-
Original Article
Analysis of the Excess of Papanicolaou Tests in Brazil from 2006 to 2015
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):40-46
02-28-2022
Summary
Original ArticleAnalysis of the Excess of Papanicolaou Tests in Brazil from 2006 to 2015
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):40-46
02-28-2022Views115See moreAbstract
Objective
To analyze the quantity of cervical smears, also designated Papanicolaou tests, between 2006 and 2015 in all the Federal units of Brazil, as well as to verify the quantity of exams collected outside the recommended age range and the economic impact of such excess.
Methods
The data was collected from the Ministry of Health’s database called Sistema de Informação do Câncer do Colo de Útero (SISCOLO), which contains all the test results collected nationwide by the Unified Health System (SUS, in the Portuguese acronym). From that, the number of exams and the age range of thewomen who underwent them were analyzed; besides, these numbers were stratified according to the state of where the exam was performed. The quantity of exams collected outside the recommended age range was verified, and, so, the economic impact generated was noted.
Results
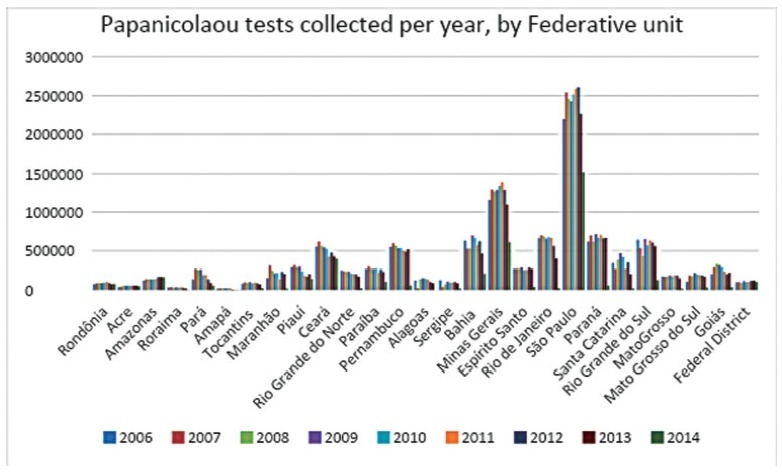
Between 2006and2015, 87,425,549Papanicolaoutestswere collected in Brazil. Of these, 20,215,052 testswere collected outside the age range recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health; this number corresponded to 23.12% of all exams. From such data, considering that each Pap smear collected by SUS generates a cost of BRL 7.30 to the government, according to the information in the Tabela SUS dated September 2018, there was a total charge of BRL 147,569,880 for tests collected outside the protocol.
Conclusion
In Brazil, according to the Ministry of Health’s protocol about the recommended practices on collecting Pap smears, whose newest edition dates of 2016, it is recommended that Pap smears are collected inwomen from a specific age range, inwhom the potential diagnosing advantages overcome the onus of overdiagnosis or of a lesion with great regression potential. However, such protocols have not been correctly followed, promoting more than 20 million tests in excess, and an exorbitant cost for the Brazilian public health system. It is relevant to take measures to correctly use the official protocol, reducing the patients risks, as well as the economic impact for SUS.
-
Original Article
Assessment of Length of Maternal Cervix between 18 and 24 weeks of Gestation in a Low-Risk Brazilian Population
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):647-652
12-01-2017
Summary
Original ArticleAssessment of Length of Maternal Cervix between 18 and 24 weeks of Gestation in a Low-Risk Brazilian Population
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):647-652
12-01-2017Views113See moreAbstract
Purpose
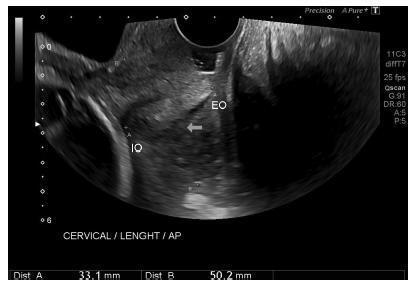
To determine cervical biometry in pregnant women between 18 and 24 weeks of gestation and the ideal mode of measurement of cervical length in cases of curved and straight cervical morphology.
Methods
The uterine cervices of 752 low-risk pregnant women were assessed using transvaginal ultrasound in a prospective cross-sectional study. In women with straight uterine cervices, cervical biometry was performed in a continuous manner. In women with curved uterine cervices, the biometry was performed using both the continuous and segmented techniques (in segments joining the cervical os). Polynomial regression models were created to assess the correlation between the cervical length and gestational age. The paired Student t-test was used to comparemeasuring techniques.
Results
The cervical biometry results did not vary significantly with the gestational age and were best represented by linear regression (R2 = 0.0075 with the continuous technique, and R2 = 0.0017 with the segmented technique). Up to the 21st week of gestation, there was a predominance of curved uterine cervix morphology (58.9%), whereas the straight morphology predominated after this gestational age (54.2%). There was a significant difference between the continuous and the segmented measuring methods in all the assessed gestational ages (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Cervical biometry in pregnant women between 18 and 24 weeks was represented by a linear regression, independently of the measuring mode. The ideal measuring technique was the transvaginal ultrasound performed at a gestational age 21 weeks.
-
Original Article
Reference Ranges for Ultrasonographic Measurements of the Uterine Cervix in Low-Risk Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):443-452
09-01-2017
Summary
Original ArticleReference Ranges for Ultrasonographic Measurements of the Uterine Cervix in Low-Risk Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):443-452
09-01-2017Views152See moreAbstract
Objective
To define transvaginal ultrasound reference ranges for uterine cervix measurements according to gestational age (GA) in low-risk pregnancies.
Methods
Cohort of low-risk pregnantwomen undergoing transvaginal ultrasound exams every 4 weeks, comprisingmeasurements of the cervical length and volume, the transverse and anteroposterior diameters of the cervix, and distance fromthe entrance of the uterine artery into the cervix until the internal os. The inter- and intraobserver variabilities were assessed with the linear correlation coefficient and the Student t-test. Within each period of GA, 2.5, 10, 50, 90 and 97.5 percentiles were estimated, and the variation by GA was assessed with analysis of variance for dependent samples. Mean values and Student t-test were used to compare the values stratified by control variables.
Results
After confirming the high reproducibility of the method, 172 women followed in this cohort presented a reduction in cervical length, with an increase in volume and in the anteroposterior and transverse diameters during pregnancy. Smaller cervical lengths were associated with younger age, lower parity, and absence of previous cesarean section (C-section).
Conclusion
In the studied population, we observed cervical length shortening throughout pregnancy, suggesting a physiological reduction mainly in the vaginal portion of the cervix. In order to better predict pretermbirth, cervical insufficiency and premature rupture of membranes, reference curves and specific cut-off values need to be validated.
-
Relatos de Casos
Compound nevus of the uterine cervix: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):50-52
05-02-1998
Summary
Relatos de CasosCompound nevus of the uterine cervix: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):50-52
05-02-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000100009
Views83See moreCompound nevus of the uterine cervix is very rare. Benign and malignant melanotic lesions of endo and exocervix have been rarely documented. The present case of compound nevus in the uterine exocervix was found in a 47-year-old woman without gynecologic complaints. Diagnosis was suspected by colposcopic evaluation and confirmed trough histopathological examination. The treatment was concluded with total abdominal hysterectomy based on the possible malignant transformation of these lesions and the difficult patient follow-up.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Prevention of preterm birth: use of digital examination and transvaginal ultrasonography
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):350-356
04-11-1998
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisPrevention of preterm birth: use of digital examination and transvaginal ultrasonography
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):350-356
04-11-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600008
Views81See moreObjective: to evaluate the uterine cervix by digital and transvaginal ultrasound examinations in pregnant women at high risk of having premature delivery. Methods: during the period between February 1995 and September 1997, 38 pregnant women at high risk of having premature delivery between the 20th and 36th week of gestation were examined. These patients were submitted weekly to both digital and transvaginal ultrasound examinations. The digital examination evaluated the uterine cervix using two parameters: length and dilation. The transvaginal ultrasound studied the length and the anteroposterior diameter of the uterine cervix. The behavior of these cervical measurements was analyzed throughout the pregnancies. The two methods were compared regarding cervical evaluation and accuracy of premature birth diagnosis. Results: the rate of premature deliveries was 18.4% (7/38). Digital examination resulted in cervical evaluations with variation coefficients of 30.3% for length and 193% for dilation. Transvaginal ultrasound resulted in cervical evaluations with variation coefficients of 14.7% and 26.5% for the anteroposterior diameter and length, respectively. The cervical length measures obtained on ultrasound were always greater than those obtained on digital examination. Through analysis with the hypothesis test, an indirect relationship was observed between the cervical length and the gestational period for digital examination and ultrasound study (p<0.05 and p<0.01, respectively), and a direct relationship between the cervical dilation and the gestational age observed on the digital examination (p<0.01). Conclusions: among the parameters studied by means of the digital and transvaginal ultrasound examinations, the ultrasound cervical length presented the best accuracy in the diagnosis of premature birth, proving to be more reliable for the evaluation of cervical alterations in pregnant women at high risk of premature delivery.
-
Relato de Caso
Clear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Endocervix in a 7-year-old Child
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):411-414
04-09-1998
Summary
Relato de CasoClear Cell Adenocarcinoma of the Endocervix in a 7-year-old Child
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):411-414
04-09-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700007
Views63See moreClear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina and cervix is a rare disease associated commonly with the use of diethylstilbestrol (DES) during pregnancy. The most commom complaint is irregular vaginal bleeding, which could be confused with vaginitis in children and abnormalities in the hypothalamic-pituitary axis in adolescents. We report a case of clear cell adenocarcinoma of the endocervix in a 7-year-old child who was attended at the Children and Adolescent Gynecology Sector, and we call attention to the diagnosis of genital cancer which, in spite of its rarity at this age, must be considered in children with genital bleeding.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Duration of Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Invasive Carcinoma of the Cervix in Relation to Age at Diagnosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(10):565-569
04-04-1998
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisDuration of Intraepithelial Neoplasia and Invasive Carcinoma of the Cervix in Relation to Age at Diagnosis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(10):565-569
04-04-1998DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998001000004
Views76See morePurpose: to estimate the duration of cervical neoplasia from human pappilomavirus (HPV) infection to advanced invasive carcinoma, using as paremeter the mean age of the women at diagnosis. Methods: this cross-sectional study included 1,177 women with HPV infection, 1,561 with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and 773 with invasive carcinoma. Results: the mean ages of CIN 1 and CIN 2 on diagnosis were not statistically different. The mean duration of CIN 2 was 2.2 years. The mean duration of CIN 3 was 10.3 years, with 4.1 years as severe dysplasia and 6.2 years as carcinoma in situ (CIS). The mean duration of high grade squamous intraepithelial lesions was 12.5 years. The duration means of invasive carcinoma stages Ia, Ib and II were 3.0, 2.7 and 3.7 years, respectively. Conclusions: according to the results, CIN 1 and CIN 2 may arise directly from HPV infection and most of these lesions are transient. CIS presented the longest duration and the mean asymptomatic period of cervical neoplasia is 18.2 years. These results were discussed considering the present knowledge of the natural history of cervical carcinoma and other studies on duration of this neoplasia.
-
Trabalhos Originais
Risk factors for relapse of HPV-induced lesions of the female genital tract
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):201-205
03-14-1999
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisRisk factors for relapse of HPV-induced lesions of the female genital tract
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(4):201-205
03-14-1999DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000400004
Views69See morePurpose: evaluation of the risk factors [lesion grade, seropositivity for type 1 acquired immunodeficiency virus (HIV-1) and association with pregnancy ] for relapse of human papillomavirus (HPV) induced lesions of the female genital tract. Patients and Methods: seventy patients with a clinical, colposcopic and cytologic diagnosis of HPV infection were studied. Clinical follow-up lasted at least 6 months after the initial treatment, thus permitting the evaluation of the therapeutic results. Twenty-seven of these patients were pregnant and 12 were seropositive for HIV-1. The remaining 44 patients were not in the pregnancy-puerperium cycle and 14 of them were HIV-1 positive. According to cytologic criteria, the cervical lesions were classified as changes associated with HPV or grade I cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN I) (low grade lesions) or CIN II/III (high grade lesions). Data were analyzed statistically by the exact Fisher test, with the level of significance set at p<0.05. The therapeutic scheme for lesions limited to the uterine cervix was cryo- or electrocautery (EC), whereas topical 5-fluorouracil was used for the diffused lesions through the vaginal wall. For the lesions in the vulvoperineal region, 80% trichloroacetic acid was used, and when they were voluminous, EC was applied. Among the pregnant women, a cryocautery was used for lesions limited to the cervix and EC for diffuse lesions. Results: among the HIV-1-negative pregnant women there was an 87.5% rate of recurrence when the lesions were in the cervix-vagina, and no recurrence when the lesions were vulvoperineal. In contrast, seropositive pregnant women presented 100% recurrence regardless of the site of the lesion. Among nonpregnant HIV negative women, 20 and 24% recurrence was observed in the cervix-vagina and in the vulvoperineal region, respectively, as opposed to 87.5 and 100% recurrence, respectively, for the same regions among HIV positive women. The lesions associated with CIN showed a higher frequency of recurrence with increasing CIN grade and a synergistic effect with the association of HIV-1 and pregnancy. Conclusions: the recurrence rate for women treated for HPV-induced lesions is high and the association with pregnancy, HIV and increased grade of the intraepithelial lesions are synergistic factors in the determination of therapeutic failure. The site of implantation of HPV-induced lesions is of prognostic significance only when the infection is not associated with HIV.


