-
Original Article
Access and adequacy of antenatal care in a city in Brazil during two phases of the COVID-19 pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo87
10-23-2024
Summary
Original ArticleAccess and adequacy of antenatal care in a city in Brazil during two phases of the COVID-19 pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo87
10-23-2024Views146Abstract
Objective:
To compare access and suitability of antenatal care between years 2020 and 2022 among postpartum individuals at a Hospital in Florianopolis, and evaluate factors associated with antenatal suitability.
Methods:
Observational, cross-sectional, and quantitative study carried out in 2022. Collected data were compared with the database of a previous similar study carried out in the same setting in 2020. Data were extracted from medical records and prenatal booklets, in addition to a face-to-face questionnaire. Adequacy was measured using the Carvalho and Novaes index and health access was qualitatively evaluated. Socio-demographic and antenatal variables were analyzed. A statistical significance level of 0.05 was considered. Open-ended questions were categorized for analysis.
Results:
395 postpartum individuals were included. Antenatal care was adequate for 48.6% in 2020 and 69.1% in 2022. Among the barriers to access, 56% reported difficulty in scheduling appointments and/or exams and 23% complained of reduced healthcare staff due to strikes, COVID-19, among others. Adequate antenatal care was associated with being pregnant in 2022, being referred to high-risk units (PNAR), and not reporting difficulties in access. Also, it was associated with twice the chance of investigation for gestational diabetes (GDM) and syphilis.
Conclusion:
The 2022 post-vaccination period showed higher antenatal adequacy. The main difficulty for postpartum individuals was scheduling appointments and/or exams. Having antenatal care in 2022, no reports of difficulty in access, and follow-up at a high-risk unit were associated with antenatal adequacy.
Key-words COVID-19Delivery of health careDiabetesGestationalpandemicsPostpartum periodPregnancyPrenatal caresurveys and questionnairesVaccinationSee more -
Review Article
Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination for Cancer Patients: Risk or Benefit?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):602-608
08-15-2022
Summary
Review ArticleCoronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccination for Cancer Patients: Risk or Benefit?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):602-608
08-15-2022Views114See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of the present study is to list the published clinical trials on coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccines, to describe the mechanism of action of the identified vaccines, and to identify protocols regarding safety, status, and prioritization of cancer patients for vaccination.
Methods
This is a systematic review with a limited literature search conducted by an information specialist; key resources such as PubMed and websites of major cancer organizations were searched. The main search terms were COVID-19, vaccination, cancer, and breast and gynecological cancers.
Results
Cancer patients infected with the new coronavirus are at high risk of complications and death, but we still know little about the risks and benefits of vaccination for COVID-19 in these patients. In an ideal scenario, all cancer patients should have their immunization status updated before beginning treatment, but this is not always possible.
Conclusion
Patients with breast or gynecological cancers who are receiving treatment or are in the 5-year posttreatment period should be included in the priority group for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccination.
-
Original Article
School-based HPV Vaccination: The Challenges in a Brazilian Initiative
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):926-931
01-24-2021
Summary
Original ArticleSchool-based HPV Vaccination: The Challenges in a Brazilian Initiative
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):926-931
01-24-2021Views194See moreAbstract
Objective
The present study assesses the implementation and the impact after 2 years of a school-based human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination program in a Brazilian city.
Methods
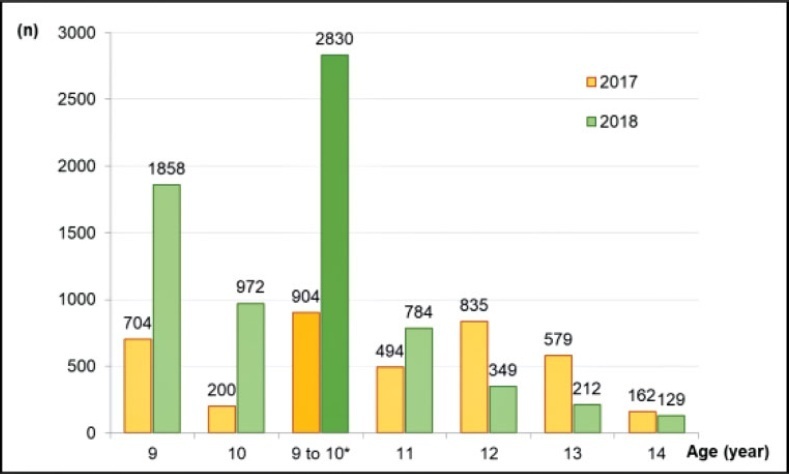
A prospective study assessing the implementation of the program, offering quadrivalent HPV vaccine in two annual doses to girls and boys aged from 9 to 10 years old. The program was started in the city of Indaiatuba, state of São Paulo, Brazil, in 2018, and had authorization from the National Immunization Program. The number of HPV vaccine first doses applied and the coverage in 2018 was calculated and compared to the year 2017. There were described events that have influenced the results.
Results
The program invited 4,878 children through schools (87.1% of the target population), and 7.5% refused vaccination. Several concurrent events required or competed for health professionals of the vaccination teams. The coverage of the first dose (between 9 and 10 years old) was 16.1% in 2017 and increased to 50.5% in 2018 (p < 0.0001). The first dose in all ages increased 78% in 2018 compared with 2017 (6,636/3,733). Competing demands over the program continued in 2019, and the first dose coverage dropped (26.9%). For 2020, a municipal law instituted school-based vaccination and the creation of dedicated teams for vaccination, and these strategies are waiting to be tested.
Conclusion
School-based annual HPV vaccination in children between 9 and 10 years old was feasible and increased vaccination coverage, regardless of gender, although the program was vulnerable to competing events.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Prevalence of hepatitis B in parturients and perinatal serologic profile
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(8):571-576
12-15-2003
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisPrevalence of hepatitis B in parturients and perinatal serologic profile
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(8):571-576
12-15-2003DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000800005
Views52See morePURPOSE: to estimate the prevalence of the hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in parturients admitted to the "Instituto Materno-Infantil de Pernambuco (IMIP)", Recife-PE, and to determine the serologic profile of the positive ones. METHODS: this is a prospective cross-sectional study where the VIDAS and VIDAS HBs systems were used for detection and confirmation of HBsAg, respectively. The parturients were randomly selected. In HBsAg+ patients, the other serologic markers were tested by the use of the AxSYM automated system. The newborn babies of HBsAg+ mothers were vaccinated with the Engerix B vaccine. RESULTS: among 1584 parturients, there were 9 (0.6%) HBsAg positive. None of them had anti-HBc IgM, thus they were all prevalent cases. In 1/9 (11.1%) of the HBsAg+ mothers, HBeAg was isolated and in 4/9 (44.4%), this antigen circulated along with its antibody, hence the importance of establishing the different magnitudes of risk of vertical transmission. Except for two newborn babies from a twin pregnancy (one with low birth weight), all presented seroconversion to anti-HBs with 3 doses of the vaccine. The premature twin babies showed seroconvertion only after the fourth dose of the vaccine. CONCLUSIONS: the prevalence of hepatitis B among parturients at IMIP is relatively low and all patients diagnosed had the chronic form of the infection.


