- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Resumos de Teses06-19-2002
Linfonodo Sentinela no Carcinoma Infiltrativo Inicial de Mama: Estudo de sua Localização e de sua Capacidade Preditiva em Relação ao Estado da Axila
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):69-69
Views38

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Resumos de TesesLinfonodo Sentinela no Carcinoma Infiltrativo Inicial de Mama: Estudo de sua Localização e de sua Capacidade Preditiva em Relação ao Estado da Axila
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):69-69
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100014
Views38Linfonodo Sentinela no Carcinoma Infiltrativo Inicial de Mama: Estudo de sua Localização e de sua Capacidade Preditiva em Relação ao Estado da Axila […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses06-19-2002
Avaliação da Função Ovariana Pós-histerectomia Total Abdominal em Mulheres no Menacme
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):69-69
Views76

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Resumos de TesesAvaliação da Função Ovariana Pós-histerectomia Total Abdominal em Mulheres no Menacme
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):69-69
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100013
Views76Avaliação da Função Ovariana Pós-histerectomia Total Abdominal em Mulheres no Menacme […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses06-19-2002
Efeitos do Tabagismo na Circulação Arterial Materna e Fetal: Estudo Através do Método Doppler
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):68-68
Views52

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Resumos de TesesEfeitos do Tabagismo na Circulação Arterial Materna e Fetal: Estudo Através do Método Doppler
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):68-68
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100012
Views52Efeitos do Tabagismo na Circulação Arterial Materna e Fetal: Estudo Através do Método Doppler […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses06-19-2002
Terapia com Raloxifeno na Pós-menopausa: Efeitos sobre o Sistema Hemostático
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):67-67
Views44PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 13212
- Abstract Views: 26
- Captures
- Readers: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Resumos de TesesTerapia com Raloxifeno na Pós-menopausa: Efeitos sobre o Sistema Hemostático
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):67-67
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100010
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 13212
- Abstract Views: 26
- Captures
- Readers: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Resumos de Teses06-19-2002
Efeitos da Metiltestosterona sobre a Sexualidade, Metabolismo Lipoproteíco e Hepático e Níveis de Testosterona em Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa em Uso de Reposição Estroprogestativa
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):67-68
Views53

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Resumos de TesesEfeitos da Metiltestosterona sobre a Sexualidade, Metabolismo Lipoproteíco e Hepático e Níveis de Testosterona em Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa em Uso de Reposição Estroprogestativa
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):67-68
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100011
Views53Efeitos da Metiltestosterona sobre a Sexualidade, Metabolismo Lipoproteíco e Hepático e Níveis de Testosterona em Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa em Uso de Reposição Estroprogestativa […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article06-19-2002
Knowledge and Opinion of Brazilian Researchers About Informed Consent
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):59-65
Views86

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleKnowledge and Opinion of Brazilian Researchers About Informed Consent
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):59-65
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100009
Views86Introduction: the Resolution 196/96 of the Conselho Nacional de Saúde (National Council of Health/Ministry of Health) presents the main Brazilian guidelines on research involving human subjects, including the content of written informed consent. Purpose: to present the knowledge and opinion of Brazilian researchers on the contents of Resolution 196/96, specifically related to the informed consent form. Subjects and methods: forty-six doctors responsible for the area of gynecology at Brazilian universities, four directors of research centers and 31 researchers who participated in a study related to fertility regulation during the 12 months preceding September, 2000. Subjects completed a self-reporting questionnaire. Data were analyzed by the chi² test. Results: most subjects declared that they knew the Resolution 196/96 and considered it adequate, although difficult to comply with; they considered that all studies should have an informed consent form, and knew that its content should guarantee confidentiality. More researchers than those responsible for gynecology department/directors knew that the informed consent form should be prepared by the principal investigator. Significantly more responsible for gynecology department/directors than researchers declared that subjects must always sign (or put their thumb print if they do not know how to write) on the informed consent form. Subjects declared that payment of expenses resulting from participation in a study must always be explained in the informed consent form. Conclusion: despite the wide dissemination of the Resolution 196/96, it was not known by all the researchers nor by all those responsible for gynecology departament/directors. The majority agreed with the contents required by the Resolution for the informed consent form.
Key-words Ethics CommitteeInformed consentSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article06-19-2002
p53 Protein Overexpression as a Prognostic Marker for Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia III Recurrence/Progression
- Isabel Cristina Chulvis do Val Guimarães,
- Gutemberg Leão de Almeida Filho,
- Maria da Glória de Carvalho,
- Christina Maeda Takiya,
- Aldo Franklin Ferreira Reis, [ … ],
- Maria Consuelo Gondim
Views160

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original Articlep53 Protein Overexpression as a Prognostic Marker for Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia III Recurrence/Progression
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):51-57
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100008
- Isabel Cristina Chulvis do Val Guimarães,
- Gutemberg Leão de Almeida Filho,
- Maria da Glória de Carvalho,
- Christina Maeda Takiya,
- Aldo Franklin Ferreira Reis,
- Paulo Marcos Valiante,
- Maria Consuelo Gondim
Views160See morePurpose: to evaluate p53 overexpression value in vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) III recurrence/progression. Methods: twenty patients with undifferentiated VIN III were selected and followed up every six months for four years and divided into two groups: fourteen without and six with recurrence/progression lesion. The recurrence/progression cases were distributed as follows: in three patients recurrence occurred only once; in two, twice, and only one progressed to squamous cancer. In both groups the site of vulvar lesion and p53 overexpression and immunostaining pattern were analyzed. A similar study was performed in recurrence/progression cases, besides the analysis of the time interval to occur the arise of recurrence/progression. Results: recurrence was observed in 25% of the cases and, in 5%, progression to carcinoma. The mean time interval for recurrence was 24.5 months. Multifocal location of the initial lesion was the predominant form (50%) in both groups. In the majority of the cases (87.5%) recurrence/progression occurred at the same site of the initial vulvar lesion. p53 overexpression was observed in 50% of the VIN III primary lesions and in 75% of the recurrence/progression cases. Conclusions: p53 overexpression seems to play an important role in VIN III pathogenesis and may predict the clinical course of the lesions. VIN III recurrence/progression has a tendency to occur in the same area of the initial lesion, suggesting the presence of molecular disturbance.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article06-19-2002
Endometrial Adenocarcinoma Frequency in a Hysteroscopy Outpatient Clinic: A Multicenter Study
- Francesco Antonio Viscomi,
- Sonia Maria Rolim Rosa Lima,
- José Mendes Aldrighi,
- Mauro Fernando Kürten Ihlenfeld
Views94PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 2
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 48963
- Abstract Views: 649
- Captures
- Readers: 10


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleEndometrial Adenocarcinoma Frequency in a Hysteroscopy Outpatient Clinic: A Multicenter Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):45-50
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100007
- Francesco Antonio Viscomi,
- Sonia Maria Rolim Rosa Lima,
- José Mendes Aldrighi,
- Mauro Fernando Kürten Ihlenfeld
Views94Purpose: to perform a census about the frequency of endometrial adenocarcinoma of women submitted to diagnostic hysteroscopy in five Brazilian hysteroscopic centers in São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, Salvador, Caxias do Sul and Porto Alegre. Methods: information was collected from standard questionnaires about the presence of endometrial adenocarcinoma, hysteroscopic staging and histologic type, in pre- and postmenopausal women. Results: among 6,466 hysteroscopic procedures, endometrial adenocarcinoma was present in 92 patients (1.4%), confirmed by histology in 79 (1.2%) cases. For the hysteroscopic diagnosis of endometrial adenocarcinoma confirmed by histology, a sensitivity of 85.9%, specificity of 100%, positive predictive value of 100% and negative predictive value of 98.6% were obtained. In the premenopausal group, among 3,845 hysteroscopic exams, endometrial cancer was present in 83 (3.2%) and confirmed by histology in 71 cases (2.7%). Conclusions: this study points out the importance of epidemiological methods in the diagnostic and prevention programs of endometrial cancer, specially in postmenopause, revealing the need for further epidemiological studies on endometrial adenocarcinoma diagnostis and prevention programs.
Key-words Cancer screeningEndometrial neoplasmsEndometrial neoplasms, epidemiologyEndometrial neoplasms, histologyHysteroscopySee morePlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 2
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 48963
- Abstract Views: 649
- Captures
- Readers: 10


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT05-16-2025
Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS4
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTMayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS4
Views47See moreKey points
•Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome (MRKH) is the leading cause of vaginal agenesis.
•It is characterized by primary amenorrhea with typical adrenarche and telarche and may be associated with congenital urological and skeletal conditions that should be investigated.
•Differential diagnoses include: vaginal obstructions (imperforate hymen, distal vaginal atresia, transverse vaginal septum), uterine obstructions (cervical atresia), and differences in sexual development (gonadal dysgenesis, complete androgen insensitivity and congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to CYP17 deficiency).
•Laboratory tests (testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone [FSH] and karyotype) and radiological tests (pelvic ultrasound and MRI) are necessary.
•Vaginal dilation is the first line of treatment with high success rates.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 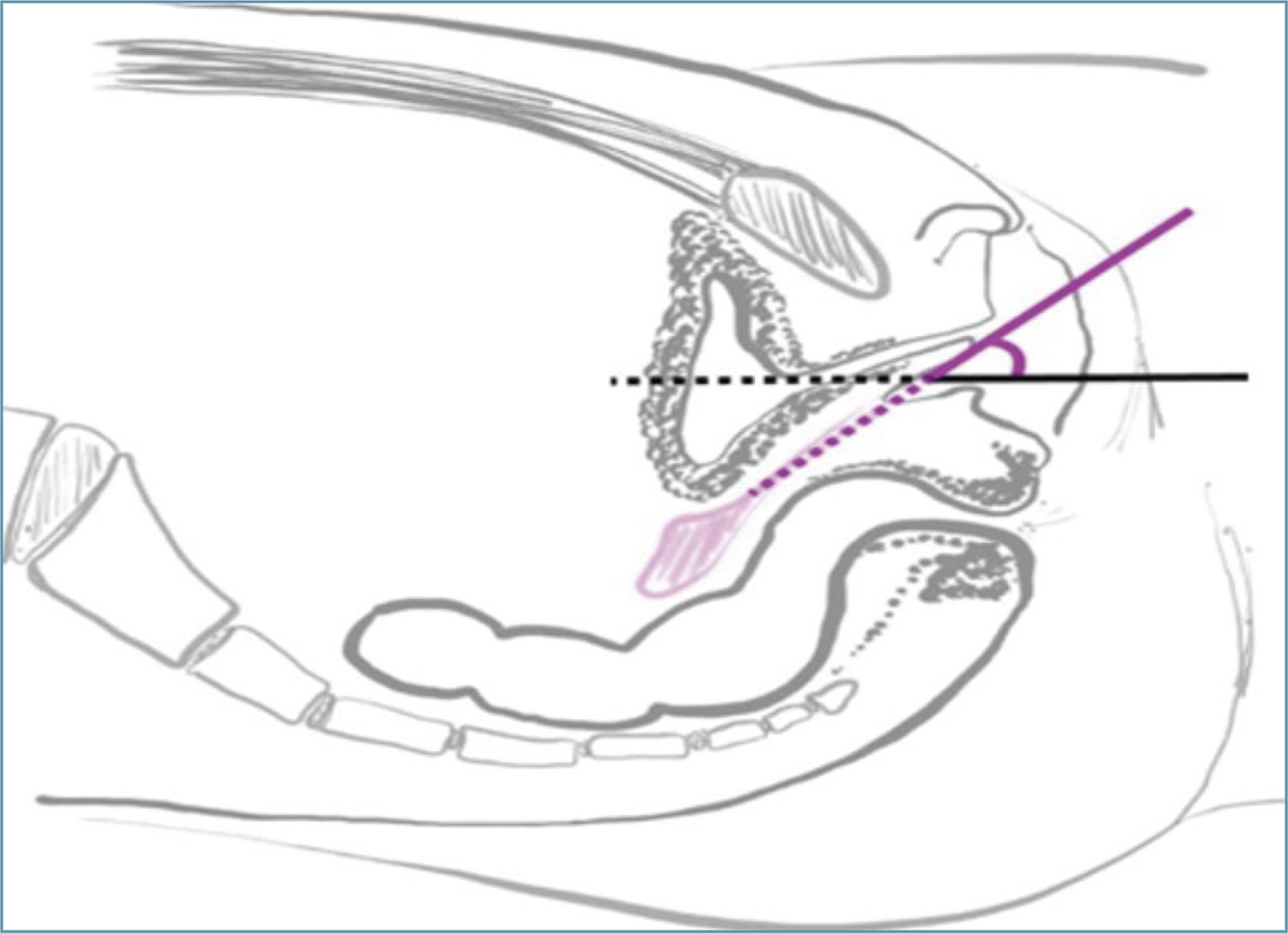
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Depression, anxiety, sexual function and quality of life in women with hyperprolactinemia
- Renan Massao Nakamura
 ,
, - Daniela Angerame Yela
 ,
, - Amanda Carvalho Santos
 ,
, - Beatriz Cipriano Ribas
 ,
, - Pedro Henrique Silva Rosa e
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto

Abstract
Original ArticleDepression, anxiety, sexual function and quality of life in women with hyperprolactinemia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo7
- Renan Massao Nakamura
 ,
, - Daniela Angerame Yela
 ,
, - Amanda Carvalho Santos
 ,
, - Beatriz Cipriano Ribas
 ,
, - Pedro Henrique Silva Rosa e
 ,
, - Bianca Netto Motta
 ,
, - Gabriela Pravatta Rezende
 ,
, - Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto

Views57Abstract
Objective:
To evaluate anxiety, depression, sexual function and quality of life in women with hyperprolactinemia.
Methods:
Cross-sectional study with 80 women divided into two groups: 30 women with hyperprolactinemia (Study Group) followed and treated at the endocrine gynecology outpatient clinic and 50 women without hyperprolactinemia, with regular menstrual cycles (Control Group) followed at the family planning outpatient clinic of the State University of Campinas from June 2021 to October 2022. Sociodemographic characteristics, quality of life (SF-36 Questionnaire), sexual function (Female Sexual Function Index Questionnaire), depression (Beck Depression Inventory) and anxiety (Beck Anxiety Scale) were evaluated in both groups. Categorical variables were described as absolute frequency and percentage; numerical variables as mean and standard deviation. Comparison of numerical variables between two groups was performed by Mann-Whitney test, while categorical were compared by Chi-Square or Fisher’s exact tests.
Results:
The mean age of women with hyperprolactinemia was 39.6±8.1 years and the Control Group was 31.2±9.5 years (p<0.001). There was no difference in anxiety scores (p=0.66), depression (p=0.08) and general sexual function (p=0.08) in both groups. However, women with hyperprolactinemia had lower scores in the domains of pain and arousal and worse functional capacity than Control Group (p<0.05).
Conclusion:
Women with hyperprolactinemia under treatment do not show any impairment in their anxiety, depression and sexual function when compared to women without hyperprolactinemia. However, analysis of quality of life showed that women with hyperprolactinemia have poor functional capacity.
Key-words AnxietyDepressionHyperpituitarismHyperprolactinemiaQuality of lifesexual functionsurveys and questionnairesSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Renan Massao Nakamura
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Hysterectomy rates per resident in final year of training in teaching hospitals: an ecologic study
- Luiza Nestori Chiozzotto
 ,
, - Nino José Wilson Moterani Júnior
 ,
, - Laura Bresciani Bento Gonçalves Moterani
 ,
, - Vinicius César Moterani
 ,
, - Francisco José Candido dos Reis

Abstract
Original ArticleHysterectomy rates per resident in final year of training in teaching hospitals: an ecologic study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo24
- Luiza Nestori Chiozzotto
 ,
, - Nino José Wilson Moterani Júnior
 ,
, - Laura Bresciani Bento Gonçalves Moterani
 ,
, - Vinicius César Moterani
 ,
, - Francisco José Candido dos Reis

Views98Abstract
Objective:
Analyze the hysterectomy rates per resident in graduation year in teaching hospitals in the state of São Paulo (Brazil).
Methods:
We selected teaching hospitals in the state of São Paulo and gathered information from two public databases to estimate the hysterectomy rates per resident in their final year of training between 2009 and 2019.
Results:
Between 2009 and 2019, there was a 37.5% increase in the number of residents in their final year of training, a 4.31% increase in the number of hysterectomies, and a drop in the hysterectomy rates per resident of 24.1%. The reduction of the rate of hysterectomy per resident was more pronounced for vaginal route (46.4%) followed by abdominal route (23.3%). The ratio of laparoscopic hysterectomy per resident increased 264% during the period, however, this route was used in only 7% of the surgeries in 2019.
Conclusions:
The hysterectomy rates per resident in their final year of training showed a notable reduction. This trend, particularly pronounced in vaginal and abdominal routes, signals a shift towards minimally invasive techniques.
Key-words Clinical competenceEducation, medicalHospitals, teachingHysterectomylearning curveMedical staff, hospitalPhysiciansStudents, medicalSurgical procedures, operativeSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 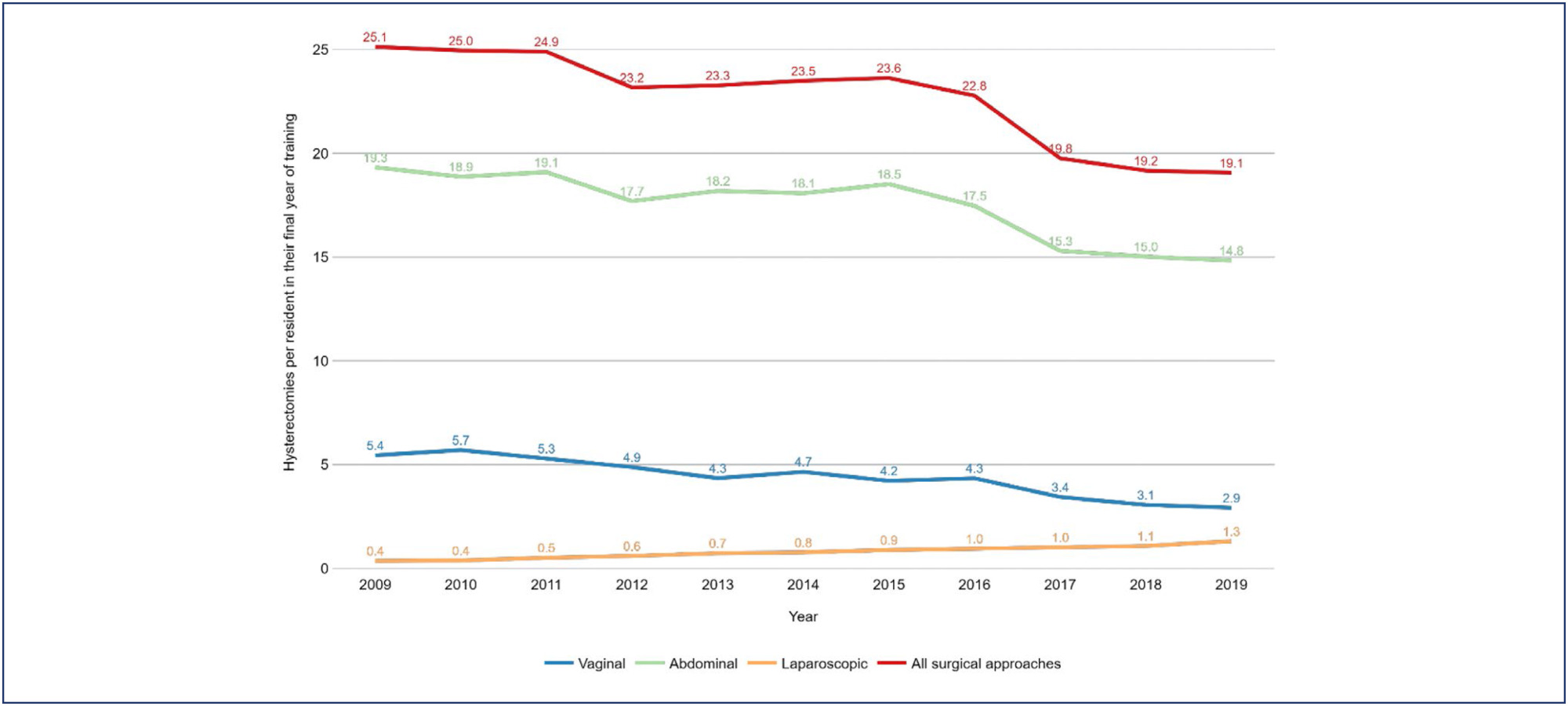
- Luiza Nestori Chiozzotto
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Prevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome among women with recurrent pregnancy loss: a cohort study
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Daniel Dias Ribeiro
 ,
, - Janaína Campos Senra
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos dos Reis

Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome among women with recurrent pregnancy loss: a cohort study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo23
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Daniel Dias Ribeiro
 ,
, - Janaína Campos Senra
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos dos Reis

Views89Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) among women experiencing recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL).
Methods:
A cross-sectional was conducted, reviewing the medical records of 134 women with a history of two or more miscarriages, treated between January 2014 and May 2024 at a tertiary university center in Belo Horizonte, Brazil. APS screening was performed by assessing anticardiolipin (IgG and IgM), lupus anticoagulant, and anti-β2-glycoprotein-1 (IgG and IgM) antibodies, based on Sapporo criteria. All tests were performed during non-pregnant periods and at least 12 weeks after the last miscarriage.
Results:
The study included 134 women with a mean age of 33.8 ± 5.7 years. The number of prior miscarriages ranged from 2 to 11 per couple. Among the patients who presented the lupus anticoagulant, only two (1.49%) tested positive in two samples, as per revised Sapporo criteria. Considering IgG and IgM anticardiolipin antibodies, four patients (2.98%) tested positive in two samples according to old Sapporo criteria, with one patient having a positive IgG test in two samples, two having positive IgM in two samples and a single patient having both positive tests. None of the 56 patients tested positive for anti-β2-glycoprotein-1 antibodies in two samples.
Conclusion:
The prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies, in line with revised Sapporo criteria, is low among Brazilian women with recurrent pregnancy loss, consistent with recent studies in literature. Ensuring the appropriateness of diagnostic criteria is crucial to avoid unnecessary treatment with platelet anticoagulants and heparin in this population.
Key-words Abortion, habitualAbortion, spontaneousAntibodiesAnticardiolipinAntiphospholipid syndromePrevalenceThrombophiliaSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
-
Original Article04-30-2025
An assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
Abstract
Original ArticleAn assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
Views86Abstract
Objective:
In vitro, fertilization is the primary treatment method for infertility. Follicular fluid analysis is an approach used to optimize the results of assisted reproductive techniques. Oxidative stress represents the imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and their detoxification. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative Stress Index levels are the main oxidative stress markers. This study investigated the effects of oxidative stress markers on infertility etiology, embryo quality, and success of In vitro fertilization.
Methods:
Before enrolling in the ICSI-ET cycle, participants had their FSH and LH levels assessed on the second day of the cycle. The ovarian degrees of the participants were evaluated by transvaginal ultrasonography. Participants underwent controlled ovarian stimulation using the GnRH antagonist protocol. TV-USG and serial E2 measurements were performed at appropriate intervals to follow follicular development. Follicle sizes, quantity, and endometrial thickness were recorded. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative analyses were conducted using Rel Assay Diagnostics Assay Kits.
Results:
The average number of total oocytes in the participants was 10.25±6.66, and the average of mature M2 stage oocytes was 6.71±3.72. The average number of fertilized oocytes was 4.65±2.81. Fertilization rates were calculated as approximately 54.75±25.58%. A statistically significant positive correlation was found between embryo quality and serum Total Antioxidant Status levels (p=0.004). Similarly, a significant positive correlation was observed between embryo quality and follicular Total Antioxidant Status values (r = 0.42, p = 0.01).
Conclusion:
This study concluded that oxidative stress markers affect certain stages of the IVF treatment process.
Key-words AntioxidantsFertilization in vitroFollicular fluidInfertilityOocytesOxidantsOxidative stressSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 
-
Review Article04-30-2025
Letrozole and clomiphene versus letrozole alone for ovulation induction in women with PCOS: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Karine Eskandar
 ,
, - Juliana Almeida Oliveira
 ,
, - Sandro Augusto Ribeiro
 ,
, - Matheus Pedrotti Chavez
 ,
, - Ana Isabela de Araujo Zotti
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Andrea Mora de Marco Novellino

Abstract
Review ArticleLetrozole and clomiphene versus letrozole alone for ovulation induction in women with PCOS: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo21
- Karine Eskandar
 ,
, - Juliana Almeida Oliveira
 ,
, - Sandro Augusto Ribeiro
 ,
, - Matheus Pedrotti Chavez
 ,
, - Ana Isabela de Araujo Zotti
 ,
, - Yasmin Jardim Meirelles Dias
 ,
, - Andrea Mora de Marco Novellino

Views100Abstract
Objective:
We aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of letrozole and clomiphene versus letrozole alone for ovulation induction in patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
Data Sources:
We systematically searched EMBASE, PubMed, and Cochrane databases on October 31, 2024.
Study selection:
We included studies of women with PCOS treated with a combination of clomiphene and letrozole or letrozole alone to induce ovulation that reported any of the outcomes of interest, namely rate of mature follicles and ovulation, ovulation, pregnancy, miscarriages, endometrial thickness, and number of mature follicles.
Data collection:
We pooled odds ratios (OR) and mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) using a random effects model using R statistical software, version 4.2.1. Heterogeneity was assessed with I statistics, and a random effects model was used.
Data Synthesis:
Four RCTs and two observational studies comprising 592 patients were included. Combined therapy was associated with a higher rate of a mature follicle (OR 2.74; 95% CI 1.72-4.37; p< 0.001; I=0%) and ovulation (OR 2.55; 95% CI 1.57-4.12; p< 0.001; I=35.9%). The number of mature follicles, number of pregnancies, thickness of endometrial lining, and the incidence of adverse events, including headache, abdominal bloating, fatigue, back pain, breast discomfort, and night sweats, were similar between groups.
Conclusion:
In women with anovulatory infertility secondary to PCOS, letrozole and clomiphene citrate combined therapy was associated with improved mature follicle and ovulation rates, with a similar safety profile compared to letrozole alone. However, no significant impact was observed on pregnancy rates.
Key-words ClomipheneInfertility, femaleLetrozoleOvulationOvulation InductionPolycystic ovary syndromeSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 
- Karine Eskandar
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Incidence of small-for-gestational-age newborns in pregnant women with COVID-19
- Gustavo dos Santos Raupp
 ,
, - Renato Teixeira Souza
 ,
, - Maria Laura Costa
 ,
, - Jose Guilherme Cecatti
 ,
, - Annerose Barros
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Janete Vettorazzi

Abstract
Original ArticleIncidence of small-for-gestational-age newborns in pregnant women with COVID-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo20
- Gustavo dos Santos Raupp
 ,
, - Renato Teixeira Souza
 ,
, - Maria Laura Costa
 ,
, - Jose Guilherme Cecatti
 ,
, - Annerose Barros
 ,
, - Ellen Machado Arlindo
 ,
, - Edson Vieira Cunha Filho
 ,
, - Janete Vettorazzi

Views82Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to assess the incidence of small for gestational age (SGA) newborns in pregnant women infected with COVID-19 and examine the associated neonatal outcomes.
Methods:
This study involved a secondary analysis of the REBRACO Network, a prospective cohort study conducted in 15 maternity hospitals in Brazil before the introduction of COVID-19 vaccination (February 2020 to February 2021). Demographic data of pregnant women tested for COVID-19 were analyzed, and fetal outcomes were compared between women with positive and negative COVID-19 results who had SGA fetuses.
Results:
A total of 729 symptomatic pregnant women with COVID-19 were included in the study. However, there were 248 participants with missing information regarding childbirth or loss of follow-up, and 107 participants without confirmatory tests for COVID-19. Among the remaining participants, 198 had confirmed COVID-19 and 176 tested negative. The incidence of SGA among women with COVID-19 was 22.4%, whereas the incidence among women who tested negative for COVID-19 was 14.8%. SGA newborns born to COVID-19 positive pregnant women were 1.6 times more likely to experience adverse outcomes (such as prematurity, stillbirth, neonatal death, and admission to a neonatal ICU) compared to non-SGA newborns [OR = 1.655 (1.145 – 2.394); P=0.017]. In SGA newborns of pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection, mechanical ventilation use was found to be associated with the infection [OR = 0.692 (0.562 – 0.853); P=0.002].
Conclusion:
The higher incidence of SGA newborns and its stronger association with prematurity in pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection suggest that COVID-19 infection is a significant factor contributing to neonatal morbidity and mortality.
Key-words coronavirus infectionsCOVID-19Infant, newbornInfant, small for gestational agematernal healthPregnancy complicationsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 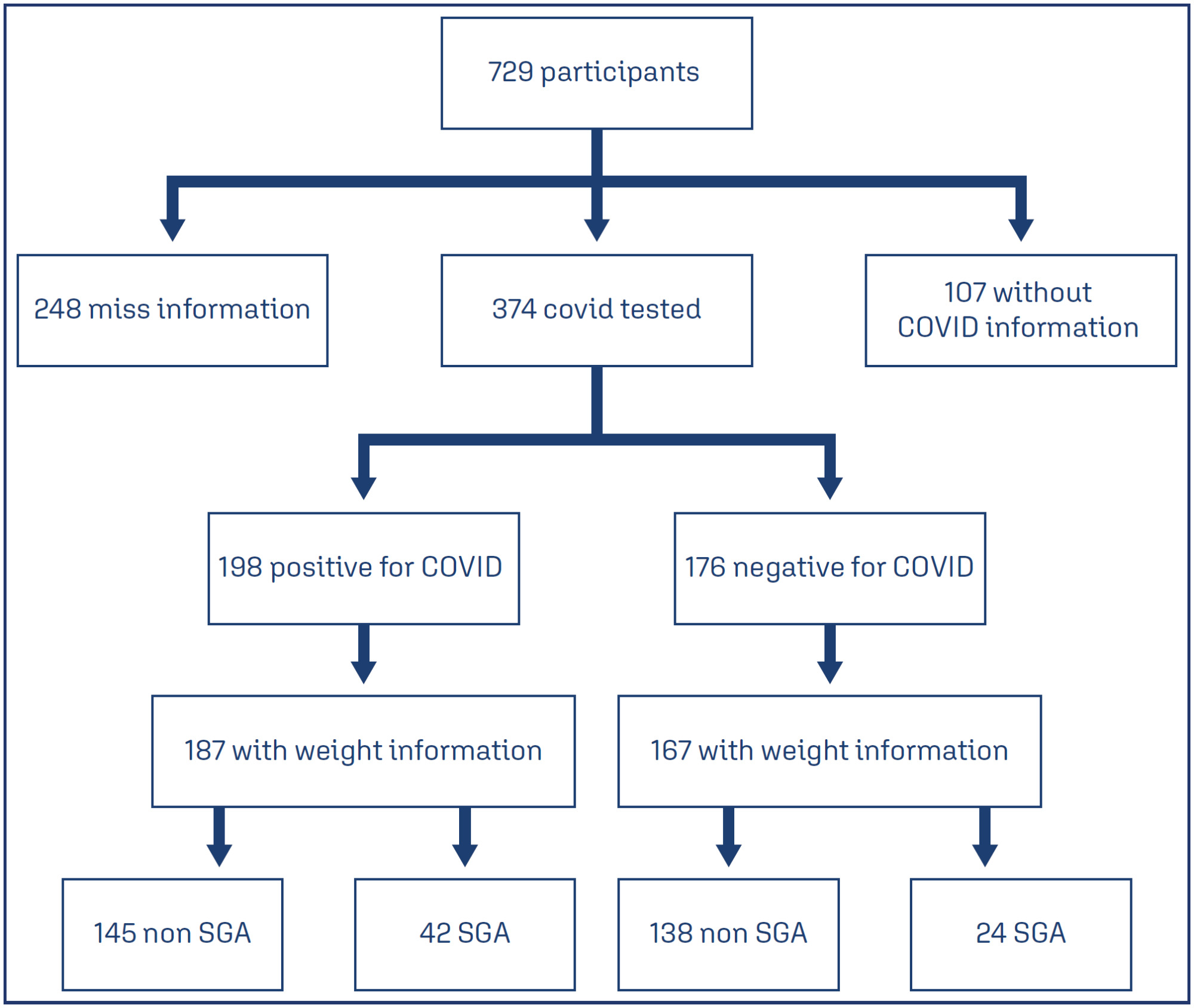
- Gustavo dos Santos Raupp
-
Review Article04-30-2025
Efficacy of tranexamic acid application in gynecology and obstetrics procedures: a umbrella review of systematic reviews of randomized trials
- Nicole Cristina Lottermann
 ,
, - Nathalia Luiza Andreazza
 ,
, - Matheus de Araújo Moura Cavalcante
 ,
, - Laura Andrade Fernandez
 ,
, - Carla Vitola Gonçalvez
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Linjie Zhang

Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy of tranexamic acid application in gynecology and obstetrics procedures: a umbrella review of systematic reviews of randomized trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo18
- Nicole Cristina Lottermann
 ,
, - Nathalia Luiza Andreazza
 ,
, - Matheus de Araújo Moura Cavalcante
 ,
, - Laura Andrade Fernandez
 ,
, - Carla Vitola Gonçalvez
 ,
, - Linjie Zhang

Views86Abstract
Objective:
This umbrella review aimed to synthesize evidence from systematic reviews of clinical trials on the efficacy of tranexamic acid in gynecology and obstetrics procedures.
Methods:
We searched Medline, Embase, SciELO and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews on March 11, 2024, using the term “tranexamic acid”. Four reviewers independently select studies and extract data. We assessed the quality of systematic review and the quality of evidence, using AMSTAR 2 and GRADE tools, respectively.
Results:
Of 651 systematic reviews identified, 16 reviews with 96663 patients were included. The surgical procedures were cesarean section, myomectomy, hysterectomy, and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia surgery. All reviews showed a statistically significant and clinically relevant reduction in intraoperative and post-procedure blood loss, associated with intravenous or topical use of tranexamic acid. Tranexamic acid resulted in a significant reduction in the need for blood transfusions and a less pronounced drop in postoperative hematocrit and hemoglobin levels in cesarean section. Several reviews addressed the same question, but the number of included trials varied substantially, which might indicate flaws in search and selection of studies of these reviews. The quality of systematic reviews was low or critically low, and the quality of evidence was moderate.
Conclusions:
This umbrella review shows that tranexamic acid can reduce blood loss and hemorrhage in gynecology and obstetrics procedures. High quality systematic reviews are still needed.
Key-words Blood transfusionCesarean sectionEfficacyGynecologic surgical procedureshematocritHemorrhageHysterectomyObstetric surgical proceduresTranexamic acidUterine cervical dysplasiauterine myomectomySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 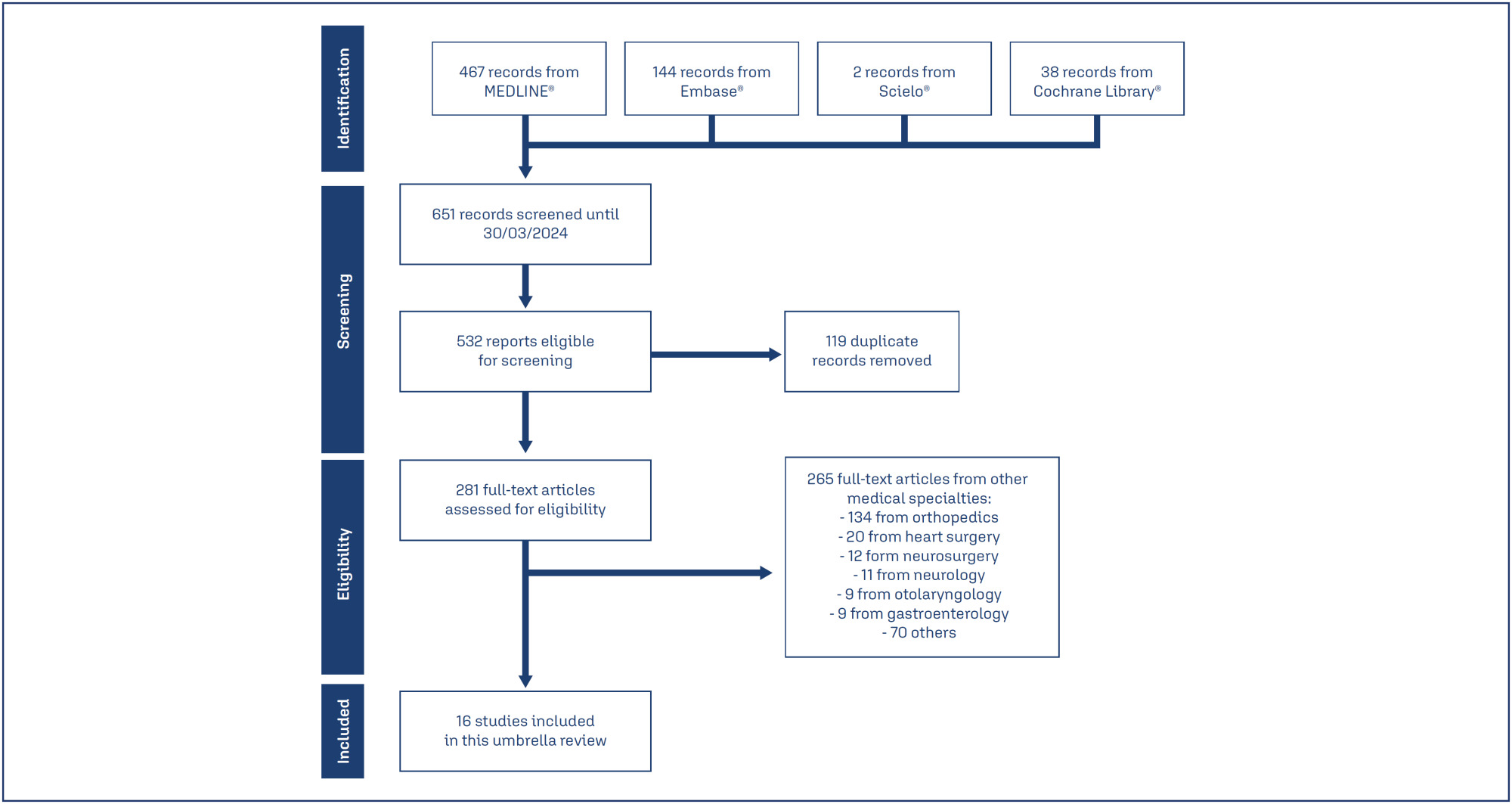
- Nicole Cristina Lottermann
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Assessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
- Ayse Cigdem Bayrak
 ,
, - Erdem Fadiloglu
 ,
, - Haticegul Tuncer
 ,
, - Edip Alptug Kir
 ,
, - Umutcan Kayikci
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Ozgur Deren

Abstract
Original ArticleAssessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo17
- Ayse Cigdem Bayrak
 ,
, - Erdem Fadiloglu
 ,
, - Haticegul Tuncer
 ,
, - Edip Alptug Kir
 ,
, - Umutcan Kayikci
 ,
, - Ozgur Deren

Views68Abstract
Objective:
This retrospective study aimed to investigate blood-based immune-inflammatory biomarkers (IIBs) in predicting neonatal outcomes in pregnancies with pregestational diabetes mellitus (PGDM).PIV[(neutrophil×platelet×monocyte)/lymphocyte)], SII (neutrophil×platelet/lymphocyte), and NLR neutrophil/lymphocyte) values were evaluated in all three trimesters, and their correlation with neonatal outcomes was examined.
Methods:
We included 82 cases of PGDM pregnancies delivered after 32 weeks. Maternal age, gravidity, parity, types of diabetes, and route of delivery were noted. For neonatal outcomes, we recorded gestational age at birth, birth weight percentile, existence of fetal growth restriction, LGA, neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) requirement, Apgar Score <7 at 1, 5, or 10 minutes, need for positive pressure ventilation (PPV), need for mechanical ventilation, hypoglycaemia, hyperbilirubinemia and the need for phototherapy. PIV, SII and NLR values were calculated in each trimester and their association with adverse neonatal outcomes was analyzed.
Results:
We could not detect any consistent and significant correlation between SII and PIV values and adverse neonatal outcomes for each trimester. There was a correlation between 3rd trimester NLR and adverse neonatal outcomes, including APGAR <7, the requirement for PPV and mechanical ventilation (p=0.056, 0.013 and 0.060, respectively).
Conclusion:
While SII and PIV values did not consistently correlate with adverse neonatal outcomes throughout each trimester in PGDM pregnancies, 3rd-trimester NLR showed a notable association with the requirement for PPV with statistical significance and with Apgar Score <7 and the requirement for mechanical ventilation without statistical significance. NLR in the third trimester may hold potential as a predictive marker for specific adverse neonatal outcomes in PGDM pregnancies, warranting further investigation.
Key-words biomarkersDiabetes mellitusGestational ageHypoglycemiaInfant, newbornIntensive care units, neonatalLymphocytesMaternal ageMonocytesNeuthrophilsPregancyPregnancy in diabetesRespiration, artificialSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ayse Cigdem Bayrak
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Effects of domestic violence on menopausal symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo16
Abstract
Original ArticleEffects of domestic violence on menopausal symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo16
Views76Abstract
Objective:
To investigate the association between lifetime experience of domestic violence and climacteric symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life in climacteric women in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted with 700 pre-, peri-, and postmenopausal women, recruited online via an anonymous questionnaire (REDCap platform). Women aged 40 to 65 years, residing in Rio Grande do Sul, and classified by the STRAW+10 criteria were included. Climacteric symptoms and sexual function were assessed using the 10-item Cervantes Scale (CS-10) and the 6-item Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI-6). Data were analyzed using SPSS version 18.0; quantitative data as median [IQR], qualitative as frequencies. Group comparisons used Kruskal-Wallis, Chi-Square, and Spearman’s correlation between violence against women (VAW) and/or climacteric groups on CS-10 or FSFI-6. Significance was set at 5%.
Results:
The median [IQR] age of pre- (46 [43 – 50] years), peri- (50 [47 – 52] years), and postmenopausal (55 [51 – 58] years) were different among groups. Prevalence rates of psychological (38.8%), sexual (34.9%), and physical (21.3%) violence were observed. Postmenopausal women showed the poorest outcomes. Premenopausal women experiencing violence had severe anxiety, while postmenopausal women reported feeling worthless. Various sexual dysfunctions were associated with violence, including low desire, lubrication issues, and sexual pain.
Conclusions:
Domestic violence was linked to worse climacteric symptoms, sexual function, and quality of life, particularly in postmenopausal women. These findings underscore the need for improved care and public policies to enhance safety and well-being among women of all ages.
Key-words AnxietyClimactericDomestic violenceMenopausePostmenopauseQuality of lifeSexualitysurveys and questionnairesViolence against womenSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 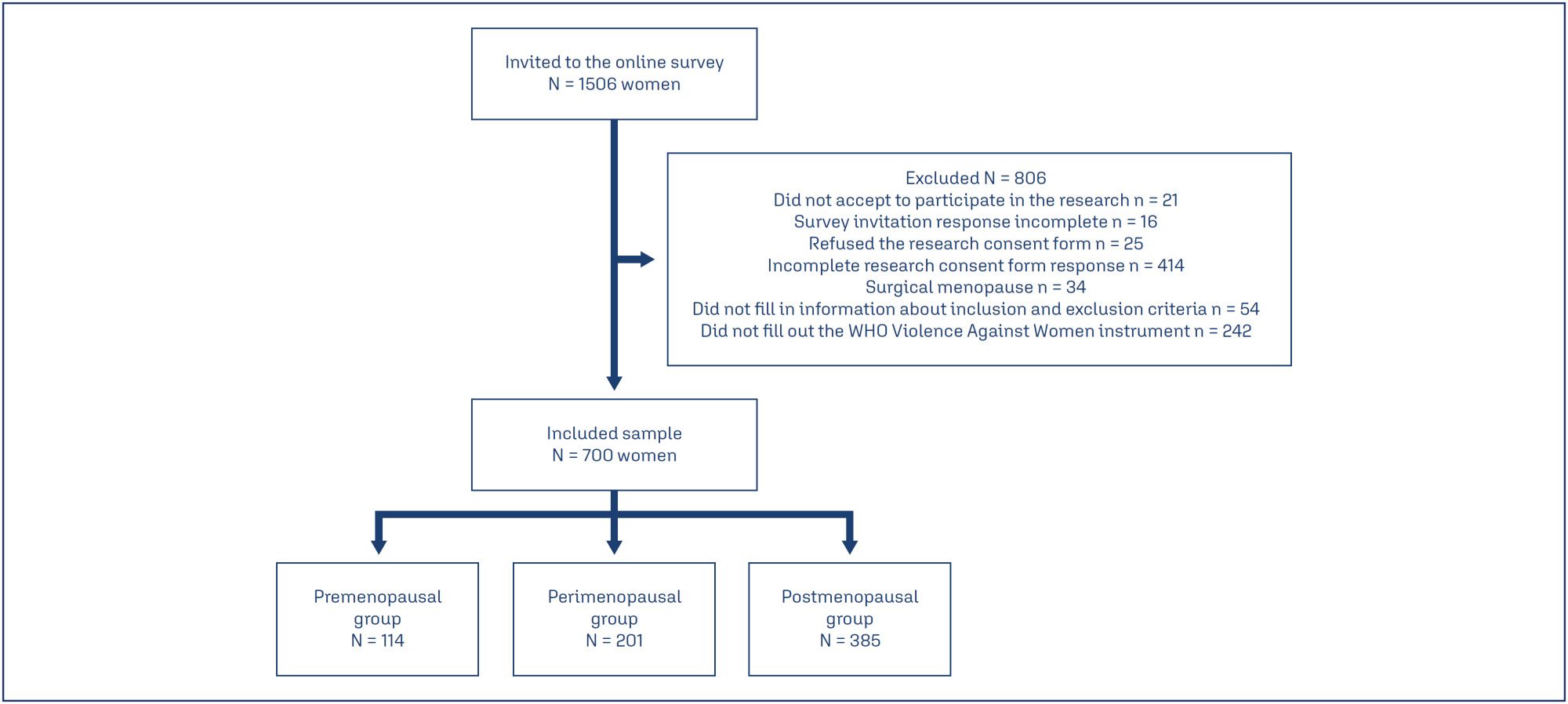
-
Original Article04-30-2025
The ımpact of demographic and obstetric factors on perception of traumatic birth and breastfeeding attitudes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo15
Abstract
Original ArticleThe ımpact of demographic and obstetric factors on perception of traumatic birth and breastfeeding attitudes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo15
Views49Abstract
Objective:
This study aims to examine the effects of sociodemographic and obstetric factors on traumatic birth perception and breastfeeding attitudes in primiparous mothers who have had a vaginal birth in the early postpartum period.
Methods:
The sample of the research, developed with a cross-sectional and correlational design, consisted of 252 women residing in a province in the Western Black Sea region of Türkiye. The data were obtained by employing a Personal Information Form, Traumatic Childbirth Perception Scale, and Breastfeeding Attitudes of The Evaluation Scale. Data analysis was conducted using the statistical programming language R (R version 4.3.3).
Results:
Women who were not employed, had a planned pregnancy, and did not experience health problems during pregnancy had higher mean breastfeeding attitude scores, and this difference was statistically significant. It was determined that a one-unit increase in gestational week led to an average increase of 1.926 units in breastfeeding attitude score, and a one-unit increase in Traumatic Childbirth Perception Scale score led to an average decrease of 0.110 units in breastfeeding attitude score. The mean traumatic childbirth perception scores of women living in urban areas were found to be lower than those living in villages or towns, and the difference was statistically significant.
Conclusion:
The research findings indicate that gestational age, perception of traumatic childbirth, and certain sociodemographic factors significantly affect breastfeeding attitudes. Additionally, mothers living in urban areas have a lower perception of traumatic childbirth. Therefore, individualized approaches to childbirth and breastfeeding support are crucial.
Key-words Breast feedingDelivery, obstetricParturitionperceptionPostpartum periodSociodemographic factorsStress disorders, post-traumaticSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 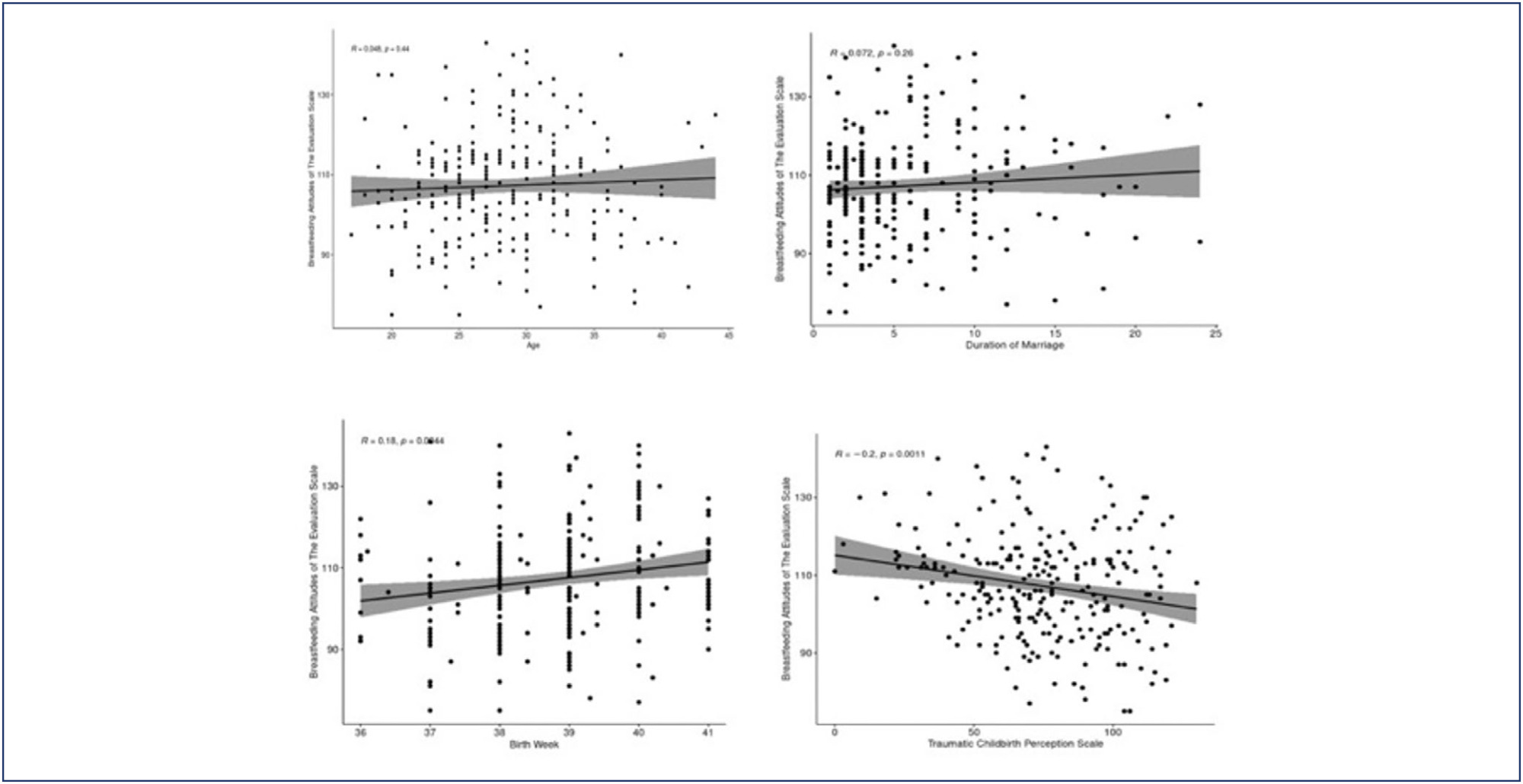
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Clinical and epidemiological profile of pregnant and postpartum women affected by COVID-19 who required respiratory support
- Carolina Maria Pires Cunha
 ,
, - Melania Maria Ramos Amorim
 ,
, - Julianna de Azevedo Guendler
 ,
, - Alex Sandro Rolland Souza
 ,
, - Leila Katz

Abstract
Original ArticleClinical and epidemiological profile of pregnant and postpartum women affected by COVID-19 who required respiratory support
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo14
- Carolina Maria Pires Cunha
 ,
, - Melania Maria Ramos Amorim
 ,
, - Julianna de Azevedo Guendler
 ,
, - Alex Sandro Rolland Souza
 ,
, - Leila Katz

Views50Abstract
Objective:
This study described the clinical and epidemiological profile and the management provided to pregnant and postpartum women with COVID-19 who required respiratory support.
Methods:
A descriptive study was conducted with pregnant and postpartum women with confirmed COVID-19 who received care between April 2020 and December 2021 in eight referral centers in northeastern Brazil. Statistical analysis was conducted using Epi-Info 7.2.5 and Medcalc, version 20.112.
Results:
Of the 720 patients admitted, 208 (32.7%) required respiratory support. Mean age of the participants was 28.9±7.1 years. Most (52.8%) were brown-skinned; 31.3% had little formal schooling; 41.1% had a personal income and 23.1% were married. Around half were referred from another hospital. Overall, 36.8% were obese and 36.9% were hypertensive. Criteria for severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) were present in 80.7% of cases. Overall, 151 patients (74.7%) required corticoids, and 150 (76.1%) were admitted to an intensive care unit. Non-invasive ventilation was needed in 89.4% of cases, with nasal catheters being the most common type (55.3% of cases). Invasive mechanical ventilation was necessary in 35.5% of cases and 91.6% had a cesarean section. Maternal near miss and death occurred in 24% and 12.9% of cases, respectively.
Conclusion:
Pregnant and postpartum women with COVID-19 who required respiratory support were predominantly brown-skinned, in the third trimester of pregnancy and had been referred from another hospital. The cesarean section rate was high; the presence of criteria for SARS was common and the rates of COVID-19-related maternal near miss and death were high.
Clinical Trials registry:
NCT04462367
Key-words Cesarian sectionCOVID-19Intensive care unitsNear miss, healthcareNoninvasive ventilationObesityPostpartum periodPregnancyPregnancy trimester, thirdRespiration, artificialSARS-CoV-2severe acute respiratory syndromeSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 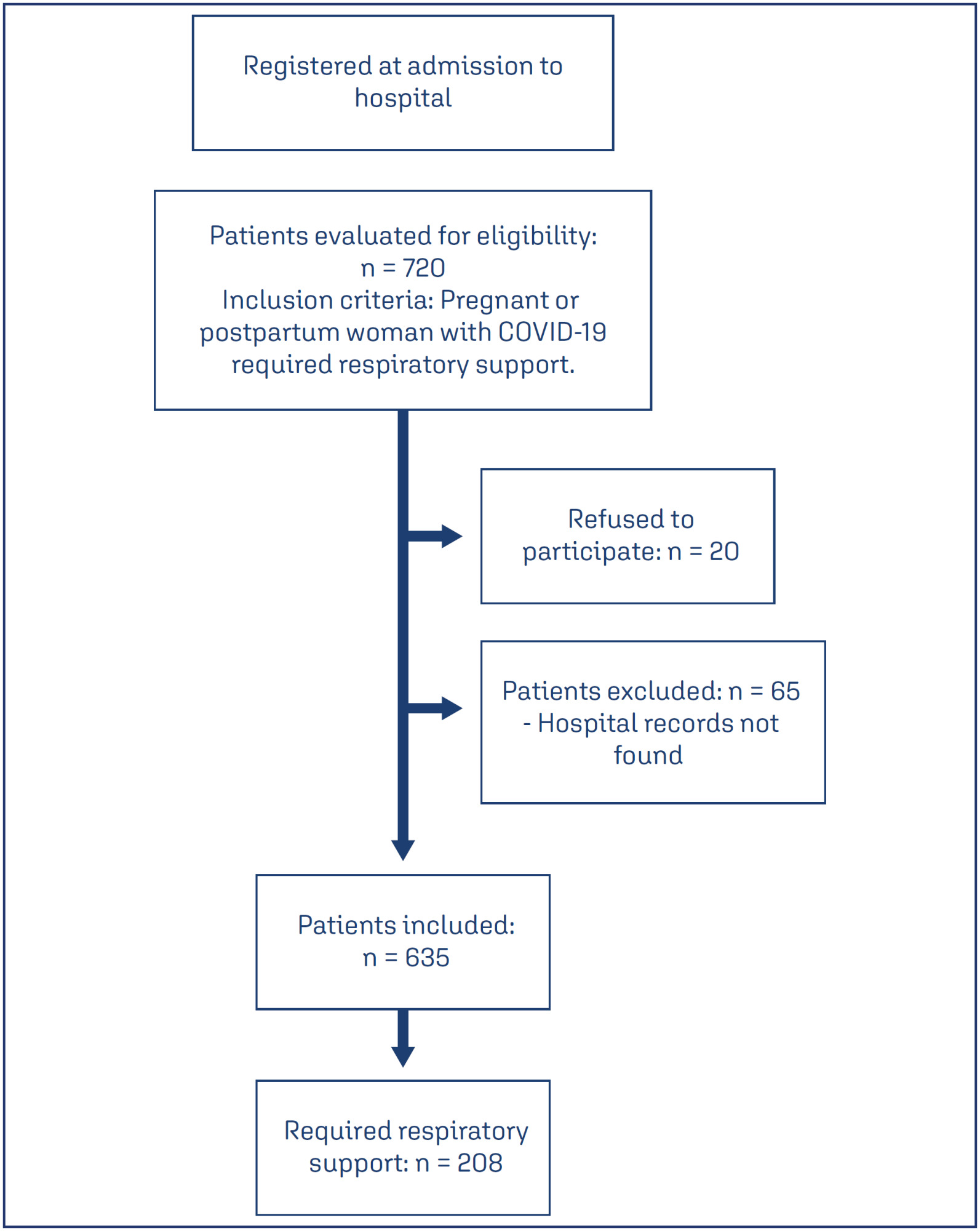
- Carolina Maria Pires Cunha
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Evaluation of pathological complete response rates in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy
- Gabriella Ferezini Oliveira de Sá
 ,
, - Pedro Vilar de Oliveira Villarim
 ,
, - Pedro Hortêncio Saboia da Escossia Melo
 ,
, - Ayane Cristine Alves Sarmento
 ,
, - Ana Katherine Gonçalves
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Cristina Rocha de Medeiros Miranda

Abstract
Original ArticleEvaluation of pathological complete response rates in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo13
- Gabriella Ferezini Oliveira de Sá
 ,
, - Pedro Vilar de Oliveira Villarim
 ,
, - Pedro Hortêncio Saboia da Escossia Melo
 ,
, - Ayane Cristine Alves Sarmento
 ,
, - Ana Katherine Gonçalves
 ,
, - Kleyton Santos de Medeiros
 ,
, - Cristina Rocha de Medeiros Miranda

Views60See moreAbstract
Objective:
This study aims to assess the rate of pathological complete response (pCR) in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy and to explore its correlation with clinical, molecular, and prognostic factors.
Methods:
We conducted this retrospective observational study at Liga Contra o Câncer, a major public oncology reference center in Northeast Brazil. We included patients diagnosed with breast cancer who initiated neoadjuvant therapy between June 2018 and June 2019. Patients with a history of recurrent breast cancer or those who did not undergo surgery were excluded. The primary outcome was the pCR rate, with secondary outcomes including Overall Survival (OS), Disease-Free Survival (DFS), mortality, and disease recurrence. Follow-up extended until August 2022. We performed multivariate Cox regression analysis to correlate outcomes with predetermined variables.
Results:
Of the 292 included patients, 63 (21.6%) achieved pCR. The mean follow-up duration was 42.8 months. Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed an association between pCR and the AC-TH regimen [OR = 2.4; 95%CI = 1.13 – 5.24; p=0.023], as well as between pCR and HER2-positive tumors [OR 2.49; 95% CI = 1.14 – 5.86; p=0.028]. Complete pathological response was associated with higher DFS [HR 0.33; 95%CI 0.13-0.86; p=0.024].
Conclusion:
Neoadjuvant therapy demonstrated significant efficacy in achieving pathological response in breast cancer patients. We observed a strong association between the AC-TH regimen, HER2-positive status, and pCR.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 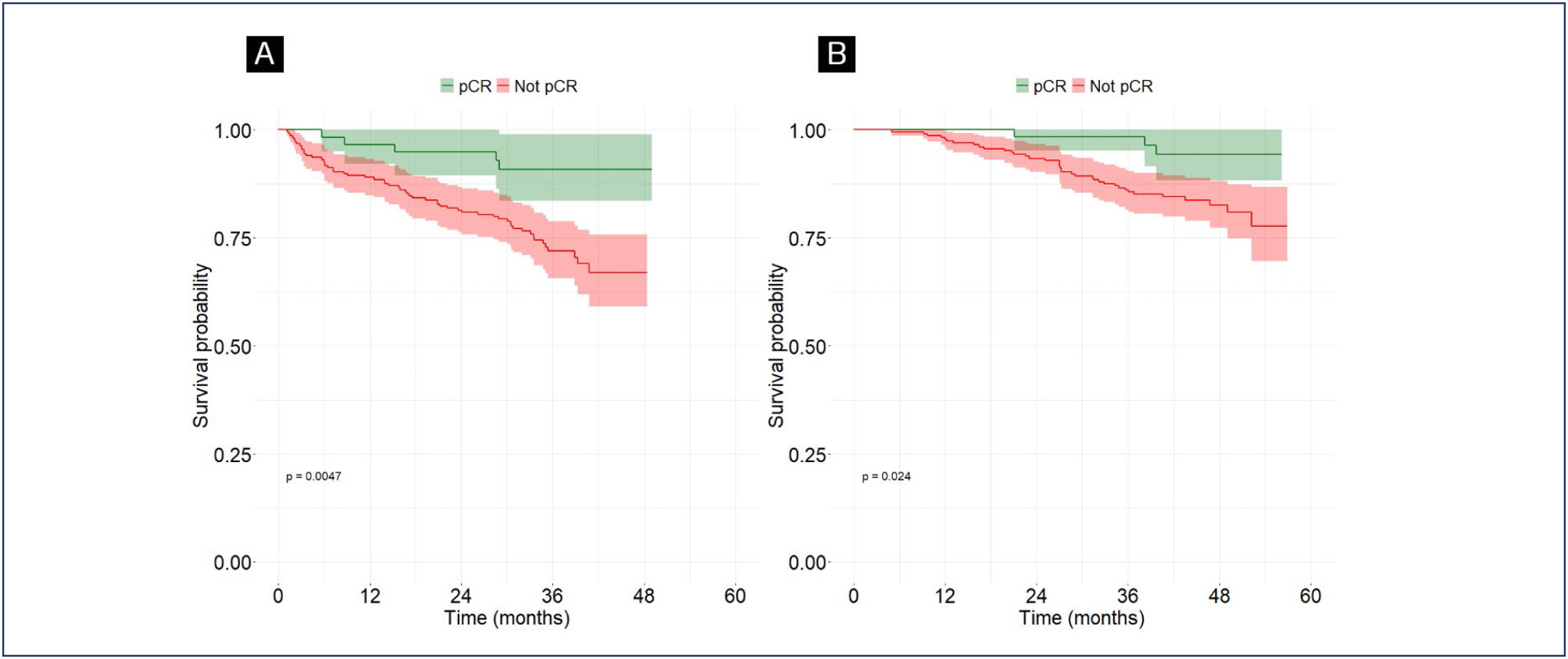
- Gabriella Ferezini Oliveira de Sá
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT03-28-2025
Follow-up of women after gynecological cancer treatment
- Agnaldo Lopes da Silva Filho
 ,
, - Mariana Seabra Leite Praça
 ,
, - Matheus Eduardo Soares Pinhati
 ,
, - Laura Guimarães Castro
 ,
, - Renato Moretti-Marques
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Eduardo Batista Cândido

Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTFollow-up of women after gynecological cancer treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS3
- Agnaldo Lopes da Silva Filho
 ,
, - Mariana Seabra Leite Praça
 ,
, - Matheus Eduardo Soares Pinhati
 ,
, - Laura Guimarães Castro
 ,
, - Renato Moretti-Marques
 ,
, - Angélica Nogueira-Rodrigues
 ,
, - Eduardo Batista Cândido

Views176See moreKey points
•The population of female cancer survivors has increased over the last few years, highlighting the importance of appropriate follow-up of these patients.
•The main objective of long-term follow-up for patients treated for cancer is the early detection of recurrences, whether local, lymph node or distant metastases.
•Symptom assessment and physical examination play an important role in the follow-up of patients treated for gynecological neoplasms.
•The use of laboratory or imaging tests to detect recurrence in asymptomatic patients should be based on evidence that it improves survival or provides less morbid treatments, also considering cost and availability.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Agnaldo Lopes da Silva Filho
-
Letter to the Editor03-18-2025
Comment on: Access and adequacy of antenatal care in during two phases of the COVID-19 pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo12
Abstract
Letter to the EditorComment on: Access and adequacy of antenatal care in during two phases of the COVID-19 pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo12
Views176The publication on “Access and adequacy of antenatal care in a city in Brazil during two phases of the COVID-19 pandemic.”() Is an interesting issue. This study investigated antenatal care consumption and appropriateness among postpartum caregivers at Florianópolis Hospital from 2020 to 2022, with an emphasis on socio-demographic characteristics and antenatal care. Although this study […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Letter to the Editor03-18-2025
Use of calcium during pregnancy: far beyond pre-eclampsia
- Melania Maria Ramos Amorim
 ,
, - Marina Amorim Albuquerque
 ,
, - Lucas Félix
 ,
, - Anna Catharina Carneiro da Cunha
 ,
, - Leila Katz

Abstract
Letter to the EditorUse of calcium during pregnancy: far beyond pre-eclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo11
- Melania Maria Ramos Amorim
 ,
, - Marina Amorim Albuquerque
 ,
, - Lucas Félix
 ,
, - Anna Catharina Carneiro da Cunha
 ,
, - Leila Katz

Views191Dear Editor,We read with interest the Editorial of the Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia (RBGO) in which Braga et al. present the initiative of the state of Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) for prediction and secondary prevention of pre-eclampsia.() The authors highlight universal calcium supplementation during pregnancy as a significant innovation, implemented for the first […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Melania Maria Ramos Amorim
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)

