-
Original Article
Prevalence of macrosomic newborn and maternal and neonatal complications in a high-risk maternity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo48
06-27-2024
Summary
Original ArticlePrevalence of macrosomic newborn and maternal and neonatal complications in a high-risk maternity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo48
06-27-2024Views141Abstract
Objective
Evaluate the prevalence of macrosomic newborns (birth weight above 4000 grams) in a high-risk maternity from 2014 to 2019, as well as the maternal characteristics involved, risk factors, mode of delivery and associated outcomes, comparing newborns weighing 4000-4500 grams and those weighing above 4500 grams.
Methods
This is an observational study, case-control type, carried out by searching for data in hospital’s own system and clinical records. The criteria for inclusion in the study were all patients monitored at the service who had newborns with birth weight equal than or greater than 4000 grams in the period from January 2014 to December 2019, being subsequently divided into two subgroups (newborns with 4000 to 4500 grams and newborns above 4500 grams). After being collected, the variables were transcribed into a database, arranged in frequency tables. For treatment and statistical analysis of the data, Excel and R software were used. This tool was used to create graphs and tables that helped in the interpretation of the results. The statistical analysis of the variables collected included both simple descriptive analyzes as well as inferential statistics, with univariate, bivariate and multivariate analysis.
Results
From 2014 to 2019, 3.3% of deliveries were macrosomic newborns. The average gestational age in the birth was 39.4 weeks. The most common mode of delivery (65%) was cesarean section. Diabetes mellitus was present in 30% of the deliveries studied and glycemic control was absent in most patients. Among the vaginal deliveries, only 6% were instrumented and there was shoulder dystocia in 21% of the cases. The majority (62%) of newborns had some complication, with jaundice (35%) being the most common.
Conclusion
Birth weight above 4000 grams had a statistically significant impact on the occurrence of neonatal complications, such as hypoglycemia, respiratory distress and 5th minute APGAR less than 7, especially if birth weight was above 4500 grams. Gestational age was also shown to be statistically significant associated with neonatal complications, the lower, the greater the risk. Thus, macrosomia is strongly linked to complications, especially neonatal complications.
Key-words Diabetes, gestationalFetal macrosomiaFetal weightJaundice, neonatalPregnancy, high riskRisk factorsShoulder dystociaSee more -
Original Article
Women’s Obstetric History and Midtrimester Cervical Length Measurements by 2D/3D and Doppler Ultrasound
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):540-546
10-23-2020
Summary
Original ArticleWomen’s Obstetric History and Midtrimester Cervical Length Measurements by 2D/3D and Doppler Ultrasound
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):540-546
10-23-2020Views147Abstract
Objective
The aim of the present study was to compare the obstetric history and both two- and tri-dimensional ultrasound parameters according to different cervical lengths.
Methods
The present cross-sectional study analyzed 248 midtrimester pregnant women according to cervical length and compared the data with the obstetric history and 2D/3D ultrasound parameters. Patients were divided into 3 groups according to cervical length: The Short Cervix group for cervical lengths ≥ 15mm and< 25mm(n= 68), the Very Short Cervix group for cervical lengths< 15mm (n = 18) and the Control group, composed of 162 pregnant women with uterine cervical lengths ≥ 25mm.
Results
When analyzing the obstetric history of only non-nulliparous patients, a significant association between the presence of a short cervix in the current pregnancy and at least one previous preterm birth was reported (p = 0.021). Cervical length and volume were positively correlated (Pearson coefficient = 0.587, p < 0.0001). The flow index (FI) parameter of cervical vascularization was significantly different between the Control and Very Short Cervix groups. However, after linear regression, in the presence of volume information, we found no association between the groups and FI. Uterine artery Doppler was also not related to cervical shortening.
Conclusion
The present study showed a significant association between the presence of a short cervix in the current pregnancy and at least one previous preterm birth. None of the vascularization indexes correlate with cervical length as an independent parameter. Uterine artery Doppler findings do not correlate with cervical length.
Key-words Cervical length measurementCervix uteriPregnancy trimester, secondPregnancy, high riskreproductive historySee more -
Original Article
Trends Associated with Stillbirth in a Maternity Hospital School in the North Zone of São Paulo: A Cross-Sectional Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):597-606
11-07-2019
Summary
Original ArticleTrends Associated with Stillbirth in a Maternity Hospital School in the North Zone of São Paulo: A Cross-Sectional Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(10):597-606
11-07-2019Views139See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate conditions associated with stillbirth (SB), and possible trends related with it, in a maternity hospital school in the North zone of São Paulo.
Methods
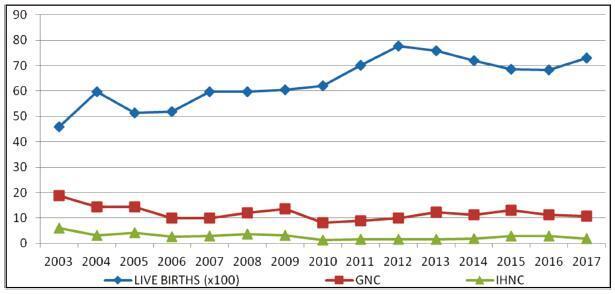
An observational, cross-sectional study conducted at the Hospital Maternidade- escola de Vila Nova Cachoeirinha with 1,139 SBs in the period of 2003 to 2017. Cases of intermediate SB (ISB) (weight between 500 and 999 g) and late SB (LSB) (weight ≥ 1,000 g) were compared. We evaluated clinical data, laboratory tests, and fetal and placental studies. Data were stored in Windows Excel (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA) worksheets, according to which graphs and tables were constructed. We used the statistical software SPSS for Windows version 18.0 (SPSS In., Chicago, IL, USA), estimating the prevalence ratio (PR) and odds ratio (OR), considering the 95% confidence interval (95% CI).
Results
The general SB rate was 11.9%, and the in-hospital SB rate was 2.8%. Pregnant women younger than 16 years of age were more likely to have ISB (OR 0.32, 0.15- 0.76), while patients older than 40 years old had a higher chance of LSB (PR 0.85, 0.72- 0.99). A total of 25.7% of the general population did not have prenatal care, and 77.1% of the cases presented fetal death at admission. The cases of ISB had a statistically significant association with home birth (OR 0.61, 0.46-0.80). Cesarean section was performed in 16.1% of the subjects, and misoprostol was the most used method for induction. Necropsy and placental study of the fetuses were performed, respectively, in 94.2% and 97.3% of the cases. Associated causes were not identified in 22.1% of the cases, and the main causes identified were amniotic sac infections (27.9%), fetal malformations (12.5%), placental abruption (11.2%), hypertensive syndromes (8.5%), and maternal syphilis (3.9%), the latter with an increasing trend.
Conclusion
Among the factors associated to SB were: hypertensive syndromes, amniotic sac infections, fetal malformations, placental abruption and syphilis. There was a growing trend in the number of cases of syphilis, which translates an alert. Diagnostic limitations justify indeterminate causes.
-
Artigos Originais
Evaluation of corticosteroid administration in situations of suspected imminent preterm delivery: a retrospective cohort study in a tertiary centre
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):467-472
10-01-2015
Summary
Artigos OriginaisEvaluation of corticosteroid administration in situations of suspected imminent preterm delivery: a retrospective cohort study in a tertiary centre
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(10):467-472
10-01-2015DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005440
Views78Abstract
PURPOSE
The administration of a single-course antenatal corticosteroid treatment is recommended for pregnant women between 24 and 34 weeks with risk of premature birth. The maximum effect is achieved when antenatal corticosteroids are administered between 24h and 7 days before delivery. The objective of this study was to evaluate the occurrence of birth within seven days of corticosteroid therapy in major obstetric situations with risk of preterm birth
METHODS
Retrospective cohort study including 209 pregnant women hospitalized in risk of preterm delivery, submitted to corticosteroid therapy for fetal lung maturation. The study was carried out between January 2012 and March 2014 at a university hospital. Main outcome measure was the number of women who delivered within 7 da ys after antenatal corticosteroid administration. Two groups were defined according to the reason for starting corticosteroids: threatened preterm labour (Group APPT) and other indications for corticosteroid therapy (Group RPPT). A Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was performed and a p value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
46.4% (n=97) of pregnant women gave birth in the seven days following corticosteroid administration. Delivery within 7 days occurred more frequently on group 2 in comparison to group 1 (57.3 versus42.4%; p=0.001). There is a statistically significant difference between the survival curve for groups 1 and 2, with a hazard ratio for delivery within 7 days 1.71 times higher for group 2 (95%CI 1.23-2.37; p<0.001)
CONCLUSION
It can be concluded that the probability of an event (birth within 7 days after corticosteroids) is smaller in the group of pregnant women admitted in the context of threatened preterm labor than for other indications. The use of corticosteroids in pregnant women admitted for suspected preterm labor should be subject to rigorous clinical evaluation
Key-words Adrenal cortex hormones/administration & dosageAdrenal cortex hormones/therapeutic useObstetric labor, prematurePregnancy, high riskSurvival analysisSee more -
Relato de Caso
Beta thalassemia major and pregnancy during adolescence: report of two cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):291-296
06-01-2015
Summary
Relato de CasoBeta thalassemia major and pregnancy during adolescence: report of two cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(6):291-296
06-01-2015DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005169
Views136See moreBeta thalassemia major is a rare hereditary blood disease in which impaired synthesis
of beta globin chains causes severe anemia. Medical treatment consists of chronic
blood transfusions and iron chelation. We describe two cases of adolescents with beta
thalassemia major with unplanned pregnancies and late onset of prenatal care. One had
worsening of anemia with increased transfusional requirement, fetal growth
restriction, and placental senescence. The other was also diagnosed with
hypothyroidism and low maternal weight, and was admitted twice during pregnancy due
to dengue shock syndrome and influenza H1N1-associated respiratory infection. She
also developed fetal growth restriction and underwent vaginal delivery at term
complicated by uterine hypotonia. Both patients required blood transfusions after
birth and chose medroxyprogesterone as a contraceptive method afterwards. This report
highlights the importance of medical advice on contraceptive methods for these women
and the role of a specialized prenatal follow-up in association with a
hematologist. -
Artigos Originais
Podocyturia in pregnant women with chronic hypertension may predict kidney injury?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):172-177
04-01-2015
Summary
Artigos OriginaisPodocyturia in pregnant women with chronic hypertension may predict kidney injury?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(4):172-177
04-01-2015DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005238
Views129See morePURPOSE:
To evaluate the presence of podocyturia in chronic hypertensive pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy and its possible association with renal disease.
METHODS:
This was an observational study of a convenience sample of 38 chronic hypertensive pregnant women. The podocytes were labeled by the indirect immunofluorescence technique with anti-podocin and diamidino-phenylindole (DAPI). The count was made on 30 random fields analyzed and corrected according to urinary creatinine (podocytes/mg creatinine). The patients were assigned to two groups: NG (normal glomerular function), up to 100 podocytes, and GP (probable glomerulopathy), more than 100 podocytes. Urinary creatinine was measured by the alkaline picrate method. The variables analyzed were body mass index, gestational age, and systolic and diastolic blood pressure at the time of sample collection. Data were analyzed using the SPSS - version 16.0 (IBM - USA). Statistical analysis was performed by the χ2 test, and significant differences were considered when p<0.05.
RESULTS:
The median podocyte count was 20.3 (0.0-98.1) for group GN, and 176.9 (109.1-490.6) for GP. The mean body mass index was 30.2 kg/m2 (SD=5.6), mean gestational age was 35.1 weeks (SD=2.5), median systolic blood pressure was 130.0 mmHg (100.0-160.0) and median diastolic blood pressure was 80.0 mmHg (60.0-110.0). There was no significant correlation between podocyturia and body mass index (p=0.305), gestational age (p=0.392), systolic blood pressure (p=0.540) or diastolic blood pressure (p=0.540).
CONCLUSIONS:
In this study, there was no podocyturia pattern consistent with the presence of active renal disease, although some of the women studied (15.8%) exhibited a significant loss. We believe that it is premature to recommend the inclusion of the determination of podocyturia in routine prenatal clinical practice in chronically hypertensive pregnant women.
-
Artigos Originais
Maternal mortality in a reference center in the Brazilian Southeast
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(9):388-393
11-06-2013
Summary
Artigos OriginaisMaternal mortality in a reference center in the Brazilian Southeast
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(9):388-393
11-06-2013DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000900002
Views90PURPOSE: To describe the prevalence of maternal mortality at a tertiary care hospital and to assessits preventability. METHODS: This study, through the analysis of maternal deaths that occurred during the period from 1999 to 2010 at a reference in Campinas - Brazil, CAISM/ UNICAMP, discusses some of the factors associated with the main causes of death and some structural problems of structure of the health services. It is a retrospective descriptive study with evaluation of sociodemographic variables and the medical and obstetric history of women, and the causes of death. RESULTS: The majority of maternal deaths occurred due to direct obstetric (45%) and avoidable (36%) causes, in women with preterm gestation, who delivered by cesarean section (56%) and received various management procedures, including blood transfusion, ICU admission and need for laparotomy and/or hysterectomy. The hospital transfer was associated with the predominance of direct obstetric (19 versus 6, p=0.02) and avoidable causes (22 versus 9, p=0.01). CONCLUSIONS: We conclude that, despite current advances in Obstetrics, infections and hypertensive disorders are still the predominant causes of maternal mortality. We observed an increase of clinical-surgical conditions and neoplasms as causes of death among women during pregnancy.
Key-words BrazilMaternal mortalityMaternal welfarePregnancy complications, infectiousPregnancy, high riskSee more -
Artigos Originais
Urine test to diagnose urinary tract infection in highh-risk pregant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(11):488-493
12-20-2012
Summary
Artigos OriginaisUrine test to diagnose urinary tract infection in highh-risk pregant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(11):488-493
12-20-2012DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001100002
Views110See morePURPOSE: To identify the accuracy of urinalysis in the diagnosis of urinary tract infection in pregnant women at high risk. METHODS: a prospective, cross-sectional study was conducted on 164 pregnant women admitted to the high-risk the ward of the Instituto de Medicina Integral Prof. Fernando Figueira (IMIP) during the period from January to June 2011. Patients who had been taking antibiotics in the last ten days were excluded. All patients were subjected to simple urine tests and urine culture at the beginning of their admission. The agreement between the results of the examinations was evaluated by Kappa indices (K), and accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and positive (PPV) and negative (NPV) predictive values were also determined. RESULTS: When only the presence of pus cells in urinalysis was used as a diagnostic criterion suggesting bacteriuria, there was a poor agreement when compared to uroculture (K=0.16). Accuracy was 61%, sensitivity 62.5%, and specificity 60.6%. PPV was 27.78% and NPV was 87%. CONCLUSION: The presence of alteration of urinalysis does not necessarily indicate an ongoing urinary tract infection, with urine culture being necessary. However, when urinalysis data are normal, uroculture may be avoided.


