Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(7):348-355
To identify the epidemiological risk factors for congenital anomalies (CAs) and the impact of these fetal malformations on the perinatal outcomes.
This prospective cohort study comprised 275 women whose fetuses had CAs. Maternal variables to establish potential risk factors for each group of CA and perinatal outcomes were evaluated. The primary outcome was CA. Secondary outcomes included: fetal growth restriction (FGR); fetal distress (FD); premature rupture of membranes (PROM); oligohydramnios or polyhydramnios; preterm delivery (PTD); stillbirth; cesarean section; low birth weight; Apgar score < 7 at the 1st and 5th minutes; need for assisted ventilation at birth; neonatal infection; need for surgical treatment; early neonatal death; and hospitalization time. Chi-square (x2) test and multilevel regression analysis were applied to compare the groups and determine the effects of maternal characteristics on the incidence of CAs.
The general prevalence of CAs was of 2.4%. Several maternal characteristics were associated to CAs, such as: age; skin color; level of education; parity; folic acid supplementation; tobacco use; and history of previous miscarriage. There were no significant differences among the CA groups in relation to FGR, FD, PROM, 1-minute Apgar score > 7, and need for assisted ventilation at birth. On the other hand, the prevalence of the other considered outcomes varied significantly among groups. Preterm delivery was significantly more frequent in gastrointestinal tract/abdominal wall defects. The stillbirth rate was increased in all CAs, mainly in isolated fetal hydrops (odds ratio [OR]: 27.13; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 2.90-253.47). Hospitalization time was higher for the urinary tract and congenital heart disease groups (p < 0.01). Neonatal death was significantly less frequent in the central nervous system anomalies group.
It was possible to identify several risk factors for CAs. Adverse perinatal outcomes were presented in all CA groups, and may differ according to the type of CA considered.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):293-300
To assess the prevalence of depressive symptoms and their association with social, psychological, behavioral and obstetric characteristics in pregnant women.
This is a cross-sectional study. The sample consisted of 375 pregnant women who attended prenatal clinics in two public maternity hospitals located in the city of Goiania, Brazil. To testify the depressive symptoms, we used the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). A descriptive statistical analysis was performed using programs such as CDC EPI-INFO(tm), version 7.1.5, and Statistical Package for Social Sciences (IBM SPSS), version 21.0.
the patients had probable depressive symptoms (15.47%) and possible depressive symptoms (25.33%). The bivariate analysis showed a significant association among "depressive symptoms" and the following variables: "single or divorced" (prevalence ratio, PR = 2.08; 95% confidence interval, CI = 1.26 to 3.44); "physical activity during pregnancy" (PR = 3.96; 95%CI = 1.28 to 12.31); exposure to "psychological/emotional" violence (PR = 4.74; 95%CI = 2.94 to 7.64); "prior mental problem" (PR = 2.66; 95%CI =1.49 to 4.73) and "obstetric complications during pregnancy" (PR = 2.53; 95%CI = 1.55 to 4.13). The multivariate analysis confirmed the association of these depressive symptoms with the variables "suffered psychological/emotional violence" (odds ratio, OR = 5.821; 95%CI = 2.939 to 11.528); "physical activity during pregnancy" (OR = 3.885; 95%CI = 1.060 to 14.231); "obstetric complications during pregnancy" (OR = 2.442; 95%CI = 1.233 to 4.834) and "single or divorced" (OR = 2.943; 95%CI = 1.326 to 6.533).
the prevalence of depressive symptoms among pregnant women is of 15.47%, and emotional violence is the main factor associated with gestational depression.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(6):287-292
betatrophin has been reported to boost β cell expansion in insulin resistant states. Pregnancy is a well-recognized physiological state of insulin resistance. Betatrophin levels in pregnant women and their relationships with metabolic variables remain to be elucidated.
A total of 49 pregnant women and 31 age-matched unpregnant women with normal glucose regulation (UP-NGR) were included. Among these subjects, according to results from 75 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), 22 women were diagnosed as having gestational diabetes mellitus ( GDM ).
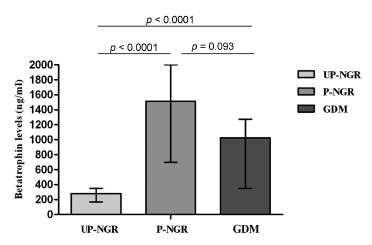
Our study found that pregnant women, regardless of their glucose regulation status, had remarkably higher triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), fasting insulin (FINS), homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and homeostasis model assessment of β-cell function (HOMA-β). However, GDM patients had much lower HOMA-β compared with those of pregnant women with normal glucose regulation (P-NGR). Participants of the P-NGR group had almost 4 times higher levels of betatrophin than those of the UP-NGR group. Although betatrophin levels were lower in the GDM group than those of the P-NGR group, the difference did not reach statistical significance. Spearman correlation analysis showed that betatrophin levels were positively and significantly associated with total cholesterol, triglycerides, highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c), FINS and HOMA-β. However, adjustments of TC, TG and HDL-c eliminated the association between HOMA-β and betatrophin.
Pregnant women have significantly higher betatrophin levels in comparison to unpregnant women. Betatrophin levels are positively and significantly associated with β cell function and lipid levels. Furthermore, lipids may contribute to
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(4):177-182
The amniotic fluid volume (AFV) is known as a predictor for the wellness of a fetus. We aimed to investigate whether N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NTproBNP) levels reflect AFV abnormalities in otherwise normal fetuses.
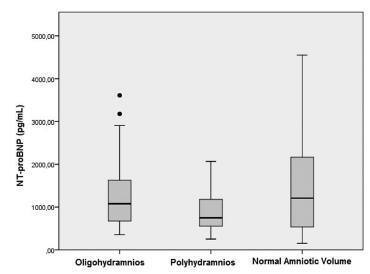
We recruited 24 women with isolated oligohydramnios, 23 women with isolated polyhydramnios, and 36 women with normal AFV at a tertiary referral center. NT-proBNP levels in umbilical venous samples and the individual characteristics of the three groups were compared. One-way ANOVA and Kruskal-Wallis analysis of variance were used for multi-group comparisons of continuous variables. When a significant difference was detected, the Scheffe test was performed as a post-hoc analysis. Proportions were compared using the Chi-square (2) test.
Maternal age, body mass indices, weight gained in pregnancy and NT-proBNP levels were similar among the three groups. Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes significantly correlated with NT-proBNP levels in all newborns (Spearman's r = 0.23 ; p = 0.03 and Spearman's r = 0.24; p = 0.02, respectively). The umbilical venous NTproBNP levels did not differ between newborns who needed mechanical ventilation and those who didn't (p = 0.595).
NT-proBNP is a biomolecule that may provide insights into the pathogenesis of fetal circulatory problems and subsequent renal failure. Further investigations are warranted.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(3):127-131
The purpose of this study is to verify the use ofmedicinal plants by pregnant women treated at four Basic Health Units and at a public maternity facility in Brazil s northeast.
This is a cross-sectional, quantitative study, performed between February and April 2014. The subjects were 178 pregnant women, aged 18 to 42 years. To collect data, a structured questionnaire with dichotomous and multiple choice questions was used. To verify the correlation between the variables, Pearson s chi-square test was used.
The study showed that 30.9% of the pregnant women used medicinal plants, and boldo was the most cited (35.4%). All the plants utilized, except lemongrass, have toxic effects in pregnancy, according to Resolution SES/RJ N° 1757. There was no statistically significant correlation between social class and use of medicinal plants.
The health of the study participants and their unborn children is at risk due to the inappropriate use of medicinal plants.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):20-26
To evaluate the correlation of the levels of fructosamine and of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) with the frequency of blood glucose self-monitoring values out of the treatment target range in pregnant women with diabetes mellitus.
We performed an observational, retrospective, cross-sectional study, including all pregnant women with diabetes who attended prenatal care visits at a tertiary teaching hospital during the year of 2014 and who presented at least 20 days of blood glucose self-monitoring prior to assessment of serum levels of fructosamine and HbA1c. Capillary blood glucose values out of the treatment target range were considered "hypoglycemia" when lower than 70 mg/dL and "hyperglycemia" when above the glycemic therapeutic target. We evaluated the correlation of the levels of fructosamine and of HbA1c with the frequencies of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia recorded in the glucometer device by performing Tau-b of Kendall correlation tests. Next, linear regression tests were performed between the levels of HbA1c and of fructosamine and the frequencies of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.
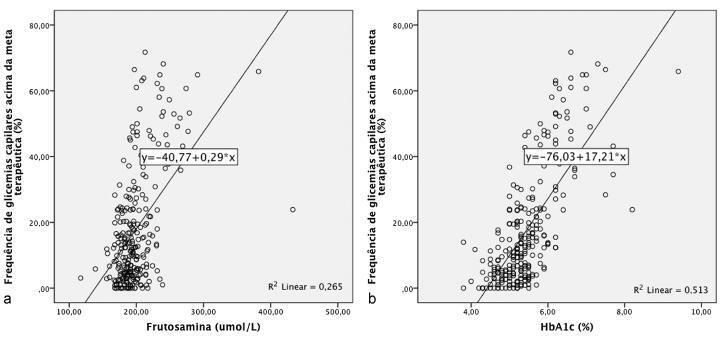
We included 158 pregnant women, from whom 266 blood samples were obtained for assessing fructosamine and HbA1c levels. Measurements of fructosamine and of HbA1c presented, respectively, Kendall's τ coefficient of 0.29 (p < 0.001) and 0.50 (p < 0.001) regarding the frequency of hyperglycemia, and of 0.09 (p = 0.046) and 0.25 (p < 0.001) regarding the frequency of hypoglycemia. In the linear regression model, levels of fructosamine and of HbA1c respectively presented determination coefficients R2 = 0.265 (p < 0.001) and R2 = 0.513 (p < 0.001) for the prediction of hyperglycemia, and R2 = 0.033 (p = 0.003) and R2 = 0.059 (p < 0.001) for the prediction of hypoglycemia.
Levels of fructosamine and of HbA1c presented a weak to moderate correlation with the frequencies of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia at blood glucose self-monitoring and were not able to accurately translate the deviations from the glycemic goals in pregnant women with diabetes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):27-34
To determine differences in some nutritional aspects of pregnant women assisted at prenatal care services in a country town and in a metropolitan area.
Pregnant women received prenatal care in the city of Belo Horizonte (BH), metropolitan area, and Paula Cândido (PC), a country town. A Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) containing socioeconomic information and information about eating habits was applied. In addition,weight and height were measured on the occasion of the visits and the women were ask to give their prepregnancy weight for subsequent BMI calculation. Data were analyzed according to region and trimester of pregnancy using the SPSS software version 15.0, the t-test to compare averages and the chi-square test of independence, with the level of significance set at 5%.
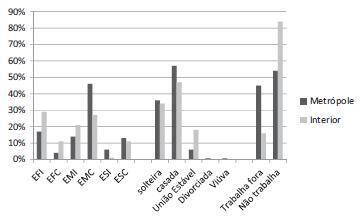
240 pregnant women were included, 90 fromthe country town and 150 from themetropolitan area. Of these,most weremarried (BH = 56.6%; PC = 46.6%) and did not work outside the home (BH = 54.0%; PC = 84.4%). They predominantly had 3-4 meals/ day during the 1st and 2nd quarters (BH = 54.0 and 46%; PC = 66.7 and 63.3%, respectively) and had 5-6 meals/day during Q3 in BH (44%). There was significant weight gain only in the 1st quarter (BH: 58,0%; PC: 53.3%). Weight gain versus eating habits was significant for the variables "lunch or dinner away from home" for the 1st quarter in BH (p = 0.006), "How many times they consume milk" in the 1 st quarter in PC (p = 0.03), and "How many times they consume junk food" in the 3rd quarter in BH (p = 0.009).
Pregnant woman showed proper eating habits in both regions despite the prevalence of pregestational overweight in BH and a low level of education and income, especially in the country town, an indicator that may be unfavorable for the nutrition of pregnant women during this period. Studies of association between eating habits and newborn health will provide more information about nutrition during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):571-577
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320150005419
To evaluate the nutritional and psychological factors associated with the occurrence of the practice of pica in pregnant women attending a public hospital in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
The study was based on a descriptive design with exploratory features, and conducted on 13 adult and adolescent pregnant women aged 16 to 40 years with a diagnosis of pica in the current pregnancy. Pica was diagnosed by a nutritionist in a standardized interview situation, when questions about the occurrence and frequency of pica, and types of substance ingestion were investigated. After signing the Informed Consent Form (ICF), all participants were evaluated by a nutritionist and seven of them were submitted to psychological assessment with standardized instruments to evaluate stress and anxiety, and to assess coping strategies.
The type of pica most frequently reported was pagophagia (30.8%) and the consumption of fruit with salt (30.8%). The most prevalent coping strategies were "religious practice-focused" and "seeking social support", both presented by 42% of the pregnant women. We observed the occurrence of some degree of stress and anxiety in all pregnant women, as well as comorbidities (69.2%) and gastrointestinal symptoms (84.6%).
Considering that pica may be associated with increased perinatal risk, it is very important to investigate this disorder during prenatal care, and to dopt obstetric, psychological and nutritional preventive practices to reduce the complications for mother and fetus.