Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(9):427-431
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000900008
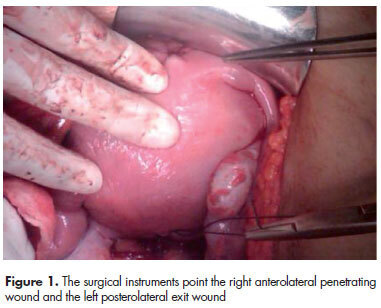
Crime and violence have become a public health problem. Pregnant women have not been the exception and gunshot injuries occupy an important place as a cause of trauma. An important fact is that pregnant women, who suffer trauma, are special patients because pregnancy causes physiological and anatomical changes. Management of these patients should be multidisciplinary, by the general surgeon, the obstetrician and the neonatologist. However, even trauma referral centers could neither have the staff nor the ideal training for these specific cases. In this context we present the following case.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(6):268-273
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000600006
PURPOSE: To describe the anthropometric and pregnancy characteristics of women with HIV/AIDS, assisted by the Brazilian National Health System and the birth weight of their newborns. METHODS: The participants were women assisted at public STD/AIDS clinics of the Municipal Health system of São Paulo. The anthropometric characteristics were evaluated by trained nutritionists and other information was obtained from the medical records. For comparison of the survey data to those of the general population, secondary maternal and pregnancy data were obtained from live birth certificates through the Live Birth Information System. Continuous variables were summarized as mean and standard deviation or as the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles and minimum and maximum values. The other variables are presented as percentages. Means were compared by the Student's t-test or Kruskal-Wallis test depending on the fulfillment of assumptions, with the decision based on the p value. RESULTS: We found the presence of inadequate maternal nutrition according to triceps skinfold (60.9%). The BMI/gestational age showed the presence of underweight (18.5%) and overweight or obesity (40%). There was no association between disease status (HIV or AIDS) and weight, height, and lean or fat mass. Mean newborn birth weight was lower than the value for the general population without infection or disease. The results of this study indicate the need to develop adapted curves to allow a more accurate nutritional assessment of this population group.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):226-232
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000500007
PURPOSE: To determine the HPV prevalence and genotypes and to identify factors associated with infection in pregnant and non-pregnant women with positive or negative HIV-1, treated in Gynecology and Obstetrics Ambulatories and in Health Primary Units, in Rio Grande, Rio Grande do Sul State, Brazil. METHODS: Cervical cells samples from 302 patients were analyzed for HPV presence and genotypes were determined by nested and sequencing polymerase chain reaction. We calculated prevalence ratios associated with the studied variables by Fisher's exact or χ² tests, and Poisson's regression. Women with insufficient material were excluded from the study. RESULTS: HPV was detected in 55 of the 302 women included in the study (18.2%); of these, 31 were pregnant, showing a significant association for HPV (p=0.04) when compared to non-pregnant ones. Risk factors for the infection were: patients aged <20 years-old (p=0.04), early initiation of sexual life (p=0.04), absence of cytological test (p=0.01), diagnosis of altered cytology (p=0.001), and counting <349 cells/mm³ (p=0.05). However, multi-parity was found to be a protective factor for the infection (p=0.01). Multivariate analysis showed that age <20 years-old (PR=2.8; 95%CI 1.0 - 7.7, p=0.04) and an altered cytological result (PR=11.1; 95%CI 3.0 - 4.1, p=0.001) were significantly associated with infection. HPV genotype was determined in 47 samples (85.4%) presenting one genotype per infection: eight HPV 16 and 58; six HPV 6; four HPV 18 and 33; three HPV 53 and 82; two HPV 83 and 61; one HPV 31, 35, 45, 64, 68, 71 and 85. CONCLUSIONS: The prevalence of HPV detection was 18.2%, the most frequent genotypes were 16 and 58, and sociodemographic and gynecological factors were associated with viral infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(11):518-523
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001100007
PURPOSE: To determine the prevalence and risk factors associated with failure of voluntary screening for cervical cancer during the gestational period in Rio Grande, Rio Grande do Sul State, Southern Brazil. METHODS: Previously trained interviewers applied a standardized questionnaire in the maternity to all mothers from this municipality who had delivered from January 1st to December 31st 2010 to obtain information about the demographic characteristics of the pregnant women, family socioeconomic status, and prenatal care received. The χ² test was used to compare proportions and Poisson regression with robust adjustment of variance was used in the multivariate analysis. RESULTS: Among the 2,288 respondents, 33% were not submitted to the Pap smear during pregnancy. Two thirds of these women stated that they were not aware of the need to perform it, 18% were not screened out of fear or shame, and the rest for other reasons. After adjustment, the highest prevalence ratios (PR) for noncompliance with the Pap smear occurred among young women (PR=1.5; 95%CI 1.25 - 1.80), with lower educational level (PR=1.5; 95%CI 1.12 - 2.12), who were living without a partner (PR=1.4; 95%CI 1.24 - 1.62), smokers (PR=1.2; 95%CI 1.07 - 1.39), who did not plan the current pregnancy (PR=1.3; 95%CI 1,21 - 1.61), who had attended less than six medical visits during the prenatal period (PR=1.4; 95%CI 1.32 - 1.69) and among users of oral contraceptives (PR=1.2; 95%CI 1.04 - 1.38). CONCLUSIONS: The higher the risk for uterine cervical cancer, the less likely a pregnant woman is to undergo a Pap smear. This definitely contributed to the increased morbidity and mortality from this disease in this setting.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(9):397-402
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000900002
PURPOSES: To analyze the sociodemographic and behavioral profile of sex partners, the proportion of those inadequately treated as well as to verify how many of them were inadequately treated and why some were not treated. METHODS: Quantitative study with data collected from May to October, 2008 at five public maternities in Fortaleza, Ceará. A survey was carried out with parturients who were hospitalized with syphilis and had a stable sex partner. We analyzed sociodemographic variables and those related to communication, diagnosis and treatment of sex partners. The data were entered into the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences and were analyzed using frequency distributions, measures of central tendency and dispersion. RESULTS: The study included 56 pregnant women. Most sexual partners were young adults aged on average 29 years, 50% of them had studied for less than seven years, 82.1 worked and 46.4% had a family income of less than a minimum wage. Of all the partners, 92.9% were the child's father and 69.6% lived with the women. Fifty percent and 12% were alcohol and drug users, respectively. Most partners (75.0%) were told about the diagnosis by the women, and in 78.6% of cases they were aware of the VDRL result before or during the prenatal period. However, 25.0% of the women did not communicate the result to their partners for the following reasons: not knowing the importance of the partner's treatment (50.0%), not being together after the diagnosis (42.9%) and having a quarrel (7.1%). Of the partners who were informed about the result before or during the prenatal period, 56.0% were treated and six (42.8%) were considered to have been properly treated. Among the ones who did not receive treatment, 63.6% refused it because they did not feel sick, because they did not believe in the treatment and because they were afraid of injections. CONCLUSIONS: Partners are told about the syphilis diagnosis of the pregnant women; however, only a few are properly treated.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(8):376-380
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000800006
PURPOSES: To describe the process of gait initiation of pregnant women and to compare the behavior of the pressure center in the three trimesters of pregnancy. METHODS: Fifty-seven low-risk pregnant women were evaluated, aged 18 to 35 years, selected for convenience location during the three trimesters of pregnancy. The women were divided into three groups of 19 subjects each, according to gestational age - 1st quarter (4-12 weeks), 2nd quarter (13-28 weeks), and 3rd quarter (29-42 weeks,). Each patient was positioned standing up with one foot on each AMTI force platform until she heard a beep indicating that she should start walking a distance of four meter. Data were analyzed using the SPSS software. The Kolmogorov Smirnov test, Tukey's test and Spearman correlation coefficient were used for group comparisons, with 5% significance level in all tests. RESULTS: Significant differences were found between the 1st quarter (GFT) and 3rd quarter (GTT) groups regarding mediolateral oscillation amplitude (GFT: 0.4 cm and GTT: 0.2 cm) and mediolateral displacement rate (GFT: 0.9 cm/s and GTT: 0.4 cm/s). There was a gradual decrease in anteroposterior and mediolateral oscillation rate, and in the speed of displacement from platform 1 to platform 2 in GFT. There was a significant difference in oscillation amplitude and mediolateral displacement speed between GFT and GTT. CONCLUSION: The variables analyzed showed minor differences and do not constitute an imminent risk for the stability dynamics of pregnant woman.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(8):386-393
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000800008
PURPOSE: To evaluate sociodemographic, behavioral and reproductive factors and morbidities associated with inadequate weight gain during pregnancy. METHODS: Cohort study conducted from December 2007 to August 2008 with women in the first trimester of pregnancy looking for prenatal care in the Public Health System who lived in the cities of Petrópolis or Queimados, Rio de Janeiro state (Brazil). Women with multiple pregnancy, who had a miscarriage in the index pregnancy or who lacked information for the assessment of pregravid nutritional status or weight gain were excluded. Pregravid nutritional status and weight gain during pregnancy were determined according to the criterion established by the Institute of Medicine (IOM). Statistical analysis was performed using a multinomial logistic regression model. RESULTS: A total of 1,287 women were included in the study; 26.6% of them were overweight or obese while 11% were underweight. Inadequate weight gain during pregnancy was observed in 71.4% of pregnant women; 35.6% of them did not gain enough weight while 35.8% gained more weight than recommended by the IOM. In the multivariate analysis, women with hypertension (OR=2.1; 95%CI 1.4-3.1), pregravid overweight (OR=2.5; 95%CI 1.4-4.5) or obesity (OR=2.7; 95%CI 1.8-3.9) and who had a higher educational level were more likely to gain more weight than recommended, while pregravid underweight (OR=0.6; 95%CI 0.4-0.9) represented a protection against excessive gain. CONCLUSION: Pregravid nutritional diagnosis and weight gain monitoring should be actions effectively instituted in the routine of health professionals.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(7):296-303
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000700002
PURPOSE: To determine the pattern of alcohol use before and during pregnancy and associated risk factors in puerperal women hospitalized in a public university hospital in Southeastern Brazil. METHODS: Between June and September 2009, 493 puerperae were consecutively evaluated. Those with cognitive impairment were excluded from the study. The AUDIT and CAGE questionnaires were used to diagnose alcohol use/abuse before pregnancy, in addition to the T-ACE during pregnancy. Another questionnaire was applied to collect sociodemographic data, such as age, educational level, marital status, and household income. The χ² test was used in the statistical analysis and the Odds Ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (95%CI) were calculated. A p-value <0.05 was considered to be significant. RESULTS: Before pregnancy, the CAGE was positive in 50/405 (12.3%) women and the AUDIT identified alcohol use in 331 (67.1%), which was of low risk in 233 (47.3%), risky in 73 (14.8%), and harmful or indicating possible alcohol dependence in 25 (5%). During pregnancy, the CAGE was positive in 53/405 (13.1%) women and the T-ACE in 84 (17%); the AUDIT identified alcohol use in 114 women, which was of low risk in 73 (14.8%), risky in 27 (5.5%), and harmful or indicating possible alcohol dependence in 14 (2.8%). During pregnancy, alcohol use was more frequent (OR=2.8; 95%CI 1.2 - 6.2) among women with a lower educational level (8.8 versus 3.3%) and more frequent (OR=3.8; 95%CI 1.3 - 11.1) among those who did not cohabit with a partner (6 versus 1.7%). Among pregnant women who drank alcohol, 49/114 (43%) were advised to stop drinking. CONCLUSIONS: Alarming alcohol use was observed during pregnancy, especially among pregnant women with a lower educational level and those who did not cohabit with a partner. There was a low frequency of counseling aimed at abstinence and the AUDIT was the instrument that most frequently diagnosed alcohol consumption.