Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):493-500
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800010
The interest of modern obstetrics in labor induction can be demonstrated by the huge amount of scientific articles published during the last few years. The advances of medicine in general and particularly of obstetrics allowed that more risky pregnancies reach term or near term, with a maternal or fetal indication for pregnancy interruption before the spontaneous onset of labor and delivery. This leads the obstetrician to the situation of choosing between cesarean section and labor induction. With the aim of helping the obstetrician to make the choice for labor induction and thus collaborate with the reduction in cesarean section rates, it is necessary that an accessible, cheap, safe, effective, easy to be used method with good acceptability is available. Although several methods of labor induction reported in medical literature do exist, it is known that there is no ideal method. However, among them, two are highlighted. The first is oxytocin, which has the advantages of promoting physiologic uterine contractions of labor and reverting uterine hypercontractility when suspended. The other method is misoprostol, nowadays the most used, which ripens the uterine cervix and induces uterine contractions of labor. However, there are still some controversies regarding its ideal dose, route and safety.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):442-449
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800002
PURPOSE: to establish the frequency of acute toxoplasmosis in pregnant women, vertical transmission rate and the perinatal results of the infected fetuses and also to evaluate the relationship between the most used maternal-fetal diagnostic tests for toxoplasmosis during pregnancy and the relationship between age and acute toxoplasmosis infection during pregnancy. METHODS: longitudinal prospective study of 32,512 pregnant women attended by The Pregnancy Protection Program of the State of Mato Grosso do Sul - Brazil, from November 2002 to October 2003. ELISA (IgG and IgM) and IgG avidity test were performed for maternal diagnosis and amniotic fluid PCR for fetal investigation of the infection. The relationship between data was analyzed statistically by the chi2 or two-sided Fisher's exact test in contingency tables. RESULTS: a 0.42% frequency of acute Toxoplasma gondii infection among pregnant population was found, where 92% were previously exposed and 8% were susceptible. Among IgM-positive pregnant women, the age ranged from 14 to 39 years, with a mean of 23±5.9 years. There was no statistically significant relationship between age and maternal acute T. gondii infection (p=0.73). The vertical transmission rate was 3.9%. A statistically significant relationship was shown (p=0.001) between a lower avidity IgG test (<30%) and the presence of fetal infection and a higher IgG avidity test (>60%) and the absence of fetal infection. There was a statistically significant association (p=0.001) between fetal infection (amniotic fluid PCR) and neonatal infection. CONCLUSIONS: maternal acute toxoplasmosis frequency was lower than the Brazilian national parameters, whereas vertical transmission rate did not differ from the rates found in other studies. The IgG avidity test, when associated with gestational age and the examination date, was useful to evaluate the therapeutical options and to consider the risk of vertical transmission when performed before 12 weeks. Positive PCR in amniotic fluid showed a positive relationship with the worst neonatal prognosis, being a specific method in diagnosing intrauterine fetal infection.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):316-322
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the relationship between renal transplantation and pregnancy through the analysis of clinical and obstetric intercurrent events and perinatal outcomes. METHODS: a retrospective series of 39 cases of pregnancy in 37 women with renal transplantation from January 1997 to December 2003 was evaluated. A control group consisted of 66 pregnant women with no previous clinical pathologies. This group received prenatal care and these patients delivered during 2002 and 2003. Preeclampsia, premature rupture of membranes, premature delivery, and intrauterine growth restriction were used to compare these variables. Demographic characteristics of these groups were related to the mean age at conception, ethnic characteristics and obstetric past. Regarding renal transplantation the type of donator and used immunosuppressive drugs were evaluated. The studied clinical variables were chronic hypertension, anemia and urinary tract infection. The interval between the surgery and conception, occurrence of dysfunction, rejection and loss of the allograft were characteristcs related to the allograft. Obstetric variables were related to the type of delivery, incidence of preeclampsia and premature rupture of membranes. Perinatal outcomes were premature delivery and intrauterine growth restriction and these results were compared with renal function. The used statistical methods were the chi2 and Fisher's exact tests. The significance level was fixed always as less than or equal to 0.05 (5%). RESULTS: the mean age at conception was 27 years. The live donator was the most frequent among the patients. Among the immunosuppressive drugs, cyclosporine was the most used. Chronic hypertension occurred in 82% of the cases, anemia in 77% and urinary tract infection in 38.5%. The incidence of renal dysfunction was 47.4% and preeclampsia was the main cause. The loss of the renal transplantation occurred in 10.2%. Delivery by cesarean section was performed in 53.8% of the patients, and the main causes were hypertensive syndromes. Preeclampsia occurred in 28.2%. Among the perinatal outcomes, premature delivery occurred in 46.1% of the cases, with a significant relation to creatinine level greater than or equal to 1.5 mg/dL at the start of prenatal care. Another observed intercurrent event was intrauterine growth restriction, which occurred in 41.0%, and here we found no relation between this event and creatinine levels. CONCLUSIONS: young patients constituted the study group. Chronic hypertension, anemia and urinary tract infection were very common. Renal dysfunction was frequent and must be investigated during prenatal care. There were four cases of loss of the transplant due to clinical or obstetric causes. Cesarean delivery had the highest incidence, but vaginal delivery should be the first choice in these cases. Preeclampsia occurred very frequently and this complication should be considered as a high risk. Preterm delivery and intrauterine growth restriction were the main perinatal complications. Premature deliveries before 37 weeks of gestation were related to allograft function.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(6):310-315
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000600004
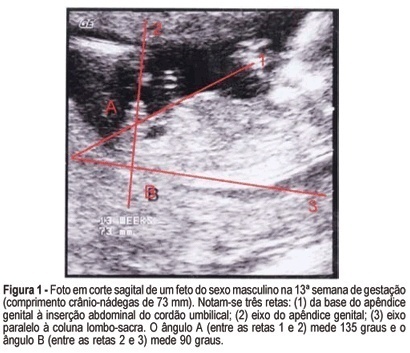
PURPOSE: to evaluate the accuracy of fetal gender prediction at 11 to 13 weeks and 6 days by measuring the anterior and posterior genital tubercle angles. MESTHODS: the anterior and posterior genital tubercle angles were measured in a midsagittal plane in 455 fetuses from 11 to 13 weeks and 6 days. The probability of a correct fetal sex prediction (confirmed after birth) was categorized in accordance with the angle measurements, gestational age and crump-rump length. The optimal accuracy cutoffs were derived from a ROC-plot. The interobserver variability was evaluated by a Bland-Altman plot. RESULTS: the correct fetal sex prediction rate increased with gestational age and crump-rump length. Using a 42-degree anterior angle as a cutoff, a correct fetal sex prediction occurred in 72% of the fetuses from 11 to 11 weeks and 6 days, 86% from 12 to 12 weeks and 6 days and 88% from 13 to 13 weeks and 6 days. Using a 24-degree posterior angle as a cutoff, a correct fetal gender prediction occurred in 70, 87 and 87%, respectively. The interobserver variability evaluation revealed a mean difference between paired measurements of 15.7 and 9 degrees for the posterior and anterior angles, respectively. CONCLUSION: the measurement of the genital tubercle angles showed a high accuracy in correctly predicting the fetal sex from the 12th week of gestation on. However, accuracy was still not high enough for clinical use in pregnancies at risk of serious X-linked diseases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(1):7-12
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000100002
Purpose: to compare the capacity of diagnosing oligohy-dramnios by ultrasound using different measures of the maximum pool depth of amniotic fluid in comparison to the amniotic fluid index among normal pregnant women from the 36th to the 42nd week of gestation. Methods: a descriptive study of diagnostic validity was perfomed, on 875 normal pregnant women who were studied through routine obstetric ultrasound examinations, including the measure of the maximum pool depth for the diagnosis of oligohydramnios, using the amniotic fluid index as the gold standard. The data were analyzed through sensitivity and specificity of the maximum pool depth of amniotic fluid using 10, 20 and 30 mm cut-offs, in comparison to the amniotic fluid index values of the normal curve in percentiles 2.5 and 10 for different gestational ages. Results: the maximum pool depth had a poor sensitivity to diagnose oligohydramnios when 10 and 20 mm were used as cut-offs, and good sensitivity and specificity when 30 mm was used, in comparison to the amniotic fluid values in percentiles 2.5 and 10. The best sensitivity and specificity of the maximum pool depth were when found using a 30 mm cut-off in comparison to 2.5 percentile to diagnose oligohydramnios. Conclusions: the capacity to diagnose oligohydramnios by the measure of the maximum pool depth is satisfactory only with the cut-off of 30 mm
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(5):283-288
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000500009
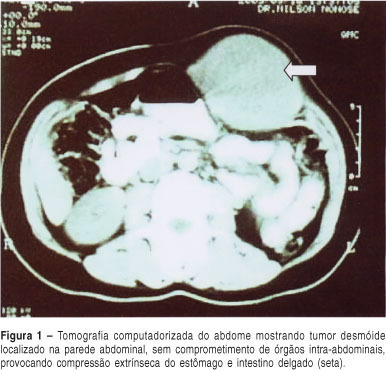
Desmoid tumors are neoplasms of the conjunctive tissue that are characterized by exclusive locoregional growth, frequent recurrence and minimal metastatic potential. They mainly affect individuals with familial adenomatous polyposis of the colon, and rarely occur isolated. The single form of this neoplasm most frequently appears in women of reproductive age, and during pregnancy. A case of a desmoid tumor of large proportions located in the abdominal wall is described. It appeared at the 17th week of pregnancy in a woman without any history of familial adenomatous polyposis. The neoplasm was totally extirpated, with the use of a polypropylene prosthesis for reconstitution of the abdominal wall. One year after the surgery, the patient continues to be well, while using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the prevention of relapses.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(4):174-180
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000400003
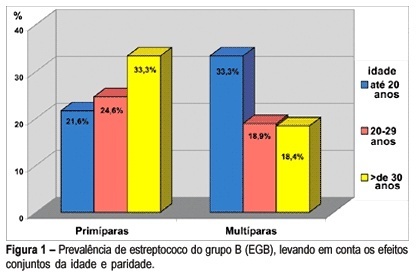
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of group B Streptococcus (GBS) in pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy and explore the factors potentially associated with colonization. METHODS: a sample of 273 pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy, from the prenatal care center in Southern Brasil, was investigated. Vaginal and anorectal samples were collected and innoculated in Todd-Hewitt selective broth supplemented with 10 µg/mL colistin and 15 µg/mL nalidixic acid and afterwards cultured on defibrinated sheep blood agar plates. All suspected colonies were submitted to the agglutination test for detection of the specific group B antigen. The Camp test was used for GBS identification in non-hemolytic varieties. Demographic, socioeconomic, reproductive, and clinico-obstetric data were also analyzed. Prevalence ratio (PR) was used as risk measurement. Confidence interval was considered significant at the level of 95% (alpha=0.05). RESULTS: prevalence of Streptococcus (GBS) colonization amounted to 21.6% (59), 9.9% (27) of pregnant women showing positivity in both sites; vaginal site colonization was found in 6.95% (19) of the women and 4.75% (13) of the samples showed positivity only in the anal site. GBS prevalence was slightly higher in pregnant women under 20 years, in those with less schooling and in primiparae and was twice as high among those who did not reported spontaneous abortion, but with no statistical significance. No difference was found in GBS prevalence according to the history of sexually transmittted diseases and tabagism. When analyzed together, the factors detected as potentially associated with colonization by GBS were: primiparae over 30 years (PR=1.55) and women with more than one sexual partner and increased frequency of sexual activity (p<0.05) (55,6 vs 20.5%; p<0.05). No difference regarding prevalence was found to exist in relation to the history of sexually transmitted diseases, previous spontaneous abortion and tabagism. CONCLUSION: these results confirm the need for routine collection for GBS culture from both sites (vaginal and anal) in all pregnant women in the third trimester of pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(4):168-173
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000400002
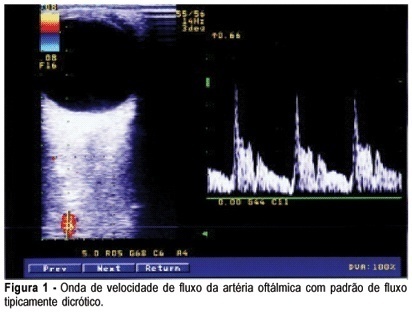
PURPOSE: to evaluate ophthalmic and retinal central artery Doppler indices during the second and third trimesters of normal pregnancy and to compare the right with left eye Doppler indices of normotensive women. METHODS: a cross-sectional study which evaluated central retinal and ophthalmic artery Doppler velocimetry values of 51 normal pregnant women, in the 20th to 38th week of gestation. The following values were analyzed: pulsatility and resistance indexes (PI, RI), peak systolic and end-diastolic flow velocity (PSV, EDFV) and peak velocity ratio (PVR). The Doppler indices in the right and left eyes were studied by the median. The paired Student's t test was used to confront the right and left eye values and the Pearson linear correlation analysis was performed to study the value changes throughout the gestation, with the level of significance set at 5%. RESULTS: Doppler velocimetry indices of ophthalmic and central retinal arteries (median values) were, respectively: PI=1.83; RI=0.78; PSV=34.20; EDFV=6.80; PVR=0.48 and PI=1.34; RI=0.70; PSV=7.40; EDFV=2.10. There was no significant difference between the right and left side Doppler values. Linear correlation analysis showed no association between the arterial values and pregnancy age. CONCLUSION: the unilateral analysis of ophthalmic and central retinal artery Doppler velocimetry values can be used in systemic maternal disease. There is no significant change in ophthalmic and central retinal artery Doppler velocimetry values throughout normal pregnancy.