Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):535-544
To investigate the feasibility of pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) through gametherapy for relieving urinary symptoms of climacteric women with stress ormixed urinary incontinence (UI).
Randomized clinical trial, divided into two groups: Gametherapy (G_Game) and Control (G_Control). Both groups received recommendations about unsupervised PFMT, and G_Game also received supervised PFMT through gametherapy. After 5 consecutive weeks, the feasibility was investigated considering participant adherence, urinary symptoms (evaluated by the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire-Urinary Incontinence Short Form [ICIQ-UI-SF] questionnaire), and pelvic floor function (PERFECT Scheme: power, endurance, repetition and fast). The Fisher exact, Kruskal-Wallis, Wilcoxon sign paired, and Mann-Whitney U tests were used by intention-to-treat analysis, using STATA 15.1 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA) software.
The present study included 20 women per group and observed a higher adherence in G_Game. In the intragroup analysis, a decrease in the ICIQ-UI-SF score was observed in both groups (14.0 to 10.0; 13.5 to 0), associated with increased endurance (2.5 to 3.5; 2.5 to 4.0) in G_Control and G_Game, respectively. Moreover, there was a concomitant increase in pelvic floor muscles (PFMs) power (2.0 to 3.0), repetition (3.0 to 5.0), and fast (10.0 to 10.0) in G_Game. In the intergroup analysis, a reduction of UI was observed (p<0.001; r=0.8), as well an increase in PFM power (p=0.027, r=0.2) and endurance (p=0.033; r=0.3) in G_Game.
The feasibility of supervised PFMT through gametherapy was identified by observing participant adherence, relief of urinary symptoms, and improvement in PFM function.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):632-639
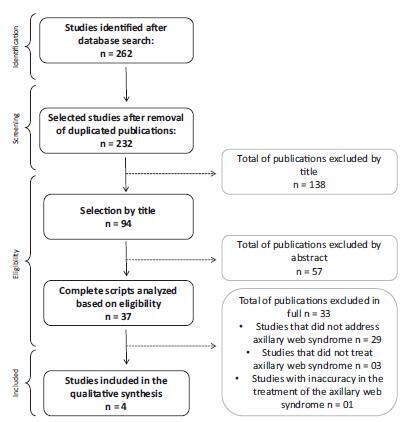
Axillary web syndrome is characterized as a physical-functional complication that impacts the quality of life of women who have undergone treatment for breast cancer. The present study aims to verify the physiotherapy treatment available for axillary web syndrome after surgery for breast cancer in the context of evidence-based practice. The selection criteria included papers discussing treatment protocols used for axillary web syndrome after treatment for breast cancer. The search was performed in the MEDLINE, Scopus, PEDro and LILACS databases using the terms axillary web syndrome, lymphadenectomy and breast cancer, focusing on women with a previous diagnosis of breast cancer who underwent surgery with lymphadenectomy as part of their treatment. From the 262 studies found, 4 articles that used physiotherapy treatment were selected. The physiotherapy treatment was based on lymphatic drainage, tissue mobilization, stretching and strengthening. The four selected articles had the same outcome: improvement in arm pain and shoulder function and/or dissipation of the axillary cord. Although axillary web syndrome seems to be as frequent and detrimental as other morbidities after cancer treatment, there are few studies on this subject. The publications are even scarcer when considering studies with an interventional approach. Randomized controlled trials are necessary to support the rehabilitation resources for axillary web syndrome.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):125-130
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200007
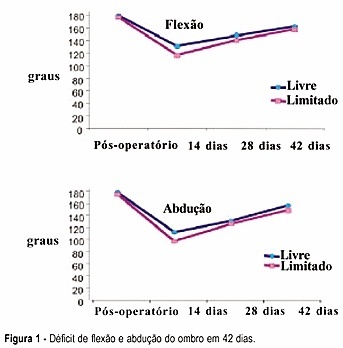
PURPOSE: to evaluate the efficacy of a physical exercise protocol in the recovery of shoulder movement in women who underwent complete axillary lymph node dissection due to breast carcinoma, comparing free and restricted amplitude movements. METHODS: 59 women who underwent complete axillary lymph node dissection associated with modified mastectomy (46) or quadrantectomy (13) were included in this clinical, prospective and randomized study. On the first day after surgery 30 women were randomized to do the shoulder movement with free amplitude and 29 women had this amplitude restricted to 90º in the first 15 days. Nineteen exercises were done, three sessions per week, for six weeks. Mean (± standard error) deficits of shoulder flexion and abduction were compared, as well as gross and adjusted incidence rates of seroma and dehiscence. RESULTS: 42 days after surgery, flexion and abduction means were similar in the two groups. Both presented a mean flexion deficit (17.2º and 21.6º, respectively), and abduction deficit (19.7º and 26.6º, respectively). The incidence rates of seroma and dehiscence were neither related to exercise nor to the type of surgery, time of drain permanence, number of dissected or compromised lymph nodes, age or obesity. CONCLUSION: early physiotherapy with free movement of the women's shoulder was associated neither with functional capacity nor with postsurgical complications.