-
Review Article
Clinical Procedures for the Prevention of Preeclampsia in Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):659-668
12-21-2020
Summary
Review ArticleClinical Procedures for the Prevention of Preeclampsia in Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):659-668
12-21-2020Views247See moreAbstract
Objective
To identify the most effective procedures recommended for the prevention of preeclampsia.
Data Sources
A systematic review was performed in the following databases: Pubmed/MEDLINE, CINAHL, Web of Science, Cochrane and LILACS via the Virtual Health Library (VHL). A manual search was also performed to find additional references. The risk of bias, the quality of the evidence, and the classification of the strength of the recommendations were evaluated using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) approach.
Selection of Studies
In the initial search in the databases, the total number of articles retrieved was 351, and 2 were retrieved through the manual search; after duplicate articles were removed, 333 citations remained. After a thorough review of the titles and abstracts, 315 references were excluded. Accordingly, 18 articles were maintained for selection of the complete text (phase 2). This process led to the exclusion of 6 studies. In total, 12 articles were selected for data extraction and qualitative synthesis.
Data Collection
The articles selected for the study were analyzed, and we inserted the synthesis of the evidence in the online software GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool (GDT) (McMaster University and Evidence Prime Inc. All right reserved. McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontário, Canada); thus, it was possible to develop a table of evidence, with the quality of the evidence and the classification of the strength of the recommendations.
Data Synthesis
In total, seven studies recommended the individual use of aspirin, or aspirin combined with calcium, heparin or dipyridamole. The use of calcium alone or in combination with phytonutrients was also highlighted. All of the studies were with women at a high risk of developing preeclampsia.
Conclusion
According to the studies evaluated, the administration of aspirin is still the best procedure to be used in the clinical practice to prevent preeclampsia.
-
Original Article
The Influence of Preeclampsia, Advanced Maternal Age and Maternal Obesity in Neonatal Outcomes Among Women with Gestational Diabetes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):607-613
12-21-2020
Summary
Original ArticleThe Influence of Preeclampsia, Advanced Maternal Age and Maternal Obesity in Neonatal Outcomes Among Women with Gestational Diabetes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):607-613
12-21-2020Views244See moreAbstract
Objective
The present study aims to analyze adverse fetal or neonatal outcomes in women with gestational diabetes, including fetal death, preterm deliveries, birthweight, neonatal morbidity and mortality, as well as the synergic effect of concomitant pregnancy risk factors and poor obstetric outcomes, as advanced maternal age, maternal obesity and pre-eclampsia in their worsening.
Methods
The present cohort retrospective study included all pregnant women with gestational diabetes, with surveillance and childbirth at the Hospital da Senhora da Oliveira during the years of 2017 and 2018. The data were collected from the medical electronic records registered in health informatic programs Sclinico and Obscare, and statistical simple and multivariate analysis was done using IBM SPSS Statistics.
Results
The study participants included 301 pregnant women that contributed to 7.36% of the total institution childbirths of the same years, in a total of 300 live births. It was analyzed the influence of pre-eclampsia coexistence in neonatal morbidity (p = 0.004), in the occurrence of newborns of low and very low birthweight (p < 0.01) and in preterm deliveries (p < 0.01). The influence of maternal obesity (p = 0.270; p = 0.992; p = 0.684) and of advanced maternal age in these 3 outcomes was also analyzed (p = 0,806; p = 0.879; p = 0.985).Using a multivariate analysis, the only models with statistic significance to predict the three neonatal outcomes included only pre-eclampsia (p = 0.04; p < 0.01; p < 0.01).
Conclusion
Only coexistence of pre-eclampsia showed an association with adverse neonatal outcomes (neonatal morbidity, newborns of low and very low birthweight and preterm deliveries) and can be used as a predictor of them in women with gestational diabetes.
-
Original Article
Interaction Between NOS3 and HMOX1 on Antihypertensive Drug Responsiveness in Preeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):460-467
09-25-2020
Summary
Original ArticleInteraction Between NOS3 and HMOX1 on Antihypertensive Drug Responsiveness in Preeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):460-467
09-25-2020Views215See moreAbstract
Objective
We examined the interaction of polymorphisms in the genes heme oxygenase- 1 (HMOX1) and nitric oxide synthase (NOS3) in patients with preeclampsia (PE) as well as the responsiveness to methyldopa and to total antihypertensive therapy.
Methods
The genes HMOX1 (rs2071746, A/T) and NOS3 (rs1799983, G/T) were genotyped using TaqMan allele discrimination assays (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA ), and the levels of enzyme heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Results
We found interactions between genotypes of the HMOX-1 and NOS3 genes and responsiveness tomethyldopa and that PE genotyped as AT presents lower levels of protein HO-1 compared with AA.
Conclusion
We found interactions between the HMOX-1 and NOS3 genes and responsiveness to methyldopa and that the HMOX1 polymorphism affects the levels of enzyme HO-1 in responsiveness to methyldopa and to total antihypertensive therapy. These data suggest impact of the combination of these two polymorphisms on antihypertensive responsiveness in PE.
-
Original Article
Screening for Preeclampsia in the First Trimester and Aspirin Prophylaxis: Our First Year
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):390-396
08-26-2020
Summary
Original ArticleScreening for Preeclampsia in the First Trimester and Aspirin Prophylaxis: Our First Year
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):390-396
08-26-2020Views128See moreAbstract
Objective
Preeclampsia is a major cause of perinatal and maternal morbidity and mortality. Our objective is to assess the performance of a combined screening test for preeclampsia in the first trimester and the prophylactic use of low-dose aspirin.
Methods
Prospective study of all women attending our hospital for the first-trimester screening of aneuploidies, between March 2017 and February 2018 (n = 1,297). The exclusion criteria weremultiple pregnancy andmajor fetal abnormalities. Preeclampsia screening was performed with an algorithm that includes maternal characteristics, and biophysical and biochemical biomarkers. High-risk was defined as a risk ≥ 1:50 of earlyonset preeclampsia (before 34 weeks), in which cases low-dose aspirin (150mg at night) was offered to these women from screening until 36 weeks.
Results
From the 1,272 enrolled participants, the majority were Caucasian (1,051; 82.6%) and multiparous (658, 51.7%). Fifty patients (3.9%) screened high-risk for preeclampsia, and all started a low-dose aspirin regimen, with good compliance (96%). Early-onset preeclampsia was found in 3 pregnant women (0.24%), and total preeclampsia was diagnosed in 25 (2.02%), compared with 28 (0.75%) cases of early preeclampsia (p = 0.0099) and 98 (2.62%) of total preeclampsia (p = 0.2904) before the implementation of screening.
Conclusion
There was a lower incidence of both, early-onset and total preeclampsia, after the introduction of universal screening and prophylactic use of low-dose aspirin. This reduction was statistically significant in early-onset preeclampsia. The association of a first-trimester combined screening model and aspirin prophylaxis appears to be useful in predicting and reducing the incidence of early-onset preeclampsia, in a routine care setting.
-
Original Article
Maternal and Perinatal Outcomes of Pregnancies Complicated by Chronic Hypertension Followed at a Referral Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):248-254
06-22-2020
Summary
Original ArticleMaternal and Perinatal Outcomes of Pregnancies Complicated by Chronic Hypertension Followed at a Referral Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):248-254
06-22-2020Views201See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess maternal and perinatal outcomes of pregnancies in women with chronic hypertension (CH). Methods Retrospective cohort of women with CH followed at a referral center for a 5 year period (2012-2017). Data were obtained from medical charts review and described as means and frequencies, and a Poisson regression was performed to identify factors independently associated to the occurrence of superimposed preeclampsia (sPE).
Results
A total of 385 women were included in the present study; the majority were > than 30 years old, multiparous, mostly white and obese before pregnancy. One third had pre-eclampsia (PE) in a previous pregnancy and 17% of them had organ damage associated with hypertension, mainly kidney dysfunction. A total of 85% of the patients used aspirin and calcium carbonate for pre-eclampsia prophylaxis and our frequency of sPE was 40%, with an early onset (32.98 ± 6.14 weeks). Of those, 40% had severe features of PE, including 5 cases of HELLP syndrome; however, no cases of eclampsia or maternal death were reported. C-section incidence was high, gestational age at birth was 36 weeks, and nearly a third (115 cases) of newborns had complications at birth One third of the women remained using antihypertensive drugs after pregnancy.
Conclusion
Chronic hypertension is related with the high occurrence of PE, C-sections, prematurity and neonatal complications. Close surveillance and multidisciplinary care are important for early diagnosis of complications.
-
Original Article
The Role of Ischemia-modified Albumin as a Biomarker in Preeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(3):133-139
04-22-2020
Summary
Original ArticleThe Role of Ischemia-modified Albumin as a Biomarker in Preeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(3):133-139
04-22-2020Views130See moreAbstract
Objective
Ischemia-modified albumin (IMA)is a modified type of albumin protein that is formed under oxidative stress. This study aims to compare the levels of serum IMA between normotensive and preeclamptic pregnancies and to evaluate the relationship between the severity of the disease.
Methods
A total of 90 pregnant women aged between 18 and 45 years participated in this cross-sectional study. The levels of serum IMA were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 30 preeclamptic pregnant women with the severe signs of the disease, 30 preeclamptic pregnant women, and 30 normotensive pregnant women.. The study was designed as a cross-sectional clinical study.
Results
When the demographic characteristics were examined, statistically significant differences were found between the groups in terms of age, gestational week at birth and blood pressure. Age was higher in the preeclampsia with signs of severity group than in the normotensive group (p = 0.033). Pregnancy week was significantly the lowest in the preeclampsia with the severity signs group (p = 0.004). In normotensive patients, IMA levels were lower than in the preeclampsia groups (p = 0.001) but there was no significant difference in terms of severity of disease (p = 0.191). According to laboratory data; only the creatinine level was significantly different between the groups.
Conclusion
The levels of serum IMA were higher in patients with preeclampsia than in healthy pregnancies. However, there was no significant correlation in terms of preeclampsia severity; more extensive, prospective and long-term studies are needed.
-
Original Article
Circulating Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-4 levels are not a Predictor of Preeclampsia in the period between 20 and 25 Weeks of Gestation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):757-762
12-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticleCirculating Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-4 levels are not a Predictor of Preeclampsia in the period between 20 and 25 Weeks of Gestation
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):757-762
12-01-2018Views169See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate whether the circulating level of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase- 4 (TIMP-4) in the period between 20 and 25 weeks of gestation is a predictor of preeclampsia.
Methods
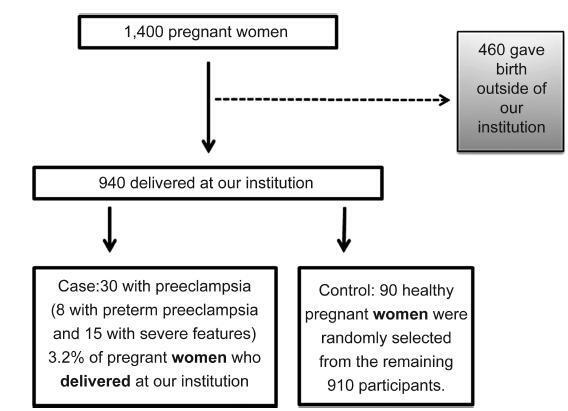
We have performed a case-control study, nested in a prospective study cohort in Ribeirão Preto, in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Of the 1,400 pregnant women evaluated between 20 and 25 weeks of gestation, 460 delivered in hospitals outside of our institution. Of the 940 pregnant women who completed the protocol, 30 developed preeclampsia. Healthy pregnant women (controls, n = 90) were randomly selected from the remaining 910 participants. From blood samples collected between 20 and 25 weeks of gestation, we performed a screening of 55 angiogenesis-related proteins in 4 cases and 4 controls. The protein TIMP-4 was the most differentially expressed between cases and controls. Therefore, wemeasured this protein in all cases (n = 30) and controls selected (n = 90).
Results
There were no differences in the plasma TIMP-4 levels of cases compared with controls (1,144 263 versus 1,160 362 pg/mL, respectively; p > 0.05).
Conclusion
Plasma TIMP-4 levels were not altered at 20 to 25 weeks of gestation, before the manifestation of clinical symptoms; therefore, they are not good predictors of the development of preeclampsia.
-
Review Articles
Evaluation of Preeclampsia Results after Use of Metformin in Gestation: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):713-721
11-01-2018
Summary
Review ArticlesEvaluation of Preeclampsia Results after Use of Metformin in Gestation: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):713-721
11-01-2018Views170See moreAbstract
Objective
Does the use of metformin have an influence on the outcomes of preeclampsia (PE)?
Sources of Data
The descriptors pregnancy, metformin, treatment, and preeclampsia associated with the Boolean operators AND and OR were found in the MEDLINE, LILACS, Embase and Cochrane databases. A flowchart with exclusion criteria and inclusion strategy using the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) protocol, and eligibility criteria was used. Data were extracted regarding the type of study, the applied dosage, treatment time, segment, bias risks, and the Patient, Intervention, Comparison and Outcome (PICO) strategy to identify the quality of the study.
Selection of Studies
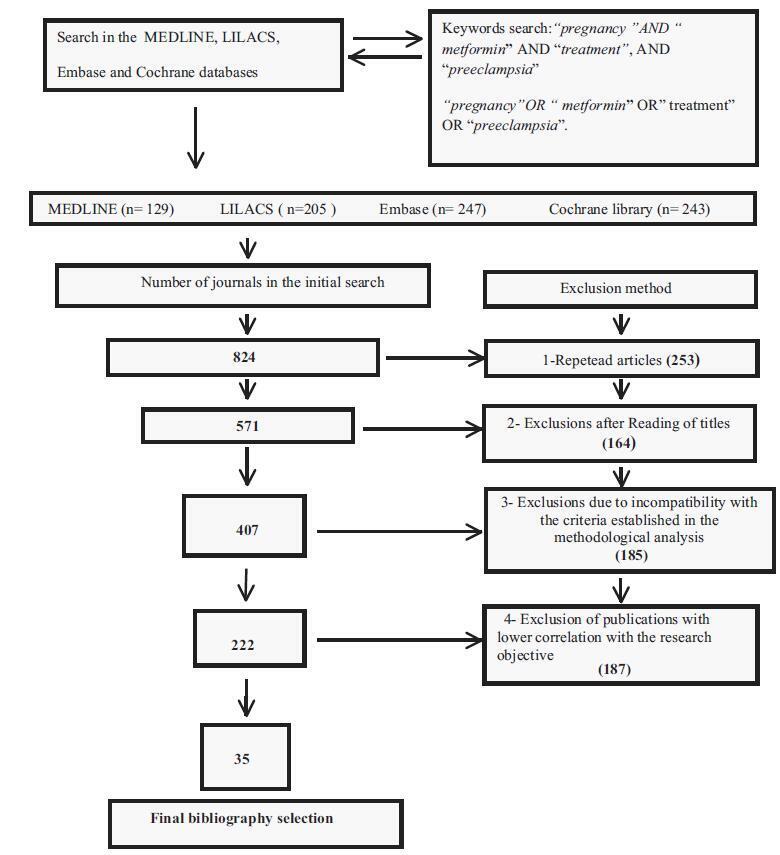
Total number of journals in the initial search (n= 824); exclusions from repeated articles on different search engines (n= 253); exclusions after reading the titles, when the title had no correlations with the proposed theme (n= 164); exclusions due to incompatibility with the criteria established in the methodological analysis (n= 185), exclusion of articles with lower correlation with the objective of the present study (n= 187); and final bibliographic selection (n= 35).
Data Collection
At first, a systematic review of the literature was performed. Subsequently, from the main selection, randomized and non-randomized trials with metformin that presented their results in absolute and relative numbers of PE outcomes were selected. The variables were treated statistically in the meta-analysis with the Review Manager software (RevMan), version 5.3. Copenhagen: Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Denmark in the Hovedistaden region.
Synthesis of Data
The study showed that metmorfin presented greater preventive effects for pregnancy-induced hypertension and was less effective for PE.
Conclusion
Metformin may gain place in preventive treatments for PE, once the dosages, the gestational age, and treatment time are particularly evaluated. A methodological strategy with an improved perspective of innovative and/or carefully progressive dosages during pregnancy to avoid side effects and the possibility of maternal-fetal risks is suggested.