Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo9
00-00-2024
To analyze the amount of muscle and the presence of sarcopenia in postmenopausal women using different methods, verifying the agreement between them as to skeletal muscle mass (SMM).
This cross-sectional observational study was conducted with postmenopausal women aged ≥ 50 years. SMM was obtained from a predictive equation, Bioelectrical Impedance (BIA), and Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA). The skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) and the appendicular skeletal muscle mass index (ASMI) were calculated. The cut-off point of SMI was determined for the population itself. The agreement between the SMI obtained using the different methods was verified. Sarcopenia was diagnosed according to the criteria proposed by the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2). The significance level adopted for all tests was 5.0%.
A total of 112 women were evaluated, with an average age of 66.1 ± 5.65 years. Among them, 51.8% were sufficiently active and 43.8% were overweight and obese. The SMI cut-offs were 6.46 kg/m2 for the predictive equation and 7.66 kg/m2 for BIA, with high sensitivity and specificity. There was an excellent agreement in the identification of SMM by the predictive equation (0.89 [0.824-0.917], p < 0.001) and BIA (0.92 [0.883-0.945], p < 0.001), in reference to DXA. The prevalence of sarcopenia was 0.9%, 1.8%, and 2.7% according to BIA, DXA, and the predictive equation, respectively.
The predictive equation showed the expected agreement in estimating skeletal muscle mass in postmenopausal women, offering a viable and accurate alternative.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):32-39
02-28-2022
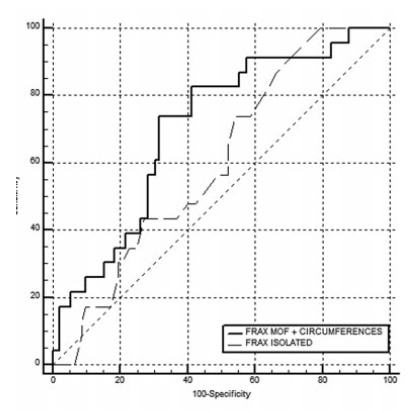
To evaluate the improvement in screening accuracy of the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) for the risk of developing osteoporosis among young postmenopausal women by associating with it clinical muscle mass measures.
A sample of postmenopausal women was submitted to calcaneal quantitative ultrasound (QUS), application of the FRAX questionnaire, and screening for the risk of developing sarcopenia at a health fair held in the city of São Bernardo do Campo in 2019. The sample also underwent anthropometric measurements, muscle mass, walking speed and handgrip tests. A major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) risk ≥ 8.5% on the FRAX, a classification of medium risk on the clinical guideline of the National Osteoporosis Guideline Group (NOGG), and a QUS T-score ≤ -1.8 sd were considered risks of having low bone mass, and QUS T-score ≤ -2.5sd, risk of having fractures.
In total, 198 women were evaluated, with a median age of 64±7.7 years, median body mass index (BMI) of 27.3±5.3 kg/m2 and median QUS T-score of -1.3±1.3 sd. The accuracy of the FRAX with a MOF risk ≥ 8.5% to identify women with T-scores ≤ -1.8 sd was poor, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.604 (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 0.509-0.694) for women under 65 years of age, and of 0.642 (95%CI: 0.571-0.709) when age was not considered. Including data on muscle mass in the statistical analysis led to a significant improvement for the group of women under 65 years of age, with an AUC of 0,705 (95%CI: 0.612-0.786). The ability of the high-risk NOGG tool to identify T-scores ≤ -1.8 sd was limited.
Clinical muscle mass measurements increased the accuracy of the FRAX to screen for osteoporosis in women aged under 65 years.