- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Original Article04-11-1998
Prenatal diagnosis of fetal lung maturity in high-risk pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):315-321
Views73

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePrenatal diagnosis of fetal lung maturity in high-risk pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):315-321
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600004
Views73See moreThe objective was to evaluate the accuracy of the foam stability test, lecithin/sphingomyelin (LS) ratio, presence of phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and lung profile (L/S ratio > 1.7 and PG present simultaneously) in 121 consecutive high-risk gestations at the São Paulo Hospital from January 1990 to January 1995. Delivery occurred within 3 days of fetal lung maturation testing. This is a prospective study in which the sensitivity, specificity, positive (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) of all the tests were determined. Neonatal respiratory outcome and amniocentesis results were stratified by gestational age for comparison. The distribution of the studied population according to maternal pathology was diabetes mellitus (48), hypertensive disorders (41), Rh isoimmunization (14) and miscellaneous (18). Respiratory distress (RD) was present in 33 infants (27.2%), mainly in the diabetic group. There was no false negative using lung profile (all patients) and foam stability tests among hypertensive pregnancies (specificity 100%), but there were about 20% to 50% false positives in the other tests. Overall, all four tests had a low PPV: 23% for foam test, 51% for L/S ratio, 63% for PG, 61% for lung profile, and high NPV: 92% for foam test, 88% for L/S ratio, 89% for PG and 100% for lung profile. All tests had less accuracy in the diabetic pregnant women. This study shows that the presence of PG and L/S ratio > 1.7 in the amniotic fluid of high-risk pregnancies confirms maturity with a very low risk to develop RD and that the foam stability test was useful as a first-line test to predict the absence of surfactant-deficient respiratory distress syndrome, particularly in hypertensive pregnant women.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-11-1998
The effects of nomegestrol acetate subdermal implant on carbohydrate metabolism, serum lipoproteins and on hepatic function
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):309-313
Views104

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleThe effects of nomegestrol acetate subdermal implant on carbohydrate metabolism, serum lipoproteins and on hepatic function
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):309-313
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600003
Views104Objective: to evaluate variations in body weight, arterial blood pressure, fasting glucose, HbA1C, insulin, total cholesterol, HDL-C, LDL-C, triglycerides, Sgot, SGPT, GGT and bilirubin in women bearing a single subdermal Silastic implant containing 55 mg (+ 10%) of nomegestrol acetate during two years. Methods: eighteen healthy volunteers of reproductive age who desired to use anticonceptive drugs and who did not present contraindications to hormonal contraception participated in the study. All women were investigated before starting treatment and were followed-up for two years. At the end of the first year the capsules were inserted. Results: body weight increased from 54.9 + 1.5 kg at admission to 55.3 + 2.0 kg at 12 months of use (p<0.05) and from 56.0 + 2.7 kg at 24 months of use. There was a slight increase in arterial blood pressure, both systolic and diastolic, at month 12 (p<0.01). At month 24, the arterial blood pressure was not significantly different from the values at admission. All values were within the normal range. Insulin, HbA1C, LDL-C and GGT remained unchanged during the use of the implant. A significant decrease in total cholesterol (p<0.05) was observed in the third month and of HDL-C (p<0.01) in the sixth month. All lipoprotein alterations were inconsistent and values were within the normal range. Significant increases in fast glucose (p<0.05 and p<0.01) were observed in the third and sixth months, respectively. Significant SGOT decreases (p<0.05, p<0.01 and p<0.05) were observed in months 6, 18 and 24, respectively, and of SGPT (p<0.05) in month 18. Significant bilirubin increase (p<0.05) was observed only in the third month of implant use. All these variations remained within the normal range. Conclusions: these results show that, within the normal range, fasting glucose variations do not correlate with alterations in insulin levels. The slight serum lipoprotein, SGTO, SGPT and insulin alterations were transient. No clinical effects could be observed regarding lipoproteins, carbohydrate metabolism, insulin levels and liver function among the users during the two years.
Key-words ContraceptionCorbohydrate metabolismInjectable contraceptive drugsLiver functionProgesteroneSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-11-1998
Mammographic density variation in users and nonusers of hormonal replacement therapy
- Cesar Cabello dos Santos,
- Aarão Mendes Pinto-Neto,
- Lúcia Helena Simões Costa-Paiva,
- Henrique Benedito Brenelli
Abstract
Original ArticleMammographic density variation in users and nonusers of hormonal replacement therapy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):303-308
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600002
- Cesar Cabello dos Santos,
- Aarão Mendes Pinto-Neto,
- Lúcia Helena Simões Costa-Paiva,
- Henrique Benedito Brenelli
Views78See moreObjective: to compare mammographic density changes, case by case, according to image digitization in three consecutive evaluations of users or nonusers of hormonal replacement therapy (HRT). Methods: 59 postmenopausal women were evaluated, 43 being users of cyclic or continuous estro-progestin hormonal replacement therapy, and 16 nonusers. The criteria of inclusion were: amenorrhea for at least 12 months, a normal mammographic examination at the beginning of the HRT (users) or the clinical follow-up without HRT (nonusers), at two incidences (mediolateral and craniocaudal). The following variables were used for the evaluation of mammary density: initial change – the difference between the first mammography after HRT performed in 12 ± 3 months and the mammography performed before HRT-and final change – the difference between the second mammography after HRT performed in 24 ± 3 months and the mammography performed before HRT. Wilcoxon and c² tests were used in order to evaluate the differences in mammographic density changes. Results: more than half (56.3%) of the women, HRT users with initial increase in mammographic density remained with the increase after the final evaluation. This finding was not significant (p=0.617). In the same group, the initial nonincrease was significantly associated with the final nonincrease (p=0.017). Among the nonusers, all breasts that were not totally fat at the initial evaluation presented a mammographic density decrease at the final evaluation. Conclusions: the majority of HRT users presenting mammographic density increase at the first evaluation, after approximately one year of use, remained with the increase at a second evaluation. After some time, the nonusers tended to present a significant mammographic density decrease (p=0.003).


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
A FEBRASGO e as ações voltadas para a promoção da saúde
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):301-301
Abstract


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses04-10-1998
Avaliação longitudinal de aspectos imunológicos e virológicos durante a gravidez e puerpério em mulheres portadoras do vírus da imunodeficiência humana tipo 1 (HIV-1)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):170-170
Abstract
Resumos de TesesAvaliação longitudinal de aspectos imunológicos e virológicos durante a gravidez e puerpério em mulheres portadoras do vírus da imunodeficiência humana tipo 1 (HIV-1)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):170-170
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300011
Views74Avaliação Longitudinal de Aspectos Imunológicos e Virológicos Durante a Gravidez e Puerpério em Mulheres Portadoras do Vírus da Imunodeficiência Humana Tipo 1 (HIV-1)[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses04-10-1998
A dopplervelocimetria com mapeamento em cores dos ramos intramiometriais da artéria uterina de mulheres na pós-menopausa, com e sem carcinoma de endométrio
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-170
Abstract
Resumos de TesesA dopplervelocimetria com mapeamento em cores dos ramos intramiometriais da artéria uterina de mulheres na pós-menopausa, com e sem carcinoma de endométrio
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-170
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300010
Views60A Dopplervelocimetria com Mapeamento em Cores dos Ramos Intramiometriais da Artéria Uterina de Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa, com e sem Carcinoma de Endométrio[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses04-10-1998
Avaliação da esteroidogênese das supra-renais em mulheres normais por meio dos testes de ACTH simples de depósito
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-169
Abstract
Resumos de TesesAvaliação da esteroidogênese das supra-renais em mulheres normais por meio dos testes de ACTH simples de depósito
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-169
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300009
Views58Avaliação da Esteroidogênese das Supra-Renais em Mulheres Normais por Meio dos Testes de ACTH Simples de Depósito[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-10-1998
Recurrent HELLP syndrome: report on two cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):165-167
Views63

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Case ReportRecurrent HELLP syndrome: report on two cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):165-167
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300008
Views63See moreHELLP syndrome is a severe complication of preeclampsia that increases maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. Two cases of recurrent HELLP syndrome are described, maternal death occurring in one of the cases. This study is a warning about the increased risk of HELLP syndrome in the next pregnancy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Original Article04-09-2024
Factors associated with the absence of postpartum consultations in a high-risk population
- Ana Carolina Gomes Pereira
 ,
, - Tábata Regina Zumpano dos Santos
 ,
, - Helymar da Costa Machado
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani de Castro Surita

Views385

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleFactors associated with the absence of postpartum consultations in a high-risk population
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo23
- Ana Carolina Gomes Pereira
 ,
, - Tábata Regina Zumpano dos Santos
 ,
, - Helymar da Costa Machado
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani de Castro Surita

Views385See moreAbstract
Objective:
To assess the rate of missed postpartum appointments at a referral center for high-risk pregnancy and compare puerperal women who did and did not attend these appointments to identify related factors.
Methods:
This was a retrospective cross-sectional study with all women scheduled for postpartum consultations at a high-risk obstetrics service in 2018. The variables selected to compare women were personal, obstetric, and perinatal. The variables of interest were obtained from the hospital’s electronic medical records. Statistical analyses were performed using the Chi-square, Fisher’s exact, or Mann–Whitney tests. For the variable of the interbirth interval, a receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was used to best discriminate whether or not patients attended the postpartum consultation. The significance level for the statistical tests was 5%.
Results:
A total of 1,629 women scheduled for postpartum consultations in 2018 were included. The rate of missing the postpartum consultation was 34.8%. A shorter interbirth interval (p = 0.039), previous use of psychoactive substances (p = 0.027), current or former smoking (p = 0.003), and multiparity (p < 0.001) were associated with non-attendance.
Conclusion:
This study showed a high rate of postpartum appointment non-attendance. This is particularly relevant because it was demonstrated in a high-risk obstetric service linked to clinical severity or social vulnerability cases. This highlights the need for new approaches to puerperal women before hospital discharge and new tools to increase adherence to postpartum consultations, especially for multiparous women.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ana Carolina Gomes Pereira
-
Review Article04-09-2024
Timing of semen cryopreservation: before or after processing?
- Ana Paula de Souza Kussler
 ,
, - Ivan Cunha Bustamante Filho
 ,
, - Elisa Negri
 ,
, - Edison Capp
 ,
, - Helena von Eye Corleta

Abstract
Review ArticleTiming of semen cryopreservation: before or after processing?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo36
- Ana Paula de Souza Kussler
 ,
, - Ivan Cunha Bustamante Filho
 ,
, - Elisa Negri
 ,
, - Edison Capp
 ,
, - Helena von Eye Corleta

Views383Abstract
Objective:
Seminal cryopreservation causes significant damage to the sperm; therefore, different methods of cryopreservation have been studied. The aim of the study was to compare the effects of density gradient processing and washing/centrifugation with seminal plasma removal for cryopreservation in semen parameters.
Methods:
Seminal samples of 26 normozoospermic patients were divided into 3 parts: with seminal plasma; after washing/centrifugation; and after selection through density gradient. The samples were cryopreserved for at least two weeks. Motility, sperm count, morphology and viability were evaluated before cryopreservation and after thawing.
Results:
Density gradient processing selected motile and viable sperm with normal morphology in fresh samples (p<0.05). Cryopreservation negatively affected all sperm parameters regardless of the processing performed, and even if the sperm recovery was lower in the density gradient after the thawing, progressive motility, total motility, viability and morphology remained higher (p<0.05).
Conclusion:
Cryopreservation significantly compromises sperm parameters (motility, morphology, viability). In normozoospermic patients, the density gradients select better quality spermatozoa compared to other processing methods; this benefit was kept after thawing.
Key-words CentrifugationCryopreservationDensity gradientSemenSeminal plasmaSperm countSperm washSpermatozoaSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ana Paula de Souza Kussler
-
Original Article00-00-2024
Comparison of medical image interpretation time between conventional and automated methods of breast ultrasound
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo15
Views378

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleComparison of medical image interpretation time between conventional and automated methods of breast ultrasound
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo15
Views378See moreAbstract
Objective:
To compare the medical image interpretation’s time between the conventional and automated methods of breast ultrasound in patients with breast lesions. Secondarily, to evaluate the agreement between the two methods and interobservers.
Methods:
This is a cross-sectional study with prospective data collection. The agreement’s degrees were established in relation to the breast lesions’s ultrasound descriptors. To determine the accuracy of each method, a biopsy of suspicious lesions was performed, considering the histopathological result as the diagnostic gold standard.
Results:
We evaluated 27 women. Conventional ultrasound used an average medical time of 10.77 minutes (± 2.55) greater than the average of 7.38 minutes (± 2.06) for automated ultrasound (p<0.001). The degrees of agreement between the methods ranged from 0.75 to 0.95 for researcher 1 and from 0.71 to 0.98 for researcher 2. Among the researchers, the degrees of agreement were between 0.63 and 1 for automated ultrasound and between 0.68 and 1 for conventional ultrasound. The area of the ROC curve for the conventional method was 0.67 (p=0.003) for researcher 1 and 0.72 (p<0.001) for researcher 2. The area of the ROC curve for the automated method was 0. 69 (p=0.001) for researcher 1 and 0.78 (p<0.001) for researcher 2.
Conclusion:
We observed less time devoted by the physician to automated ultrasound compared to conventional ultrasound, maintaining accuracy. There was substantial or strong to perfect interobserver agreement and substantial or strong to almost perfect agreement between the methods.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article07-30-2021
Interventions among Pregnant Women in the Field of Music Therapy: A Systematic Review
- Bruna Mayumi Omori Shimada
 ,
, - Magda da Silva Oliveira Menezes dos Santos
 ,
, - Mayara Alvares Cabral
 ,
, - Vanessa Oliveira Silva
 ,
, - Gislaine Cristina Vagetti

Views368

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleInterventions among Pregnant Women in the Field of Music Therapy: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(5):403-413
- Bruna Mayumi Omori Shimada
 ,
, - Magda da Silva Oliveira Menezes dos Santos
 ,
, - Mayara Alvares Cabral
 ,
, - Vanessa Oliveira Silva
 ,
, - Gislaine Cristina Vagetti

Views368See moreAbstract
Objective
To investigate in the literature the studies on the benefits ofmusic therapy interventions among pregnant women in the prenatal, delivery and postpartum periods.
Data Sources
The search for articles was carried out in the following electronic databases: VHL, LILACS, SciELO, Portal CAPES, PsycINFO, ERIC, PubMed/Medline, and journals specialized in this field: Revista Brasileira de Musicoterapia (“Brazilian Journal of Music Therapy”) and Voices.
Study Selection
Descriptors in Portuguese (musicoterapia, gravidez, gestantes, revisão), English (music therapy, pregnancy, pregnant women, review) and Spanish (musicoterapia, embarazo, mujeres embarazadas, revisión) were used. The search was delimited between January 2009 and June 2019. The process of selection and evaluation of the articles was performed through peer review.
Data Collectio
n The following data were extracted: article title, year of publication, journal, author(s), database, country and date of collection, purpose of the study, sample size, type of care, intervention, instruments used, results, and conclusion. The data were organized in chronological order based on the year of publication of thestudy.
Summary of the Data
In total, 146 articles were identified, and only 23 studies were included in this systematic review. The articles found indicate among their results relaxation, decreased levels of anxiety, psychosocial stress and depression, decreased pain, increase in the maternal bond, improvement in the quality of sleep, control of the fetal heart rate and maternal blood pressure, and decreased intake of drugs in the postoperative period.
Conclusion
Music therapy during the prenatal, delivery and postpartum periods can provide benefits to pregnant women and newborns, thus justifying its importance in this field.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Bruna Mayumi Omori Shimada
-
Review Article08-15-2022
The Correlation between Chlamydia Trachomatis and Female Infertility: A Systematic Review
- Laura Gazal Passos
 ,
, - Paula Terraciano
 ,
, - Nicole Wolf
 ,
, - Fernanda dos Santos de Oliveira
 ,
, - Isabel de Almeida
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Eduardo Pandolfi Passos

Views369

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleThe Correlation between Chlamydia Trachomatis and Female Infertility: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):614-620
- Laura Gazal Passos
 ,
, - Paula Terraciano
 ,
, - Nicole Wolf
 ,
, - Fernanda dos Santos de Oliveira
 ,
, - Isabel de Almeida
 ,
, - Eduardo Pandolfi Passos

Views369Abstract
The impact of Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) infection on female’s fertility is not completely established yet, since the level of evidence associating these factors is still weak. Hence, the goal of the present review is to contribute to a better elucidation of this matter. The electronic database chosen was the Medline/PubMed, with the last survey on May 11, 2021. Publication date was used as a filter, with the previous 5 years having been selected. The following describers were used: chlamydia trachomatis AND infertility; chlamydia trachomatis AND tubal alteration AND infertility; chlamydia AND low pregnancy rates. From the 322 studies screened, 293 that failed to meet our eligibility criteria were excluded. Subsequently, we removed seven studies for not having the possible correlation between CT infections and female infertility as its main focus, and three for being about sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in general. Moreover, two studies designed as reviews were also excluded. Ergo, we included 17 studies in our qualitative analysis. The authors conducted research individually and analyzed carefully the studies selected. As we retrieved the information needed for our study through reading the texts, no contact was made with the authors of the studies selected. This systematic review corroborates the hypothesis that CT infection potentiates female infertility, as 76.47% of the included studies found a positive correlation between them. We conclude that there is an important association between CT infection and female infertility. Ergo, making CT screening part of the infertility investigation routine is relevant and has a reasonable justification.
Key-words Chlamydia trachomatishuman reproductionInfertilitySexually transmitted diseasestubal factor infertilitySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Laura Gazal Passos
-
Letter to the Editor04-09-2024
Letter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
Abstract
Letter to the EditorLetter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
Views367Dear Editor,First and foremost, we express our gratitude towards the authors for their clear and concise description of the positive effects of aerobic and strength training on dynamic stability.() Additionally, their ability to provide a focused and informative introduction section is commendable. The study piqued our interest in further exploring the benefits of aerobic and […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article00-00-2024
Prevalence of colorectal symptoms and anal incontinence in patients with pelvic organ prolapse attended at an outpatient urogynecology service
- Marco Arellano
 ,
, - Fernanda Santis-Moya
 ,
, - Andrea Maluenda
 ,
, - Alejandro Pattillo
 ,
, - Bernardita Blümel
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Javier Pizarro-Berdichevsky

Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of colorectal symptoms and anal incontinence in patients with pelvic organ prolapse attended at an outpatient urogynecology service
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo10
- Marco Arellano
 ,
, - Fernanda Santis-Moya
 ,
, - Andrea Maluenda
 ,
, - Alejandro Pattillo
 ,
, - Bernardita Blümel
 ,
, - Dominga Pohlhammer
 ,
, - Silvana Gonzalez
 ,
, - Javier Pizarro-Berdichevsky

Views365See moreAbstract
Objective:
To analyze data of patients with symptomatic pelvic organ prolapse evaluated with PFDI20 and its subscales to report the prevalence of lower gastrointestinal symptoms and anal incontinence in the population of a public hospital and analyze its impact on quality of life.
Methods:
Cross-sectional study of patients with symptomatic POP. Patients were evaluated with demographic data, POP-Q, pelvic floor ultrasonography, urological parameters, and pelvic floor symptoms (PFDI-20), and quality of life (P-QoL) surveys. Patients were classified as CRADI-8 “positive” for colorectal symptoms, with responses “moderate” in at least 3 and/or “severe” in at least 2 of the items in the CRADI-8 questionnaires.
Results:
One hundred thirteen patients were included. 42.5% (48) were considered positive for colorectal symptoms on CRADI-8. 53.4% presented anal incontinence. No significant differences were found in sociodemographic variables, POP-Q stage, ultrasound parameters, or urological parameters. Positive patients had a significantly worse result in PFDI-20, POPDI (48 vs 28; p<0.001), UDI6 (51 vs 24; p<0.001), and in the areas of social limitation (44.4 vs 22.2; p = 0.045), sleep- energy (61.5 vs 44.4; p = 0.08), and severity (56.8 vs 43.7, p=0.015) according to P-QoL.
Conclusion:
Moderate or severe colorectal symptoms are seen in 40% of patients with symptomatic POP in our unit. Full evaluation of pelvic floor dysfunction symptoms should be performed routinely in urogynecology units.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Marco Arellano
-
Review Article02-28-2022
Efficacy of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in the Reduction of Pain and Opioid Requirement in Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Hysterectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Claudia López-Ruiz
 ,
, - Jerutsa Catalina Orjuela
 ,
, - Diego Fernando Rojas-Gualdrón
 ,
, - Marcela Jimenez-Arango
 ,
, - José Fernando de los Ríos
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Claudia Vargas

Views363

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in the Reduction of Pain and Opioid Requirement in Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Hysterectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):55-66
- Claudia López-Ruiz
 ,
, - Jerutsa Catalina Orjuela
 ,
, - Diego Fernando Rojas-Gualdrón
 ,
, - Marcela Jimenez-Arango
 ,
, - José Fernando de los Ríos
 ,
, - Elsa Maria Vásquez-Trespalacios
 ,
, - Claudia Vargas

Views363Abstract
Objective
To summarize the available evidence of TAP Block in efficacy in laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy.
Data Sources
We searched databases and gray literature for randomized controlled trials in which transversus abdominis plane (TAP) block was compared with placebo or with no treatment in patients who underwent laparoscopic or robot-assisted hysterectomy.
Method of Study
Selection Two researchers independently evaluated the eligibility of the selected articles. Tabulation, Integration, and Results Seven studies were selected, involving 518 patients. Early postoperative pain showed a difference in the mean mean difference (MD): – 1.17 (95% confidence interval [CI]: – 1.87-0.46) in pain scale scores (I2=68%), which was statistically significant in favor of using TAP block, but without clinical relevance; late postoperative pain: DM 0.001 (95%CI: – 0.43-0.44; I2=69%); opioid requirement: DM 0.36 (95%CI: – 0.94-1.68; I2=80%); and incidence of nausea and vomiting with a difference of 95%CI=- 0.11 (- 0.215-0.006) in favor of TAP.
Conclusion
With moderate strength of evidence, due to the high heterogeneity and imbalance in baseline characteristics among studies, the results indicate that TAP block should not be considered as a clinically relevant analgesic technique to improve postoperative pain in laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy, despite statistical significance in early postoperative pain scale scores.
Key-words laparoscopic hysterectomyOpioidPainrobotic-assisted hysterectomytransversus abdominis plane blockSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 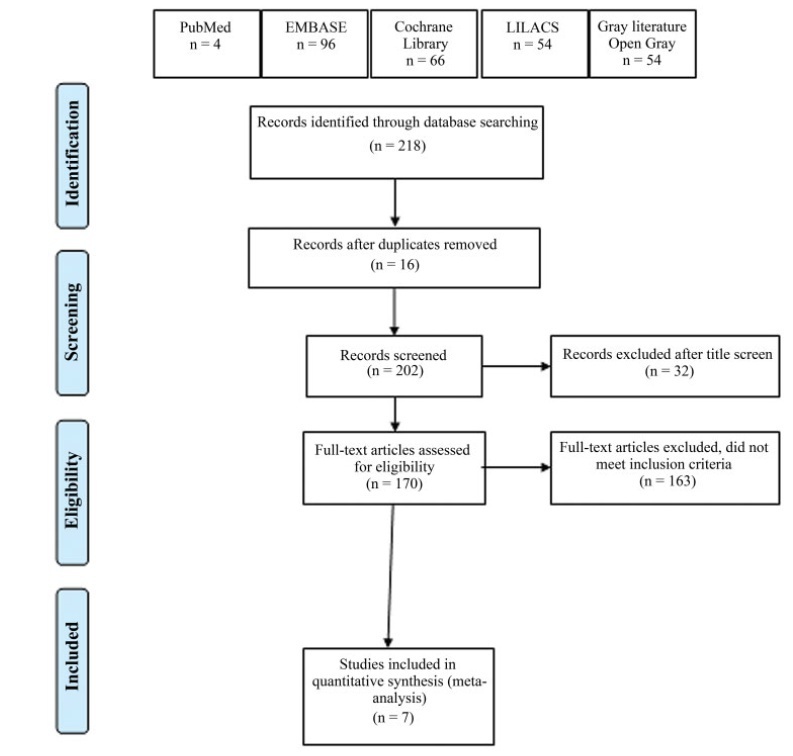
- Claudia López-Ruiz
-
Review Article03-24-2022
Commercial Surrogacy: An Overview
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1141-1158
Views353

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleCommercial Surrogacy: An Overview
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1141-1158
Views353See moreAbstract
Objective
Surrogacy is the process in which a woman carries and delivers a baby to other person or couple, known as intended parents. When carriers are paid for surrogacy, this is known as commercial surrogacy. The objective of the present work is to review the legal, ethical, social, and cultural aspects of commercial surrogacy, as well as the current panorama worldwide.
Methods
This is a review of the literature published in the 21st century on commercial surrogacy.
Results
A total of 248 articles were included as the core of the present review. The demand for surrogate treatments by women without uterus or with important uterine disorders, single men and same-sex male couples is constantly increasing worldwide. This reproductive treatment has important ethical dilemmas. In addition, legislation defers widely worldwide and is in constant change. Therefore, patients look more and more for treatments abroad, which can lead to important legal problems between countries with different laws. Commercial surrogacy is practiced in several countries, in most of which there is no specific legislation. Some countries have taken restrictive measures against this technique because of reports of exploitation of carriers.
Conclusion
Commercial surrogacy is a common practice, despite important ethical and legal dilemmas. As a consequence of diverse national legislations, patients frequently resort to international commercial surrogacy programs. As of today, there is no standard international legal context, and this practice remains largely unregulated.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article07-30-2021
The Female Athlete Triad/Relative Energy Deficiency in Sports (RED-S)
- Alexandra Ruivo Coelho
 ,
, - Gonçalo Cardoso
 ,
, - Marta Espanhol Brito
 ,
, - Inês Neves Gomes
 ,
, - Maria João Cascais

Views406

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleThe Female Athlete Triad/Relative Energy Deficiency in Sports (RED-S)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(5):395-402
- Alexandra Ruivo Coelho
 ,
, - Gonçalo Cardoso
 ,
, - Marta Espanhol Brito
 ,
, - Inês Neves Gomes
 ,
, - Maria João Cascais

Views406See moreAbstract
In a healthy athlete, the caloric intake is sufficient for sports energy needs and body physiological functions, allowing a balance between energy availability, bone metabolism, andmenstrual cycle.Onthe other hand, an imbalance causedby low energy availability dueto a restrictive diet, eating disorders or long periods of energy expenditure leads to multisystemic deregulation favoring the essential functions of the body. This phenomenon, described as the female athlete triad, occurs in a considerable percentage of high-performance athletes, with harmful consequences for their future. The present review was carried out based on a critical analysis of themost recent publications available and aims to provide a global perception of the topic relative energy deficit in sport (RED-S). The objective is to promote theacquisition ofmore consolidated knowledgeon an undervaluedtheme, enabling the acquisition of preventive strategies, early diagnosis and/or appropriate treatment.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Alexandra Ruivo Coelho
-
Original Article03-04-2022
Screening of Perinatal Depression Using the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale
- Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
 ,
, - Guilherme Guarany Cardoso Magalhães Luzetti
 ,
, - Márcia Maria Auxiliadora Rosalém
 ,
, - Corintio Mariani Neto

Views409

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleScreening of Perinatal Depression Using the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):452-457
- Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
 ,
, - Guilherme Guarany Cardoso Magalhães Luzetti
 ,
, - Márcia Maria Auxiliadora Rosalém
 ,
, - Corintio Mariani Neto

Views409See moreAbstract
Objective
To detect depression during pregnancy and in the immediate postpartum period using the Edinburgh postpartum depression scale (EPDS).
Methods
Cross sectional study of 315 women, aged between 14 and 44 years, who received perinatal care at the Leonor Mendes de Barros Hospital, in São Paulo, between July 1st, 2019 and October 30th, 2020. The cutoff point suggesting depression was ≥ 12.
Results
The screening indicated 62 (19.7%) patients experiencing depression. Low family income, multiparity, fewer prenatal appointments, antecedents of emotional disorders, dissatisfaction with the pregnancy, poor relationship with the partner, and psychological aggression were all risk factors associated with depression in pregnancy or in the immediate postpartum period. Antecedents of depression and psychology aggression during pregnancy were significant variables for predicting perinatal depression in the multivariate analysis.
Conclusion
There is a significant association between the occurrence of perinatal depression and the aforementioned psychosocial factors. Screening patients with the EPDS during perinatal and postpartum care could facilitate establishing a line of care to improve the wellbeing of mother and infant.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
-
Original Article04-08-2022
Prevalence of Premenstrual Syndrome and Associated Factors Among Academics of a University in Midwest Brazil
- Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
 ,
, - Fernanda Rassi Alvarenga
 ,
, - Marcelo Ramos
 ,
, - Débora Luiza Franken
 ,
, - Juvenal Soares Dias da Costa
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Vera Maria Vieira Paniz

Views311

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of Premenstrual Syndrome and Associated Factors Among Academics of a University in Midwest Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):133-141
- Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
 ,
, - Fernanda Rassi Alvarenga
 ,
, - Marcelo Ramos
 ,
, - Débora Luiza Franken
 ,
, - Juvenal Soares Dias da Costa
 ,
, - Marcos Pascoal Pattussi
 ,
, - Vera Maria Vieira Paniz

Views311Abstract
Objective
To investigate the prevalence of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) in university students, the factors associated with PMS, the most prevalent symptoms, and the interference of symptoms in academic, family, social, and work activities.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 1,115 university students aged ≥ 18 years from the University of Rio Verde, Goiás. Premenstrual syndrome and PMDD were identified using the Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool. Associations with sociodemographic, behavioral, reproductive, nutritional, and health factors were investigated using the Poisson regression.
Results
The prevalence of PMS was 46.9% (95% confidence interval [CI] 44.0-49.8), and of PMDD, 11.1% (95% CI 9.3-13.0). The most prevalent symptoms were physical, such as breast tenderness, bloating, e weight gain (73%); followed by psychological ones such as overeating/food cravings, tearful/more sensitive to rejection (> 60%). More than 30% of the patients reported that the symptoms interfered in a moderate-tosevere way in their social and academic activities. After adjusted analysis, PMS was more prevalent in those who were attending the 1st/2nd semester of college (prevalence ratio [PR] 1.44; 95% CI 1.14-1.80), those who consumed alcohol in the last 30 days (PR 1.23; 95% CI 1.04-1.47), and those who had depression (PR 1.49; 95% CI 1.30-1.71).
Conclusion
Almost half of the university students had PMS and ~ 11%, PMDD. Physical symptoms were themost common and interfered in amoderate-to-severe way in various aspects of life. Attending the first semesters, consuming alcohol, and having depression were risk factors for PMS. The identification of risk factors for PMS is essential to prevent symptoms and reduce the impact of the syndrome.
Key-words Cross-sectional studiespremenstrual dysphoric disorderPremenstrual syndromeRisk factorsStudentsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
-
Review Article07-30-2021
Interventions among Pregnant Women in the Field of Music Therapy: A Systematic Review
- Bruna Mayumi Omori Shimada
 ,
, - Magda da Silva Oliveira Menezes dos Santos
 ,
, - Mayara Alvares Cabral
 ,
, - Vanessa Oliveira Silva
 ,
, - Gislaine Cristina Vagetti

Views368

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleInterventions among Pregnant Women in the Field of Music Therapy: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(5):403-413
- Bruna Mayumi Omori Shimada
 ,
, - Magda da Silva Oliveira Menezes dos Santos
 ,
, - Mayara Alvares Cabral
 ,
, - Vanessa Oliveira Silva
 ,
, - Gislaine Cristina Vagetti

Views368See moreAbstract
Objective
To investigate in the literature the studies on the benefits ofmusic therapy interventions among pregnant women in the prenatal, delivery and postpartum periods.
Data Sources
The search for articles was carried out in the following electronic databases: VHL, LILACS, SciELO, Portal CAPES, PsycINFO, ERIC, PubMed/Medline, and journals specialized in this field: Revista Brasileira de Musicoterapia (“Brazilian Journal of Music Therapy”) and Voices.
Study Selection
Descriptors in Portuguese (musicoterapia, gravidez, gestantes, revisão), English (music therapy, pregnancy, pregnant women, review) and Spanish (musicoterapia, embarazo, mujeres embarazadas, revisión) were used. The search was delimited between January 2009 and June 2019. The process of selection and evaluation of the articles was performed through peer review.
Data Collectio
n The following data were extracted: article title, year of publication, journal, author(s), database, country and date of collection, purpose of the study, sample size, type of care, intervention, instruments used, results, and conclusion. The data were organized in chronological order based on the year of publication of thestudy.
Summary of the Data
In total, 146 articles were identified, and only 23 studies were included in this systematic review. The articles found indicate among their results relaxation, decreased levels of anxiety, psychosocial stress and depression, decreased pain, increase in the maternal bond, improvement in the quality of sleep, control of the fetal heart rate and maternal blood pressure, and decreased intake of drugs in the postoperative period.
Conclusion
Music therapy during the prenatal, delivery and postpartum periods can provide benefits to pregnant women and newborns, thus justifying its importance in this field.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Bruna Mayumi Omori Shimada
-
Review Article06-27-2022
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Endometriosis, Psychological Based Intervention: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):295-303
Views324

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleCognitive Behavioral Therapy in Endometriosis, Psychological Based Intervention: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):295-303
Views324Abstract
Introduction
Endometriosis is an inflammatory disease that affects women of reproductive age, causing pain and the possibility of infertility. Endometriosis was associated to low life quality and research shows the impact of endometriosis in several areas of life, justifying how these patients are more likely to develop depression, anxiety, and stress.
Objective
The aim of the present systematic review was to explore the field of psychology in endometriosis, identifying studies that used the cognitive behavioral therapy technique as a treatment for endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain.
Methods
The keywords used were Endometriosis and Behavioral Therapy; Behavioral Disciplines and Activities; Cognitive Behavioral Therapy; Mental Health; Psychological Techniques; Psychology; Psychotherapy; Mental Health Services; and the search was performed in the following databases: PubMed/Medline, Scielo, Lilacs, and Capes. The study followed the PRISMA guidelines and all studies whose intervention strategy used was related to cognitive-behavioral therapy were considered.
Results
Of the 129 articles found, only 5 were selected, and it was possible to identify that the psychological intervention whose approach brought cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques promoted a decrease in the sensation of pain, improvements in the scores of depression and stress, and significant changes in aspects of quality of life such as vitality, physical and social functioning, emotional well-being, control, and autonomy.
Conclusion
Cognitive-behavioral therapy can be very promising to take care of the emotional side of those who have endometriosis However, the present systematic review highlights the need to develop more structured studies with consistent, clear and replicablemethods to reach a psychological intervention protocol for patients who live with this gynecological-physical-emotional condition.
Key-words Chronic pelvic paincognitive behavioral therapyEndometriosispsychological interventionQuality of lifesystematic reviewsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article08-15-2022
The Correlation between Chlamydia Trachomatis and Female Infertility: A Systematic Review
- Laura Gazal Passos
 ,
, - Paula Terraciano
 ,
, - Nicole Wolf
 ,
, - Fernanda dos Santos de Oliveira
 ,
, - Isabel de Almeida
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Eduardo Pandolfi Passos

Views369

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleThe Correlation between Chlamydia Trachomatis and Female Infertility: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):614-620
- Laura Gazal Passos
 ,
, - Paula Terraciano
 ,
, - Nicole Wolf
 ,
, - Fernanda dos Santos de Oliveira
 ,
, - Isabel de Almeida
 ,
, - Eduardo Pandolfi Passos

Views369Abstract
The impact of Chlamydia trachomatis (CT) infection on female’s fertility is not completely established yet, since the level of evidence associating these factors is still weak. Hence, the goal of the present review is to contribute to a better elucidation of this matter. The electronic database chosen was the Medline/PubMed, with the last survey on May 11, 2021. Publication date was used as a filter, with the previous 5 years having been selected. The following describers were used: chlamydia trachomatis AND infertility; chlamydia trachomatis AND tubal alteration AND infertility; chlamydia AND low pregnancy rates. From the 322 studies screened, 293 that failed to meet our eligibility criteria were excluded. Subsequently, we removed seven studies for not having the possible correlation between CT infections and female infertility as its main focus, and three for being about sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in general. Moreover, two studies designed as reviews were also excluded. Ergo, we included 17 studies in our qualitative analysis. The authors conducted research individually and analyzed carefully the studies selected. As we retrieved the information needed for our study through reading the texts, no contact was made with the authors of the studies selected. This systematic review corroborates the hypothesis that CT infection potentiates female infertility, as 76.47% of the included studies found a positive correlation between them. We conclude that there is an important association between CT infection and female infertility. Ergo, making CT screening part of the infertility investigation routine is relevant and has a reasonable justification.
Key-words Chlamydia trachomatishuman reproductionInfertilitySexually transmitted diseasestubal factor infertilitySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Laura Gazal Passos
-
Review Article06-27-2022
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Adolescence: Challenges in Diagnosis and Management
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):425-433
Views336

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePolycystic Ovary Syndrome in Adolescence: Challenges in Diagnosis and Management
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):425-433
Views336See moreAbstract
Diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) during adolescence is challenging since normal pubertal development overlap typical features of this syndrome. The authors aim to summarize the existing evidence concerning PCOS in adolescence, particularly its diagnostic criteria and therapeutic options. A search throughout medical databases such as PubMed and MedScape was performed. Diagnostic criteria include irregular menstrual cycles according to time postmenarche and evidence of clinical hyperandrogenism and/or biochemical hyperandrogenism, provided other causes have been excluded. Polycystic ovarianmorphology ought not to be used as a diagnostic criterion. Treatment should targetmanifestations and/or comorbidities, even in the absence of a definite diagnosis. Lifestyle interventions are the first-line treatment. Combined oral contraceptives, metformin or antiandrogens may also be considered as adjuvants. Screening for PCOS in adolescence is crucial as it allows an early intervention on the symptoms and comorbidities presented leading to better long-term reproductive and metabolic outcomes.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
