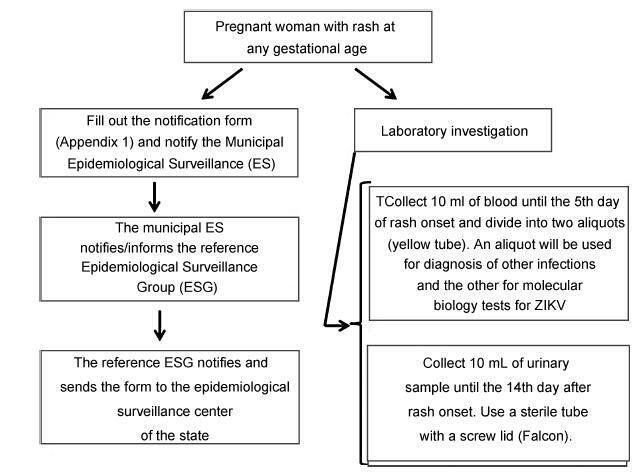
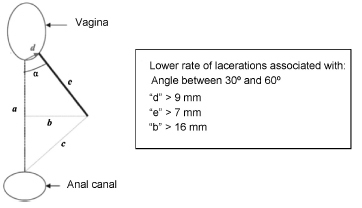
-
Original Article08-07-1999
The use of sulfonylureas by pregnant diabetic women and fetal malformations
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):393-397
Abstract
Original ArticleThe use of sulfonylureas by pregnant diabetic women and fetal malformations
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):393-397
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000700005
Views90Purpose: to evaluate a possible relationship between fetal malformations (FM) and the use of sulfonylureas (SF) by diabetic pregnant women. Methods: we retrospectively studied 35 type 2 diabetic pregnant women followed at the Pathological Prenatal Care Outpatient Clinic of the University Hospital, Faculty of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, from 1993 to 1995. Twenty-two of these women had been inadvertently using sulfonylureas during the 1st trimester of gestation (SF group). We determined their prevalence of FM and compared it to that observed for pregnant diabetic women who were only on diet or insulin therapy (group C). We also analyzed other variables such as time of disease, age, metabolic control, and prenatal care. Results: there was no significant difference between groups in terms of age range, duration of diabetes, glycemic control, or early start of prenatal care, with the prevalence of FM being similar for the two groups (8.3% in group C and 13.6% in group SF). The malformations observed in group SF were: renal agenesis, pulmonary hypoplasia and ribbon gonads (patient 1); short limbs and abnormally implanted toes (patient 2); cleft palate, low implanted ears, neck webbing and saddle nose (patient 3), and micrognathia, dysplastic ears, imperforate anus, hypospadia, polydactily, ventricular septal defect and atrial septal defect (patient 4) in group C. Conclusions: these data do not allow us to attribute the malformations detected in group SF to the use of sulfonylureas, although not usually described alterations in diabetic embryopathy occurred in this group.
Key-words Diabetes mellitusFetal malformationsSee more -
Original Article08-07-1999
Amnioinfusion during labor with meconium-stained amniotic fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):389-392
Abstract
Original ArticleAmnioinfusion during labor with meconium-stained amniotic fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):389-392
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000700004
Views95See morePurpose: to report the personal experience with the use of the amnioinfusion technique in patients in labor presenting meconial amniotic fluid, and the incidence of complications, the meconium aspiration syndrome and of cesarean sections. Method: twenty patients at term and in labor with meconial amniotic fluid were evaluated retrospectively, at the delivery ward at two public institutions of Rio Grande do Sul. An initial infusion of 1.000 ml of normal saline solution at room temperature, at an infusion rate of 20-30 ml per minute was initiated and then reduced to 3 ml per minute. The liquid was drained by elevating the cephalic pole. Results: the procedure was feasible when a nasogastric catheter was used. None of the patients presented major complications related to the procedure. None of the neonates presented meconium below their vocal cords. The cesarean section rate was 3/20 (15%). Conclusion: the amnioinfusion is a low-cost and feasible technique that did not show any complication in this study.
-
Original Article08-07-1999
Fetal pulse oximetry: relationship between oxygen saturation at second stage of labor and the umbilical artery pH at birth
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):381-384
Abstract
Original ArticleFetal pulse oximetry: relationship between oxygen saturation at second stage of labor and the umbilical artery pH at birth
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):381-384
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000700003
Views93See morePurpose: to study the correlation between fetal oxygen saturation measured by pulse oximetry during second stage of labor and umbilical artery pH at birth. Patients and Methods: fetal oxygen saturation (FSpO2) was monitored by pulse oximetry during the second stage of labor in 64 singleton pregnancies at term, with vertex presentation. Umbilical blood was sampled immediately after delivery for subsequent measurement of venous and arterial blood gases and pH. All fetuses maintained FSpO2 > or = 30% through the first stage of labor, until the start of second stage. Results: the mean FSpO2 at the second stage of labor correlated significantly with umbilical artery pH at birth (n = 64, r = 0.79, p <0.001). There was no significant corre-lation between FSpO2 at the second stage of labor and umbilical artery oxygen saturation at birth. Conclusion: fetal oxygen saturation measured by pulse oximetry during second stage of labor has a good correlation with umbilical artery pH at birth.
-
Original Article08-07-1999
Reverse blood flow in ductus venosus: new perspective in detection of chromosomal abnormalities
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):371-376
Abstract
Original ArticleReverse blood flow in ductus venosus: new perspective in detection of chromosomal abnormalities
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):371-376
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000700002
Views143See morePurpose: to evaluate the possible value of pulsed and color Doppler of ductus venosus blood flow in the screening for chromosomal abnormalities at 10-14 weeks of gestation. Methods: the ductus venosus flow velocity waveforms and the nuchal translucency (NT) thickness were obtained immediately before the chorionic villus sample in 26 pregnancies. We employed the following criteria for the suspicion of chromosomal defects: reverse or absent flow during atrial contraction and NT greater or equal to 3 mm. We calculated the sensitivity, the specificity, the negative and positive predictive value for each of the above items. Results: there were 9 chromosomal abnormalities (3 cases of trisomy 21, 2 cases of trisomy 13, 1 case of trisomy 9, 1 case of trisomy 22, 1 triploidy and 1 monosomy X). Abnormal ductus venosus flow was observed in all cases (sensitivity of 100%). In the normal fetuses (17 cases) only 1 had abnormal flow (specificity of 94%). Concerning NT, the sensitivity and the specificity were 88% and 76%, respectively. Conclusion: our preliminary results suggest that the presence of chromosomal abnormalities may be strongly suspected when an increased NT thickness is associated with an absent or reverse flow in the ductus venosus. We speculated that both methods are valid in the screening of chromosomal defects.
-
08-07-1999
As sociedades científicas, sua proliferação e a ética
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):370-370
-
08-07-1999
Avaliação dos padrões vasculares uterino e placentário no primeiro trimestre das gestações normal e patológica
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(5):302-302
Abstract
Avaliação dos padrões vasculares uterino e placentário no primeiro trimestre das gestações normal e patológica
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(5):302-302
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000500012
Views63Avaliação dos Padrões Vasculares Uterino e Placentário no Primeiro Trimestre das Gestações Normal e Patológica […]See more -
08-07-1999
Dopplervelocimetria das artérias uterinas, arqueadas e espiraladas no prognóstico de receptividade endometrail de mulheres em ciclos estimulados para fertilização in vitro
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(5):302-302
Abstract
Dopplervelocimetria das artérias uterinas, arqueadas e espiraladas no prognóstico de receptividade endometrail de mulheres em ciclos estimulados para fertilização in vitro
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(5):302-302
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000500013
Views55Dopplervelocimetria das Artérias Uterinas, Arqueadas e Espiraladas no Prognóstico de Receptividade Endometrail de Mulheres em Ciclos Estimulados para Fertilização In Vitro […]See more -
08-07-1999
Estudo anatomoclínico do carcinoma ductal invasivo da mama em pacientes axila-negativas associado à identificação dos receptores de estrogênio
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(5):301-301
Abstract
Estudo anatomoclínico do carcinoma ductal invasivo da mama em pacientes axila-negativas associado à identificação dos receptores de estrogênio
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(5):301-301
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000500010
Views64Estudo Anatomoclínico do Carcinoma Ductal Invasivo da Mama em Pacientes Axila-Negativas Associado à Identificação dos Receptores de Estrogênio. […]See more
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Maternal mortality (46)Postpartum period (46)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)