Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(4):211-217
05-18-2020
To reveal the changes in the quality of life reported by women with Human papillomavirus (HPV)-induced lesions.
This is a cross-sectional, descriptive-exploratory study of a qualitative approach performed from June to August 2016. Semi-structured face-to-face interviews based on five questions on the concept of quality of life were used. The data were submitted to thematic analysis. All ethical aspects have been contemplated.
A total of 20 women aged between 25 and 59 years old were interviewed. From the analysis of the data, the following thematic units emerged: physical and emotional changes, especially complaints of pruritus, discharge and pain, worry, fear, shame and sadness; changes in sexual and affective relationships with decreased libido, dyspareunia and interruption of sexual activity; changes in social relationships resulting in absenteeism at work.
Human papillomavirus infection impairs the quality of life of women as it significantly affects sexual, affective, physical, emotional, and everyday habits. Therefore, HPV infection can lead to exponential changes in the quality of life of women, which can be mitigated by the availability of sources of support such as family, friends and the multi-professional team, helping to improve knowledge and cope with HPV.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):90-95
04-17-2020
To describe clinical and sociodemographic characteristics of women with deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE) and assess their quality of life (QOL) during 6 months of medical treatment.
A descriptive cross-sectional study of 60 women diagnosed with DIE either by surgery or image methods (ultrasound or magnetic resonance), who received clinical treatment for at least 6 months in the Universidade de Campinas, Campinas, state of São Paulo, Brazil. Both the SF-36 and the EHP-30 questionnaires were used to assess the quality of life.
The mean age of the patients was 37.7 ± 6.0 years old, with 50% presenting dysmenorrhea; 57% dyspareunia; and 50% chronic pelvic pain. The SF-36 and the EHP-30 revealed impaired quality of life. In the SF-36, the worst domains were limitation due to emotional aspects (40.2 ± 43.1) and self-esteem and disposition (46.1 ± 24.8), whereas in the EHP-30 they were social well-being (50.3 ± 30.6); infertility (48.0 ± 36.3); and sexual intercourse (54.0 ± 32.1).
Although clinically treated, women with deep endometriosis present impairment in different domains of quality of life regardless of the questionnaire used for evaluation.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(9):548-554
09-30-2019
To evaluate the existence of an association between ultrasound findings and epidemiological and clinical factors using results obtained from the EHP-30 questionnaire in women with ovarian endometriosis.
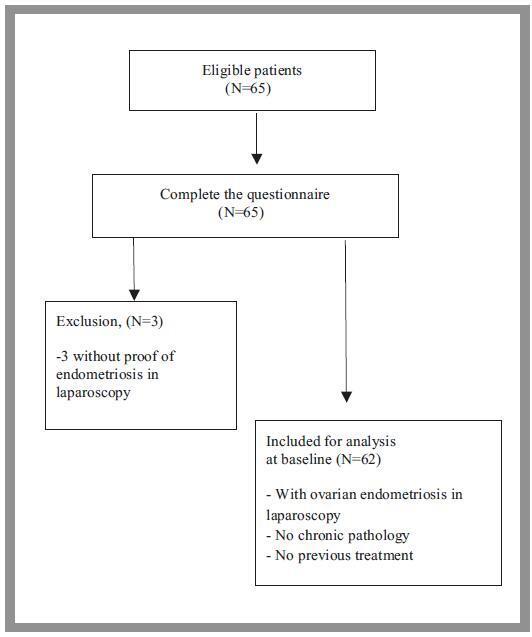
A cross-sectional observational study was performed between July 2012 and May 2015, in which patients with chronic pelvic pain suggestive of endometrioma, as indicated by the results from a transvaginal pelvic ultrasonography, completed the standardized Endometriosis Health Profile - 30 (EHP-30) questionnaire to access quality-of-life scores before beginning treatment for endometriosis. A total of 65 patients were included. The data was analyzed in the statistical program IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) for the comparison of data through linear multiple regression.
The suitability of the linear regression model was confirmed by the histogram of the dependent variable and the residue distribution plot, confirming the trend of linearity as well as the homogeneous dispersion of the residues. The mean age of the patients was 39.7 ± 7.1 years old. Themajority was Caucasian (64.5%), had completed higher education (56.5%) and was nulligravida (40.3%). Infertility was present in 48.4% of the patients studied. Out of the total sample, 80.6% of the cases were symptomatic and complained mainly of acyclic pain, 79% of dysmenorrhea, and 61.3% of dyspareunia. This reflects the negative influence of endometriosis on the quality of life of patients with this disease.
Dyspareunia and acyclic pain were independent factors of correlation with high scores in the EHP-30 questionnaire, reflecting a worse quality of life.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):312-317
06-27-2019
To evaluate the quality of life among university students with premenstrual syndrome (PMS).
The cross-sectional study was conducted at the Faculdade Pernambucana de Saúde, in Recife, Brazil, between August 2016 and July 2017. Sociodemographic, gynecological, and lifestyle variables, and PMS occurrence, were investigated among 642 students. The short form of the World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL Bref) questionnaire was used to evaluate four domains of the quality of life of the students: physical, mental, social relationships, and environmental. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists’ criteria were used to define PMS.
Of the 642 students, 49.9% had PMS, 23.3% had mild PMS and 26.6% had premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD). Most of the students were between 18 and 24 years old, had regular menstrual cycles, and practiced physical activity. Regarding the physical and mental domains of the WHOQOL-Bref questionnaire, a statisticallysignificant difference was observed between the students who did not have and those who had mild or PMDD (p < 0.001). A difference was also found between the students who did not have PMS and those who had mild PMS in the social relationships (p = 0.001) and environmental domains (p = 0.009).
Mild PMS and PMDD are prevalent among university students on healthrelated courses, and the syndrome can affect the students’ self-assessment of all the domains of quality of life.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(4):242-248
06-19-2019
To analyze the factors associated with health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in women with cervical cancer (CC) in a single center in Rio de Janeiro, state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
A cross-sectional study in women with a diagnosis of CC followed-up in the gynecology outpatient clinic of the Hospital do Câncer II (HCII, in the Portuguese acronym) of the Instituto Nacional de Câncer (INCA, in the Portuguese acronym). The data were collected from March to August 2015. Women with palliative care, communication/cognition difficulty, undergoing simultaneous treatment for other types of cancer, or undergoing chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy were excluded. For the evaluation of the HRQoL, a specific questionnaire for women with CC was used (Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy - Cervix Cancer [FACT-Cx]). The total score of the questionnaire ranges from 0 to 168, with higher scores indicating a better HRQoL.
A total of 115 women were included in the present study, with a mean age of 52.64 years old (standard deviation [SD] = 12.13). The domains of emotional (16.61; SD = 4.55) and functional well-being (17.63; SD = 6.15) were those which presented the worst scores. The factors that had an association with better HRQoL in women with CC were having a current occupation, a longer time since the treatment and diagnosis, and women who had undergone hysterectomy.
Considering the domains of HRQoL of the women treated for cervical cancer, a better score was observed in the domains of physical and social/family wellbeing. For most domains, better scores were found between those with a current occupation, with a longer time after the diagnosis and treatment, and among those who had undergone a hysterectomy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(4):236-241
06-19-2019
To compare sexual function and quality of life (QOL) among intrauterine contraceptive (copper-intrauterine device [Cu-IUD] or the 52-mg 20 μg/day levonorgestrel- releasing intrauterine system [LNG-IUS]) users.
This was part of a cross-sectional study. Women aged between 18 and 49 years old, in a heterosexual relationship, reporting sexual intercourse in the previous 4 weeks, using Cu-IUD (Group 1) or LNG-IUS (Group 2) responded to a questionnaire with sociodemographic information, to the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), to the World Health Organization QOL Questionnaire Abbreviated Version (WHOQOL-BREF), and to a questionnaire about the contraceptive method used. The Student t-test, the Pearson χ2 test or the Fisher exact test, and the Mann-Whitney test were used for the analysis. For the adjusted comparison, we have used the analysis of covariance (ANCOVA). A multiple regression analyzing factors related to FSFI 26.55 was done. Significance was established at p < 0.05.
A total of 347 women in Group 1 (mean age of 32.3 ± 7.5 years old) and of 298 in Group 2 (mean age of 32.7 ± 6.4 years old) completed the questionnaires.Most women had ≥ 8 years of schooling, were in amonogamous relationship, and had had ≤ 2 pregnancies. A total of 122 Cu-IUD and of 87 LNG-IUS users scored ≤ 26.55 on the FSFI. Significant lower scores in physical, environmental, and overall QOL domains in the WHOQOL-BREF questionnaire were found in Group 1. More women using the Cu- IUD were not satisfied with the method.
We did not find significant differences in sexual function; there was a lower score in some domains of QOL among women who used the Cu-IUD. It was not possible to ensure that those differences were related to the contraceptive method.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):191-198
03-01-2019
To identify the quality of life (QoL) assessment instruments related to the health of women with fecal incontinence (FI) or anal incontinence (AI).
Systematic review conducted in the Virtual Health Library (VHL), PubMed and Cochrane Library databases. The descriptors used were: Questionnaire, Questionnaires, Quality of life, validation, validation Studies, anal incontinence, fecal incontinence and constipation. The search was performed between December 26, 2017 and the beginning of January 2018. The limits used were female gender.
Initially, 5,143 articles were obtained in the search. The articles of validation for Portuguese of questionnaires for the evaluation of the impact of FI/AI on the QoL of women were considered eligible.
The article search was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyzes (PRISMA) guidelines.
Of the 5,143 articles, only 2 fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria: Fecal Incontinence Quality of Life (FIQL) and the Wexner scale (WS). The FIQL evaluates the QoL related to FI, not covering flatus incontinence. The WS assesses flatus incontinence and the severity of the AI. The WS obtained an interclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.932 and a Cronbach α coefficient > 0.90. The FIQL obtained intraexaminer and interexaminer reproducibility ranging from 0.929 to 0.957 and from 0.944 to 0.969, respectively.
The WS and the FIQL have satisfactory reliability and validity for use during gynecological consultations.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):66-71
02-01-2018
To evaluate the impact of sexual function (SF) in the quality of life (QoL) of women with premature ovarian insufficiency (POI).
Case-control study in which 80women with POIwere evaluated using estrogen plus progestogen therapy, compared with 80 women matched by age (2 years) and presenting preserved gonadal function. Sexual function was evaluated using the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), and the QoL was evaluated using theWorld Health Organization's (WHO) QoL assessment instrument (WHOQoL-BREF).
The mean age of the women with POI and of the control group was 38.4 ± 7.3 years and 38.1 ± 7.3 years respectively. The QoL, was worse among the POI group, and there were significant differences in the physical (63.4 ± 17.4 and 72.7 ± 15.2 respectively, p = 0.0004) and psychological (63.2 ± 14.6 and 69.3 ± 13.9 respectively, p = 0.0075) domains among this group when compared with the control group. Women with POI presented significantly lower arousal, lubrication, orgasm and satisfaction, more dyspareunia and a worse FSFI scores when compared with the control group. All aspects of SF correlate directly with the worsening of the QoL regarding social relationships.
Women with POI showed worse QoL and SF than the control group. The psychological aspects (desire, excitement, orgasm and sexual satisfaction) of SF had greater influence on the parameters of the QoL, while the physical aspects (pain and lubrication) had a low impact on the QoL. The poor SF in women with POI is directly correlated with a worsening acrossmultiple domains of the QoL; however, the negative impact is particularly important in the social domain. These results suggest that the improvement in sexuality can improve the social interactions of women with POI.