Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(2):92-97
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000200009
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL) is an endemic disease in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, mainly in the areas near the Paraguay and Paraná rivers. An increasing number of cases have been occurring especially in the state capital Campo Grande, with consequent occurrence of VL cases in pregnant women. This situation causes an elevated risk of vertical transmission of the parasite. In this report, we describe a case of VL in a pregnant woman followed up by our group, who was treated with liposomal amphotericin B, with no vertical transmission of the parasite. In our report, we demonstrate a therapeutic option for kala-azar during pregnancy, since antimoniate, the first-choice drug, is not prescribed during the gestational period.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(8):627-632
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000800006
OBJECTIVE: to establish the rate of toxoplasmosis soroprevalence in postpartum women, attended in two hospitals of the Public Health System (SUS) in Cuiabá, and its correlation with age, previous abortion and women's knowledge of the disease. METHODS: a cross-sectional study including 205 women with ages from 14 to 43 (mean 22.4) years old, attended in these hospitals for two months, in the first or second days postpartum. Each woman answered a short questionnaire and had peripheral blood sample collected. Blood samples were stored at 20°C until assay. The seroprevalence was determined by quantitative detection of specific IgG antibody against Toxoplasma gondii, using a microparticle enzyme immunoassay. All samples were assayed at the same time. RESULTS: The average number of pregnancies in the women included in this study was 2.2, and the majority of them was pregnant for the first time. The seroprevalence found was 70.7% (165 of 205 women). No statistical correlation was found between seroprevalence and age (p = 0.967) or previous abortion (p = 0.82). Most of the women in this study (78%) did not know about toxoplasmosis and no statistical correlation was found between this condition and seroprevalence (p = 0.49). CONCLUSION: the high seroprevalence found in the present study is in accordance with surveys previously reported in our country and other developing countries. Among the women included in this study, an expressive number (29.3%) is still under risk of contamination. The lack of statistical correlation between seroprevalence and women's age, lack of knowledge about the disease and report of previous abortion is in accordance with some previous studies and in disagreement with others.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(6):413-418
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000600005
PURPOSE: to determine the existence of association between blood pressure rise and plasma ANP and BNP levels in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia, considering the existence of a hypertensive state before pregnancy and supportive drug influence on these hormones. METHODS: in a case-control transversal study, 86 pregnant women were assessed regarding arterial pressure level and plasma ANP and BNP levels. Clinical and laboratory tests were carried out to diagnose preeclampsia and the use of hypotensive drugs and magnesium sulfate was considered. Hormone determinations were obtained through radioimmunoassay, after extraction in C18 Sep-pak columns. Correlation was investigated by means and regression analysis in the whole group of pregnant women and in specific groups, considering prior hypertension. RESULTS: plasma ANP values were 41.5±7.3, 78.4±13.1 and 89.2±13.4pg/mL (p<0.00001) and plasma BNP values were 79.5±15.8, 176.7±42.2 and 208.3±63.5 pg/mL (p=0.005), respectively, for mean blood pressure =107 mmHg, 107-139 mmHg and =140 mmHg. It was verified that the positive correlation between plasma ANP concentrations and pressure levels in preeclampsia did not depend on the existence of a hypertensive state before pregnancy (p<0.0001: preeclampsia and p<0.01: preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension), whereas BNP dosages were not associated with the arterial pressure in the group with arterial hypertension prior to pregnancy (p=0.004: preeclampsia and p=0.18: preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension). CONCLUSION: aggravation of hypertension in preeclampsia correlates with serum ANP and BNP concentrations, although BNP values may be influenced by the existence of a prior hypertensive state.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(3):163-167
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000300004
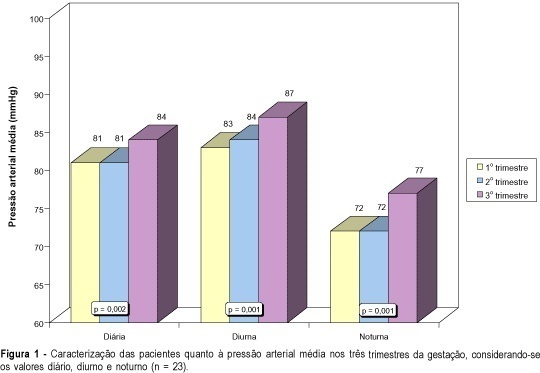
PURPOSE: to show longitudinally the profiles and parameters of pressure rhythm and heart rate in normotensive pregnant women during the three trimesters of pregnancy. PATIENTS AND METHODS: the longitudinal and random study involved 23 normotensive pregnant women, mean age 23.3 ± 3.9 years, recruited from the prenatal clinics of the "Maternidade-Escola Hilda Brandão - Santa Casa de Belo Horizonte/MG". Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring was done every three months (up to 14 weeks, between 18 and 28 weeks and between 32 and 40 weeks, using the SpaceLabs monitor, model 90207. RESULTS: a significant increase (p<0.01) in the 24-h systolic (115 and 104 mmHg), diastolic (73 and 61 mmHg) and average diurnal and nocturnal blood pressures (87 and 77 mmHg respectively), was noticed in the third trimester of pregnancy. Mother's diurnal blood pressure and heart rate (83, 84 and 87 mmHg; 94, 95 and 93 bpm) were significantly higher than the nocturnal measurements (72, 72 and 77 mmHg; 74, 79 and 79 bpm), in the three trimesters. Mother's heart frequency did not change during progress of pregnancy. CONCLUSION: increase in blood pressure during the third trimester of pregnancy could be shown. Maternal daily and diurnal heart rate did not change when the three trimesters were compared. The nocturnal heart rate was significantly lower in the first trimester as compared to the other trimesters.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(5):331-335
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000500005
PURPOSE: to evaluate whether there is an association between recurrent spontaneous abortion and atopy. METHODS: this was a case-control study with 230 women: 71 with a history of recurrent spontaneous abortion (group A) and 159 with a history of successful pregnancy (group B). The evaluation included a questionnaire in order to investigate the personal history of atopy, considering symptoms of atopic dermatitis, urticaria, rhinitis, asthma, conjunctivitis and gastric or intestinal symptoms. The presence of specific IgE in response to a pool of inhalants, Phadiatop, detected by an enzymatic fluorescence reaction in blood was also investigated. The data were analyzed by Fisher's exact test and a p value < 0.05 was set as level of significance. RESULTS: a positive history of atopy was observed in 57.7% of group A patients and in 55.3% of group B patients. The incidence of positive IgE against Phadiatop was 38% and 33.9% in groups A and B, respectively. Association of allergy disease with positive Phadiatop (presence of specific IgE) was detected in 28.2% of group A and in 22% of group B patients. There was no significant difference between the groups. CONCLUSIONS: we did not observe any association between recurrent spontaneous abortion and atopy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(5):309-316
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000500002
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of domestic physical violence among women who delivered at a tertiary center in the Northeast of Brazil, to study the main risk factors associated with domestic violence, and to determine perinatal outcome. METHODS: a cross-sectional study was conducted, enrolling 420 women who delivered at a tertiary center in Recife (Brazil) with fetuses weighing more than 500 g. They were submitted to interviews with open and closed questions. The prevalence of domestic physical violence was determined. Statistical analysis was performed using c² and Fisher's exact tests at a 5% level of significance. The prevalence ratio was determined as measurement of relative risk of violence. Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed and the adjusted risk was calculated. RESULTS: the prevalence of domestic physical violence was 13.1% (95% CI = 10.1-16.6) and 7.4% (95% CI = 5.2-10.2) before and during pregnancy, respectively. The pattern of violence has changed during pregnancy: stopped in 43.6%, was reduced in 27.3% and increased in 11% of the victims. After multivariate analysis the variables that persisted strongly associated with violence were low female educational level, history of violence in the women´s family, partner's use of alcohol and unemployment. Perinatal outcome was studied and a significantly higher frequency of neonatal death was observed among victims of domestic violence. CONCLUSIONS: a high prevalence of domestic physical violence was observed (about 13%) in women who delivered at a tertiary center in Northeast of Brazil. The main risk factors were low educational level and previous familiar history of violence in the women's family, alcohol use by and unemployment of their partners. Neonatal mortality was increased in victims of violence.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(6):397-402
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000600009
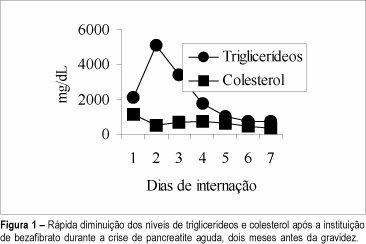
Severe hypertriglyceridemia during pregnancy rarely occurs but it frequently produces complications, such as acute pancreatitis, a serious health risk both for the mother and the fetus. The treatment of a patient who had had acute pancreatitis due to hypertriglyceridemia (triglyceridemia = 5100 mg/dl) two months before fecundation is presented in this paper. During gestation, bezafibrate was substituted for 3.0 g omega-3 fatty acids (14% eicosapentaenoic and 11.13% docosahexaenoic acids). With this therapy, the triglyceride levels were maintained below 800 mg/dl, which is considered to be the safe limit to avoid acute pancreatitis. No complication occurred during pregnancy, the patient delivered vaginally (40 weeks), and the newborn (3075 g) did not present any morphological alterations. We conclude that an adequate diet and the use of omega-3 fatty acids were effective in preventing acute pancreatitis in this pregnant woman with serious hypertriglyceridemia. This therapeutic approach may be used alternatively to other treatments currently utilized for familial hypertriglyceridemia in pregnancy.
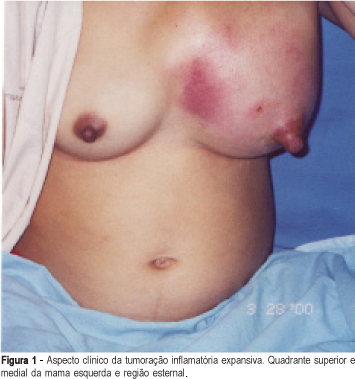
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2001;23(9):605-607
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000900009
Actinomycosis of the breast is a rare inflammatory disease that has been infrequently reported. It can be primary actinomycosis of the breast, when caused by lesions of the mammary skin and secondary, when there is thoracic or pleural infection; it has extremely variable clinical presentations and may simulate mastitis and malignancies such as inflammatory carcinoma. The diagnosis is confirmed by culture and by finding typical actinomycotic colonies. The usual treatment is surgical drainage and intravenous and oral long-term administration of antibiotics. The authors present a case of actinomycosis of the breast in a 12-week pregnant woman who presented a tumor in the left breast.