-
Original Article
Analysis of vaginal microbiota before and after treatment of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions of the uterine cervix
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo86
12-04-2024
Summary
Original ArticleAnalysis of vaginal microbiota before and after treatment of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions of the uterine cervix
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo86
12-04-2024Views173Abstract
Objective:
HPV infection is considered the most common sexually transmitted virus today. The persistence of HPV is the main cause for the development of precursor lesions and cervical cancer. There are environmental and non-environmental factors that contribute to the persistence of the virus. Studies indicate a possible relationship between the vaginal microbiota (environmental factor) and the risk of high-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions and cervical cancer. This study evaluates the association between the type of vaginal microbiota and the occurrence of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervix.
Methods:
Observational, longitudinal, prospective, and analytical studies carried out between 2019 and 2021, which evaluated the vaginal microbiota of patients diagnosed with high-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesion before and after treatment in two collections with an interval of 6 months, using scrapings and vaginal swabs.
Results:
In Group I (with lesions) 28 women participated and 29 in Group II (without lesions). According to Nugent, in the initial collection of Group I, 16 women (57%) had lactobacillary microbiota, eight (28%) intermediate, and four (14%) coccus. In Group II, twenty-one (75%) were lactobacillary, one (3%) was intermediate, and seven (24%) werecoccus. With p=0.03.
Conclusion:
According to Nugent's criteria, there was an association between the type of vaginal microbiota and the occurrence of high-grade cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervix. The same was not observed in the Donders classification. Studies with a larger sample are needed to confirm our results.
Key-words CervixuterimicrobiotaPapillomavirus infectionssquamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervixUterine cervical neoplasmsVaginosis, bacterialSee more -
Original Article/Oncology
Risk Profile of High-grade Cervical Lesions and Cervical Cancer Considering the Combination of Cytology, HPV Genotype, and Age among Women Undergoing Colposcopy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):689-698
12-05-2023
Summary
Original Article/OncologyRisk Profile of High-grade Cervical Lesions and Cervical Cancer Considering the Combination of Cytology, HPV Genotype, and Age among Women Undergoing Colposcopy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):689-698
12-05-2023Views172Abstract
Objective
The present study aims to establish a risk profile for high-grade cervical lesions and cervical cancer (CIN2 + ) in women undergoing colposcopy at the Hospital do Câncer de Barretos, through the analysis of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection, cervical cytology, and patient's age.
Methods
Retrospective cross-sectional study based on a computerized database of women aged ≥ 18 years old who underwent colposcopy at the Prevention Department of the Hospital do Câncer de Barretos from 2017 to 2019.
Results
A total of 3,411 women were included, 58.0% were positive for high-risk-HPV test, with a higher prevalence of CIN2+ for HPV16 (30.3%) and other HPV (45.0%). Cytological findings that suggest invasive cervical cancer (squamous cells or adenocarcinoma), regardless of the status of HPV test, showed 100% diagnosis of CIN2 + , while atypias that suggest high-grade lesions, HSIL and ASC-H, positive for HPV test, showed in 86 and 55.2%, respectively, diagnosis of CIN2 + . ASC-H cytological results among women aged > 40 years old and negative HPV were mainly associated with benign findings. We observed that ≤ CIN1 has a higher prevalence among older women with negative HPV, while for high-grade lesions there is an increase among young women HPV16- and/or 18-positive. In cancer diagnosis, we observed a predominance of HPV 16/18 regardless of the age group.
Conclusion
The highest risks of precursor lesions and cervical cancer were found among women with positive HPV 16/18 tests and severe cytological atypia in population screening tests. In addition, cytological findings of ASC-H HPV negative in women > 40 years old usually represent benign findings in histological investigation.
Key-words ColposcopyPapillomavirus infectionsrisksquamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervixUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more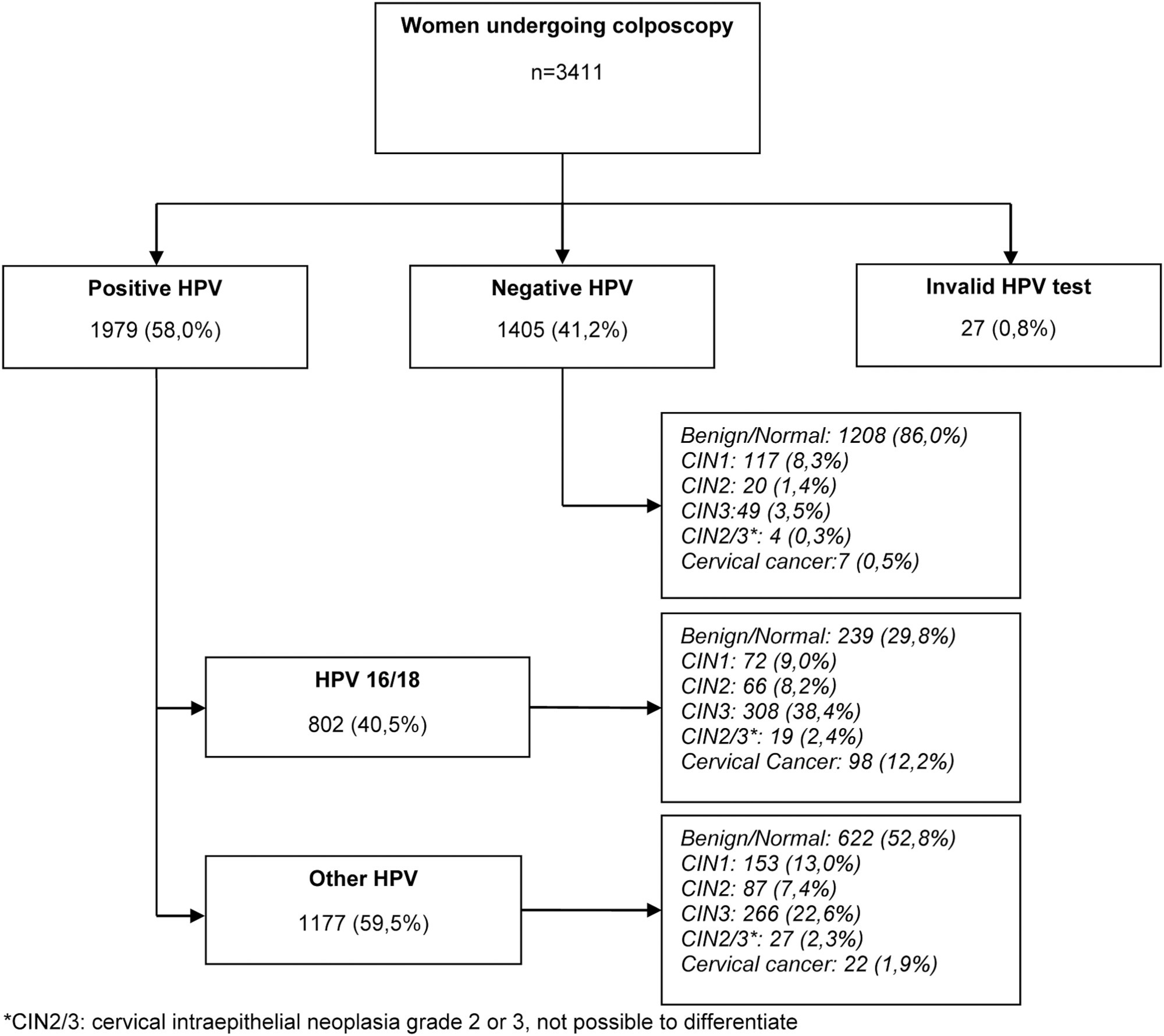
-
Original Article
Performance of Conventional Cytology and Colposcopy for the Diagnosis of Cervical Squamous and Glandular Neoplasias
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):410-416
07-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticlePerformance of Conventional Cytology and Colposcopy for the Diagnosis of Cervical Squamous and Glandular Neoplasias
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):410-416
07-01-2018Views137Abstract
Objective
To estimate the cytological and colposcopic performances for the diagnosis of cervical neoplasias.
Methods
Cross-sectional retrospective study with data from patients’ charts. The participants underwent colposcopy, guided biopsies, and excision when needed. The cytological and colposcopic categorization followed the Bethesda System and the international colposcopic terminologies. The cytology and colposcopy performances were evaluated by sensitivity (SE), specificity (SP), positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) analyses with 95% confidence interval (95% CI).
Results
From 1,571 participants, a total of 1,154 (73.4%) were diagnosed with cervical squamous intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or worse (CIN 2+), 114 (7.2%) with adenocarcinoma in situ or worse (AIS+), 615 (39.2%) presented atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion or worse (ASC-H+) cytology, and 934 (59.4%) presented major or suspicious for invasion colposcopic abnormalities. The SE, SP, PPV, and NPV of ASC-H+ for diagnoses of CIN 2+ and AIS+ were, respectively: 44% (95% CI: 41-47) and 72% (95% CI: 67-76), 79% (95% CI: 77-81) and 79% (95% CI: 75-83), 88% (95% CI: 87-90) and 55% (95% CI: 50-60), and 28% (95% CI: 26-31) and 88% (95% CI: 85-91). The SE, SP, PPV, and NPV of major or suspicious for invasion colposcopic abnormalities for diagnoses of CIN 2+ and AIS+were, respectively: 62% (95% CI: 60-65) and 86% (95% CI: 83-89), 59% (95% CI: 57-62) and 59% (95% CI: 55-64), 85% (95% CI: 83-87) and 44% (95% CI: 40-49), and 29% (95% CI: 27-32) and 92% (95% CI: 89-94).
Conclusion
The SE analyses results of ASC-H+ and major or suspicious for invasion colposcopic abnormalities were higher for diagnoses of glandular neoplasias. These results confirm the role of cytology in identifying women at risk who will have their final diagnoses settled by colposcopy and histology.
Key-words adenocarcinoma in situCervical intraepithelial neoplasiaColposcopyPapanicolaou testSensitivity and specificitysquamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervixUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more