the following tests performed during the antepartum period for fetal assessment: cardiotocography, fetal biophysical profile, amniotic fluid index and umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry. RESULTS: A total of 96 pregnancies with the following diagnoses were analyzed: gestational thrombocytopenia (n=37, 38.5%) hypersplenism (n=32, 33.3%), immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP, n=14, 14.6%), secondary immune thrombocytopenia (n=6, 6.3%), bone marrow aplasia (n=3, 3.1%), and others (n=4, 4.1%). Cardiotocography showed normal results in 94% of cases, a fetal biophysical profile with an index of 8 or 10 in 96.9% and an amniotic fluid index >5.0 cm in 89.6%. Doppler umbilical artery velocimetry showed normal results in 96.9% of cases. In the analysis of the major groups of thrombocytopenia, the diagnosis of oligohydramnios was found to be significantly more frequent in the group with ITP (28.6%) compared to the other groups (gestational thrombocytopenia: 5.4% and hypersplenism: 9.4%, p=0.04). CONCLUSIONS: This study indicates that in pregnancies complicated by moderate or severe maternal thrombocytopenia, even though the fetal well-being remains preserved in most cases, fetal surveillance is important in pregnant women with ITP, with emphasis on amniotic fluid volume evaluation due to its association with oligohydramnios.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article01-10-2013
Quality of clinical studies published in the RBGO over one decade (1999-2009): methodological and ethical aspects and statistical procedures
- Joceline Cássia Ferezini de Sá,
- Gabriela Marini,
- Rafael Bottaro Gelaleti,
- João Batista da Silva,
- George Dantas de Azevedo, [ … ],
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge
Abstract
Original ArticleQuality of clinical studies published in the RBGO over one decade (1999-2009): methodological and ethical aspects and statistical procedures
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(11):477-482
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001100001
- Joceline Cássia Ferezini de Sá,
- Gabriela Marini,
- Rafael Bottaro Gelaleti,
- João Batista da Silva,
- George Dantas de Azevedo,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge
Views121PURPOSE: To evaluate the methodological and statistical design evolution of the publications in the Brazilian Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics (RBGO) from resolution 196/96. METHODS: A review of 133 articles published in 1999 (65) and 2009 (68) was performed by two independent reviewers with training in clinical epidemiology and methodology of scientific research. We included all original clinical articles, case and series reports and excluded editorials, letters to the editor, systematic reviews, experimental studies, opinion articles, besides abstracts of theses and dissertations. Characteristics related to the methodological quality of the studies were analyzed in each article using a checklist that evaluated two criteria: methodological aspects and statistical procedures. We used descriptive statistics and the χ2 test for comparison of the two years. RESULTS: There was a difference between 1999 and 2009 regarding the study and statistical design, with more accuracy in the procedures and the use of more robust tests between 1999 and 2009. CONCLUSIONS: In RBGO, we observed an evolution in the methods of published articles and a more in-depth use of the statistical analyses, with more sophisticated tests such as regression and multilevel analyses, which are essential techniques for the knowledge and planning of health interventions, leading to fewer interpretation errors.
Key-words Clinical trials as topicEthics Committees, researchEthics, researchGynecologyHelsinki DeclarationObstetricsPeriodicals as topicScientific misconductStatisticsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report12-01-2015
Renal vein thrombosis in the puerperium: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):593-597
Abstract
Case ReportRenal vein thrombosis in the puerperium: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):593-597
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320150005455
Views109Abstract
Pregnancy and puerperium are periods of blood hypercoagulability and, therefore, of risk for thromboembolic events. Renal vein thrombosis is a serious and infrequent condition of difficult diagnosis. This study reported a case of renal vein thrombosis in the puerperium, and described the clinical case, risk factors, diagnostic methods, and treatment instituted.
Key-words Case reportsPostpartum periodPregnancy complications, hematologicThrombophiliaVenous thrombosisSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article06-27-2024
Prevalence of karyotype alterations in couples with recurrent pregnancy loss in a tertiary center in Brazil
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Ines Katerina Damasceno Cavallo Cruzeiro
 ,
, - Cezar Antônio Abreu de Souza
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos Reis

Views175

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of karyotype alterations in couples with recurrent pregnancy loss in a tertiary center in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo51
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Ines Katerina Damasceno Cavallo Cruzeiro
 ,
, - Cezar Antônio Abreu de Souza
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos Reis

Views175Abstract
Objective
To assess the prevalence and type of chromosomal abnormalities in Brazilian couples with recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) and compare the clinical characteristics of couples with and without chromosome abnormalities.
Methods
We assessed the medical records of 127 couples with a history of two or more miscarriages, referred to a tertiary academic hospital in Belo Horizonte, Brazil, from January 2014 to May 2023. Karyotype was generated from peripheral blood lymphocyte cultures, and cytogenetic analysis was performed according to standard protocols by heat-denatured Giemsa (RHG) banding.
Results
Abnormal karyotypes were detected in 10 couples (7.8%). The prevalence of chromosomal abnormalities was higher among females (6.3%) compared to males (2.0%), but this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.192). The mean number of miscarriages was. 3.3 ± 1.1 in couples with chromosome abnormalities and 3.1 ± 1.5 in couples without chromosome abnormalities (p=0.681). Numerical chromosomal anomalies (6 cases) were more frequent than structural anomalies. Four women presented low-grade Turner mosaicism. No differences were found between couples with and without karyotype alterations, except for maternal age, which was higher in the group with chromosome alterations.
Conclusion
The prevalence of parental chromosomal alterations in our study was higher than in most series described in the literature and was associated with increased maternal age. These findings suggest that karyotyping should be part of the investigation for Brazilian couples with RPL, as identifying the genetic etiology may have implications for subsequent pregnancies.
Key-words Abortion, habitualAbortion, spontaneousChromosome aberrationsKaryotypeTranslocation, geneticSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
-
Original Article11-01-2018
Obstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
- Sule Ozel,
- Selen Yaman,
- Hatice Kansu-Celik,
- Necati Hancerliogullari,
- Nurgul Balci, [ … ],
- Yaprak Engin-Ustun
Views174

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleObstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):673-679
- Sule Ozel,
- Selen Yaman,
- Hatice Kansu-Celik,
- Necati Hancerliogullari,
- Nurgul Balci,
- Yaprak Engin-Ustun
Views174See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to analyze and compare obstetric and neonatal outcomes between Syrian refugees and ethnic Turkish women.
Methods
Retrospective, observational study. A total of 576 Syrian refugees and 576 ethnic Turkish women were included in this study, which was conducted between January 2015 and December 2015 at a tertiary maternity training hospital in Ankara, Turkey. The demographic characteristics, obstetric and neonatal outcomes were compared. The primary outcomes were pregnancy outcomes and cesarean rates between the groups
Results
The mean age was significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). Mean gravidity, proportion of adolescent pregnancies, proportion of pregnant women aged 12 to 19 years, and number of pregnancies at < 18 years were significantly higher among the refugee women (p< 0.001). Rates of antenatal follow-up, double testing, triple testing, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) screening, and iron replacement therapy were significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). The primary Cesarean section rate was significantly lower in the refugee group (p= 0.034). Pregnancies in the refugee group were more complicated, with higher rates of preterm delivery (< 37 weeks), preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), and low birth weight (< 2,500 g) when compared with the control group (4.2% versus 0.7%, p< 0.001; 1.6% versus 0.2%, p= 0.011; and 12% versus 5.8%, p< 0.001, respectively). Low education level (odds ratio [OR] = 1.7, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.5–0.1), and weight gain during pregnancy (OR = 1.7, 95% CI = 0.5–0.1) were found to be significant indicators for preterm birth/PPROM and low birthweight.
Conclusion
Syrian refugees had increased risks of certain adverse obstetric outcomes, including preterm delivery, PPROM, lower birth weight, and anemia. Several factors may influence these findings; thus, refugee women would benefit from more targeted care during pregnancy and childbirth.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Editorial09-01-2018
Maternal Mortality in Brazil: Proposals and Strategies for its Reduction
- Rodolfo Carvalho Pacagnella,
- Marcos Nakamura-Pereira,
- Flavia Gomes-Sponholz,
- Regina Amélia Lopes Pessoa de Aguiar,
- Gláucia Virginia de Queiroz Lins Guerra, [ … ],
- Olímpio Barbosa de Moraes Filho
Views223

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
EditorialMaternal Mortality in Brazil: Proposals and Strategies for its Reduction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):501-506
- Rodolfo Carvalho Pacagnella,
- Marcos Nakamura-Pereira,
- Flavia Gomes-Sponholz,
- Regina Amélia Lopes Pessoa de Aguiar,
- Gláucia Virginia de Queiroz Lins Guerra,
- Carmen Simone Grilo Diniz,
- Brenno Belazi Nery de Souza Campos,
- Eliana Martorano Amaral,
- Olímpio Barbosa de Moraes Filho
Views223Maternal mortality is one of the health indicators that most reflect the social conditions of women. The inequities observed in this indicator between high- and low-income countries and among regions in the same country are explained by differences in the provision, in the access, and in the quality of obstetric care and of family planning. […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article06-27-2019
Quality of Life among University Students with Premenstrual Syndrome
- Fernanda Figueira Victor,
- Ariani Impieri Souza,
- Cynthia Danúbia Tavares Barreiros,
- João Lucas Nunes de Barros,
- Flavia Anchielle Carvalho da Silva, [ … ],
- Ana Laura Carneiro Gomes Ferreira

Views266

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleQuality of Life among University Students with Premenstrual Syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):312-317
- Fernanda Figueira Victor,
- Ariani Impieri Souza,
- Cynthia Danúbia Tavares Barreiros,
- João Lucas Nunes de Barros,
- Flavia Anchielle Carvalho da Silva,
- Ana Laura Carneiro Gomes Ferreira

Views266Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the quality of life among university students with premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
Methods
The cross-sectional study was conducted at the Faculdade Pernambucana de Saúde, in Recife, Brazil, between August 2016 and July 2017. Sociodemographic, gynecological, and lifestyle variables, and PMS occurrence, were investigated among 642 students. The short form of the World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL Bref) questionnaire was used to evaluate four domains of the quality of life of the students: physical, mental, social relationships, and environmental. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ criteria were used to define PMS.
Results
Of the 642 students, 49.9% had PMS, 23.3% had mild PMS and 26.6% had premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). Most of the students were between 18 and 24 years old, had regular menstrual cycles, and practiced physical activity. Regarding the physical and mental domains of the WHOQOL-Bref questionnaire, a statisticallysignificant difference was observed between the students who did not have and those who had mild or PMDD (p < 0.001). A difference was also found between the students who did not have PMS and those who had mild PMS in the social relationships (p = 0.001) and environmental domains (p = 0.009).
Conclusion
Mild PMS and PMDD are prevalent among university students on healthrelated courses, and the syndrome can affect the students’ self-assessment of all the domains of quality of life.
Key-words medical studentMenstruation disturbancespremenstrual dysphoric disorderPremenstrual syndromeQuality of lifeSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article06-01-2016
Selective Episiotomy: Indications, Techinique, and Association with Severe Perineal Lacerations
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):301-307
Views198

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleSelective Episiotomy: Indications, Techinique, and Association with Severe Perineal Lacerations
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):301-307
Views198See moreAbstract
Introduction
Episiotomy is a controversial procedure, especially because the discussion that surrounds it has gone beyond the field of scientific debate, being adopted as an indicator of the “humanization of childbirth”. The scientific literature indicates that episiotomy should not be performed routinely, but selectively.
Objectives
To review the literature in order to assess whether the implementation of selective episiotomy protects against severe perineal lacerations, the indications for the procedure, and the best technique to perform it.
Methods
A literature search was performed in PubMed using the terms episiotomy or perineal lacerations, and the filter clinical trial. The articles concerning the risk of severe perineal lacerations with or without episiotomy, perineal protection, or episiotomy techniques were selected.
Results
A total of 141 articles were identified, and 24 of them were included in the review. Out of the 13 studies that evaluated the risk of severe lacerations with and without episiotomy, 5 demonstrated a protective role of selective episiotomy, and 4 showed no significant differences between the groups. Three small studies confirmed the finding that episiotomy should be performed selectively and not routinely, and one study showed that midline episiotomy increased the risk of severe lacerations. The most cited indications were primiparity, fetal weight greater than 4 kg, prolonged second stage, operative delivery, and shoulder dystocia. As for the surgical technique, episiotomies performed with wider angles (> 40°) and earlier in the second stage (before “crowning “) appeared to be more protective.
Conclusions
Selective episiotomy decreases the risk of severe lacerations when compared with the non-performance or the performance of routine episiotomy. The use of a proper surgical technique is fundamental to obtain better results, especially in relation to the angle of incision, the distance from the vaginal introitus, and the correct timing for performing the procedure. Not performing the episiotomy when indicated or not applying the correct technique may increase the risk of severe perineal lacerations.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 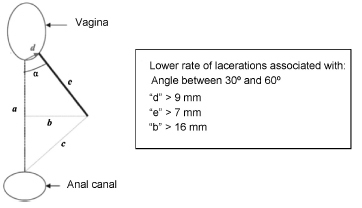
-
Review Article08-01-2017
Physical Activity during Pregnancy: Recommendations and Assessment Tools
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):424-432
Views237

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePhysical Activity during Pregnancy: Recommendations and Assessment Tools
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):424-432
Views237See moreAbstract
The literature that supports and recommends the practice of exercise during pregnancy is extensive.However, although a more complete research on ways to evaluate the physical activity performedby pregnant women has been perfomed, it is found that there is no gold standard and that the articles in the area are inconclusive. Thus, the objective of the present article is to review relevant aspects, such as, technique and applicability of the different methods for the assessment of physical activity during pregnancy to providemore reliable and safe information for health professionals to encourage their pregnant patients to engage in the practice of physical activity. This review concluded that all tools for the analysis of physical activity have limitations. Thus, it is necessary to establish the objectives of evaluation in an appropriate manner, as well as to determine their viability and costeffectiveness for the population under study.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article02-01-2017
Predictors of cesarean delivery in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):60-65
Views232

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePredictors of cesarean delivery in pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(2):60-65
Views232See moreAbstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to evaluate which risk factors may lead patients with gestational diabetes mellitus to cesarean delivery.
Methods
This was a retrospective, descriptive study. The subjects of the study were pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus attending a public maternity hospital in the south of Brazil. The primary outcomes assessed were based on maternal and fetal characteristics. The data were correlated using an odds ratio (OR) with a 95% confidence interval (95%CI), calculated using multinomial logistic regression.
Results
A total of 392 patients with gestational diabetes mellitus were analyzed, and 57.4% of them had cesarean deliveries. Among the maternal characteristics, the mean age of the patients and the pregestational body mass index were greater when a cesarean delivery was performed (p = 0.029 and p < 0.01 respectively). Gestational age at birth, newborn weight, weight class according to gestational age, and Apgar score were not significant. The analysis of the OR showed that the chance of cesarean delivery was 2.25 times (95%CI = 1.49-2.39) greater if the pregnant woman was obese, 4.6 times (95%CI = 3.017-7.150) greater if she was a primigravida, and 5.2 times (95% CI = 2.702-10.003) greater if she had a previous cesarean delivery. The other parameters analyzed showed no differences.
Conclusion
The factors that led to an increase in the occurrence of cesarean deliveries included history of a prior cesarean section, first pregnancy, and obesity.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Editorial12-01-2015
Maternal mortality and the new objectives of sustainable development (2016-2030)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):549-551
Views104

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
EditorialMaternal mortality and the new objectives of sustainable development (2016-2030)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):549-551


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article08-21-2015
Increased oxidative stress markers may be a promising indicator of risk for primary ovarian insufficiency: a cross-sectional case control study
- Aytekin Tokmak,
- Gülçin Yıldırım,
- Esma Sarıkaya,
- Mehmet Çınar,
- Nihal Boğdaycıoğlu, [ … ],
- Nafiye Yılmaz
Views91

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleIncreased oxidative stress markers may be a promising indicator of risk for primary ovarian insufficiency: a cross-sectional case control study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(9):411-416
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005397
- Aytekin Tokmak,
- Gülçin Yıldırım,
- Esma Sarıkaya,
- Mehmet Çınar,
- Nihal Boğdaycıoğlu,
- Fatma Meriç Yılmaz,
- Nafiye Yılmaz
Views91See morePURPOSE:
The aim of this study was to evaluate serum levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (INOS), myeloperoxidase (MPO), total antioxidant status (TAS), and total oxidative status (TOS) in women with primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) and to compare them with healthy fertile women. We also examined the possible risk factors associated with POI.
METHODS:
This cross-sectional case control study was conducted in Zekai Tahir Burak Women’s Health Education and Research Hospital. The study population consisted of 44 women with POI (study group) and 36 healthy fertile women (control group). In all patients, serum levels of INOS, MPO, TAS, and TOS were determined. INOS and MPO levels were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay whereas colorimetric method was used for evaluating TAS and TOS levels. Age, body mass index (BMI), obstetric history, smoking status, family history, comorbidities, sonographic findings, complete blood count values, C-reactive protein and baseline hormone levels were also analyzed. Student’s t-test or Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare continuous variables between the groups; categorical data were evaluated by using Pearson χ2 or Fisher exact test, when appropriate. Binary logistic regression method was used to identify risk factors for POI.
RESULTS:
We found significantly elevated levels of INOS (234.1±749.5 versus133.8±143.0; p=0.005), MPO (3,438.7±1,228.6 versus 2,481.9±1,230.1; p=0.001), and TOS (4.3±1.4 versus 3.6±1.4; p=0.02) in the sera of the study group when compared to the BMI-age matched control group. However, difference in serum levels of TAS were not significant between the 2 groups (1.7±0.2 versus 1.6±0.2; p=0.15). Logistic regression method demonstrated that BMI <25 kg/m2, nulliparity, family history of POI, smoking, and elevated serum levels of INOS, MPO, and TOS were independent risk factors for POI.
CONCLUSION:
We found an increase in INOS, MPO, and TOS in women with POI. These serum markers may be promising in early diagnosis of POI. Further large-scale studies are required to determine whether oxidative stress markers have a role in diagnosing POI.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
