-
Original Article
Mid-pregnancy circulating cytokine levels, placental efficiency and their relationship with preterm birth
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo58
07-26-2024
Summary
Original ArticleMid-pregnancy circulating cytokine levels, placental efficiency and their relationship with preterm birth
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo58
07-26-2024Views130See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess a panel of cytokines and placental insufficiency with the risk of preterm delivery (PTD).
Methods
Nested case-control study into the BRISA birth cohort. Eighty-two mother-infant-placenta pairs were selected at 20+0 to 25+6 weeks. Circulating biomarker levels were performed using Luminex flowmetric xMAP technology. Cytokines classified as Th1, Th2 or Th17 and other biomarkers were selected. The ratio between birth weight and placental weight (BW/PW) was used as a proxy for placental efficiency. Spearman correlation, univariate analyses and logistic regression models were calculated. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios were calculated using the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve.
Results
Mean gestational age was 250 days, 14,6% were small for gestational age, 4,8% large for gestational age and 13,4% stunted. Placental efficiency was higher for term newborns (p<0,001), and 18/22 (81%) preterm biomarker values were higher than the control group. Th1 cytokines were highly correlated, while the weakest correlation was observed in other biomarkers. Less education was associated with a higher risk of PTD (p = 0.046), while there was no appreciable difference in the risk of PTD for placental insufficiency. Biomarkers showed negligible adjusted OR of PTD (0.90 to 1.02). IL-6, IL-8, IL-1β, TNFβ, IL-4, IL-13, GCSF, MIP1A, VEGF, EGF, and FGF2 presented a higher sensitivity ranging from 75.56% to 91.11%.
Conclusion
IL-8, IL-12p40, IL-4, IL-13, GCSF, MIP1B, and GMSF in asymptomatic pregnant women were associated with PTD. This finding suggests an activation of maternal inflammatory response.
-
Review Article
Online scientific research on placentophagy: a bibliometric analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo4
03-14-2024
Summary
Review ArticleOnline scientific research on placentophagy: a bibliometric analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo4
03-14-2024Views218See moreAbstract
Objective:
To classify the bibliometric indicators of online scientific research on placentophagy.
Methods:
A bibliometric study was conducted to quantify the scientific production of authors and institutions with the aim of highlighting the growth and impact of these publications nationally and internationally. The Bradford Law, network maps, and textual statistics were used, with searches conducted in libraries and databases in October 2021.
Results:
The sample consisted of 64 articles, whose primary authors were associated with 49 institutions, and mostly with degrees in anthropology. The United States of America was the country that published the most papers on the theme, and most studies were reviews with individual production. Through the term analysis, it was found that the predominant themes regarding placentophagy were the following: Alternative therapy for women's health, methodologies used for research in this area, period of placenta ingestion (postpartum period), and its benefits.
Conclusion:
The bibliometric indicators found are essential for the development of future research.
-
Original Article
Association of placental histopathological findings with COVID-19 and its predictive factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo3
00-00-2024
Summary
Original ArticleAssociation of placental histopathological findings with COVID-19 and its predictive factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo3
00-00-2024Views403See moreAbstract
Objective:
The aims of the study are to describe the association of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) with the abnormal histopathological findings in human placenta and to highlight the potential predictors of these histopathological findings.
Methods:
A retrospective cohort study, held in two obstetric units from January 2021- 2022, 34 patients who were confirmed cases of COVID- 19 were followed up till the time of delivery as their placenta were sent for histopathology. Patients diagnosed with other viral infections, chorioamnionitis, or were known case of as pre-term or term pre labour rupture of membrans (PROM) were excluded as well as pre exisiting diabetes mellitus or pre-eclampsia. Data analysis were performed using STATA software version 16.
Result:
Specific histopatological findings (fetal vascular malperfusion, maternal vascular malperfusion, inflammatory pathology and thrombotic finding) were significantly high among 13 (38.2%) of the study group who got infected earlier in pregnancy (P<0.001). The period between the diagnosis of COVID-19 and the delivery significantly increases the odds of the presence of pathological findings by 2.75 times for each week the patients getting infected earlier.
Conclusion:
Association of abnormal placental histopathological findings with COVID-19 infection in pregnancy and the potential predictor for the occurrence of placental findings is the longer duration between the diagnosis of the infection and the delivery.
-
Review
Doppler Ultrasound of the Umbilical Artery: Clinical Application
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):519-531
04-11-2022
Summary
ReviewDoppler Ultrasound of the Umbilical Artery: Clinical Application
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):519-531
04-11-2022Views173See moreAbstract
Objective
To provide a survey of relevant literature on umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound use in clinical practice, technical considerations and limitations, and future perspectives.
Methods
Literature searches were conducted in PubMed and Medline, restricted to articles written in English. Additionally, the references of all analyzed studies were searched to obtain necessary information.
Results
The use of this technique as a routine surveillance method is only recommended for high-risk pregnancies with impaired placentation. Meta-analyses of randomized trials have established that obstetric management guided by umbilical artery Doppler findings can improve perinatal mortality and morbidity. The values of the indices of Umbilical artery Doppler decrease with advancing gestational age; however, a lack of consensus on reference ranges prevails.
Conclusion
Important clinical decisions are based on the information obtained with umbilical artery Doppler ultrasound. Future efforts in research are imperative to overcome the current limitations of the technique.
-
Original Article
Expression of Endothelin-1 and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Normal and Preeclamptic Placentae
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):125-132
04-08-2022
Summary
Original ArticleExpression of Endothelin-1 and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Normal and Preeclamptic Placentae
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):125-132
04-08-2022Views134See moreAbstract
Objective
To investigate the expression of endothelin-1 (ET-1) and endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase (eNOS) in normal and preeclamptic (PE) placentae.
Methods
The present cross-sectional analytical study was performed in normal and PE primigravidae (n=10 in each group) who were admitted to the North Okkalapa General and Teaching Hospital from February 2019 to February 2020. Serum samples were collected immediately before delivery, and placental tissues were collected immediately after emergency or elective cesarean section. The expression of placental eNOS was measured by western blot, and the levels of ET-1 in placental tissue homogenates and in the serum were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Results
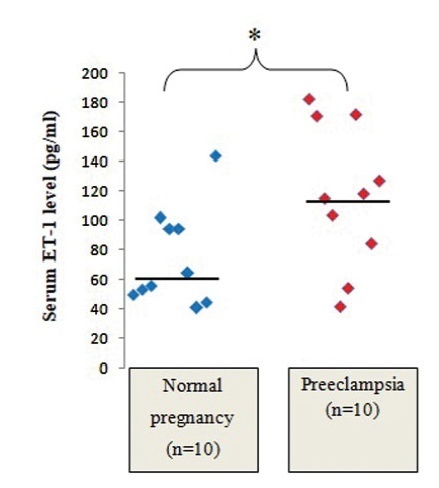
The PEgrouphadsignificantly higher serumlevelsof ET-1(median: 116.56 pg/mL; IQR: 89.14-159.62 pg/mL) than the normal group (median: 60.02 pg/mL; IQR: 50.89-94.37 pg/mL) (p<0.05). However, statistically significant differences were not observed in the levels of ET-1 in placental tissue homogenates between normal and PE placentae (median: 0.007 pg/μg of total protein; IQR: 0.002-0.0123 pg/μg of total protein; andmedian: 0.005 pg/μg of total protein; IQR: 0.003-0.016 pg/μg of total protein respectively). The median and IQR values of relative placental eNOS expression were significantly higher in the PE group than in the normal group (p<0.05). The serum levels of ET-1 level were not significantly correlated with placental ET-1 expression, and neither there was a significant correlation between placental ET-1 and eNOS expression in any of the groups.
Conclusion
The serum levels of ET-1 were significantly higher in PE pregnant women compared with normal pregnant women, while the ET-1 levels of placental tissue homogenates were not significantly different. Serum ET-1 rather than placental ET-1 might play a major role in the pathogenesis of PE.
-
Review Article
Placental Findings in Preterm and Term Preeclampsia: An Integrative Review of the Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):560-569
10-18-2021
Summary
Review ArticlePlacental Findings in Preterm and Term Preeclampsia: An Integrative Review of the Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):560-569
10-18-2021Views170Abstract
Introduction
Preeclampsia (PE) is a pregnancy complication associated with increased maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. The disease presents with recent onset hypertension (after 20 weeks of gestation) and proteinuria, and can progress to multiple organ dysfunction, with worse outcomes among early onset preeclampsia (EOP) cases (<34 weeks). The placenta is considered the root cause of PE; it represents the interface between the mother and the fetus, and acts as a macromembrane between the two circulations, due to its villous and vascular structures. Therefore, in pathological conditions, macroscopic and microscopic evaluation can provide clinically useful information that can confirm diagnosis and enlighten about outcomes and future therapeutic benefit.
Objective
To perform an integrative review of the literature on pathological placental findings associated to preeclampsia (comparing EOP and late onset preeclampsia [LOP]) and its impacts on clinical manifestations.
Results:
Cases of EOP presented worse maternal and perinatal outcomes, and pathophysiological and anatomopathological findings were different between EOP and LOP placentas, with less placental perfusion, greater placental pathological changes with less villous volume (villous hypoplasia), greater amount of trophoblastic debris, syncytial nodules, microcalcification, villous infarcts, decidual arteriolopathy in EOP placentas when compared with LOP placentas. Clinically, the use of low doses of aspirin has been shown to be effective in preventing PE, as well asmagnesium sulfate in preventing seizures in cases of severe features.
Conclusion
The anatomopathological characteristics between EOP and LOP are significantly different, with large morphological changes in cases of EOP, such as
Key-words anatomopathological characteristicsmaternal mortality and morbidityPlacentapreeclampsia early onsetpreeclampsia late onsetSee more -
Review Article
SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Placental Pathology Infecção por SARS-CoV-2 e patologia placentária
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):474-479
06-02-2021
Summary
Review ArticleSARS-CoV-2 Infection and Placental Pathology Infecção por SARS-CoV-2 e patologia placentária
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):474-479
06-02-2021Views159See moreAbstract
Placental pathophysiology in SARS-CoV-2 infection can help researchers understand more about the infection and its impact on thematernal/neonatal outcomes. This brief review provides an overview about some aspects of the placental pathology in SARSCoV- 2 infection. In total, 11 papers were included. The current literature suggests that there are no specific histopathological characteristics in the placenta related to SARSCoV- 2 infection, but placentas frominfected women aremore likely to show findings of maternal and/or fetal malperfusion. The most common findings in placentas from infected women were fibrin deposition and intense recruitment of inflammatory infiltrates. The transplacental transmission of this virus is unlikely to occur, probably due to low expression of the receptor for SARS-CoV-2 in placental cell types. Further studies are needed to improve our knowledge about the interaction between the virus and the mother-fetus dyad and the impact on maternal and neonatal/fetal outcomes.



