Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo16
00-00-2024
Dysmenorrhea is the pain related to menstruation; to screen for the symptoms, a working ability, location, intensity of days of pain, and dysmenorrhea (WaLIDD) score was created. The purpose of this work was to culturally adapt and assess the measurement properties of the WaLIDD score for dysmenorrhea in Brazilian women.
In this cross-sectional online study, we evaluated women with and without dysmenorrhea. Criterion validity and construct validity were assessed, respectively, by the Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC) curve and correlations with the bodily pain and social functioning domains of medical outcomes study 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36), self-report of absenteeism and Stanford Presenteeism Scale for presenteeism. Test-retest reliability and measurement errors were assessed, respectively, by intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and Bland and Altman Graph.
430 women completed the test, 238 (55.4%) women had dysmenorrhea, and 199 (46.3%) answered the questionnaire twice for the retest. The cutoff points ≥4, ≥5, and ≥5 could discriminate between women with and without dysmenorrhea, absenteeism, and presenteeism related to dysmenorrhea, respectively. Correlations between SF-36 – pain and social functioning domains and WaLIDD score were weak to strong and negative. For WaLIDD total Score, ICC was 0.95 and the limits of agreement were −1.54 and 1.62.
WaLIDD score is a short, valid and reliable instrument to screen and predict dysmenorrhea and could predict absenteeism and presenteeism related to dysmenorrhea in Brazilian women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo7
00-00-2024
To validate the 10-item Cervantes Scale (CS-10) among Brazilian women.
This is a cross-sectional observational study involving women in the community aged 40–55 years in the Southern region of Brazil. They completed a general health, habits and socio-demographic questionnaire, the CS-10 and the Women’s Health Questionnaire (WHQ). Women unable to understand the survey, not consenting to participate, or having incapacity imposing difficulties during the completion of the questionnaire were excluded. A Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) was conducted with the AMOS 16.0 software. Chi-square of degrees of freedom (χ2/df), the Comparative Fit Index (CFI), the Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) and the Root-Mean-Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) were used as indices of goodness of fit. Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was used for internal consistency.
A total of 422 women were included (premenopausal n=35, perimenopausal n=172, postmenopausal n=215). The CFA for the CS-10 showed a good fit (χ²/df=1.454, CFI=0.989; TLI=0.985; RMSEA=0.033; CI 90%=0.002-0.052; PCLOSE=0.921; Model p=0.049). Good reliability was established in CS-10 and WHQ (Cronbach’s alpha=0.724). Postmenopausal women had higher total CS-10 scores (p≤0.0001), reflecting worse quality of life (QoL) related to menopause symptoms and confirming the greater symptomatology evaluated by high total scores for WHQ found in this population when compared to those in the premenopausal period (p=0.041).
The CS-10 is a consistent tool for health-related QoL in Brazilian mid-aged women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(10):575-583
12-11-2023
In the present study, our aim was to translate, adapt, and validate the Pelvic Health History Form (a quality of life [QoL] questionnaire) of the International Pelvic Pain Society (IPPS) from English to Portuguese.
The study was approved by the Ethics and Research Committee (CEP, in the Portuguese acronym) and the IPPS. The "Transcultural Adaptation" method comprised 5 stages: translation, synthesis, backtranslation, expert review, and pretest. Cultural adaptation and validation included cognitive interviews and statistical analysis of unanswered items (> 15%) in 14 clinic patients from CPP and endometriosis clinic at Santa Casa de São Paulo.
Strong equivalences were established between the USA and Brazil questionnaires in terms of semantics, idioms, experiences, and concepts. Eighteen culturally inappropriate items were identified and adjusted using the revised response rate index. The subjective form underwent rigorous assessments, confirming its accurate measurement of intended targets.
The methodology showed efficiency and equivalence, confirming its validity. The user-friendly format and inclusion of translated, adapted, and validated instruments in Portuguese make the form valuable for evaluating pelvic health, with potential for future research.
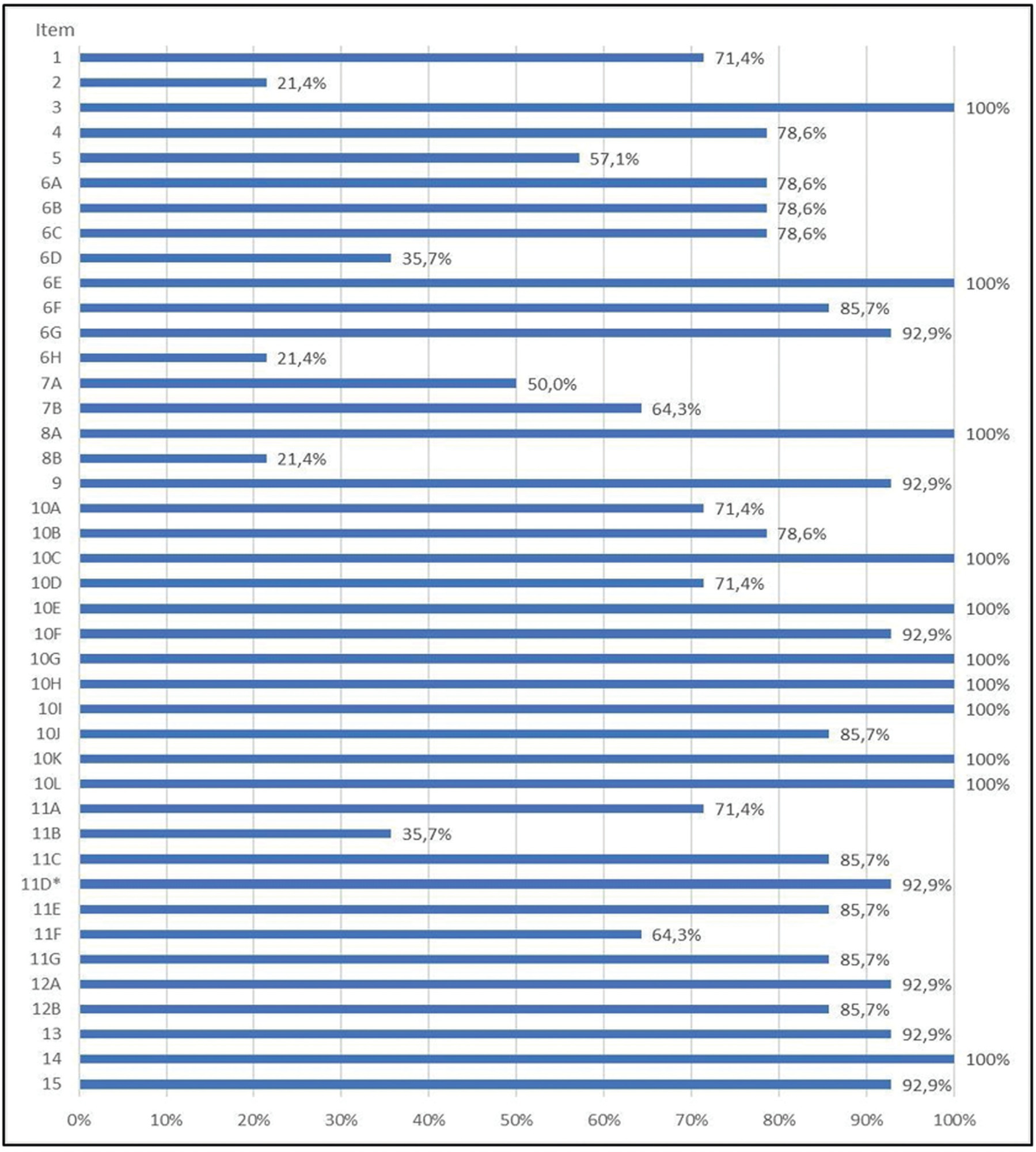
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):191-198
03-01-2019
To identify the quality of life (QoL) assessment instruments related to the health of women with fecal incontinence (FI) or anal incontinence (AI).
Systematic review conducted in the Virtual Health Library (VHL), PubMed and Cochrane Library databases. The descriptors used were: Questionnaire, Questionnaires, Quality of life, validation, validation Studies, anal incontinence, fecal incontinence and constipation. The search was performed between December 26, 2017 and the beginning of January 2018. The limits used were female gender.
Initially, 5,143 articles were obtained in the search. The articles of validation for Portuguese of questionnaires for the evaluation of the impact of FI/AI on the QoL of women were considered eligible.
The article search was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyzes (PRISMA) guidelines.
Of the 5,143 articles, only 2 fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria: Fecal Incontinence Quality of Life (FIQL) and the Wexner scale (WS). The FIQL evaluates the QoL related to FI, not covering flatus incontinence. The WS assesses flatus incontinence and the severity of the AI. The WS obtained an interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.932 and a Cronbach α coefficient > 0.90. The FIQL obtained intraexaminer and interexaminer reproducibility ranging from 0.929 to 0.957 and from 0.944 to 0.969, respectively.
The WS and the FIQL have satisfactory reliability and validity for use during gynecological consultations.