- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Trabalhos Originais
Estimation of Fetal Weight: Comparison Between a Clinical Method and Ultrasonography
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(10):551-555
04-05-1998
Views61PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 33278
- Abstract Views: 3965
- Captures
- Readers: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisEstimation of Fetal Weight: Comparison Between a Clinical Method and Ultrasonography
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(10):551-555
04-05-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998001000002
Views61See morePurpose: to assess the validity of fetal weight estimation by a method based on uterine height — Johnson’s rule. Methods: one hundred and one pregnant women and their newborn children were studied. The fetal weight was estimated using an adaptation of Johnson’s rule, which consists of the clinical application of a mathematical model to calculate the fetal weight based on the uterine height and the height of fetal presentation. The estimated weight was obtained on the day of delivery and was compared to the weight observed after birth. This, in turn, was the control of the analysis of validity of the method used. On the same date, a detailed obstetrical ultrasonography (US) was conducted which included the fetal weight, calculated by the use of Sheppard’s tables. This weight, estimated by US, was compared to the birth weight. Results: the results have proven that the clinical estimate used in this study has a similar value to that of the US calculation of birth weight. The accuracy of the clinical method, with variations of 5%, 10% and 15% between estimated and observed weights, was 55.3%, 73% and 86.7%, respectively. Those of the US were 60.7%, 75.4% and 91.1%, respectively. When comparing both sets of figures, values were not different from a statistical standpoint. Conclusion: the clinical evaluation has shown to be accurate, similarly to the US, when calculating the birth weight.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 33278
- Abstract Views: 3965
- Captures
- Readers: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses
Indice de líquido amniótico em gestantes diabéticas e a qualidade do controle glicêmico na gestação
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
04-05-1998
Views39

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Resumos de TesesIndice de líquido amniótico em gestantes diabéticas e a qualidade do controle glicêmico na gestação
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
04-05-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800011
Views39Indice de Líquido Amniótico em Gestantes Diabéticas e a Qualidade do Controle Glicêmico na Gestação.[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses
Avaliação do grau nuclear da célula maligna da mama como parâmetro de atividade proliferativa tumoral: comparação com a expressão do antígeno nuclear de proliferação celular (PCNA/ciclina)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
04-05-1998
Views51

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Resumos de TesesAvaliação do grau nuclear da célula maligna da mama como parâmetro de atividade proliferativa tumoral: comparação com a expressão do antígeno nuclear de proliferação celular (PCNA/ciclina)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
04-05-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800010
Views51Avaliação do Grau Nuclear da Célula Maligna da Mama como Parâmetro de Atividade Proliferativa Tumoral: Comparação com a Expressão do Antígeno Nuclear de Proliferação Celular (PCNA/ciclina).[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Relato de Casos
Prenatal diagnosis of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita: a case report
- Carlos Augusto Alencar Júnior,
- Francisco Edson de Lucena Feitosa,
- Mac Gontei,
- Sammya Bezerra Maia,
- Dalgimar Beserra de Meneses
04-05-1998
Views60PlumX Metrics
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 118867
- Abstract Views: 2203
- Captures
- Readers: 14
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 6


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Relato de CasosPrenatal diagnosis of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):481-484
04-05-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800009
- Carlos Augusto Alencar Júnior,
- Francisco Edson de Lucena Feitosa,
- Mac Gontei,
- Sammya Bezerra Maia,
- Dalgimar Beserra de Meneses
Views60See moreArthrogryposis multiplex congenita is characterized by multiple joint contractures present at birth. Prenatal diagnosis is difficult. There are few reports in the literature. Fetal akinesia, abnormal limb position, intrauterine growth retardation, and polyhydramnios are the main findings of the ultrasonographic diagnosis. The authors describe a case of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita ultrasonographically diagnosed in the third gestational trimester. The main findings were absence of fetal movements, polyhydramnios, symmetrical and non-symmetrical fetal growth retardation with marked decrease of abdominal and thoracic circumference, low-set ears, micrognathia, continuous flexure contracture of limbs, internal rotation of the femur, and clubfoot on the right.
PlumX Metrics
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 118867
- Abstract Views: 2203
- Captures
- Readers: 14
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 6


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Trabalhos Originais
Screening of breast cancer metastasis at preoperative work-up
- Maria Bethânia da Costa Chein,
- Luciane Maria Oliveira Brito,
- Simão Rotstein,
- Luiz Henrique Gebrim,
- Aldo Franklin F Reis, [ … ],
- Luciana Dessen Padilha
04-05-1998
Views108

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisScreening of breast cancer metastasis at preoperative work-up
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):475-479
04-05-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800008
- Maria Bethânia da Costa Chein,
- Luciane Maria Oliveira Brito,
- Simão Rotstein,
- Luiz Henrique Gebrim,
- Aldo Franklin F Reis,
- Luciana Dessen Padilha
Views108See morePurpose: to analyze the frequency of preoperative bilateral synchronic cancer and occult metastases in 454 operable breast cancer patients, at Instituto Nacional de Câncer (Brazil). Methods: the preoperative evaluation consisted of mammography, bone scan with X-ray if necessary, and chest X-ray. 260 (57.3 %) of 454 patients underwent liver echography. We calculated the cost X effectiveness ratio considering only the direct costs (monetary value) and the effectiveness was analyzed based on the number of metastases identifid by the screening tests. Results: we did not find any case of bilateral synchronic cancer, and the frequency of patients with metastasis was 2% (9/454). The diagnosis of bone metastasis was 1.5 % (7/454). The percentage of lung (2/454) and liver (1/260) metastasis was the same, 0.4 %. Most of the patients with metastases were in stage IIIb (44.5 %). The results of the screening tests showed the alteration of the initial clinical stage in 9 patients only (2%). The total cost of the screening tests for the diagnosis of systemic disease in 9 patients, was US$ 131,020.00. The cost of each diagnosed metastasise, for a total of 10 (two were found in one of the patients), was US$ 29,221.85 and the cost/effectiveness ratio was 22.3%. Conclusious: the results showed that screening for metastases in the preoperative clinical staging of breast cancer should be limited to patients symptomatic for systemic disease or in clinical stage III and that the cost/effectiveness ratio of the tests demonstrated a reduced benefit in the preoperative evaluation.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Trabalhos Originais
Second-degree family history as a risk factor for breast cancer
- Rafael Marques de Souza,
- Anderson Rech Lazzaron,
- Rafael Defferrari,
- Álvaro A. Borba,
- Luciana Scherer, [ … ],
- Antônio L. Frasson
04-05-1998
Views109PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 3
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 18588
- Abstract Views: 1099
- Captures
- Readers: 13


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisSecond-degree family history as a risk factor for breast cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):469-473
04-05-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800007
- Rafael Marques de Souza,
- Anderson Rech Lazzaron,
- Rafael Defferrari,
- Álvaro A. Borba,
- Luciana Scherer,
- Antônio L. Frasson
Views109See morePurpose: to evaluate the association between second-degree family history of breast cancer and the risk to develop the disease. Methods: case-control study of incident cases. Sixty-six incident breast cancer cases and 198 controls were selected among women who were submitted to mammography in a private clinic between January 1994 and July 1997. Cases and controls were paired regarding age, age at menarche, at first live birth, at menopause, parity, oral contraceptives and use of hormonal replacement therapy. Results: there was no significant difference between cases and controls regarding all risk factors evaluated, besides second-degree family history. Patients with breast cancer were more likely to have second-degree relatives with breast cancer when compared to controls (OR=2.77; 95% CI, 1.03-7.38; p=0.039). Conclusions: malignant neoplasm of the breast is significantly associated with a second-degree family history of this disease.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 3
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 18588
- Abstract Views: 1099
- Captures
- Readers: 13


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Trabalhos Originais
Fine needle aspiration biopsy: performance in the differential diagnosis of palpable breast masses
- Orlando José de Almeida,
- Marcelo Alvarenga,
- José Guilherme Cecatti,
- Jessé de Paula Neves Jorge,
- Júlia Kawamura Tambascia
04-05-1998
Views42PlumX Metrics
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 34099
- Abstract Views: 839
- Captures
- Readers: 11
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 2


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisFine needle aspiration biopsy: performance in the differential diagnosis of palpable breast masses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):463-467
04-05-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800006
- Orlando José de Almeida,
- Marcelo Alvarenga,
- José Guilherme Cecatti,
- Jessé de Paula Neves Jorge,
- Júlia Kawamura Tambascia
Views42See morePurpose: to evaluate, in a prospective way, the performance of the fine needle aspiration biopsy in the differential diagnosis of palpable breast masses. Method: the sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values for this test were evaluated in 102 women with age above 30 years and a palpable breast mass, who were attended at the University of Campinas. All punctures were performed by the same examiner. Results: the procedure had a sensitivity of 97%, specificity of 87%, positive predictive value of 94% and negative predictive value of 93%. The insufficient or unsatisfactory sample rate was 16% for the first aspiration, decreasing to 2% with a new procedure. Conclusions: this test showed to be highly sensitive and specific for the differential diagnosis of palpable breast masses, reassuring its great importance for the clinical approach of palpable masses.
PlumX Metrics
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 34099
- Abstract Views: 839
- Captures
- Readers: 11
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 2


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Trabalhos Originais
A randomized trial of misoprostol and placebo for cervical ripening and induction of labor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):457-462
04-05-1998
Views86

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisA randomized trial of misoprostol and placebo for cervical ripening and induction of labor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):457-462
04-05-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800005
Views86See moreObjective: to determine the efficacy and safety of misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labor in pregnant women at term when compared with placebo. Patients and Methods: fifty-one high-risk pregnant women at term, with unripe cervix, were allocated in a double-blind trial for treatment with intravaginal misoprostol (40 mg, 4/4 h) or intravaginal placebo. Results: thirty-two patients received misoprostol and 19 received placebo. The groups were homogeneous concerning maternal age, gestacional age, parity, and indication for induction (p > 0.05). In the misoprostol group the efficacy was 87.5% and in the placebo group 21.1% (p = 0.0000087). Regarding delivery, in the misoprostol group 75% had vaginal delivery and 25% abdominal delivery, and in the placebo group only 32% had vaginal delivery and 68% abdominal delivery (p = 0.0059).The Apgar score was similar. Conclusion: in this study misoprostol was effective and safe for cervical ripening and induction of labor.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Original Article
Prevalence of colorectal symptoms and anal incontinence in patients with pelvic organ prolapse attended at an outpatient urogynecology service
- Marco Arellano
 ,
, - Fernanda Santis-Moya
 ,
, - Andrea Maluenda
 ,
, - Alejandro Pattillo
 ,
, - Bernardita Blümel
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Javier Pizarro-Berdichevsky

00-00-2024
Views350

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Original ArticlePrevalence of colorectal symptoms and anal incontinence in patients with pelvic organ prolapse attended at an outpatient urogynecology service
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo10
00-00-2024- Marco Arellano
 ,
, - Fernanda Santis-Moya
 ,
, - Andrea Maluenda
 ,
, - Alejandro Pattillo
 ,
, - Bernardita Blümel
 ,
, - Dominga Pohlhammer
 ,
, - Silvana Gonzalez
 ,
, - Javier Pizarro-Berdichevsky

Views350See moreAbstract
Objective:
To analyze data of patients with symptomatic pelvic organ prolapse evaluated with PFDI20 and its subscales to report the prevalence of lower gastrointestinal symptoms and anal incontinence in the population of a public hospital and analyze its impact on quality of life.
Methods:
Cross-sectional study of patients with symptomatic POP. Patients were evaluated with demographic data, POP-Q, pelvic floor ultrasonography, urological parameters, and pelvic floor symptoms (PFDI-20), and quality of life (P-QoL) surveys. Patients were classified as CRADI-8 “positive” for colorectal symptoms, with responses “moderate” in at least 3 and/or “severe” in at least 2 of the items in the CRADI-8 questionnaires.
Results:
One hundred thirteen patients were included. 42.5% (48) were considered positive for colorectal symptoms on CRADI-8. 53.4% presented anal incontinence. No significant differences were found in sociodemographic variables, POP-Q stage, ultrasound parameters, or urological parameters. Positive patients had a significantly worse result in PFDI-20, POPDI (48 vs 28; p<0.001), UDI6 (51 vs 24; p<0.001), and in the areas of social limitation (44.4 vs 22.2; p = 0.045), sleep- energy (61.5 vs 44.4; p = 0.08), and severity (56.8 vs 43.7, p=0.015) according to P-QoL.
Conclusion:
Moderate or severe colorectal symptoms are seen in 40% of patients with symptomatic POP in our unit. Full evaluation of pelvic floor dysfunction symptoms should be performed routinely in urogynecology units.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Marco Arellano
-
Original Article
Factors associated with the absence of postpartum consultations in a high-risk population
- Ana Carolina Gomes Pereira
 ,
, - Tábata Regina Zumpano dos Santos
 ,
, - Helymar da Costa Machado
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani de Castro Surita

04-09-2024
Views349

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Original ArticleFactors associated with the absence of postpartum consultations in a high-risk population
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo23
04-09-2024- Ana Carolina Gomes Pereira
 ,
, - Tábata Regina Zumpano dos Santos
 ,
, - Helymar da Costa Machado
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani de Castro Surita

Views349See moreAbstract
Objective:
To assess the rate of missed postpartum appointments at a referral center for high-risk pregnancy and compare puerperal women who did and did not attend these appointments to identify related factors.
Methods:
This was a retrospective cross-sectional study with all women scheduled for postpartum consultations at a high-risk obstetrics service in 2018. The variables selected to compare women were personal, obstetric, and perinatal. The variables of interest were obtained from the hospital’s electronic medical records. Statistical analyses were performed using the Chi-square, Fisher’s exact, or Mann–Whitney tests. For the variable of the interbirth interval, a receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was used to best discriminate whether or not patients attended the postpartum consultation. The significance level for the statistical tests was 5%.
Results:
A total of 1,629 women scheduled for postpartum consultations in 2018 were included. The rate of missing the postpartum consultation was 34.8%. A shorter interbirth interval (p = 0.039), previous use of psychoactive substances (p = 0.027), current or former smoking (p = 0.003), and multiparity (p < 0.001) were associated with non-attendance.
Conclusion:
This study showed a high rate of postpartum appointment non-attendance. This is particularly relevant because it was demonstrated in a high-risk obstetric service linked to clinical severity or social vulnerability cases. This highlights the need for new approaches to puerperal women before hospital discharge and new tools to increase adherence to postpartum consultations, especially for multiparous women.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ana Carolina Gomes Pereira
-
Review Article
The Female Athlete Triad/Relative Energy Deficiency in Sports (RED-S)
- Alexandra Ruivo Coelho
 ,
, - Gonçalo Cardoso
 ,
, - Marta Espanhol Brito
 ,
, - Inês Neves Gomes
 ,
, - Maria João Cascais

07-30-2021
Views346

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Review ArticleThe Female Athlete Triad/Relative Energy Deficiency in Sports (RED-S)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(5):395-402
07-30-2021- Alexandra Ruivo Coelho
 ,
, - Gonçalo Cardoso
 ,
, - Marta Espanhol Brito
 ,
, - Inês Neves Gomes
 ,
, - Maria João Cascais

Views346See moreAbstract
In a healthy athlete, the caloric intake is sufficient for sports energy needs and body physiological functions, allowing a balance between energy availability, bone metabolism, andmenstrual cycle.Onthe other hand, an imbalance causedby low energy availability dueto a restrictive diet, eating disorders or long periods of energy expenditure leads to multisystemic deregulation favoring the essential functions of the body. This phenomenon, described as the female athlete triad, occurs in a considerable percentage of high-performance athletes, with harmful consequences for their future. The present review was carried out based on a critical analysis of themost recent publications available and aims to provide a global perception of the topic relative energy deficit in sport (RED-S). The objective is to promote theacquisition ofmore consolidated knowledgeon an undervaluedtheme, enabling the acquisition of preventive strategies, early diagnosis and/or appropriate treatment.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Alexandra Ruivo Coelho
-
Original Article
Screening of Perinatal Depression Using the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale
- Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
 ,
, - Guilherme Guarany Cardoso Magalhães Luzetti
 ,
, - Márcia Maria Auxiliadora Rosalém
 ,
, - Corintio Mariani Neto

03-04-2022
Views346

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Original ArticleScreening of Perinatal Depression Using the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):452-457
03-04-2022- Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
 ,
, - Guilherme Guarany Cardoso Magalhães Luzetti
 ,
, - Márcia Maria Auxiliadora Rosalém
 ,
, - Corintio Mariani Neto

Views346See moreAbstract
Objective
To detect depression during pregnancy and in the immediate postpartum period using the Edinburgh postpartum depression scale (EPDS).
Methods
Cross sectional study of 315 women, aged between 14 and 44 years, who received perinatal care at the Leonor Mendes de Barros Hospital, in São Paulo, between July 1st, 2019 and October 30th, 2020. The cutoff point suggesting depression was ≥ 12.
Results
The screening indicated 62 (19.7%) patients experiencing depression. Low family income, multiparity, fewer prenatal appointments, antecedents of emotional disorders, dissatisfaction with the pregnancy, poor relationship with the partner, and psychological aggression were all risk factors associated with depression in pregnancy or in the immediate postpartum period. Antecedents of depression and psychology aggression during pregnancy were significant variables for predicting perinatal depression in the multivariate analysis.
Conclusion
There is a significant association between the occurrence of perinatal depression and the aforementioned psychosocial factors. Screening patients with the EPDS during perinatal and postpartum care could facilitate establishing a line of care to improve the wellbeing of mother and infant.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
-
Letter to the Editor
Letter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
04-09-2024
Summary
Letter to the EditorLetter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
04-09-2024Views345Dear Editor,First and foremost, we express our gratitude towards the authors for their clear and concise description of the positive effects of aerobic and strength training on dynamic stability.() Additionally, their ability to provide a focused and informative introduction section is commendable. The study piqued our interest in further exploring the benefits of aerobic and […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article
Bacteriological characteristics of primary breast abscesses in patients from the community in the era of microbial resistance
- Vicente Sperb Antonello
 ,
, - Jessica Dallé
 ,
, - Mirela Foresti Jimenez
 ,
, - Patrícia Tramontini
 ,
, - Andrei Gustavo Reginatto

04-09-2024
Views335

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Original ArticleBacteriological characteristics of primary breast abscesses in patients from the community in the era of microbial resistance
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo34
04-09-2024- Vicente Sperb Antonello
 ,
, - Jessica Dallé
 ,
, - Mirela Foresti Jimenez
 ,
, - Patrícia Tramontini
 ,
, - Andrei Gustavo Reginatto

Views335See moreAbstract
Objective:
The aim of this study is to evaluate the etiological profile and antimicrobial resistance in breast abscess cultures from patients from the community, treated at a public hospital located in Porto Alegre, Brazil.
Methods:
This is an retrospective cross-sectional study that evaluated the medical records of patients with bacterial isolates in breast abscess secretion cultures and their antibiograms, from January 2010 to August 2022.
Results:
Based on 129 positive cultures from women from the community diagnosed with breast abscesses and treated at Fêmina Hospital, 99 (76.7%) of the patients had positive cultures for Staphylococcus sp, 91 (92%) of which were cases of Staphylococcus aureus. Regarding the resistance profile of S. aureus, 32% of the strains were resistant to clindamycin, 26% to oxacillin and 5% to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. The antimicrobials vancomycin, linezolid and tigecycline did not show resistance for S. aureus.
Conclusion:
Staphylococcus aureus was the most common pathogen found in the breast abscess isolates during the study period. Oxacillin remains a good option for hospitalized patients. The use of sulfamethoxazole plus trimethoprim should be considered as a good option for use at home, due to its low bacterial resistance, effectiveness and low cost.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Vicente Sperb Antonello
-
Original Article
Outcomes of urethral meatal preservation ventral urethroplasty for female urethral stricture: a series of cases
- João Vitor Quadra Vieira dos Santos
 ,
, - Antônio Rebello Horta Görgen
 ,
, - Tiago Bortolini
 ,
, - Gabriel Veber Moisés da Silva
 ,
, - Emanuel Burck dos Santos
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Tiago Elias Rosito

03-15-2024
Summary
Original ArticleOutcomes of urethral meatal preservation ventral urethroplasty for female urethral stricture: a series of cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo20
03-15-2024- João Vitor Quadra Vieira dos Santos
 ,
, - Antônio Rebello Horta Görgen
 ,
, - Tiago Bortolini
 ,
, - Gabriel Veber Moisés da Silva
 ,
, - Emanuel Burck dos Santos
 ,
, - Patric Machado Tavares
 ,
, - Nelson Silvonei da Silva Batezini
 ,
, - Tiago Elias Rosito

Views323Abstract
Objective:
To present a series of cases with our initial experience and short-term outcomes of a modified vaginal mucosal flap urethroplasty.
Methods:
Patients diagnosed with urethral stricture and operated by the same operative technique between January 2012 and January 2018 were followed for at least 6 months. Uroflowmetry and clinical outcomes were evaluated.
Results:
Nineteen patients were included with an average age of 56.4 years, mean preoperative Qmax of 5.3 ml/s, and PVR of 101.4 mL. After 6 months of the procedure, the mean Qmax improved to 14.7 mL/s (p<0.05), PVR decreased to 47.3 mL (p<0.05), and 84.2% of all patients reported improvement in clinical self-reported symptoms. There was an improvement in symptoms such as voiding effort in 84.2% of patients, weak stream (89.5%), and recurrent urinary tract infection (85.7%). The success rate (absence of symptoms and normal Qmax with no significant PVR) of the procedure was 84.2%.
Conclusion:
The described technique was considered effective for the treatment of female urethra stricture, with a high clinical success rate and an objective improvement of Qmax and decrease in PVR after 6 months of the procedure.
Key-words Urethral strictureUrethroplastyUrinary bladder neck obstructionUrological surgical proceduresSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - João Vitor Quadra Vieira dos Santos
-
Review Article
Efficacy of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in the Reduction of Pain and Opioid Requirement in Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Hysterectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Claudia López-Ruiz
 ,
, - Jerutsa Catalina Orjuela
 ,
, - Diego Fernando Rojas-Gualdrón
 ,
, - Marcela Jimenez-Arango
 ,
, - José Fernando de los Ríos
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Claudia Vargas

02-28-2022
Views322

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Review ArticleEfficacy of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in the Reduction of Pain and Opioid Requirement in Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Hysterectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):55-66
02-28-2022- Claudia López-Ruiz
 ,
, - Jerutsa Catalina Orjuela
 ,
, - Diego Fernando Rojas-Gualdrón
 ,
, - Marcela Jimenez-Arango
 ,
, - José Fernando de los Ríos
 ,
, - Elsa Maria Vásquez-Trespalacios
 ,
, - Claudia Vargas

Views322Abstract
Objective
To summarize the available evidence of TAP Block in efficacy in laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy.
Data Sources
We searched databases and gray literature for randomized controlled trials in which transversus abdominis plane (TAP) block was compared with placebo or with no treatment in patients who underwent laparoscopic or robot-assisted hysterectomy.
Method of Study
Selection Two researchers independently evaluated the eligibility of the selected articles. Tabulation, Integration, and Results Seven studies were selected, involving 518 patients. Early postoperative pain showed a difference in the mean mean difference (MD): – 1.17 (95% confidence interval [CI]: – 1.87-0.46) in pain scale scores (I2=68%), which was statistically significant in favor of using TAP block, but without clinical relevance; late postoperative pain: DM 0.001 (95%CI: – 0.43-0.44; I2=69%); opioid requirement: DM 0.36 (95%CI: – 0.94-1.68; I2=80%); and incidence of nausea and vomiting with a difference of 95%CI=- 0.11 (- 0.215-0.006) in favor of TAP.
Conclusion
With moderate strength of evidence, due to the high heterogeneity and imbalance in baseline characteristics among studies, the results indicate that TAP block should not be considered as a clinically relevant analgesic technique to improve postoperative pain in laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy, despite statistical significance in early postoperative pain scale scores.
Key-words laparoscopic hysterectomyOpioidPainrobotic-assisted hysterectomytransversus abdominis plane blockSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 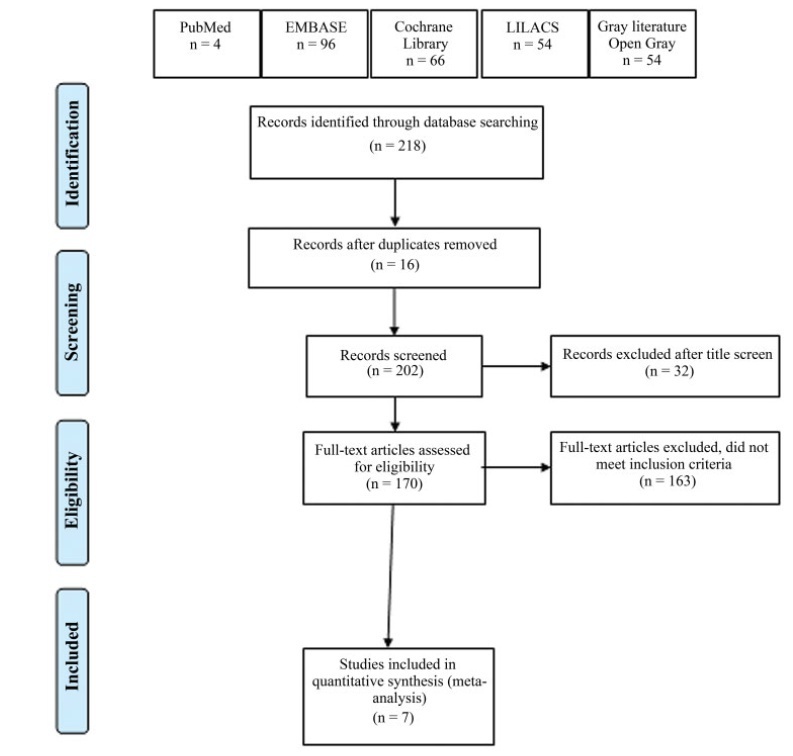
- Claudia López-Ruiz
-
Review Article
Pregestational Diabetes and Congenital Heart Defects
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):953-961
01-23-2022
Views246

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Review ArticlePregestational Diabetes and Congenital Heart Defects
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):953-961
01-23-2022Views246See moreAbstract
Studies have consistently shown a significant increase in the risk of congenital heart defects in the offspring of diabetic mothers compared with those of nondiabetic pregnancies. Evidence points that all types of pregestational diabetes have the capacity of generating cardiac malformations in a more accentuated manner than in gestational diabetes, and there seems to be an increased risk for all congenital heart defects phenotypes in the presence of maternal diabetes. Currently, the application of some therapies is under study in an attempt to reduce the risks inherent to diabetic pregnancies; however, it has not yet been possible to fully prove their effectiveness. The present review aims to better understand the mechanisms that govern the association between pregestational diabetes and congenital heart defects and how maternal diabetes interferes with fetal cardiac development, as there is still a long way to go in the investigation of this complex process.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article
Prevalence of Preeclampsia in Brazil: An Integrative Review
- José Paulo de Siqueira Guida
 ,
, - Beatriz Gadioli de Andrade
 ,
, - Luis Gabriel Ferreira Pissinatti
 ,
, - Bruna Fagundes Rodrigues
 ,
, - Caio Augusto Hartman
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Maria Laura Costa

02-09-2022
Views248

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Review ArticlePrevalence of Preeclampsia in Brazil: An Integrative Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):686-691
02-09-2022- José Paulo de Siqueira Guida
 ,
, - Beatriz Gadioli de Andrade
 ,
, - Luis Gabriel Ferreira Pissinatti
 ,
, - Bruna Fagundes Rodrigues
 ,
, - Caio Augusto Hartman
 ,
, - Maria Laura Costa

Views248See moreAbstract
Objective
To review literature and estimate the occurrence of preeclampsia and its complications in Brazil.
Methods
We performed an integrative review of the literature, and included observational studies published until August 2021 on the SciELO and PubMed databases that evaluated preeclampsia among pregnant women in Brazil. Other variables of interests were maternal death, neonatal death, hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, and low platelet count (HELLP) syndrome, and eclampsia. Three independent reviewers evaluated all retrieved studies and selected those that met inclusion criteria. A metanalysis of the prevalence of preeclampsia and eclampsia was also performed, to estimate a pooled frequency of those conditions among the studies included.
Results
We retrieved 304 studies after the initial search; of those, 10 were included in the final analysis, with a total of 52,986 women considered. The pooled prevalence of preeclampsia was of 6.7%, with a total of 2,988 cases reported. The frequency of eclampsia ranged from 1.7% to 6.2%, while the occurrence of HELLP syndrome was underreported. Prematurity associated to hypertensive disorders ranged from 0.5% to 1.72%.
Conclusion
The frequency of preeclampsia was similar to that reported in other international studies, and it is increasing in Brazil, probably due to the adoption of new diagnostic criteria. The development of a national surveillance network would be essential to understand the problem of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy in Brazil.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - José Paulo de Siqueira Guida
-
Original Article
Increased Cesarean Section Rates during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Looking for Reasons through the Robson Ten Group Classification System
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):371-376
09-08-2023
Views133

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Original ArticleIncreased Cesarean Section Rates during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Looking for Reasons through the Robson Ten Group Classification System
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):371-376
09-08-2023Views133See moreAbstract
Objective
To compare cesarean section (CS) rates according to the Robson Ten Group Classification System (RTGCS) and its indications in pregnant women admitted for childbirth during the first wave of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic with those of the previous year.
Materials and Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional study to compare women admitted for childbirth from April to October 2019 (before the pandemic) and from March to September 2020 (during the pandemic). The CSs and their indications were classified on admission according to the RTGCS, and we also collected data on the route of delivery (vaginal or CS). Both periods were compared using the Chi-squared (χ2) test or the Fisher exact test.
Results
In total, 2,493 women were included, 1,291 in the prepandemic and 1,202 in the pandemic period. There was a a significant increase in the CS rate (from 39.66% to 44.01%; p = 0.028), mostly due to maternal request (from 9.58% to 25.38%; p < 0.01). Overall, groups 5 and 2 contributed the most to the CS rates. The rates decreased among group 1 and increased among group 2 during the pandemic, with no changes in group 10.
Conclusion
There was an apparent change in the RTGSC comparing both periods, with a significant increase in CS rates, mainly by maternal request, most likely because of changes during the pandemic and uncertainties and fear concerning COVID-19.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article
Sexual Function and Associated Factors in Postmenopausal Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):522-529
10-18-2021
Views183

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Original ArticleSexual Function and Associated Factors in Postmenopausal Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):522-529
10-18-2021Views183See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the sexual function and associated factors in postmenopausal women.
Methods
This a descriptive, cross-sectional study with 380 women aged 40 to 65 years, users of public health services in 2019. Questionnaires were applied on demographic characteristics, on climacteric symptoms (menopause rating scale) and on sexual function (sexual quotient, female version). Bivariate andmultiple analyses by logistic regression were performed, with adjusted odds ratios (ORad) and 95% confidence intervals (95%CIs).
Results
More than half (243/64%) of the participating women were at risk of sexual dysfunction, with lower scores in the domains of sexual desire and interest, comfort, orgasm, and satisfaction. Women with a partner (ORad 2.07; 95%CI 1.03-4.17) and those who reported sleep problems (ORad 2.72; 95%CI 1.77-4.19), depressed mood (ORad 2.03; 95%CI 1.32-3.10), sexual complaints (ORad 8.16; 95%CI 5.06-13.15), and vaginal dryness (ORad 3.44; 95%CI 2.22-5.32) showed greater chance of sexual dysfunction.
Conclusion
There was a high prevalence of sexual dysfunction, with the influence of conjugality and climacteric symptoms on sexual function.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Systematic Review
Vertical Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review
- Ionara Diniz Evangelista Santos Barcelos
 ,
, - Ivan Andrade de Araújo Penna
 ,
, - Adriana de Góes Soligo
 ,
, - Zelma Bernardes Costa
 ,
, - Wellington Paula Martins

05-24-2021
Views186

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Systematic ReviewVertical Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):207-215
05-24-2021- Ionara Diniz Evangelista Santos Barcelos
 ,
, - Ivan Andrade de Araújo Penna
 ,
, - Adriana de Góes Soligo
 ,
, - Zelma Bernardes Costa
 ,
, - Wellington Paula Martins

Views186See moreAbstract
Objective
The evaluation of the available evidence on vertical transmission by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV)-2.
Data Sources
An electronic search was performed on June 13, 2020 on the Embase, PubMed and Scopus databases using the following search terms: (Coronavirus OR COVID-19 OR COVID19 OR SARS-CoV-2 OR SARS-CoV2 OR SARSCoV2) AND (vertical OR pregnancy OR fetal).
Selection of Studies
The electronic search resulted in a total of 2,073 records. Titles and abstracts were reviewed by two authors (WPM, IDESB), who checked for duplicates using the pre-established criteria for screening (studies published in English without limitation regarding the date or the status of the publication).
Data Collection
Data extraction was performed in a standardized way, and the final eligibility was assessed by reading the full text of the articles. We retrieved data regarding the delivery of the potential cases of vertical transmission, as well as themain findings and conclusions of systematic reviews.
Data Synthesis
The 2,073 records were reviewed; 1,000 duplicates and 896 clearly not eligible records were excluded. We evaluated the full text of 177 records, and identified only 9 suspected cases of possible vertical transmission. The only case with sufficient evidence of vertical transmission was reported in France.
Conclusion
The risk of vertical transmission by SARS-CoV-2 is probably very low. Despite several thousands of affected pregnant women, we have identified only one case that has fulfilled sufficient criteria to be confirmed as a case of vertical transmission. Well-designed observational studies evaluating large samples are still necessary to determine the risk of vertical transmission depending on the gestational age at infection.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 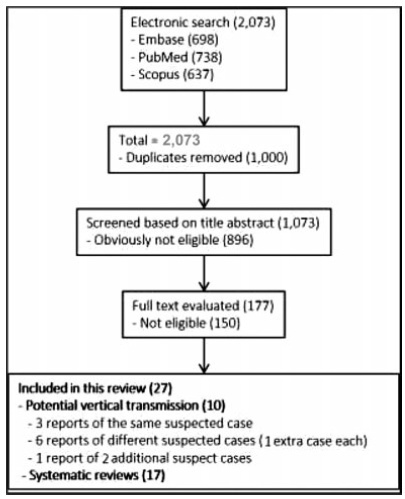
- Ionara Diniz Evangelista Santos Barcelos
-
Original Article
The COVID-19 Pandemic Impact on Breast Cancer Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study
- Erika Marina Solla Negrao
 ,
, - Cesar Cabello
 ,
, - Livia Conz
 ,
, - Edmundo Carvalho Mauad
 ,
, - Luiz Carlos Zeferino
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Diama Bhadra Vale

06-06-2022
Views208

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Original ArticleThe COVID-19 Pandemic Impact on Breast Cancer Diagnosis: A Retrospective Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(9):871-877
06-06-2022- Erika Marina Solla Negrao
 ,
, - Cesar Cabello
 ,
, - Livia Conz
 ,
, - Edmundo Carvalho Mauad
 ,
, - Luiz Carlos Zeferino
 ,
, - Diama Bhadra Vale

Views208See moreAbstract
Objective
This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic profile of breast cancer cases during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic compared with the previous year.
Methods
It is a retrospective study of cases diagnosed by a reference service in the public health system of Campinas, SP, Brazil. Two periods were analyzed: March to October 2019 (preCOVID period) and March to October 2020 (COVID-period). All women diagnosed during the periods were included. The Chi-Squared or Fisher exact and Mann-Whitney tests were used.
Results
In the preCOVID and COVID periods, breast cancers were diagnosed, respectively, in 115 vs 59 women, and the mean ages at diagnosis were 55 and 57 years (p = 0.339). In the COVID period, the family history of breast cancer was more observed (9.6% vs 29.8%, p < 0.001), cases were more frequently symptomatic (50.4% vs 79.7%, p < 0.001) and had more frequently palpable masses (56.5% vs 79.7%, p = 0.003). In symptomatic women, the mean number of days from symptom to mammography were 233.6 (458.3) in 2019 and 152.1 (151.5) in 2020 (p = 0.871). Among invasive tumors, the proportion of breast cancers in stages I and II was slightly higher in the COVID period, although not significantly (76.7% vs 82.4%, p = 0.428). Also in the COVID period, the frequency of luminal A-like tumors was lower (29.2% vs 11.8%, p = 0.018), of triple-negative tumors was twice as high (10.1% vs 21.6%, p = 0.062), and of estrogen receptor-positive tumors was lower (82.2% vs 66.0%, p = 0.030).
Conclusion
During the COVID-19 pandemic, breast cancer diagnoses were reduced. Cases detected were suggestive of a worse prognosis: symptomatic women with palpable masses and more aggressive subtypes. Indolent tumors were those more sensitive to the interruption in screening.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Erika Marina Solla Negrao
-
Review Article
Morphology and Biochemistry of Ovulation Morfologia e bioquímica da ovulação
- Sebastião Freitas de Medeiros
 ,
, - Bruna Barcelo Barbosa
 ,
, - Matheus Antonio Souto de Medeiros
 ,
, - Márcia Marly Winck Yamamoto

07-27-2021
Views210

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Review ArticleMorphology and Biochemistry of Ovulation Morfologia e bioquímica da ovulação
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):480-486
07-27-2021- Sebastião Freitas de Medeiros
 ,
, - Bruna Barcelo Barbosa
 ,
, - Matheus Antonio Souto de Medeiros
 ,
, - Márcia Marly Winck Yamamoto

Views210See moreAbstract
The process of ovulation involves multiple and iterrelated genetic, biochemical, and morphological events: cessation of the proliferation of granulosa cells, resumption of oocyte meiosis, expansion of cumulus cell-oocyte complexes, digestion of the follicle wall, and extrusion of the metaphase-II oocyte. The present narrative review examines these interrelated steps in detail. The combined or isolated roles of the folliclestimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) are highlighted. Genes indiced by the FSH genes are relevant in the cumulus expansion, and LH-induced genes are critical for the resumption ofmeiosis and digestion of the follicle wall. A nonhuman model for follicle-wall digestion and oocyte release was provided.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 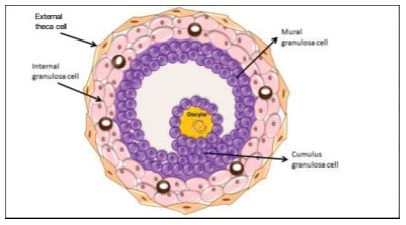
- Sebastião Freitas de Medeiros
-
Case Report
Lipschütz Ulcer: An Unusual Diagnosis that Should Not be Neglected
- Daniela Alexandra Gonçalves Pereira
 ,
, - Eliana Patrícia Pereira Teixeira
 ,
, - Ana Cláudia Martins Lopes
 ,
, - Ricardo José Pina Sarmento
 ,
, - Ana Paula Calado Lopes

07-30-2021
Views184

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Summary
Case ReportLipschütz Ulcer: An Unusual Diagnosis that Should Not be Neglected
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(5):414-416
07-30-2021- Daniela Alexandra Gonçalves Pereira
 ,
, - Eliana Patrícia Pereira Teixeira
 ,
, - Ana Cláudia Martins Lopes
 ,
, - Ricardo José Pina Sarmento
 ,
, - Ana Paula Calado Lopes

Views184See moreAbstract
The diagnosis of genital ulcers remains a challenge in clinical practice. Lipschütz ulcer is a non-sexually transmitted rare and, probably, underdiagnosed condition, characterized by the sudden onset of vulvar edema along with painful necrotic ulcerations. Despite its unknown incidence, this seems to be an uncommon entity, with sparse cases reported in the literature. We report the case of an 11-year-old girl who presented at the emergency department with vulvar ulcers. She denied any sexual intercourse. The investigation excluded sexually transmitted infections, so, knowledge of different etiologies of non-venereal ulcers became essential. The differential diagnoses are extensive and include inflammatory processes, drug reactions, trauma, and malignant tumors. Lipschütz ulcer is a diagnosis of exclusion. With the presentation of this case report, the authors aim to describe the etiology, clinical course, and outcomes of this rare disease, to allow differential diagnosis of genital ulceration.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Daniela Alexandra Gonçalves Pereira
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (251)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (103)Risk factors (103)Menopause (87)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (77)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (60)Infertility (56)Quality of life (53)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Postpartum period (44)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)Prevalence (42)

