Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo21
We conducted a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials evaluating the clinical effects of ferric carboxymaltose therapy compared to other intravenous iron in improving hemoglobin and serum ferritin in pregnant women. We also assessed the safety of ferric carboxymaltose vs. other intravenous iron.
EMBASE, PubMed, and Web of Science were searched for trials related to ferric carboxymaltose in pregnant women, published between 2005 and 2021. We also reviewed articles from google scholar. The keywords "ferric carboxymaltose," "FCM," "intravenous," "randomized," "pregnancy," "quality of life," and "neonatal outcomes" were used to search the literature. The search was limited to pregnant women.
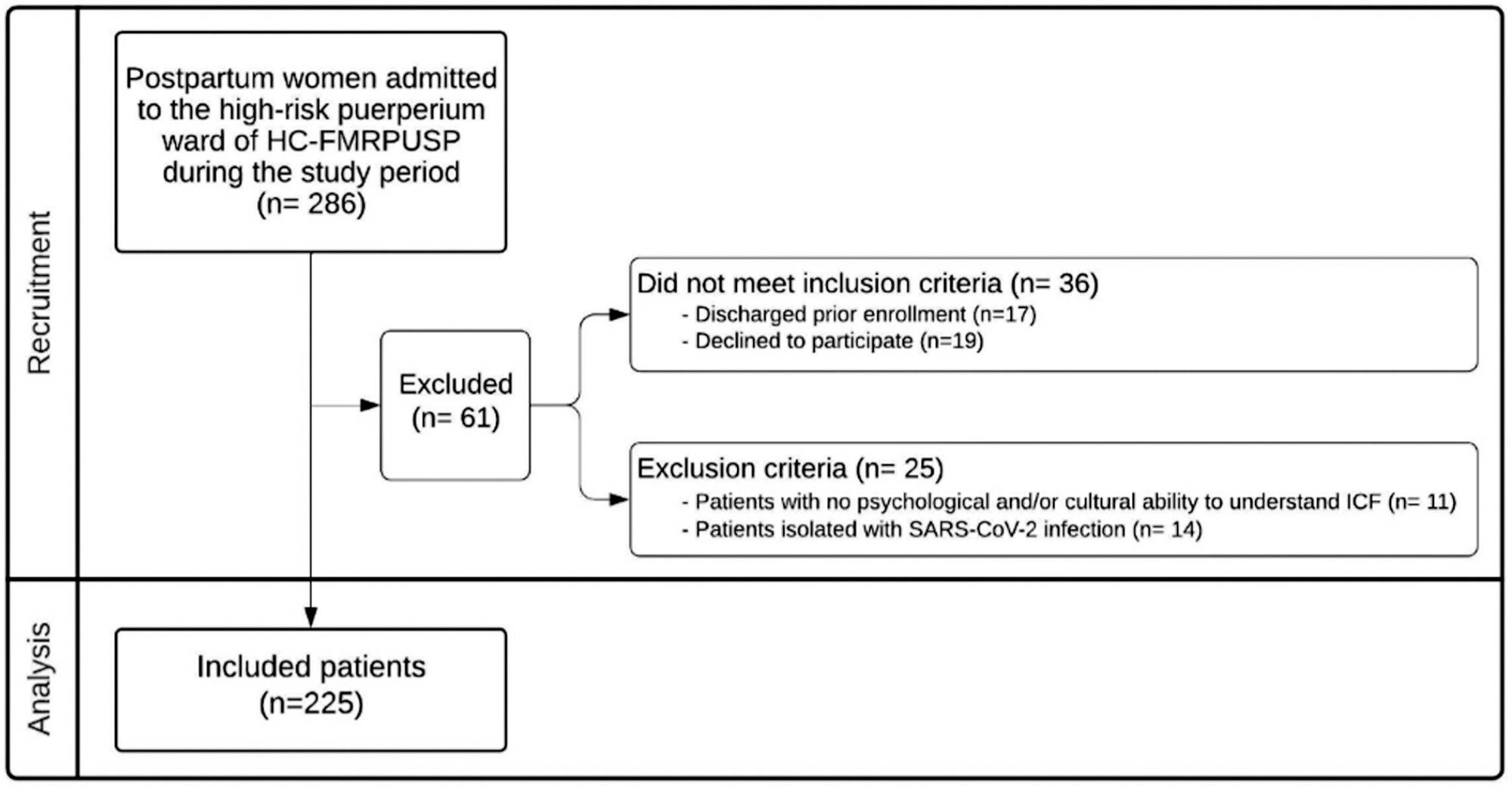
Studies related to ferric carboxymaltose in pregnancy were scanned. Observational studies, review articles, and case reports were excluded. Randomized studies in pregnant women involving ferric carboxymaltose and other intravenous iron formulations were shortlisted. Of 256 studies, nine randomized control trials were selected.
Two reviewers independently extracted data from nine selected trials
The final effect size for increase in hemoglobin after treatment was significant for ferric carboxymaltose vs. iron sucrose/iron polymaltose (standard mean difference 0.89g/dl [95% confidence interval 0.27,1.51]). The final effect size for the increase in ferritin after treatment was more for ferric carboxymaltose vs. iron sucrose/iron polymaltose (standard mean difference 22.53µg/L [-7.26, 52.33]). No serious adverse events were reported with ferric carboxymaltose or other intravenous iron.
Ferric carboxymaltose demonstrated better efficacy than other intravenous iron in increasing hemoglobin and ferritin levels in treating iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo4
To classify the bibliometric indicators of online scientific research on placentophagy.
A bibliometric study was conducted to quantify the scientific production of authors and institutions with the aim of highlighting the growth and impact of these publications nationally and internationally. The Bradford Law, network maps, and textual statistics were used, with searches conducted in libraries and databases in October 2021.
The sample consisted of 64 articles, whose primary authors were associated with 49 institutions, and mostly with degrees in anthropology. The United States of America was the country that published the most papers on the theme, and most studies were reviews with individual production. Through the term analysis, it was found that the predominant themes regarding placentophagy were the following: Alternative therapy for women's health, methodologies used for research in this area, period of placenta ingestion (postpartum period), and its benefits.
The bibliometric indicators found are essential for the development of future research.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(10):557-561
We compared thyroid volume (TV) and presence of nodular goiter (NG) in pregnant vs. non-pregnant women in an iodine-sufficient area. We also evaluated the relationship between gestational age, parity, and TV in the pregnant women group, and determined the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles of normal TV in pregnancy.
This cross-sectional study included 299 healthy women (216 pregnant) without previous thyroid diseases. Thyroid ultrasounds were performed and compared between pregnant and non-pregnant women. The range of normal distribution of TV (2.5th and 97.5th percentiles) in pregnancy was determined after excluding individuals with positive thyroid antibodies, NG, and/or abnormal serum thyrotropin (TSH) or free thyroxine (FT4).
Thyroid volume was larger among pregnant compared to non-pregnant women (8.6 vs 6.1 cm3; p< 0.001) and was positively correlated with gestational age (rs = 0.221; p = 0.001), body mass index (BMI, rs 0.165; p = 0.002), and FT4 levels (rs 0.118 p = 0.021). Nodular goiter frequency did not differ between the two groups. There was a negative correlation between TV and TSH (rs -0.13; p = 0.014). Thyroid volume was lower among primiparous compared to multiparous patients (7.8 vs 8.9; p< 0.001) and was positively correlated with parity (rs 0.161; p = 0.016). The 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles of TV were 4.23 and 16.47 cm3, respectively.
Thyroid volume was higher in pregnant compared to non-pregnant women and was positively related to parity, BMI, and gestational age in a normal iodine status population. Pregnancy did not interfere with the development of NG.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(10):568-574
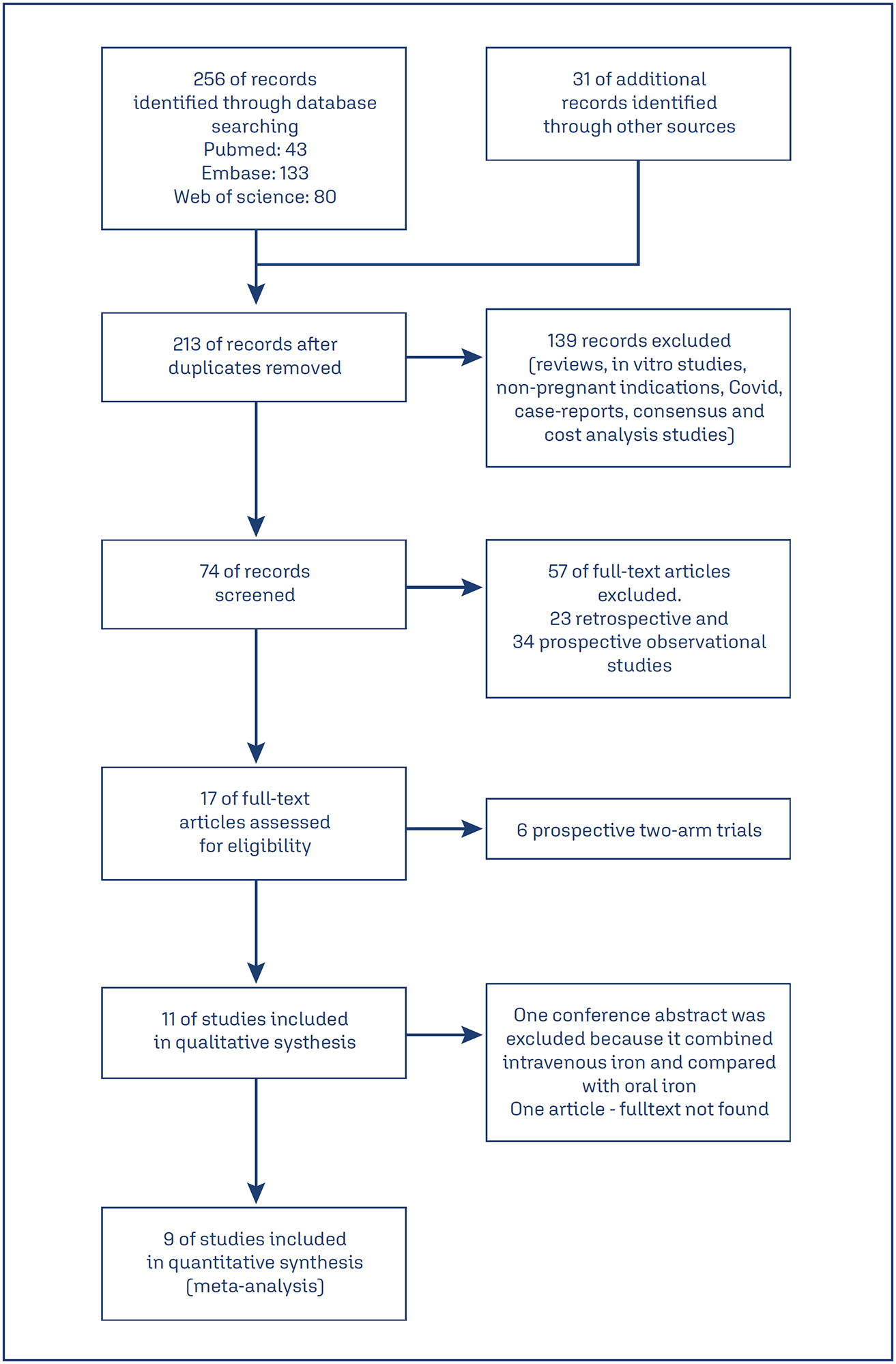
Pregnancy in women with lupus poses a higher risk of complications compared with the general population. The present study aimed to determine and describe the obstetric and neonatal outcomes of pregnant women with lupus.
We conducted an observational retrospective study of pregnant women with the diagnosis of lupus, who were selected and followed at the Maternal-Fetal Medicine Clinic of our institution between January 2013 and July 2018. We analyzed 59 pregnancies and 52 newborns, and collected data regarding sociodemographic features, the preconception period, pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum and the newborn. A descriptive analysis of the variables was performed.
In 58% of the cases, the pregnancy was uneventful. We registered flares in 25% of the cases, preeclampsia in 3%, fetal growth restriction in 12%, gestational loss in 10%, preterm labor in 10%, postpartum complications in 20%, and small for gestational age newborns in 17% of the cases.
Most pregnancies in women with lupus have favorable obstetric and neonatal outcomes. Prenatal counseling, adequate multidisciplinary surveillance, and optimized treatment of the disease are fundamental pillars for these good results.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(11):638-645
This study focused on pregnant and postpartum women during the COVID-19 pandemic, aiming to determine the attitudes and behaviors of vaccinated and unvaccinated groups, and the vaccination behaviors in the groups with and without the disease. The reasons for refusing the vaccine were also questioned.
This cross-sectional study was performed from September 2021 to October 2021. The study data were collected using a face-to-face questionnaire. The participants were pregnant women who applied to the hospital for routine antenatal care and were hospitalized, and women in the postpartum period. Additionally, pregnant and postpartum patients who were diagnosed with COVID-19 at the time of admission and were hospitalized and admitted to the intensive care unit due to this disease were also included in the study.
A total of 1,146 pregnant and postpartum women who completed the questionnaire were included in our study. Only 43 (3.8%) of the participants were vaccinated; 154 (13.4%) of the participants had comorbidities. The number of COVID-19-positive patients was 153. The lack of sufficient information about the safety of the COVID-19 vaccine is the most common reason for the refusal.
Vaccine refusal can significantly delay or hinder herd immunity, resulting in higher morbidity and mortality. Considering the adverse effects of COVID-19 on pregnancy, it is essential to understand pregnant and postpartum women's perceptions toward vaccination to end the pandemic.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(6):303-311
The lack of data on the impact of hyperglycemia and obesity on the prevalence of pregnancy-specific urinary incontinence (PSUI) led us to conduct a cross-sectional study on the prevalence and characteristics of PSUI using validated questionnaires and clinical data.
This cross-sectional study included 539 women with a gestational age of 34 weeks who visited a tertiary university hospital between 2015 and 2018. The main outcome measures were the prevalence of PSUI, the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire Short Form (ICIQ-SF), and the Incontinence Severity Index (ISI) questionnaires. The women were classified into four groups: normoglycemic lean, normoglycemic obese, hyperglycemic lean, and hyperglycemic obese. The differences between groups were tested using descriptive statistics. Associations were estimated using logistic regression analysis and presented as unadjusted and adjusted odds ratios.
Prevalence rates of PSUI were no different between groups. However, significant difference in hyperglycemic groups worse scores for severe and very severe PSUI. When adjusted data for confound factors was compared with normoglycemic lean group, the hyperglycemic obese group had significantly higher odds for severe and very severe forms of UI using ICIQ-SF (aOR 3.157; 95% CI 1.308 to 7.263) and ISI (aOR 20.324; 95% CI 2.265 to 182.329) questionnaires and highest perceived impact of PSUI (aOR 4.449; 95% CI 1.591 to 12.442).
Our data indicate that obesity and hyperglycemia during pregnancy significantly increase the odds of severe forms and perceived impact of PSUI. Therefore, further effective preventive and curative treatments are greatly needed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):142-148
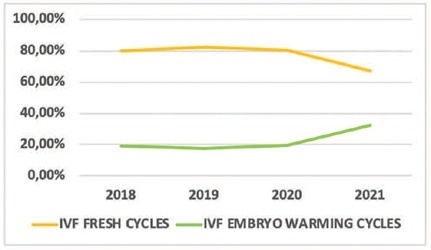
To understand the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic on in vitro fertilization (IVF) clinical pregnancy rates and analyze factors that may have influenced their outcome.
This was a retrospective observational study conducted at a tertiary-care Brazilian fertility center. All fresh IVF and embryo warming cycles performed from March 11 to December 31, 2018–2021 were analyzed, and their data were used to calculate fertilization, embryo cleavage, cycle cancellation, embryo transfer (ET), and clinical pregnancy rates. Statistical tests were used to evaluate the alterations found. Logistic regression models were used to explore the association of the categorical variables with the observed clinical pregnancy rates. Data from 2018 and 2019 (prepandemic) and 2020 and 2021 (pandemic) were grouped.
A total of 756 cycles were analyzed (n = 360 prepandemic and n = 396 pandemic). The age group of the patients, fertilization rates, and cleavage rates did not have significant differences (p > 0.05). There was a reduction in the percentage of fresh IVF and an increase in embryo warming cycles (p = 0.005) during the pandemic. There was also an increase in fresh cycle cancellations (p < 0.001) and a reduction in ET rates (p < 0.001). The pandemic had a negative impact on clinical pregnancy rates (p < 0.001) especially due to the increase in fresh cycle cancellations (p < 0.001).
Embryo warming cycles with subsequent frozen-thawed ET were presented as a viable alternative to continue assisted reproductive treatments against pandemic restrictions on fresh cycles, ensuring clinical pregnancy, albeit at a lower rate than that of the prepandemic period.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):059-064
To evaluate the seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis among puerperal women cared for at a tertiary university hospital and the level of understanding of these puerperal women about toxoplasmosis, vertical transmission, and its prophylaxis.
For this cross-sectional study, we evaluated 225 patients using presential interviews, prenatal documentation, and electronic medical records. Data were stored using Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) software. Prevalence rates were estimated by the presence of reactive IgG antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii. Data analysis was performed using the chi-square test and calculation of the odds ratio (OR). Seroreactivity to T. gondii and exposure variables (age, educational level, and parity) were analyzed using a confidence interval (95%CI) and a significance level of 5% (p < 0.05).
The seropositivity rate for T. gondii was 40%. There was no association between seroprevalence and age. Primiparity was a protective factor against seropositivity and low education was a risk factor.
Knowledge of T. gondii infection and its transmission forms was significantly limited, presenting a risk for acute maternal toxoplasmosis and vertical transmission of this protozoan. Increasing the education level regarding the risk of toxoplasmosis during pregnancy could reduce the rates of infection and vertical transmission of this parasite.