- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Original Article04-09-1998
Comparison between active management with oxytocin and expectant management for premature rupture of membranes at term
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):495-501
Abstract
Original ArticleComparison between active management with oxytocin and expectant management for premature rupture of membranes at term
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):495-501
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000900002
Views141See moreObjective: to compare the expectant versus active management with oxytocin in a Brazilian population of pregnant women with premature rupture of membranes (PROM) at term. Methods: a prospective, randomized and multicenter clinical trial was performed, evaluating variables concerning the time from PROM until the onset of labor and delivery, and maternal and neonatal hospitalization periods. Two hundred pregnant women with PROM at term were selected from four public hospitals in São Paulo state, from November 1995 to February 1997. They were randomly divided into two groups: active management, with oxytocin induction of labor until 6 h of PROM; and expectant management, waiting for the spontaneous onset of labor up to 24 h. The data were analyzed with the Epi-Info and SPSS-PC+ packages, using the statistical c², Student’s t and log-rank tests. Results: the results indicate that the differences between the two managements concern to the longer time needed for the expectant management group until onset of labor and delivery, besides the higher number of women and neonates who remained in hospital for more than three days. Conclusions: the time between admission and onset of labor and delivery, and also the latent period were longer in the expectant management group.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-09-1998
Ética em pesquisa
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(9):494-494
Abstract


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-09-1998
Estudo Controlado e Randomizado para Prevenção de Infecção Pós-Cesárea com Penicilina e Cefalotina
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):424-424
Abstract
Estudo Controlado e Randomizado para Prevenção de Infecção Pós-Cesárea com Penicilina e Cefalotina
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):424-424
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700011
Views49Estudo Controlado e Randomizado para Prevenção de Infecção Pós-Cesárea com Penicilina e Cefalotina […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-09-1998
Estudo Morfológico e Morfométrico do Endométrio de Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa Durante Terapêutica Estrogênica Contínua, Associada ao Acetato de Medroxiprogesterona a Cada Dois, Três e Quatro Meses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):423-423
Abstract
Estudo Morfológico e Morfométrico do Endométrio de Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa Durante Terapêutica Estrogênica Contínua, Associada ao Acetato de Medroxiprogesterona a Cada Dois, Três e Quatro Meses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):423-423
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700009
Views45Estudo Morfológico e Morfométrico do Endométrio de Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa Durante Terapêutica Estrogênica Contínua, Associada ao Acetato de Medroxiprogesterona a Cada Dois, Três e Quatro Meses[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-09-1998
Sangramento e Endometrite em Pacientes Portadoras de DIU Pós-Placentário na Maternidade de Encruzilhada – Recife (PE)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):423-424
Abstract
Sangramento e Endometrite em Pacientes Portadoras de DIU Pós-Placentário na Maternidade de Encruzilhada – Recife (PE)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):423-424
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700010
Views49Sangramento e Endometrite em Pacientes Portadoras de DIU Pós-Placentário na Maternidade de Encruzilhada Recife (PE) […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-09-1998
Complete Mole in Twin Pregnancy: a Case Report
- Izildinha Maestá,
- Iracema M.P. Calderon,
- Marilza V.C. Rudge,
- Magaly M. Sales,
- Fabiano P. Saggioro, [ … ],
- José Carlos Peraçoli
Abstract
Case ReportComplete Mole in Twin Pregnancy: a Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):415-419
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700008
- Izildinha Maestá,
- Iracema M.P. Calderon,
- Marilza V.C. Rudge,
- Magaly M. Sales,
- Fabiano P. Saggioro,
- José Carlos Peraçoli
Views90Twin pregnancy in which a normal fetus and a complete mole develop at the same time is a rare event. Clinical complications and malignancy are frequent in this type of disease.This report is about a case of a late diagnosis due to the presence of the fetus. The diagnosis was made when the pregnancy was interrupted and then confirmed by histopathological study and flow cytometry. The pregnancy was terminated transpelvically due to massive uterine hemorrhage. The post-molar follow-up showed the persistence of high levels of bhCG. The patient’s complete recovery was achieved after the administration of methotrexate. The diagnosis, natural history, and procedures for this rare disease are discussed in view of this case.
Key-words ChemotherapyComplete hydatidiform moleGestational trophoblastic diseaseHemorrhagePregnancy complicationsTwin pregnancyUltrasonographySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-09-1998
Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Endocervix in a 7-year-old Child
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):411-414
Views109

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Case ReportClear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Endocervix in a 7-year-old Child
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):411-414
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700007
Views109See moreClear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina and cervix is a rare disease associated commonly with the use of diethylstilbestrol (DES) during pregnancy. The most commom complaint is irregular vaginal bleeding, which could be confused with vaginitis in children and abnormalities in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis in adolescents. We report a case of clear cell adenocarcinoma of the endocervix in a 7-year-old child who was attended at the Children and Adolescent Gynecology Sector, and we call attention to the diagnosis of genital cancer which, in spite of its rarity at this age, must be considered in children with genital bleeding.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Equipments and Methods04-09-1998
Endometrial Resection by Video-Hysteroscopy: experience in a Teaching Hospital
- Caio Parente Barbosa,
- Marcelo Ettruri Santos,
- Ana Cristina Napolitano,
- Paula Harue Tamanaka,
- Emerson Barchi Cordts
Abstract
Equipments and MethodsEndometrial Resection by Video-Hysteroscopy: experience in a Teaching Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):405-410
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700006
- Caio Parente Barbosa,
- Marcelo Ettruri Santos,
- Ana Cristina Napolitano,
- Paula Harue Tamanaka,
- Emerson Barchi Cordts
Views90See moreObjective: to demonstrate the effectiveness of video-hysteroscopic endometrial resection in the treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding. Patients and method: The authors studied 60 records of patients with abnormal uterine bleeding who did not respond to clinical treatment. Results: eighty-eight percent of the patients had adequate response to the treatment (53% oligomenorrhea and 35% amenorrhea). The complication rate was 8.3% (5 uterine perforations). Conclusion: video-hysteroscopic endometrial resection is an effective technique to treat abnormal uterine bleeding which failed to respond to clinical management. The intra and postoperative complication rates are low.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Original Article01-01-2014
Doplervelocimetria da artéria uterina no segundo e terceiro trimestres para predição dos resultados gestacionais
- Maryam Afrakhteh,
- Aida Moeini,
- Morteza Sanei Taheri,
- Hamid Reza Haghighatkhah,
- Mohammad Fakhri, [ … ],
- Nina Masoom
Views392

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleDoplervelocimetria da artéria uterina no segundo e terceiro trimestres para predição dos resultados gestacionais
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(1):35-39
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032014000100008
- Maryam Afrakhteh,
- Aida Moeini,
- Morteza Sanei Taheri,
- Hamid Reza Haghighatkhah,
- Mohammad Fakhri,
- Nina Masoom
Views392OBJETIVO:
O objetivo do presente estudo longitudinal foi avaliar o valor da ultrassonografia Doppler das artérias uterinas no segundo e terceiro trimestres de gestação para a predição de desfecho adverso da gravidez em mulheres de baixo risco.
MÉTODOS:
De julho de 2011 até agosto de 2012, 205 gestantes de feto único atendidas em nossa clínica de pré-natal foram incluídas no presente estudo prospectivo e avaliadas em termos de dados demográficos e obstétricos. As pacientes foram submetidas à avaliação de ultrassom durante o segundo e terceiro trimestres, incluindo avaliação Doppler das artérias uterinas bilaterais, visando determinar os valores do índice de pulsatilidade (IP) e do índice de resistência (IR), bem como a presença de incisura diastólica precoce. O desfecho do presente estudo foi a avaliação da sensibilidade, especificidade, valor preditivo positivo (VPP) e valor negativo preditivo (VNP) da ultrassonografia Doppler das artérias uterinas para a predição de desfechos adversos da gravidez, incluindo pré-eclâmpsia, natimortalidade, descolamento prematuro da placenta e trabalho de parto prematuro.
RESULTADOS:
A média de idade das gestantes foi de 26,4±5,11 anos. Os valores de IP e IR das artérias uterinas para o primeiro (IP: 1,1±0,42 versus 1,53±0,59, p=0,002; IR: 0,55±0,09 versus 0.72±0.13, p=0,000, respectivamente) e para o terceiro trimestre (IP: 0,77±0,31 versus 1,09±0,46, p=0,000; IR: 0,46±0,10 versus 0,60±0,14, p=0,010, respectivamente) foram significativamente maiores em pacientes com desfecho adverso da gravidez em relação às mulheres com desfecho normal. A combinação de IP e IR > percentil 95 e a presença de incisura bilateral apresentou sensibilidade e especificidade de 36,1 e 97%, respectivamente, no segundo trimestre e de 57,5 e 98,2% no terceiro trimestre.
CONCLUSÕES:
Com base no presente estudo, o Doppler das artérias uterinas parece ser ferramenta valiosa para a predição de uma variedade de desfechos adversos no segundo e terceiro trimestres de gestação.
Key-words Laser-doppler flowmetryPregnancy outcomePregnancy trimester, secondPregnancy trimester, thirdUltrasonography, dopplerUterine artery/ultrasonographySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article12-21-2020
Use of GnRH Analogues in the Reduction of Submucous Fibroid for Surgical Hysteroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Thayane Delazari Corrêa
 ,
, - Isabela Maciel Caetano
 ,
, - Pedro Henrique Tannure Saraiva
 ,
, - Maurício Bechara Noviello,
- Admário Silva Santos Filho

Views291

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleUse of GnRH Analogues in the Reduction of Submucous Fibroid for Surgical Hysteroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):649-658
- Thayane Delazari Corrêa
 ,
, - Isabela Maciel Caetano
 ,
, - Pedro Henrique Tannure Saraiva
 ,
, - Maurício Bechara Noviello,
- Admário Silva Santos Filho

Views291See moreAbstract
Objective
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues (GnRH-a) have been used preoperatively before hysteroscopic myomectomy to decrease the size and vascularization of the myomas, but evidence to support this practice is weak. Our objective was to analyze the use of GnRH-a in the reduction of submucous fibroid as a facilitator for surgical hysteroscopy from published clinical trials.
Data sources
Studies from electronic databases (Pubmed, Scielo, EMBASE, Scopus, PROSPERO), published between 1980 and December 2018. The keywords used were fibroid, GnRH analogue, submucous, histeroscopy, histeroscopic resection and their correspondents in Portuguese.
Study selection
The inclusion criteria were controlled trials that evaluated the GnRH-a treatment before hysteroscopic resection of submucous myomas. Four clinical trials were included in the meta-analysis.
Data collection
Two review authors extracted the data without modification of the original data, using the agreed form. We resolved discrepancies through discussion or, if required, we consulted a third person.
Data synthesis
The present meta-analysis included a total of 213 women and showed no statistically significant differences in the use of GnRH-a compared with the control group for complete resection of submucous myoma (relative risk [RR]: 0.94; 95%; confidence interval [CI]: 0.80-1.11); operative time (mean difference [MD]: – 3.81; 95%;CI : – 3.81-2.13); fluid absorption (MD: – 65.90; 95%;CI: – 9.75-2.13); or complications (RR 0.92; 95%;CI: 0.18-4.82).
Conclusion
The present review did not support the routine preoperative use of GnRH-a prior to hysteroscopic myomectomy. However, it is not possible to determine its inferiority when compared with the other methods due to the heterogeneity of existing studies and the small sample size.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Thayane Delazari Corrêa
-
Review Article04-11-2022
Doppler Ultrasound of the Umbilical Artery: Clinical Application
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):519-531
Views251

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleDoppler Ultrasound of the Umbilical Artery: Clinical Application
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):519-531
Views251See moreAbstract
Objective
To provide a survey of relevant literature on umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound use in clinical practice, technical considerations and limitations, and future perspectives.
Methods
Literature searches were conducted in PubMed and Medline, restricted to articles written in English. Additionally, the references of all analyzed studies were searched to obtain necessary information.
Results
The use of this technique as a routine surveillance method is only recommended for high-risk pregnancies with impaired placentation. Meta-analyses of randomized trials have established that obstetric management guided by umbilical artery Doppler findings can improve perinatal mortality and morbidity. The values of the indices of Umbilical artery Doppler decrease with advancing gestational age; however, a lack of consensus on reference ranges prevails.
Conclusion
Important clinical decisions are based on the information obtained with umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound. Future efforts in research are imperative to overcome the current limitations of the technique.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article03-14-2024
Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
- Vanessa Merjane
 ,
, - Douglas Marcel Puricelli Perin
 ,
, - Patrícia Martins Gomes El Bacha
 ,
, - Beatriz Medicis Maranhão Miranda
 ,
, - Almir Galvão Vieira Bitencourt
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Wagner Iared

Views392

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleBreast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo6
- Vanessa Merjane
 ,
, - Douglas Marcel Puricelli Perin
 ,
, - Patrícia Martins Gomes El Bacha
 ,
, - Beatriz Medicis Maranhão Miranda
 ,
, - Almir Galvão Vieira Bitencourt
 ,
, - Wagner Iared

Views392See moreAbstract
BI-RADS® is a standardization system for breast imaging reports and results created by the American College of Radiology to initially address the lack of uniformity in mammography reporting. The system consists of a lexicon of descriptors, a reporting structure with final categories and recommended management, and a structure for data collection and auditing. It is accepted worldwide by all specialties involved in the care of breast diseases. Its implementation is related to the Mammography Quality Standards Act initiative in the United States (1992) and breast cancer screening. After its initial creation in 1993, four additional editions were published in 1995, 1998, 2003 and 2013. It is adopted in several countries around the world and has been translated into 6 languages. Successful breast cancer screening programs in high-income countries can be attributed in part to the widespread use of BI-RADS®. This success led to the development of similar classification systems for other organs (e.g., lung, liver, thyroid, ovaries, colon). In 1998, the structured report model was adopted in Brazil. This article highlights the pioneering and successful role of BI-RADS®, created by ACR 30 years ago, on the eve of publishing its sixth edition, which has evolved into a comprehensive quality assurance tool for multiple imaging modalities. And, especially, it contextualizes the importance of recognizing how we are using BI-RADS® in Brazil, from its implementation to the present day, with a focus on breast cancer screening.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Vanessa Merjane
-
Review Article10-07-2022
The Effects of Hysterectomy on Urinary and Sexual Functions of Women with Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review
- Mariana Alves Firmeza
 ,
, - Camila Teixeira Moreira Vasconcelos
 ,
, - José Ananias Vasconcelos Neto
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo de Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Flávio Mendes Alves
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Natália Maria de Vasconcelos Oliveira

Views262

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleThe Effects of Hysterectomy on Urinary and Sexual Functions of Women with Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):790-796
- Mariana Alves Firmeza
 ,
, - Camila Teixeira Moreira Vasconcelos
 ,
, - José Ananias Vasconcelos Neto
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo de Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Flávio Mendes Alves
 ,
, - Natália Maria de Vasconcelos Oliveira

Views262See moreAbstract
Objective
This systematic review aims at describing the prevalence of urinary and sexual symptoms among women who underwent a hysterectomy for cervical cancer.
Methods
A systematic search in six electronic databases was performed, in September 2019, by two researchers. The text search was limited to the investigation of prevalence or occurrence of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) and sexual dysfunctions in women who underwent a hysterectomy for cervical cancer. For search strategies, specific combinations of terms were used.
Results
A total of 8 studies, published between 2010 and 2018, were included in the sample. The average age of the participants ranged from 40 to 56 years, and the dysfunctions predominantly investigated in the articles were urinary symptoms (n= 8). The rates of urinary incontinence due to radical abdominal hysterectomy ranged from 7 to 31%. The same dysfunction related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy varied from 25 to 35% and to laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy varied from 25 to 47%. Nocturia ranged from 13%, before treatment, to 30%, after radical hysterectomy. The prevalence rates of dyspareunia related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy and laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy ranged from 5 to 16% and 7 to 19% respectively. The difficulty in having orgasm was related to laparoscopic radical hysterectomy (10 to 14%) and laparoscopic nerve sparing radical hysterectomy (9 to 19%).
Conclusion
Urinary and sexual dysfunctions after radical hysterectomy to treat cervical cancer are frequent events. The main reported disorders were urinary incontinence and dyspareunia.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Mariana Alves Firmeza
-
Review Article07-10-2023
Technologies Applied to the Mental Health Care of Pregnant Women: A Systematic Literature Review
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
 ,
, - Júlia Magna da Silva Teixeira
 ,
, - Roberto José Gervásio Unger
 ,
, - Vivian Genaro Motti
 ,
, - Giovanni Marcos Lovisi
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Fabiane Rossi dos Santos Grincenkov

Views261

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleTechnologies Applied to the Mental Health Care of Pregnant Women: A Systematic Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):149-159
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
 ,
, - Júlia Magna da Silva Teixeira
 ,
, - Roberto José Gervásio Unger
 ,
, - Vivian Genaro Motti
 ,
, - Giovanni Marcos Lovisi
 ,
, - Fabiane Rossi dos Santos Grincenkov

Views261See moreAbstract
Objective:
This article aims to review the literature regarding the use of technologies to promote mental health for pregnant women. We seek to: understand the strategies that pregnant women use for mental health care. Also, we investigate the existence of scientific evidence that validates such practices.
Methods:
This study follows the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews. We analyze 27 studies published between 2012 and 2019. We include publications in Portuguese, English, and Spanish.
Results:
The results revealed several different possibilities to use technology, including the use of text messages and mobile applications on smartphones. Mobile applications are the most commonly used approaches (22.5%). Regarding the strategies used, cognitive-behavioral approaches, including mood checks, relaxation exercises, and psychoeducation comprised 44.12% of the content.
Conclusion:
There is a need for further investigation and research and development efforts in this field to better understand the possibilities of intervention in mental health in the digital age.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 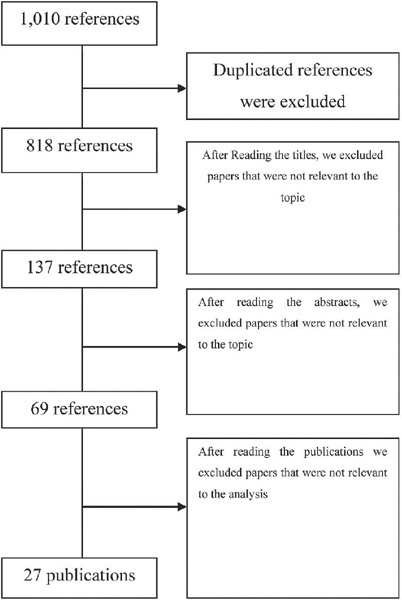
- Laís Lage de Carvalho
-
Letter to the Editor04-09-2024
Letter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
Abstract
Letter to the EditorLetter to Editor: “Combined aerobic and strength training improves dynamic stability and can prevent against static stability decline in postmenopausal women: A randomized clinical trial”
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo26
Views391Dear Editor,First and foremost, we express our gratitude towards the authors for their clear and concise description of the positive effects of aerobic and strength training on dynamic stability.() Additionally, their ability to provide a focused and informative introduction section is commendable. The study piqued our interest in further exploring the benefits of aerobic and […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article03-11-2022
Exercise and Physical Activity Levels and Associated Factors Among High-Risk Pregnant Women
- Larissa Antunes Miranda
 ,
, - Anna Caroline Ribeiro de Moura
 ,
, - Karina Tamy Kasawara
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Mayle Andrade Moreira
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Simony Lira do Nascimento

Views270

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleExercise and Physical Activity Levels and Associated Factors Among High-Risk Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):360-368
- Larissa Antunes Miranda
 ,
, - Anna Caroline Ribeiro de Moura
 ,
, - Karina Tamy Kasawara
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Mayle Andrade Moreira
 ,
, - Simony Lira do Nascimento

Views270See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the levels of physical activity and exercise practice, and examine the associated maternal characteristics; as well as the anxiety levels of high-risk pregnant women.
Methods
A cross-sectional study conducted with pregnant women at a High-risk Prenatal Clinic (HRPC) in a tertiary maternity. Pregnant women of 18 to 40-years-old, with a single fetus, and with gestational age up to 38 weeks were included. The level of physical activity and exercise practice of the study’s participants were investigated using the Pregnancy Physical Activity Questionnaire (PPAQ). Maternal sociodemographic, anthropometric, and medical data were investigated using a specific form. For anxiety levels, the short version of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) was applied. We used the Student t-test, chi-square test, odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) and multiple logistic regression. The significance level was 5%.
Results
Among the 109 pregnant women included, 82 (75.2%) were classified as sedentary/little active. The higher energy expenditure were for domestic activities (133.81±81.84 METs), followed by work-related activities (40.77±84.71 METs). Only 19.3% women exercised during pregnancy (4.76±12.47 METs), with slow walking being the most reported exercise. A higher level of education was the most important factor associated with women being moderately or vigorously active (OR=29.8; 95% CI 4.9-117.8). Nulliparity (OR=3.1; 95% CI 1.0-9.1), low levels of anxiety (OR=3.6; 95% CI 1.2-10.7), and unemployment (OR=4.8; 95% CI 1.1-19.6) were associated with the practice of exercise during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Most women with high-risk pregnancies exhibited a sedentary pattern, with low prevalence of physical exercise practice. Recognizing factors that hinder the adoption of a more physically active lifestyle is essential for an individualized guidance regarding exercise during pregnancy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Larissa Antunes Miranda
-
Original Article04-08-2022
Prevalence of Premenstrual Syndrome and Associated Factors Among Academics of a University in Midwest Brazil
- Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
 ,
, - Fernanda Rassi Alvarenga
 ,
, - Marcelo Ramos
 ,
, - Débora Luiza Franken
 ,
, - Juvenal Soares Dias da Costa
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Vera Maria Vieira Paniz

Views341

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of Premenstrual Syndrome and Associated Factors Among Academics of a University in Midwest Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):133-141
- Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
 ,
, - Fernanda Rassi Alvarenga
 ,
, - Marcelo Ramos
 ,
, - Débora Luiza Franken
 ,
, - Juvenal Soares Dias da Costa
 ,
, - Marcos Pascoal Pattussi
 ,
, - Vera Maria Vieira Paniz

Views341Abstract
Objective
To investigate the prevalence of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) in university students, the factors associated with PMS, the most prevalent symptoms, and the interference of symptoms in academic, family, social, and work activities.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 1,115 university students aged ≥ 18 years from the University of Rio Verde, Goiás. Premenstrual syndrome and PMDD were identified using the Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool. Associations with sociodemographic, behavioral, reproductive, nutritional, and health factors were investigated using the Poisson regression.
Results
The prevalence of PMS was 46.9% (95% confidence interval [CI] 44.0-49.8), and of PMDD, 11.1% (95% CI 9.3-13.0). The most prevalent symptoms were physical, such as breast tenderness, bloating, e weight gain (73%); followed by psychological ones such as overeating/food cravings, tearful/more sensitive to rejection (> 60%). More than 30% of the patients reported that the symptoms interfered in a moderate-tosevere way in their social and academic activities. After adjusted analysis, PMS was more prevalent in those who were attending the 1st/2nd semester of college (prevalence ratio [PR] 1.44; 95% CI 1.14-1.80), those who consumed alcohol in the last 30 days (PR 1.23; 95% CI 1.04-1.47), and those who had depression (PR 1.49; 95% CI 1.30-1.71).
Conclusion
Almost half of the university students had PMS and ~ 11%, PMDD. Physical symptoms were themost common and interfered in amoderate-to-severe way in various aspects of life. Attending the first semesters, consuming alcohol, and having depression were risk factors for PMS. The identification of risk factors for PMS is essential to prevent symptoms and reduce the impact of the syndrome.
Key-words Cross-sectional studiespremenstrual dysphoric disorderPremenstrual syndromeRisk factorsStudentsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ana Paula Rodrigues Rezende
-
Review Article07-22-2019
The Impact on Ovarian Reserve of Different Hemostasis Methods in Laparoscopic Cystectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Clara Micalli Ferruzzi Baracat
 ,
, - Helizabet Salomão Ayroza Abdalla-Ribeiro,
- Raquel Silveira da Cunha Araujo,
- Wanderley Marques Bernando,
- Paulo Ayroza Ribeiro
Views230

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleThe Impact on Ovarian Reserve of Different Hemostasis Methods in Laparoscopic Cystectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(6):400-408
- Clara Micalli Ferruzzi Baracat
 ,
, - Helizabet Salomão Ayroza Abdalla-Ribeiro,
- Raquel Silveira da Cunha Araujo,
- Wanderley Marques Bernando,
- Paulo Ayroza Ribeiro
Views230See moreAbstract
Objective
The objective of this review was to analyze the impact on ovarian reserve of the different hemostatic methods used during laparoscopic cystectomy.
Data Sources
The studies were identified by searching electronic databases (MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane, LILACS) and scanning reference lists of articles.
Methods of Study Selection
We selected clinical trials that assessed the influence of hemostatic techniques on ovarian reserve in patients with ovarian cysts with benign sonographic appearance submitted to laparoscopic cystectomy by stripping technique. The included trials compared different laparoscopic hemostatic techniques: suture, bipolar electrocoagulation, ultrasonic energy and hemostatic sealants. The outcomes evaluated were level of serum anti-Mullerian hormone (AMH) and antral follicle count (AFC). The possibility of publication bias was evaluated by funnel plots.
Tabulation, Integration and Results
Twelve trials involving 1,047 patients were evaluated. Laparoscopic suturewas superior to bipolar coagulationwhen evaluating serum AMHand AFC, in the 1st, 3rd, 6th and 12thmonth after surgery. In the comparison between bipolar and hemostatic sealants, the results favored the use of hemostatic agents. The use of ultrasonic energy was not superior to the use of bipolar energy.
Conclusion
We recommend suture for hemostasis during laparoscopic cystectomy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Clara Micalli Ferruzzi Baracat
-
Original Article08-01-2016
HIV Prevalence among Pregnant Women in Brazil: A National Survey
- Gerson Fernando Mendes Pereira,
- Meritxell Sabidó,
- Alessandro Caruso,
- Silvano Barbosa de Oliveira,
- Fábio Mesquita, [ … ],
- Adele Schwartz Benzaken
Views219

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleHIV Prevalence among Pregnant Women in Brazil: A National Survey
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(8):391-398
- Gerson Fernando Mendes Pereira,
- Meritxell Sabidó,
- Alessandro Caruso,
- Silvano Barbosa de Oliveira,
- Fábio Mesquita,
- Adele Schwartz Benzaken
Views219See moreAbstract
Background
This study was conducted to determine the seroprevalence of HIV among pregnant women in Brazil and to describe HIV testing coverage and the uptake of antenatal care (ANC).
Methods
Between October 2010 and January 2012, a probability sample survey of parturient women aged 15-49 years who visited public hospital delivery services in Brazil was conducted. Data were collected from prenatal reports and hospital records. Dried blood spot (DNS) samples were collected and tested for HIV.We describe the agespecific prevalence of HIV infection and ANC uptake with respect to sociodemographic factors.
Results
Of the 36,713 included women, 35,444 (96.6%) were tested for HIV during delivery admission. The overall HIV prevalence was of 0.38% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.31-0.48), and it was highest in: the 30 to 39 year-old age group (0.60% [0.40- 0.88]), in the Southern region of Brazil (0.79% [0.59-1.04]), among women who had not completed primary (0.63% [0.30-1.31]) or secondary (0.67% [0.49-0.97]) school education, and among women who self-reported as Asian (0.94% [0.28-3.10]). The HIV testing coverage during prenatal care was of 86.6% for one test and of 38.2% for two tests. Overall, 98.5% of women attended at least 1 ANC visit, 90.4% attended at least 4 visits, 71% attended at least 6 visits, and 51.7% received ANC during the 1st trimester. HIV testing coverage and ANC uptake indicators increased with increasing age and education level of education, and were highest in the Southern region.
Conclusions
Brazil presents an HIV prevalence of less than 1% and almost universal coverage of ANC. However, gaps in HIV testing and ANC during the first trimester challenge the prevention of the vertical transmission of HIV. More efforts are needed to address regional and social disparities.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 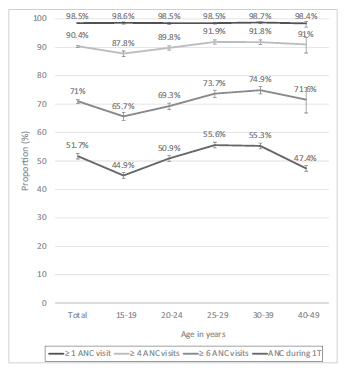
-
Review Article10-23-2020
SARS-CoV-2 and Pregnancy: A Review of the Facts
- Ricardo Mamber Czeresnia
 ,
, - Ayssa Teles Abrao Trad
 ,
, - Ingrid Schwach Werneck Britto
 ,
, - Romulo Negrini
 ,
, - Marcelo Luís Nomura
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Rodrigo Ruano

Views255

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleSARS-CoV-2 and Pregnancy: A Review of the Facts
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):562-568
- Ricardo Mamber Czeresnia
 ,
, - Ayssa Teles Abrao Trad
 ,
, - Ingrid Schwach Werneck Britto
 ,
, - Romulo Negrini
 ,
, - Marcelo Luís Nomura
 ,
, - Pedro Pires
 ,
, - Fabricio da Silva Costa
 ,
, - Roseli Mieko Yamamoto Nomura
 ,
, - Rodrigo Ruano

Views255See moreAbstract
Objective
The present comprehensive review aims to show the full extent of what is known to date and provide a more thorough view on the effects of SARS-CoV2 in pregnancy.
Methods
Between March 29 and May, 2020, the words COVID-19, SARS-CoV2, COVID- 19 and pregnancy, SARS-CoV2 and pregnancy, and SARS and pregnancy were searched in the PubMed and Google Scholar databases; the guidelines from well-known societies and institutions (Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists [RCOG], American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists [ACOG], International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology [ISUOG], Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics [FIGO]) were also included.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 outbreak resulted in a pandemic with > 3.3 million cases and 230 thousand deaths until May 2nd. It is caused by the SARS-CoV2 virus and may lead to severe pulmonary infection and multi-organ failure. Past experiences show that unique characteristics in pregnancy make pregnant women more susceptible to complications from viral infections. Yet, this has not been reported with this new virus. There are risk factors that seem to increase morbidity in pregnancy, such as obesity (body mass index [BMI] > 35), asthma and cardiovascular disease. Current reports describe an increased rate of pretermbirth and C-section. Vertical transmission


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ricardo Mamber Czeresnia
-
Original Article07-01-2016
Quality of Life in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome after a Program of Resistance Exercise Training
- Fabiene K. Picchi Ramos,
- Lúcia Alves da Silva Lara,
- Gislaine Satyko Kogure,
- Rafael Costa Silva,
- Rui Alberto Ferriani, [ … ],
- Rosana Maria dos Reis
Views278

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleQuality of Life in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome after a Program of Resistance Exercise Training
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(7):340-347
- Fabiene K. Picchi Ramos,
- Lúcia Alves da Silva Lara,
- Gislaine Satyko Kogure,
- Rafael Costa Silva,
- Rui Alberto Ferriani,
- Marcos Felipe Silva de Sá,
- Rosana Maria dos Reis
Views278See moreAbstract
Purpose
Aerobic exercises may improve quality of life (QoL) in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). However, there is no data on the effect of resistance exercise training (RET) programs on the QoL of women with PCOS. Thus, this study aimed to assess the effect of a 16-week RET program on QoL in PCOS women.
Methods
This 16-week case-control study enrolled 43 women with PCOS (PCOS group, PCOSG) and 51 healthy pre-menopausal controls aged 18 to 37 years (control group, CG). All women underwent a supervised RET program for 16 weeks, and were evaluated in two different occasions: week-0 (baseline), and week-16 (after RET). Quality of life was assessed using the 36-Item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36).
Results
Testosterone reduced significantly in both groups after RET (p < 0.01). The PCOSG had improvements in functional capacity at week-16 relative to week-0 (p = 0.02). The CG had significant improvements in vitality, social aspects, and mental health at week-16 relative to week-0 (p ≤ 0.01). There was a weak correlation between social aspects of the SF-36 domain and testosterone levels in PCOS women.
Conclusion
A 16-week RET program modestly improved QoL in women with PCOS.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article08-01-2018
Surgical Treatment for Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Letícia Maria de Oliveira,
- Marcia Maria Dias,
- Sérgio Brasileiro Martins,
- Jorge Milhem Haddad,
- Manoel João Batista Castello Girão, [ … ],
- Rodrigo de Aquino Castro
Views203

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleSurgical Treatment for Stress Urinary Incontinence in Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):477-490
- Letícia Maria de Oliveira,
- Marcia Maria Dias,
- Sérgio Brasileiro Martins,
- Jorge Milhem Haddad,
- Manoel João Batista Castello Girão,
- Rodrigo de Aquino Castro
Views203See moreAbstract
Objective
To compare surgical treatments for stress urinary incontinence in terms of efficiency and complications.
Data Sources
We searched the MEDLINE and COCHRANE databases using the terms stress urinary incontinence, surgical treatment for stress urinary incontinence and sling. Selection of Studies Forty-eight studies were selected, which amounted to a total of 6,881 patients with scores equal to or higher than 3 in the Jadad scale.
Data Collection
Each study was read by one of the authors, added to a standardized table and checked by a second author. We extracted data on intervention details, follow-up time, the results of treatment and adverse events.
Data Synthesis
Comparing retropubic versus transobturator slings, the former was superior for both objective (odds ratio [OR], 1.27; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.05-1.54) and subjective (OR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.02-1.48) cures. Between minislings versus other slings, there was a difference favoring other slings for subjective cure (OR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.39- 0.86). Between pubovaginal sling versus Burch surgery, there was a difference for both objective (OR, 2.04; 95% CI, 1.50-2.77) and subjective (OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.10-2.44) cures, favoring pubovaginal sling. Therewas no difference in the groups: midurethral slings versus Burch, pubovaginal sling versus midurethral slings, transobturator slings, minislings versus other slings (objective cure). Retropubic and pubovaginal slings are more retentionist. Retropubic slings have more bladder perforation, and transobturator slings, more leg and groin pain, neurological lesion and vaginal perforation.
Conclusion
Pubovaginal slings are superior to Burch colposuspension surgery but exhibit more retention. Retropubic slings are superior to transobturator slings, with more adverse events. Other slings are superior to minislings in the subjective aspect. There was no difference in the comparisons between midurethral slings versus Burch colposuspension surgery, pubovaginal versus midurethral slings, and inside-out versus outside-in transobturator slings.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 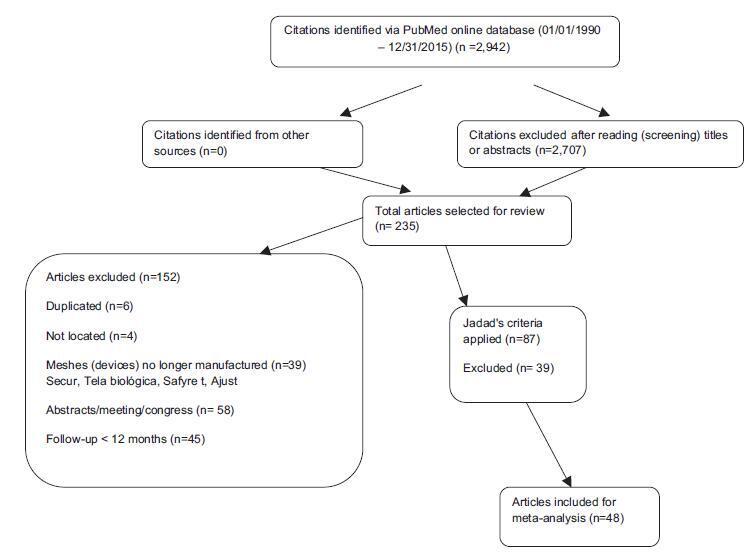
-
Original Article03-01-2018
The Burden of Indirect Causes of Maternal Morbidity and Mortality in the Processof Obstetric Transition: A Cross-Sectional Multicenter Study
- Jessica Fernandes Cirelli,
- Fernanda Garanhani Surita,
- Maria Laura Costa,
- Mary Angela Parpinelli,
- Samira Maerrawi Haddad, [ … ],
- José Guilherme Cecatti
Views203

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleThe Burden of Indirect Causes of Maternal Morbidity and Mortality in the Processof Obstetric Transition: A Cross-Sectional Multicenter Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(3):106-114
- Jessica Fernandes Cirelli,
- Fernanda Garanhani Surita,
- Maria Laura Costa,
- Mary Angela Parpinelli,
- Samira Maerrawi Haddad,
- José Guilherme Cecatti
Views203See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of this study is to evaluate the burden of indirect causes of maternal morbidity/mortality in Brazil.
Methods
Secondary analysis of a multicenter cross-sectional study conducted in 27 referral obstetric units within the Brazilian Network for Surveillance of Severe Maternal Morbidity.
Results
A total of 82,388 women were surveilled: 9,555 women with severe maternal morbidity were included, and 942 (9.9%) of them had indirect causes of morbidity/ mortality. There was an increased risk of higher severity among the indirect causes group, which presented 7.56 times increased risk of maternal death (prevalence ratio [PR]: 7.56; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 4.99-11.45). The main indirect causes of maternal death were H1N1 influenza, sepsis, cancer and cardiovascular disease. Non-public antenatal care (PR: 2.52; 95%CI: 1.70-3.74), diabetes (PR: 1.90; 95%CI: 1.24-2.90), neoplasia (PR: 1.98; 95%CI: 1.25-3.14), kidney diseases (PR: 1.99; 95%CI: 1.14-3.49), sickle cell anemia (PR: 2.50; 95%CI: 1.16-5.41) and drug addiction (PR: 1.98; 95%CI: 1.03-3.80) were independentlyassociatedwithworseresultsintheindirectcausesgroup.Someprocedures for the management of severity were more common for the indirect causes group.
Conclusion
Indirect causes were present in less than 10% of the overall cases, but they represented over 40% of maternal deaths in the current study. Indirect causes of maternal morbidity/mortality were also responsible for an increased risk of higher severity, and they were associated with worse maternal and perinatal outcomes. In middle-income countries there is a mix of indirect causes of maternal morbidity/ mortality that points to some advances in the scale of obstetric transition, but also reveals the fragility of health systems.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article06-27-2022
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Endometriosis, Psychological Based Intervention: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):295-303
Views366

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleCognitive Behavioral Therapy in Endometriosis, Psychological Based Intervention: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):295-303
Views366Abstract
Introduction
Endometriosis is an inflammatory disease that affects women of reproductive age, causing pain and the possibility of infertility. Endometriosis was associated to low life quality and research shows the impact of endometriosis in several areas of life, justifying how these patients are more likely to develop depression, anxiety, and stress.
Objective
The aim of the present systematic review was to explore the field of psychology in endometriosis, identifying studies that used the cognitive behavioral therapy technique as a treatment for endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain.
Methods
The keywords used were Endometriosis and Behavioral Therapy; Behavioral Disciplines and Activities; Cognitive Behavioral Therapy; Mental Health; Psychological Techniques; Psychology; Psychotherapy; Mental Health Services; and the search was performed in the following databases: PubMed/Medline, Scielo, Lilacs, and Capes. The study followed the PRISMA guidelines and all studies whose intervention strategy used was related to cognitive-behavioral therapy were considered.
Results
Of the 129 articles found, only 5 were selected, and it was possible to identify that the psychological intervention whose approach brought cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques promoted a decrease in the sensation of pain, improvements in the scores of depression and stress, and significant changes in aspects of quality of life such as vitality, physical and social functioning, emotional well-being, control, and autonomy.
Conclusion
Cognitive-behavioral therapy can be very promising to take care of the emotional side of those who have endometriosis However, the present systematic review highlights the need to develop more structured studies with consistent, clear and replicablemethods to reach a psychological intervention protocol for patients who live with this gynecological-physical-emotional condition.
Key-words Chronic pelvic paincognitive behavioral therapyEndometriosispsychological interventionQuality of lifesystematic reviewsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
