- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
04-11-1998
A FEBRASGO e as ações voltadas para a promoção da saúde
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):301-301
Views68

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
A FEBRASGO e as ações voltadas para a promoção da saúde
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):301-301


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-10-1998
Avaliação longitudinal de aspectos imunológicos e virológicos durante a gravidez e puerpério em mulheres portadoras do vírus da imunodeficiência humana tipo 1 (HIV-1)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):170-170
Abstract
Avaliação longitudinal de aspectos imunológicos e virológicos durante a gravidez e puerpério em mulheres portadoras do vírus da imunodeficiência humana tipo 1 (HIV-1)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):170-170
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300011
Views108Avaliação Longitudinal de Aspectos Imunológicos e Virológicos Durante a Gravidez e Puerpério em Mulheres Portadoras do Vírus da Imunodeficiência Humana Tipo 1 (HIV-1)[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-10-1998
A dopplervelocimetria com mapeamento em cores dos ramos intramiometriais da artéria uterina de mulheres na pós-menopausa, com e sem carcinoma de endométrio
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-170
Abstract
A dopplervelocimetria com mapeamento em cores dos ramos intramiometriais da artéria uterina de mulheres na pós-menopausa, com e sem carcinoma de endométrio
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-170
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300010
Views83A Dopplervelocimetria com Mapeamento em Cores dos Ramos Intramiometriais da Artéria Uterina de Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa, com e sem Carcinoma de Endométrio[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-10-1998
Avaliação da esteroidogênese das supra-renais em mulheres normais por meio dos testes de ACTH simples de depósito
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-169
Abstract
Avaliação da esteroidogênese das supra-renais em mulheres normais por meio dos testes de ACTH simples de depósito
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-169
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300009
Views80Avaliação da Esteroidogênese das Supra-Renais em Mulheres Normais por Meio dos Testes de ACTH Simples de Depósito[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-10-1998
Recurrent HELLP syndrome: report on two cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):165-167
Abstract
Case ReportRecurrent HELLP syndrome: report on two cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):165-167
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300008
Views93See moreHELLP syndrome is a severe complication of preeclampsia that increases maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. Two cases of recurrent HELLP syndrome are described, maternal death occurring in one of the cases. This study is a warning about the increased risk of HELLP syndrome in the next pregnancy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-10-1998
Fetal reanimation: a case report
- José Maria Soares Júnior,
- Wladimir Correa Taborda,
- Anna Maria Bertini,
- Jorge Francisco Kuhn dos Santos
Abstract
Case ReportFetal reanimation: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):161-163
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300007
- José Maria Soares Júnior,
- Wladimir Correa Taborda,
- Anna Maria Bertini,
- Jorge Francisco Kuhn dos Santos
Views93See moreA tocolytic treatment is described with the use of terbutaline in a case of cardiotocographic prolonged deceleration of fetal heart rate with successful outcome.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Equipments and Methods04-10-1998
A new catheter in the treatment of fetal obstructive uropathies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):155-159
Abstract
Equipments and MethodsA new catheter in the treatment of fetal obstructive uropathies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):155-159
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300006
Views83See moreManagement of prenatally diagnosed uropathies is controversial, mainly because the prognosis for these fetuses is quite different. However pioneering studies have shown that prenatal drainage of obstructed urinary tract can improve the outcome of selected fetuses. The aim of this study is to describe the experience of the Service with the treatment of fetal obstrutive uropathy with the catheter developed by the Centro de Medicina Fetal do Hospital das Clínicas da UFMG. A total of 25 fetuses with obstructive uropathy received the catheter. Three fetuses required more than one insertion. Ten of 25 (40%) shunted fetuses survived with good postnatal renal and pulmonary function. Complications occurred in 12/25 (48%) cases including: 06/25 (24%) inadequate shunt drainage or migration; 01/25 (04%) urinary ascitis; 01/25 (04%) DPP, 01/25 (04%) premature rupture of membranes, 02/25 (08%) premature labor, 01/25 (04%) scarring and fibrosis of the renal parenchyma. Three of 25 (12%) fetuses died intra-utero and 12 (48%) died during the neonatal period. In conclusion, the drainage of the obstructed urinary tract with this catheter proved to be technically feasible and safe for both mother and fetus, with a survival rate of 40%.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-10-1998
Prevalence and correlates of hiv infection and syphilis in prostitutes attending a STD/AIDS reference center
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):151-154
Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence and correlates of hiv infection and syphilis in prostitutes attending a STD/AIDS reference center
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):151-154
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300005
Views121See moreA retrospective study examining medical records of female prostitutes attending the STD/AIDS Reference Center in Vitória, Brazil from January/93 to December/96 was conducted. During this period, 180 women received medical and psychological care in this clinic. Mean age was 25.9 year (SD=6.8). Out of 180, 140 agreed to be tested for HIV, of whom 12 (8.6%) had a positive result. Among 157 women who agreed to be tested for syphilis, 144 (91.7%) had a negative result, while 13 (8.3%) had a positive one. According to the educational degree, 6 (3.3%) women were illiterate, 114 (63.3%) attended elementary school, 37 (20.6%) attended secondary school, 7 (3.9%) went to college and 16 gave no information. One hundred and forty-one patients (78.3%) were single, 17 (9.4%) married, 10 (5,5%) divorced and 4 (2.2%) widows. The frequency of condom use was: always, 56 (31.3%), sometimes, 93 (52.0%), and 30 (16.8%) never used condoms. Other STDs were reported by 89 (49.4%) women and 9 (5.0%) reported intravenous (IV) drug use. There was a significant difference between the HIV positive and the negative group only regarding IV drug abuse (p=0.031) and syphilis infection (p=0.014). The present study showed prevalence rates of HIV infection among prostitutes in Vitória much higher than those found in the general population. There is a pressing need to improve medical assistance and educational campaigns especially designed to reach this population of women, and focusing the importance of regular condom use and the risks associated with IV drug abuse.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Original Article03-27-2020
Gestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Abstract
Original ArticleGestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):12-18
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 ,
, - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Views368See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus and the main associated risk factors in the population served by the Brazilian Unified Health System in the city of Caxias do Sul, state of Rio Grande do Sul.
Materials and Methods
A descriptive, cross-sectional and retrospective study was conducted. Maternal variables were collected from the medical records of all pregnant women treated at the basic health units in 2016. Hyperglycemia during pregnancy (pregestational diabetes, overt diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus) was identified by analyzing the results of a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, as recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. Based on the data, the women were allocated into two groups: the gestational diabetes group and the no gestational diabetes group.
Results
The estimated prevalence of gestational diabetes among 2,313 pregnant women was of 5.4% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 4.56-6.45). Pregnant women with 3 or more pregnancies had twice the odds of having gestational diabetes compared with primiparous women (odds ratio [OR]=2.19; 95%CI: 1.42-3.37; p<0.001). Pregnant women aged 35 years or older had three times the odds of having gestational diabetes when compared with younger women (OR=3.01; 95%CI: 1.97-4.61; p<0.001). Overweight pregnant women were 84% more likely to develop gestational diabetes than those with a body mass index lower than 25 kg/m2 (OR =1.84; 95%CI: 1.25-2.71; p=0.002). A multivariable regression analysis showed that being overweight and being 35 years old or older were independent variables.
Conclusion
In this population, the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus was of 5.4%. Age and being overweight were predictive factors for gestational diabetes.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
-
Systematic Review05-01-2017
Zika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and Microcephaly
- Geraldo Duarte,
- Antonio Fernandes Moron,
- Artur Timerman,
- César Eduardo Fernandes,
- Corintio Mariani Neto, [ … ],
- Rossana Pulcineli Vieira Francisco
Abstract
Systematic ReviewZika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and Microcephaly
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):235-248
- Geraldo Duarte,
- Antonio Fernandes Moron,
- Artur Timerman,
- César Eduardo Fernandes,
- Corintio Mariani Neto,
- Gutemberg Leão de Almeida Filho,
- Heron Werner Junior,
- Hilka Flavia Barra do Espírito Santo,
- João Alfredo Piffero Steibel,
- João Bortoletti Filho,
- Juvenal Barreto Borriello de Andrade,
- Marcelo Burlá,
- Marcos Felipe Silva de Sá,
- Newton Eduardo Busso,
- Paulo César Giraldo,
- Renato Augusto Moreira de Sá,
- Renato Passini Junior,
- Rosiane Mattar,
- Rossana Pulcineli Vieira Francisco
Views409Abstract
From the discovery of the Zika virus (ZIKV) in 1947 in Uganda (Africa), until its arrival in South America, it was not known that it would affect human reproductive life so severely. Today, damagetothe central nervous system is known to be multiple, and microcephaly is considered the tip of the iceberg. Microcephaly actually represents the epilogue of this infection’s devastating process on the central nervous system of embryos and fetuses. As a result of central nervous system aggression by the ZIKV, this infection brings the possibility of arthrogryposis, dysphagia, deafness and visual impairment. All of these changes of varying severity directly or indirectly compromise the future life of these children, and are already considered a congenital syndrome linked to the ZIKV. Diagnosis is one of the main difficulties in the approach of this infection. Considering the clinical part, it has manifestations common to infections by the dengue virus and the chikungunya fever, varying only in subjective intensities. The most frequent clinical variables are rash, febrile state, non-purulent conjunctivitis and arthralgia, among others. In terms of laboratory resources, there are also limitations to the subsidiary diagnosis. Molecular biology tests are based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR)with reverse transcriptase (RT) action, since the ZIKV is a ribonucleic acid (RNA) virus. The RT-PCR shows serum or plasma positivity for a short period of time, no more than five days after the onset of the signs and symptoms. The ZIKVurine test is positive for a longer period, up to 14 days. There are still no reliable techniques for the serological diagnosis of this infection. If there are no complications (meningoencephalitis or Guillain-Barré syndrome), further examination is unnecessary to assess systemic impairment. However, evidence is needed to rule out other infections that also cause rashes, such as dengue, chikungunya, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, rubella, and herpes. There is no specific antiviral therapy against ZIKV, and the therapeutic approach to infected pregnant women is limited to the use of antipyretics and analgesics. Anti-inflammatory drugs should be avoided until the diagnosis of dengue is discarded. There is no need to modify the schedule of prenatal visits for pregnant women infected by ZIKV, but it is necessary to guarantee three ultrasound examinations during pregnancy for low-risk pregnancies, and monthly for pregnant women with confirmed ZIKV infection. Vaginal delivery and natural breastfeeding are advised.
Key-words arbovirus infectionsblindness/ etiologydeafness/ etiologymicrocephaly/ ultrasonographyPregnancy complicationsReal-time polymerase chain reactionZika virusSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 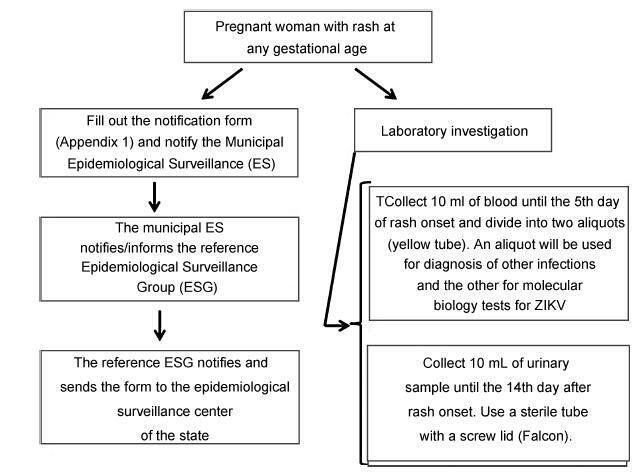
-
Review Article06-27-2022
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Adolescence: Challenges in Diagnosis and Management
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):425-433
Abstract
Review ArticlePolycystic Ovary Syndrome in Adolescence: Challenges in Diagnosis and Management
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):425-433
Views434See moreAbstract
Diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) during adolescence is challenging since normal pubertal development overlap typical features of this syndrome. The authors aim to summarize the existing evidence concerning PCOS in adolescence, particularly its diagnostic criteria and therapeutic options. A search throughout medical databases such as PubMed and MedScape was performed. Diagnostic criteria include irregular menstrual cycles according to time postmenarche and evidence of clinical hyperandrogenism and/or biochemical hyperandrogenism, provided other causes have been excluded. Polycystic ovarianmorphology ought not to be used as a diagnostic criterion. Treatment should targetmanifestations and/or comorbidities, even in the absence of a definite diagnosis. Lifestyle interventions are the first-line treatment. Combined oral contraceptives, metformin or antiandrogens may also be considered as adjuvants. Screening for PCOS in adolescence is crucial as it allows an early intervention on the symptoms and comorbidities presented leading to better long-term reproductive and metabolic outcomes.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article05-01-2018
Uterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
- Marianna Amaral Pedroso,
- Kirsten Rebecca Palmer,
- Ryan James Hodges,
- Fabricio da Silva Costa,
- Daniel Lorber Rolnik
Abstract
Review ArticleUterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):287-293
- Marianna Amaral Pedroso,
- Kirsten Rebecca Palmer,
- Ryan James Hodges,
- Fabricio da Silva Costa,
- Daniel Lorber Rolnik
Views419See moreAbstract
Objective
To perform a comprehensive review of the current evidence on the role of uterine artery Doppler, isolated or in combination with other markers, in screening for preeclampsia (PE) and fetal growth restriction (FGR) in the general population. The review included recently published large cohort studies and randomized trials.
Methods
A search of the literature was conducted usingMedline, PubMed, MeSH and ScienceDirect. Combinations of the search terms “preeclampsia,” “screening,” “prediction,” “Doppler,” “Doppler velocimetry,” “fetal growth restriction,” “small for gestational age” and “uterine artery” were used. Articles in English (excluding reviews) reporting the use of uterine artery Doppler in screening for PE and FGR were included.
Results
Thirty articles were included. As a single predictor, uterine artery Doppler detects less than 50% of the cases of PE and no more than 40% of the pregnancies affected by FGR. Logistic regression-based models that allow calculation of individual risk based on the combination of multiple markers, in turn, is able to detect ~ 75% of the cases of preterm PE and 55% of the pregnancies resulting in small for gestational age infants.
Conclusion
The use of uterine artery Doppler as a single predictive test for PE and FGR has poor accuracy. However, its combined use in predictive models is promising, being more accurate in detecting preterm PE than FGR.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article09-16-2019
Do Women have Adequate Knowledge about Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions? A Systematic Review
- Júlia Ferreira Fante,
- Thais Daniel Silva,
- Elaine Cristine Lemes Mateus-Vasconcelos,
- Cristine Homsi Jorge Ferreira,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito

Abstract
Review ArticleDo Women have Adequate Knowledge about Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions? A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):508-519
- Júlia Ferreira Fante,
- Thais Daniel Silva,
- Elaine Cristine Lemes Mateus-Vasconcelos,
- Cristine Homsi Jorge Ferreira,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito

Views387See moreAbstract
Objective
We sought to investigate whether women present adequate knowledge of the main pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) (urinary incontinence – UI, fecal incontinence – FI, and pelvic organ prolapse – POP).
Data
sources A systematic review was performed in the MEDLINE, PEDro, CENTRAL, and Cochrane databases for publications from inception to April 2018. Selection of studies A total of 3,125 studies were reviewed. Meta-analysis was not possible due to the heterogeneity of primary outcomes and the diversity of instruments for measuring knowledge. The quality of the articles included in the analysis was evaluated with the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) adapted for cross-sectional studies.
Data collection
Two authors performed data extraction into a standardized spreadsheet.
Data synthesis
Nineteen studies were included, comprising 11,512 women. About the methodological quality (NOS), most of the studies (n= 11) presented a total score of 6 out of 10. Validated questionnaires and designed pilot-tested forms were the most frequently used ways of assessing knowledge. Some studies were stratified by race, age, or group minorities. The most used questionnaire was the prolapse and incontinence knowledge questionnaire (PIKQ) (n= 5). Knowledge and/or awareness regarding PFD was low to moderate among the studies. Urinary incontinence was the most prevalent PFD investigated, and the most important risk factors associated with the lack of knowledge of the pelvic floor were: African-American ethnicity (n= 3), low educational level (n= 4), low access to information (n= 5) and socioeconomic status (n= 3).
Conclusion
Most women have a gap in the knowledge of pelvic floor muscle dysfunctions, do not understand their treatment options, and are not able to identify risk factors for these disorders.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-09-2024
Screening and prevention of preterm birth: how is it done in clinical practice?
- Roberta Bulsing dos Santos
 ,
, - Janete Vettorazzi
 ,
, - Marcos Wengrover Rosa
 ,
, - Ellen Machado Arlindo
 ,
, - Edimárlei Gonsales Valério

Abstract
Original ArticleScreening and prevention of preterm birth: how is it done in clinical practice?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo32
- Roberta Bulsing dos Santos
 ,
, - Janete Vettorazzi
 ,
, - Marcos Wengrover Rosa
 ,
, - Ellen Machado Arlindo
 ,
, - Edimárlei Gonsales Valério

Views552Abstract
Objective:
To ascertain how screening for preterm birth is performed among obstetricians working in public and private practice in a middle-income country.
Methods:
Cross-sectional study of 265 obstetrician-gynecologists employed at public and private facilities. An online questionnaire was administered, with items designed to collect data on prematurity screening and prevention practices.
Results:
The mean age of respondents was 44.5 years; 78.5% were female, and 97.7% had completed a medical residency program. Universal screening (i.e., by ultrasound measurement of cervical length) was carried out by only 11.3% of respondents in public practice; 43% request transvaginal ultrasound if the manual exam is abnormal, and 74.6% request it in pregnant women with risk factors for preterm birth. Conversely, 60.7% of respondents in private practice performed universal screening. This difference in screening practices between public and private practice was highly significant (p < 0.001). Nearly all respondents (90.6%) reported prescribing vaginal progesterone for short cervix.
Conclusion:
In the setting of this study, universal ultrasound screening to prevent preterm birth was used by just over half of doctors in private practice. In public facilities, screening was even less common. Use of vaginal progesterone in cervical shortening was highly prevalent. There is an unmet need for formal protocols for screening and prevention of preterm birth in middle-income settings.
Key-words attitudes, practiceCervical length measurementgynecologistshealth knowledgeInfant, prematureobstetriciansPreterm birthPreventionScreeningsurveys and questionnairesSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Roberta Bulsing dos Santos
-
Review Article01-23-2022
Efficacy of Hormonal and Nonhormonal Approaches to Vaginal Atrophy and Sexual Dysfunctions in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review
- Ayane Cristine Alves Sarmento
 ,
, - Ana Paula Ferreira Costa
 ,
, - Juliana Lírio
 ,
, - José Eleutério Jr
 ,
, - Pedro Vieira Baptista
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Ana Katherine Gonçalves

Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy of Hormonal and Nonhormonal Approaches to Vaginal Atrophy and Sexual Dysfunctions in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):986-994
- Ayane Cristine Alves Sarmento
 ,
, - Ana Paula Ferreira Costa
 ,
, - Juliana Lírio
 ,
, - José Eleutério Jr
 ,
, - Pedro Vieira Baptista
 ,
, - Ana Katherine Gonçalves

Views390See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy of the hormonal and nonhormonal approaches to symptoms of sexual dysfunction and vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women.
Data Sources
We conducted a search on the PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, SciELO, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) databases, as well as on clinical trial databases. We analyzed studies published between 1996 and May 30, 2020. No language restrictions were applied.
Selection of Studies
We selected randomized clinical trials that evaluated the treatment of sexual dysfunction in postmenopausal women.
Data Collection
Three authors (ACAS, APFC, and JL) reviewed each article based on its title and abstract. Relevant data were subsequently taken from the full-text article. Any discrepancies during the review were resolved by consensus between all the listed authors.
Data Synthesis
A total of 55 studies were included in the systematic review. The approaches tested to treat sexual dysfunction were as follows: lubricants and moisturizers (18 studies); phytoestrogens (14 studies); dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; 8 studies); ospemifene (5 studies); vaginal testosterone (4 studies); pelvic floor muscle exercises (2 studies); oxytocin (2 studies); vaginal CO2 laser (2 studies); lidocaine (1 study); and vitamin E vaginal suppository (1 study).
Conclusion
We identified literature that lacks coherence in terms of the proposed treatments and selected outcome measures. Despite the great diversity in treatment modalities and outcome measures, the present systematic review can shed light on potential targets for the treatment, which is deemed necessary for sexual dysfunction, assuming that most randomized trials were evaluated with a low risk of bias according to the Cochrane Collaboration risk of bias tool. The present review is registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; CRD42018100488).


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ayane Cristine Alves Sarmento
-
Original Article04-08-2022
Prevalence of Premenstrual Syndrome and Associated Factors Among Academics of a University in Midwest Brazil
- Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
 ,
, - Fernanda Rassi Alvarenga
 ,
, - Marcelo Ramos
 ,
, - Débora Luiza Franken
 ,
, - Juvenal Soares Dias da Costa
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Vera Maria Vieira Paniz

Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of Premenstrual Syndrome and Associated Factors Among Academics of a University in Midwest Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):133-141
- Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
 ,
, - Fernanda Rassi Alvarenga
 ,
, - Marcelo Ramos
 ,
, - Débora Luiza Franken
 ,
, - Juvenal Soares Dias da Costa
 ,
, - Marcos Pascoal Pattussi
 ,
, - Vera Maria Vieira Paniz

Views385Abstract
Objective
To investigate the prevalence of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) in university students, the factors associated with PMS, the most prevalent symptoms, and the interference of symptoms in academic, family, social, and work activities.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 1,115 university students aged ≥ 18 years from the University of Rio Verde, Goiás. Premenstrual syndrome and PMDD were identified using the Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool. Associations with sociodemographic, behavioral, reproductive, nutritional, and health factors were investigated using the Poisson regression.
Results
The prevalence of PMS was 46.9% (95% confidence interval [CI] 44.0-49.8), and of PMDD, 11.1% (95% CI 9.3-13.0). The most prevalent symptoms were physical, such as breast tenderness, bloating, e weight gain (73%); followed by psychological ones such as overeating/food cravings, tearful/more sensitive to rejection (> 60%). More than 30% of the patients reported that the symptoms interfered in a moderate-tosevere way in their social and academic activities. After adjusted analysis, PMS was more prevalent in those who were attending the 1st/2nd semester of college (prevalence ratio [PR] 1.44; 95% CI 1.14-1.80), those who consumed alcohol in the last 30 days (PR 1.23; 95% CI 1.04-1.47), and those who had depression (PR 1.49; 95% CI 1.30-1.71).
Conclusion
Almost half of the university students had PMS and ~ 11%, PMDD. Physical symptoms were themost common and interfered in amoderate-to-severe way in various aspects of life. Attending the first semesters, consuming alcohol, and having depression were risk factors for PMS. The identification of risk factors for PMS is essential to prevent symptoms and reduce the impact of the syndrome.
Key-words Cross-sectional studiespremenstrual dysphoric disorderPremenstrual syndromeRisk factorsStudentsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
-
Original Article06-19-2019
Health-related Quality of Life in Women with Cervical Cancer
- Larissa Nascimento dos Santos,
- Luciana Castaneda
 ,
, - Suzana Sales de Aguiar,
- Luiz Claudio Santos Thuler,
- Rosalina Jorge Koifman, [ … ],
- Anke Bergmann
Abstract
Original ArticleHealth-related Quality of Life in Women with Cervical Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(4):242-248
- Larissa Nascimento dos Santos,
- Luciana Castaneda
 ,
, - Suzana Sales de Aguiar,
- Luiz Claudio Santos Thuler,
- Rosalina Jorge Koifman,
- Anke Bergmann
Views264See moreAbstract
Objective
To analyze the factors associated with health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in women with cervical cancer (CC) in a single center in Rio de Janeiro, state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Methods
A cross-sectional study in women with a diagnosis of CC followed-up in the gynecology outpatient clinic of the Hospital do Câncer II (HCII, in the Portuguese acronym) of the Instituto Nacional de Câncer (INCA, in the Portuguese acronym). The data were collected from March to August 2015. Women with palliative care, communication/cognition difficulty, undergoing simultaneous treatment for other types of cancer, or undergoing chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy were excluded. For the evaluation of the HRQoL, a specific questionnaire for women with CC was used (Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy – Cervix Cancer [FACT-Cx]). The total score of the questionnaire ranges from 0 to 168, with higher scores indicating a better HRQoL.
Results
A total of 115 women were included in the present study, with a mean age of 52.64 years old (standard deviation [SD] = 12.13). The domains of emotional (16.61; SD = 4.55) and functional well-being (17.63; SD = 6.15) were those which presented the worst scores. The factors that had an association with better HRQoL in women with CC were having a current occupation, a longer time since the treatment and diagnosis, and women who had undergone hysterectomy.
Conclusion
Considering the domains of HRQoL of the women treated for cervical cancer, a better score was observed in the domains of physical and social/family wellbeing. For most domains, better scores were found between those with a current occupation, with a longer time after the diagnosis and treatment, and among those who had undergone a hysterectomy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article11-01-2018
Comparative Study of the Use of HPA Lanolin and Breast Milk for Treating Pain Associated with Nipple Trauma
- Corintio Mariani Neto,
- Rosemeire Sartori de Albuquerque,
- Sonia Cristina de Souza,
- Renata Oliveira Giesta,
- Andrea Penha Spinola Fernandes, [ … ],
- Bárbara Mondin
Abstract
Original ArticleComparative Study of the Use of HPA Lanolin and Breast Milk for Treating Pain Associated with Nipple Trauma
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):664-672
- Corintio Mariani Neto,
- Rosemeire Sartori de Albuquerque,
- Sonia Cristina de Souza,
- Renata Oliveira Giesta,
- Andrea Penha Spinola Fernandes,
- Bárbara Mondin
Views290Abstract
Objective
To compare two different treatments—the use of highly purified anhydrous (HPA) lanolin and expressed breast milk—for women with pain and nipple trauma during the breastfeeding process.
Method
A total of 180 puerperal women were randomly assigned to 2 groups: one was treated with HPA lanolin and the other with their own expressed breast milk. All of the participants received the same breastfeeding technique instructions and therapeutic care standard. Three assessments were performed: at the time of inclusion in the study (after randomization); after 48 hours; and after 7 days. At each interval, data was collected in relation to pain and trauma. A numerical/verbal category scale was used for the pain variable, and the nipple trauma score for the trauma variable. The results were subjected to statistical analysis using the chi-squared test, the Fisher exact test, the student t-test, and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. Generalized estimating equations were calculated using the STATA 12 statistical software package (StataCorp LLC, College Station, TX, USA) and IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 20.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA).
Results
There was pain improvement from the second to the third assessment in the group that used HPA lanolin, while the pain remained unchanged between these two periods (p< 0.001) in the breast milk group. In terms of trauma, improvement was identified in its extension and depth from the first to the third assessment, and it was higher in the HPA lanolin group than in the breast milk group (p= 0.025).
Conclusion
The treatment of pain and nipple trauma with HPA lanolin achieved better results than the one with breast milk, based on a 7-day treatment period.
Key-words breastfeeding/adverse effectsbreastfeeding/nipple painlanolin/therapeutic usenipples/injurieswound healing/drug effectsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 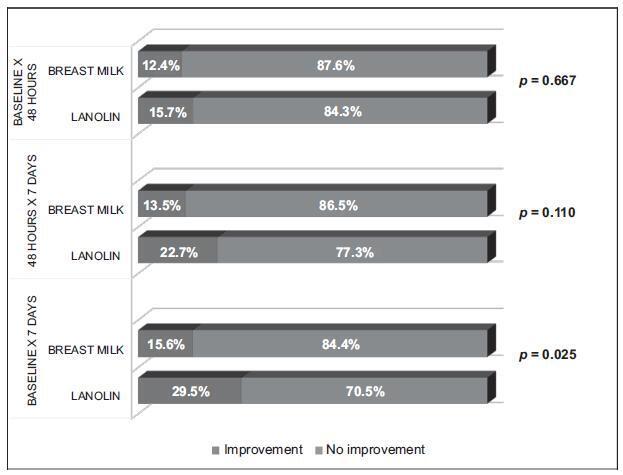
-
Original Article06-22-2020
Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Missed Abortion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):235-239
Abstract
Original ArticlePlatelet to Lymphocyte Ratio and Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio in Missed Abortion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):235-239
Views280See moreAbstract
Objective
Missed abortion occurs in ~ 15% of all clinical pregnancies. The pathogenesis is not clearly known. However, defective placentation resulting in maternal systemic inflammatory response is considered responsible for missed abortion. Platelet lymphocyte ratio (PLR) and neutrophil lymphocyte ratio (NLR) are increasingly cited parameters of inflammation in the literature. However, no study evaluated the PLR and NLR rates in missed abortions so far. The aim of the present study is to investigate whether complete blood count (CBC) inflammatory parameters such as NLR and PLR are increased in patients with missed abortion.
Methods
Medical records of 40 pregnant women whose gestation ended in missed abortion at between 6 and14 weeks of gestation and of 40 healthy pregnant women were collected and compared retrospectively. The groups were compared regarding hemoglobin, hematocrit, platelet count (PLT), mean platelet volume (MPV), platelet distribution width (PDW), PLR and NLR.
Results
Platelet distribution width, NLR and PLR values were higher in the missed abortion group compared with the healthy pregnant women group (rates are p = 0.043; p = 0.038; and p = 0.010, respectively). Hematocrit, MPV, and lymphocyte values were found to be lower in the missed abortion group compared with the healthy pregnant women group (p = 0.027, p = 0.044 and p = 0.025, respectively).
Conclusion
The PDW, NLR and PLR values of the missed abortion group were reported high; and MPV values were reported low in the present study. These findings may help to speculate a defective placentation in the pathogenesis of missed abortion.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article11-07-2019
Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome and Infertility
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):621-627
Abstract
Review ArticleAntiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome and Infertility
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):621-627
Views299See moreAbstract
Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS) is a systemic, autoimmune, prothrombotic disease characterized by persistent antiphospholipid antibodies (aPLs), thrombosis, recurrent abortion, complications during pregnancy, and occasionally thrombocytopenia. The objective of the present study was to review the pathophysiology of APS and its association with female infertility. A bibliographic review of articles of the past 20 yearswas performed at the PubMed, Scielo, and Bireme databases. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome may be associated with primary infertility, interfering with endometrial decidualization and with decreased ovarian reserve. Antiphospholipid antibodies also have direct negative effects on placentation, when they bind to the trophoblast, reducing their capacity for invasion, and proinflammatory effects, such as complement activation and neutrophil recruitment, contributing to placental insufficiency, restricted intrauterine growth, and fetal loss. In relation to thrombosis, APS results in a diffuse thrombotic diathesis, with global and diffuse dysregulation of the homeostatic balance. Knowing the pathophysiology of APS, which is closely linked to female infertility, is essential for new therapeutic approaches, specialized in immunomodulation andinflammatory signaling pathways, to provide important advances in its treatment.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article03-27-2020
Gestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Abstract
Original ArticleGestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):12-18
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 ,
, - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Views368See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus and the main associated risk factors in the population served by the Brazilian Unified Health System in the city of Caxias do Sul, state of Rio Grande do Sul.
Materials and Methods
A descriptive, cross-sectional and retrospective study was conducted. Maternal variables were collected from the medical records of all pregnant women treated at the basic health units in 2016. Hyperglycemia during pregnancy (pregestational diabetes, overt diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus) was identified by analyzing the results of a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, as recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. Based on the data, the women were allocated into two groups: the gestational diabetes group and the no gestational diabetes group.
Results
The estimated prevalence of gestational diabetes among 2,313 pregnant women was of 5.4% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 4.56-6.45). Pregnant women with 3 or more pregnancies had twice the odds of having gestational diabetes compared with primiparous women (odds ratio [OR]=2.19; 95%CI: 1.42-3.37; p<0.001). Pregnant women aged 35 years or older had three times the odds of having gestational diabetes when compared with younger women (OR=3.01; 95%CI: 1.97-4.61; p<0.001). Overweight pregnant women were 84% more likely to develop gestational diabetes than those with a body mass index lower than 25 kg/m2 (OR =1.84; 95%CI: 1.25-2.71; p=0.002). A multivariable regression analysis showed that being overweight and being 35 years old or older were independent variables.
Conclusion
In this population, the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus was of 5.4%. Age and being overweight were predictive factors for gestational diabetes.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
-
Systematic Review11-01-2017
Preterm Preeclampsia and Timing of Delivery: A Systematic Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):622-631
Abstract
Systematic ReviewPreterm Preeclampsia and Timing of Delivery: A Systematic Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):622-631
Views189See moreAbstract
Introduction
Preeclampsia, a multifactorial disease with pathophysiology not yet fully understood, is a major cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality, especially when preterm. The diagnosis is performed when there is an association between arterial hypertension and proteinuria or evidence of severity. There are unanswered questions in the literature considering the timing of delivery once preterm preeclampsia has been diagnosed, given the risk of developingmaternal complications versus the risk of adverse perinatal outcomes associated with prematurity. The objective of this systematic review is to determine the best timing of delivery for women diagnosed with preeclampsia before 37 weeks of gestation.
Methods
Systematic literature review, performed in the PubMed database, using the terms preeclampsia, parturition and timing of delivery to look for studies conducted between 2014 and 2017. Studies that compared the maternal and perinatal outcomes of women who underwent immediate delivery or delayed delivery, in the absence of evidence of severe preeclampsia, were selected.
Results
A total of 629 studies were initially retrieved. After reading the titles, 78 were selected, and their abstracts, evaluated; 16 were then evaluated in full and, in the end, 6 studies (2 randomized clinical trials and 4 observational studies) met the inclusion criteria. The results were presented according to gestational age range (< 34 weeks and between 34 and 37 weeks) and by maternal and perinatal outcomes, according to the timing of delivery, considering immediate delivery or expectant management. Before 34 weeks, thematernal outcomeswere similar, but the perinatal outcomes were significantly worse when immediate delivery occurred. Between 34 and 37 weeks, the progression to severe maternal disease was slightly higher among women undergoing expectant management, however, with better perinatal outcomes.
Conclusions
When there is no evidence of severe preeclampsia or impaired fetal wellbeing, especially before 34 weeks, the pregnancy should be carefully surveilled, and the delivery, postponed, aiming at improving the perinatal outcomes. Between 34 and 37 weeks, the decision on the timing of delivery should be shared with the pregnant woman and her family, after providing information regarding the risks of adverse outcomes associated with preeclampsia and prematurity.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article03-04-2022
Screening of Perinatal Depression Using the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale
- Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
 ,
, - Guilherme Guarany Cardoso Magalhães Luzetti
 ,
, - Márcia Maria Auxiliadora Rosalém
 ,
, - Corintio Mariani Neto

Abstract
Original ArticleScreening of Perinatal Depression Using the Edinburgh Postpartum Depression Scale
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):452-457
- Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
 ,
, - Guilherme Guarany Cardoso Magalhães Luzetti
 ,
, - Márcia Maria Auxiliadora Rosalém
 ,
, - Corintio Mariani Neto

Views526See moreAbstract
Objective
To detect depression during pregnancy and in the immediate postpartum period using the Edinburgh postpartum depression scale (EPDS).
Methods
Cross sectional study of 315 women, aged between 14 and 44 years, who received perinatal care at the Leonor Mendes de Barros Hospital, in São Paulo, between July 1st, 2019 and October 30th, 2020. The cutoff point suggesting depression was ≥ 12.
Results
The screening indicated 62 (19.7%) patients experiencing depression. Low family income, multiparity, fewer prenatal appointments, antecedents of emotional disorders, dissatisfaction with the pregnancy, poor relationship with the partner, and psychological aggression were all risk factors associated with depression in pregnancy or in the immediate postpartum period. Antecedents of depression and psychology aggression during pregnancy were significant variables for predicting perinatal depression in the multivariate analysis.
Conclusion
There is a significant association between the occurrence of perinatal depression and the aforementioned psychosocial factors. Screening patients with the EPDS during perinatal and postpartum care could facilitate establishing a line of care to improve the wellbeing of mother and infant.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Tenilson Amaral Oliveira
-
Systematic Review11-01-2017
Management of Axillary Web Syndrome after Breast Cancer: Evidence-Based Practice
- Clarissa Medeiros da Luz,
- Julia Deitos,
- Thais Cristina Siqueira,
- Marina Palú,
- Ailime Perito Feiber Heck
Abstract
Systematic ReviewManagement of Axillary Web Syndrome after Breast Cancer: Evidence-Based Practice
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):632-639
- Clarissa Medeiros da Luz,
- Julia Deitos,
- Thais Cristina Siqueira,
- Marina Palú,
- Ailime Perito Feiber Heck
Views262Abstract
Axillary web syndrome is characterized as a physical-functional complication that impacts the quality of life of women who have undergone treatment for breast cancer. The present study aims to verify the physiotherapy treatment available for axillary web syndrome after surgery for breast cancer in the context of evidence-based practice. The selection criteria included papers discussing treatment protocols used for axillary web syndrome after treatment for breast cancer. The search was performed in the MEDLINE, Scopus, PEDro and LILACS databases using the terms axillary web syndrome, lymphadenectomy and breast cancer, focusing on women with a previous diagnosis of breast cancer who underwent surgery with lymphadenectomy as part of their treatment. From the 262 studies found, 4 articles that used physiotherapy treatment were selected. The physiotherapy treatment was based on lymphatic drainage, tissue mobilization, stretching and strengthening. The four selected articles had the same outcome: improvement in arm pain and shoulder function and/or dissipation of the axillary cord. Although axillary web syndrome seems to be as frequent and detrimental as other morbidities after cancer treatment, there are few studies on this subject. The publications are even scarcer when considering studies with an interventional approach. Randomized controlled trials are necessary to support the rehabilitation resources for axillary web syndrome.
Key-words axillary web syndromeconservative treatmentcordingLymphadenectomyPhysiotherapyRehabilitationSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Maternal mortality (46)Postpartum period (46)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)

