Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 08-04-2023;45(6):325-332
To determine the efficacy of Uterine Artery Embolization in patients with bleeding acquired uterine arteriovenous malformations (AVMs).
A prospective review of all patients who underwent Uterine Artery Embolization at our institution between July 2015 and April 2022 was performed. 225 patients were diagnosed with a uterine vascular malformation on doppler and corresponding MRI imaging. All patients underwent transcatheter embolization of the uterine arteries. Embolic agents in the 375 procedures included Histoacryl glue only (n = 326), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) particles and Histoacryl glue (n = 29), PVA particles (n = 5), Gelfoam (n = 5), coils (n = 4), PVA particles and coils (n = 3), Histoacryl glue and Gelfoam (n = 2), and Histoacryl glue and coils (n = 1).
A total of 375 embolization procedures were performed in 225 patients. 90 patients required repeat embolization for recurrence of bleeding. The technical success rate of embolization was 100%. The clinical success rate was 92%: bleeding was controlled in 222 of 225 patients and three patients underwent a hysterectomy. 60 of the 225 patients had uneventful intrauterine pregnancies carried to term. The 210 patients who underwent successful embolization had no recurrence of bleeding at a median follow-up of 53 months (range, 5-122 months) after treatment. 15 patients were eventually lost to follow-up. One minor complication (0.4%) of non-flow-limiting dissection of the internal iliac artery occurred.
Uterine Artery Embolization is a safe, effective, minimally invasive method to treat uterine AVMs with long-term efficacy, which can provide the preservation of fertility.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 06-20-2022;44(8):785-789
To assess the quality of recent meta-analyses reviewing the diagnostic utility of sentinel node biopsy in endometrial cancer.
With the MeSH terms endometrial neoplasms and sentinel lymph node biopsy, PubMed and Embase databases were searched on October 21, 2020, and again on November 10, 2021, with meta-analysis and publication date filters set to since 2015. The articles included were classified with the A Measurement Tool to Assess Systematic Reviews (AMSTAR 2) assessment tool.
The database searches found 17, 7 of which, after the screening, were selected for full review by the author, finally extracting six meta-analyzes for quality analysis. The rating with the AMSTAR 2 assessment tool found that overall confidence in their results was critically low.
This study found that the quality of recent meta-analyses on the utility of the staging of endometrial cancer with sentinel node biopsy, evaluated by the AMSTAR 2 assessment tool, is classified as critically low, and, therefore, these meta-analyses are not reliable in the summary of their studies.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 01-24-2022;43(12):911-918
Currently, there are up to three different classifications for diagnosing septate uterus. The interobserver agreement among them has been poorly assessed.
A total of 50 three-dimensional (3D) volumes of a nonconsecutive series of women with suspected uterine malformation were used. Two nonexpert examiners evaluated a single 3D volume of the uterus of each woman, blinded to each other. The following measurements were performed: indentation depth, indentation angle, uterine fundal wall thickness, external fundal indentation, and indentation-to-wall-thickness (I:WT) ratio. Each observer had to assign a diagnosis in each case, according to the three classification systems (ESHRE/ESGE, ASRM, and CUME). The interobserver agreement regarding the ESHRE/ESGE, ASRM, and CUME classifications was assessed using the Cohen weighted kappa index (k). Agreement regarding the three classifications (ASRM versus ESHRE/ESGE, ASRM versus CUME, ESHRE/ESGE versus CUME) was also assessed.
The interobserver agreement between the 2 nonexpert examiners was good for the ESHRE/ESGE (k = 0.74; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.55–0.92) and very good for the ASRM and CUME classification systems (k = 0.95; 95%CI: 0.86–1.00; and k = 0.91; 95%CI: 0.79–1.00, respectively). Agreement between the ESHRE/ESGE and ASRM classifications was moderate for both examiners. Agreement between the ESHRE/ESGE and CUME classifications was moderate for examiner 1 and good for examiner 2. Agreement between the ASRM and CUME classifications was good for both examiners.
The three classifications have good (ESHRE/ESGE) or very good (ASRM and CUME) interobserver agreement. Agreement between the ASRM and CUME classifications was higher than that for the ESHRE/ESGE and ASRM and ESHRE/ESGE and CUME classifications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 11-01-2017;39(11):640-644
Approximately 1 in every 76,000 pregnancies develops within a unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn.Müllerian uterus anomalies are often asymptomatic, thus, the diagnosis is a challenge, and it is usually made during the gestation or due to its complications, such as uterine rupture, pregnancy-induced hypertension, antepartum, postpartum bleeding and intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). In order to avoid unnecessary cesarean sections and the risks they involve, the physicians should consider the several approaches and for how long it is feasible to perform labor induction in suspected cases of pregnancy in a unicornuate uterus with a rudimentary horn, despite the rarity of the anomaly. This report describes a case of a unicornuate uterus in which a pregnancy developed in the non-communicating rudimentary horn and the consequences of the delayed diagnosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 04-01-2017;39(4):149-154
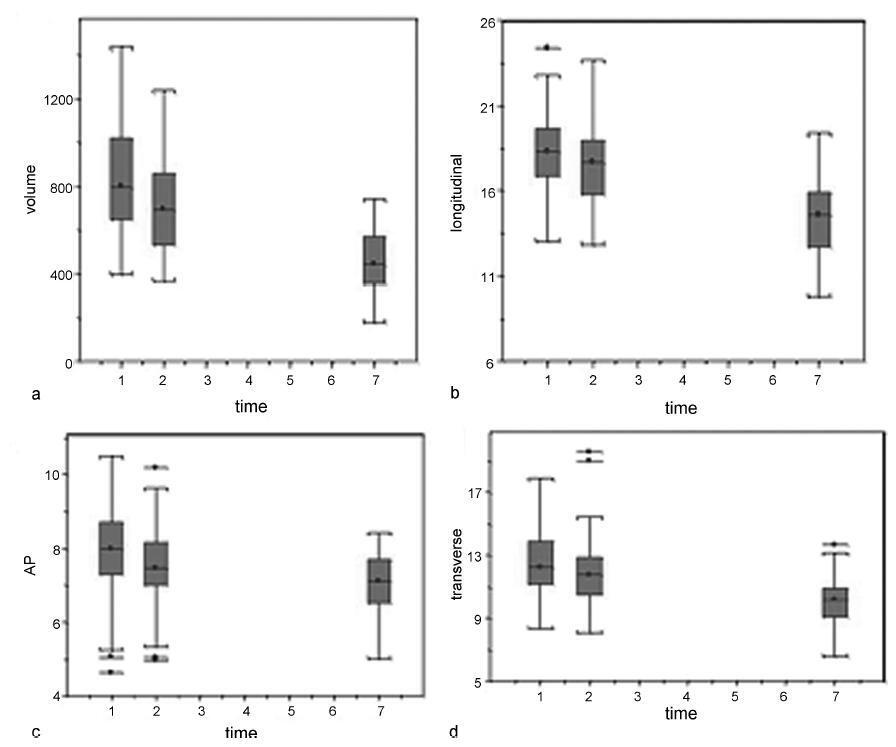
Our aim was to describe the changes observed by ultrasonography in uterine dimensions during the early puerperium among women who experienced an uncomplicated puerperium. Additionally, the influence of parity, mode of delivery, breastfeeding and birth weight on uterine involution was evaluated.
Ninety-one patients underwent an ultrasound examination on days 1 (D1), 2 (D2) and 7 (D7) of the postpartum period. The longitudinal, anteroposterior and transverse uterine diameters were measured, and the uterine volume was calculated by the formula: longitudinal diameter (LD) X anteroposterior diameter (APD) X transverse diameter (TD) X 0.45. The thickness and length of the uterine cavity were also measured.
The uterine volume and the LD, APD and TD decreased by 44.8%, 20.9%, 11.8% and 20.0% respectively. The uterine cavity thickness was reduced by 23%, and the length of the cavity was reduced by 27.2% on D7. Uterine involution was correlated inversely with parity when the day of the postpartum period was not taken into account (p= 0.01). However, when the uterine involution was correlated to parity separately, with D1, D2 or D3, no correlations were found. A significant difference occurred at D2, when it was found that the uterus had a smaller volume following cesarean section compared with vaginal delivery (p= 0.04). The high birth weight and breastfeeding were significantly related to uterine involution (p ≤ 0.01 and p= 0.04).
The sonographic evaluation of the uterus in the early puerperium should consider birth weight, breastfeeding and parity, as well as the delivery route on D2, to identify abnormalities related to uterine involution.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 04-01-2015;37(4):192-196
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005077
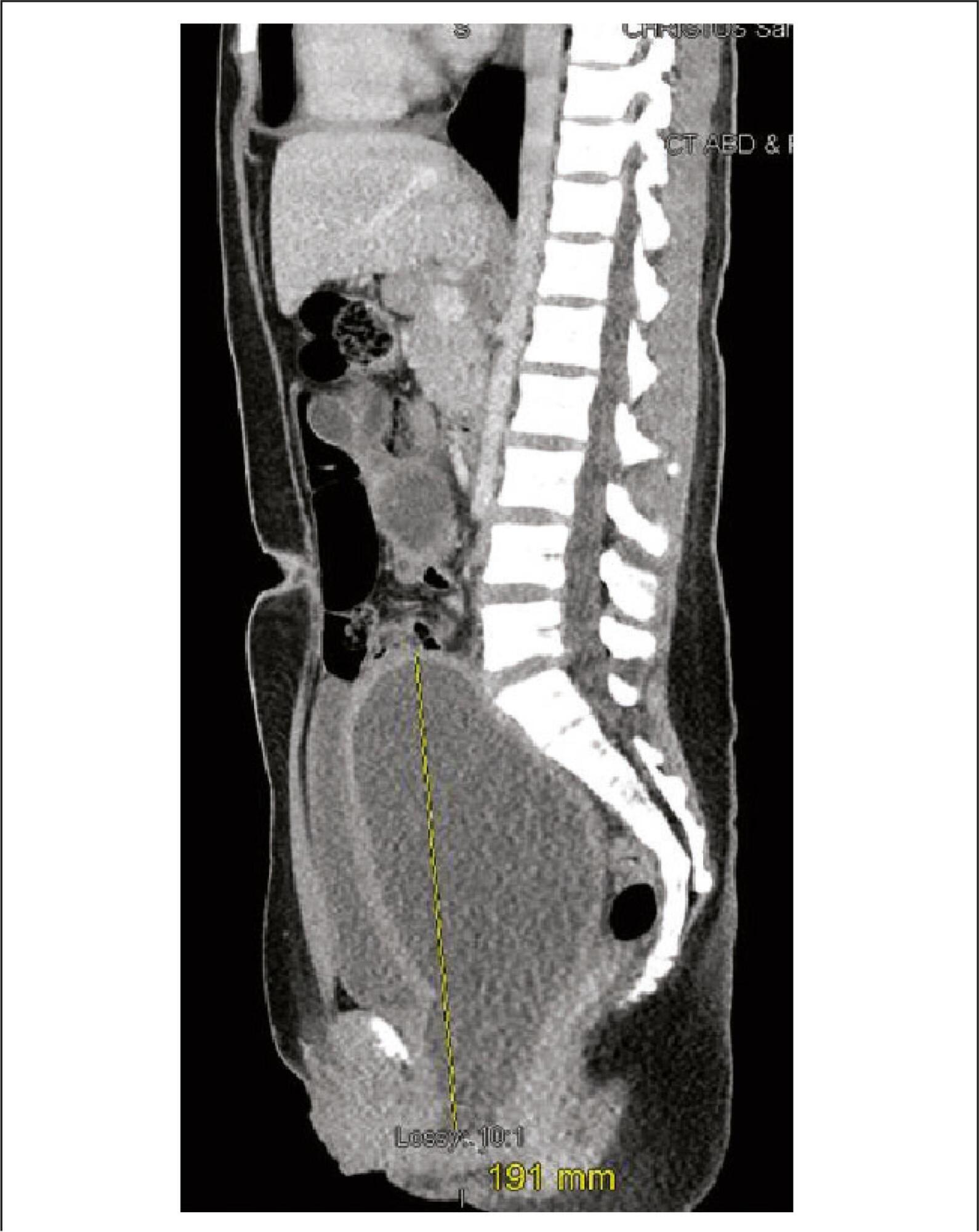
Herlyn-Werner-Wunderlich (HWW) syndrome is a rare congenital disorder of the Müllerian ducts in which there is uterus didelphys, obstructed hemivagina and unilateral renal agenesis. The most common presentation is an abdominal mass secondary to hematocolpos, pain and dysmenorrhea. However, in some cases, such as the one we present here, menses are normal due to an obstructed hemivagina, and diagnosis can be delayed. We describe evaluation and surgical management of a 13-year-old girl with this condition who was diagnosed by computed tomography (CT) scan and confirmed by pelvic ultrasound and surgical exploration, as well as a review of the literature.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 11-06-2013;35(9):427-431
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000900008
Crime and violence have become a public health problem. Pregnant women have not been the exception and gunshot injuries occupy an important place as a cause of trauma. An important fact is that pregnant women, who suffer trauma, are special patients because pregnancy causes physiological and anatomical changes. Management of these patients should be multidisciplinary, by the general surgeon, the obstetrician and the neonatologist. However, even trauma referral centers could neither have the staff nor the ideal training for these specific cases. In this context we present the following case.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 02-07-2013;35(2):49-54
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000200002
PURPOSE: To evaluate the performance of a Brazilian reference curve of fundal height (FH) regarding its capacity of screening the deviations of volume of amniotic fluid using a Brazilian reference curve of amniotic fluid index (AFI) as gold standard. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional study evaluating 753 pregnant women receiving prenatal care at the public health services of João Pessoa (PB), from March to October 2006, who had a routine ultrasound exam scheduled for after 26 weeks of gestational age. Cases with diagnoses of twin pregnancy, intrauterine fetal death and major fetal malformations were excluded. Besides socio-demographic information, data regarding fundal height measured in a standard way, estimated fetal weight, AFI and gestational age at the time of the ultrasound exam were also collected. The capacity of the FH curve to predict deviations of the amniotic fluid volume was assessed using the Brazilian curve of AFI according to gestational age as the gold standard. For this purpose, sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values were estimated for different cut-off points. RESULTS: The measurement of FH identified 10.5% of women as having low FH possibly associated with oligohydramnios and 25.2% as having high FH possibly associated with polyhydramnios. Using a Brazilian reference curve of AFI, the FH was able to poorly predict the occurrence of oligohydramnios (sensitivity ranging from 37 to 28%) and to reasonably predict the occurrence of polyhydramnios (sensitivity ranging from 88 to 69%). CONCLUSIONS: The measurement of fundal height showed a poor performance for predicting oligohydramnios and a reasonable performance for predicting polyhydramnios. Its use for this purpose is then only supported in settings where the ultrasound exam is not easily or routinely available in order to help define priorities for cases that should have this exam performed.