Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo75
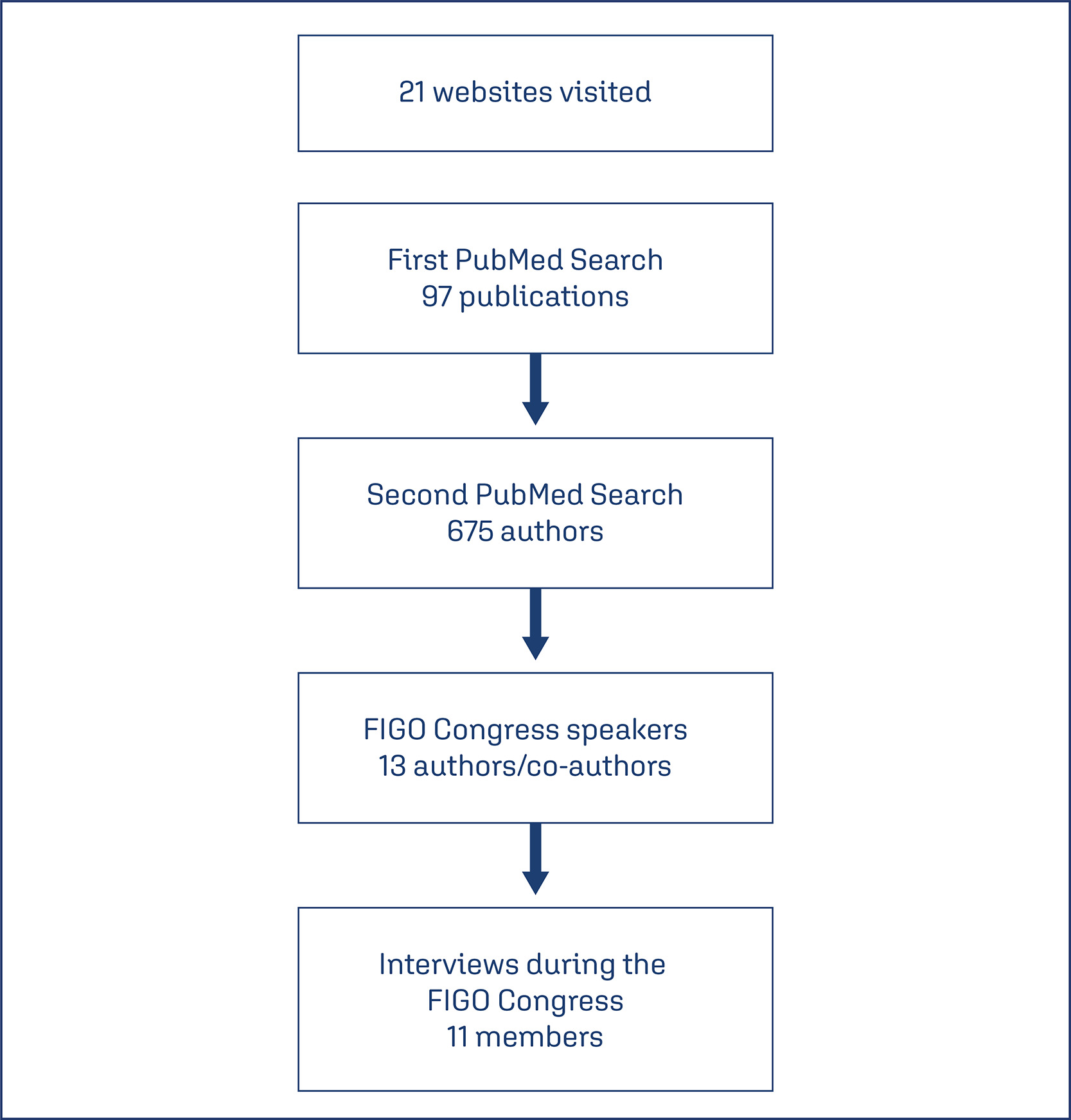
To identify the opinion of coordinators and members about the essential characteristics and to understand the research networks characteristics, to facilitate their implementation, sustainability and effectiveness so it can be replicated in low and middle-income countries.
A qualitative study using a semi-structured interview technique was conducted. We selected potential members, managers and participants of networks from publications identified in PubMed. After checking the FIGO congress program, we identified authors who were assigned as speakers at the event. An invitation was sent and interviews were scheduled.
In total, eleven interviews were performed. Coordinators and members of networks have the same goal when they decide to participate in a network. In general, they cited that these individuals had to be committed, responsible and enthusiastic people. The network should be composed also of postgraduate students. A network should allow multi-leadership, co-responsibility, autonomy and empowerment of its members. Effective communication was mentioned as an important pillar for network maintenance. Another motivation is being an author or coauthor in publications. One way to maintain a network running is social or governmental commitment, after resources expire, studies continue.
Networks are different due to the social context where they are inserted, however, some characteristics are common to all of them, such as having engaged leaders. For an effective and sustainable network, commitment and motivation in a leader and members are more in need than financial resources. Ideally, to ensure the operation of the network, the institution where the leader is linked should support this network.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo54
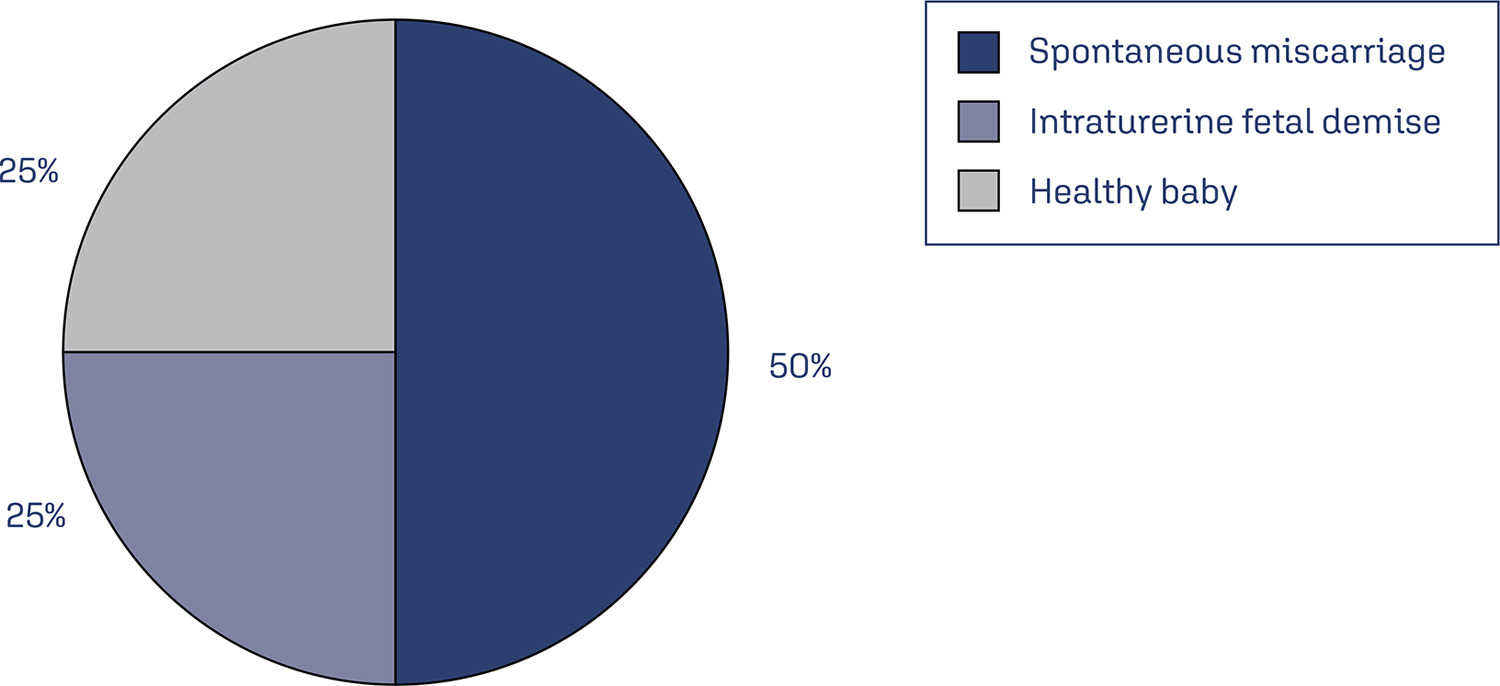
Monkeypox (MPX), an orthopoxviral disease endemic in Africa, is now a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) as declared by the World Health Organization in July 2023. Although it is generally mild, the overall case fatality rate was reported to be 3%, and the basic reproduction number (R0) is > 1 in men who have sex with men (MSM, i.e., Portugal (1.4), the United Kingdom (1.6), and Spain (1.8)). However, R0 is < 1 in other settings. In concordance with the smallpox virus, it is also expected to increase the risk of adverse outcomes for both the mother and the fetus. The outcomes of the disease in an immunocompromised state of pregnancy are scary, showing high mortality and morbidity of both mother and fetus, with up to a 75% risk of fetal side effects and a 25% risk of severe maternal diseases. Therefore, it warrants timely diagnosis and intervention. The reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT PCR) test is the standard approach to diagnosis. We summarized the recent findings of MPX on pregnancy, and the associated risk factors. We also give recommendations for active fetal surveillance, perinatal care, and good reporting to improve outcomes. The available vaccines have shown promise for primary disease prevention.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):904-910
To evaluate the mean uterine artery pulsatility index (UtAPI) in each trimester of pregnancy as a predictor of early or late pre-eclampsia (PE) in Colombian pregnant women.
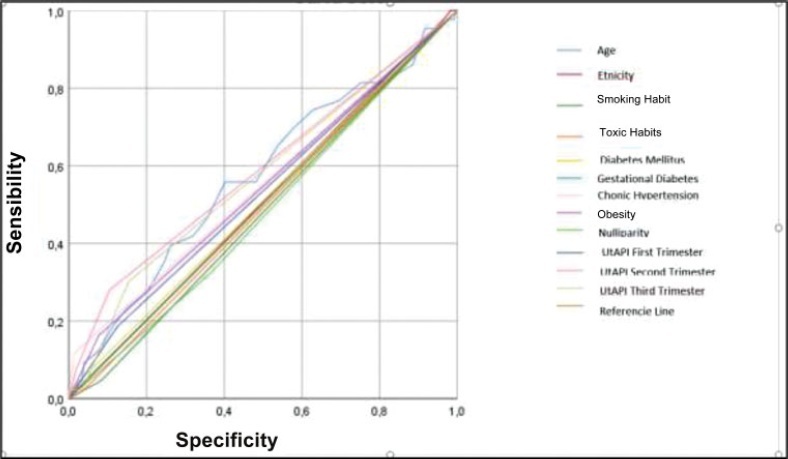
The UtAPI was measured in singleton pregnancies in each trimester. Uterine artery pulsatility index as predictor of PE was evaluated by odds ratio (OR), receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, and Kaplan-Meier diagram.
Analysis in the 1st and 3rd trimester showed that abnormal UtAPI was associated with early PE (OR: 5.99: 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.64–21.13; and OR: 10.32; 95%CI: 2.75–42.49, respectively). Sensitivity and specificity were 71.4 and 79.6%, respectively, for developing PE (area under the curve [AUC]: 0.922). The Kaplan-Meier curve showed that a UtAPI of 0.76 (95%CI: 0.58–1.0) in the 1st trimester was associated with early PE, and a UtAPI of 0.73 (95%CI: 0.55–0.97) in the 3rd trimester was associated with late PE.
Uterine arteries proved to be a useful predictor tool in the 1st and 3rd trimesters for early PE and in the 3rd trimester for late PE in a pregnant population with high prevalence of PE.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(3):130-135
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000300007
PURPOSE: It was to determine the prevalence of depressive symptoms in a sample of puerperal women from Brasília, Brazil, distinguishing cases with onset after delivery from those already present during pregnancy. METHODS: A prospective cohort study with convenience sampling of patients submitted to elective cesarean section at two private hospitals. As an instrument for assessing depressive symptoms, the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale with cutoff >13 was applied shortly before delivery and four to eight weeks after childbirth. RESULTS: Among the 107 women who completed the study, 11 (10.3%) had significant depressive symptoms during pregnancy and 12 (11.2%) during the postpartum period. Among the 12 patients with postpartum symptoms, 6 had symptoms during pregnancy, so that 5.6% of the sample had postpartum onset of depression. The higher overall frequency of depression was significantly among single women than among married women (p=0.04), a fact mainly due to a higher frequency of single women experiencing persistent depressive symptoms both before and after delivery (p=0.002). The risk of depression was not influenced by age, parity or educational level. CONCLUSION: Women with depression identified during the postpartum period comprise a heterogeneous group, in which symptoms may have started before pregnancy, during pregnancy or after childbirth. In this sample, half of the postpartum depression cases already presented symptoms during late pregnancy. Since depression can arise before and after childbirth, it may have different etiologies and, therefore, a different response to treatment, a possibility that should be considered by clinicians and researchers.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(1):34-39
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000100007
PURPOSE: To compare the maternal and perinatal outcomes of patients with placenta previa, after the adoption of a prolonged maternal hospital stay, to those of a 1991 series. METHODS: We performed a retrospective study comparing 108 cases of placenta previa hospitalized in the Maternity School Assis Chateaubriand, Universidade Federal do Ceará, during the period from 01/01/2006 to 12/31/2010, with those obtained in 1991, when 101 cases of the pathology were observed at our institution. The following maternal and perinatal data were collected: maternal age, parity, gestational age at delivery, mode of delivery, maternal stay length, Apgar scores at the 1st and 5th minutes, birth weight, adequacy of birth weight, neonatal length stay, maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality rates (maternal, fetal, neonatal and perinatal). Statistical analysis was performed using the χ² and Fisher's exact tests. The results were considered significant when p<0.05. RESULTS: In 1991, placenta previa was found in 1.13% of cases (101/8900). In the present study, the prevalence was 0.43% (108/24726). No maternal death was observed in either series. Regarding the study of 1991, the current patients were significantly younger, with lower parity, were hospitalized longer, had better Apgar scores at 1st and 5th minutes, and had longer neonatal hospitalization. Also, we identified reduction of fetal, neonatal and perinatal mortality. CONCLUSIONS: Perinatal outcomes in patients with placenta previa were significantly improved between 1991 and the years 2006 and 2010. However, we can not say whether this improvement was due to the prolonged maternal hospital stay.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(11):354-360
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001100006
PURPOSE: To analyze the association of pregnancy in adolescence and prematurity. METHODS: The study included all the patients who delivered at a teaching hospital in Maranhão State, from July to December 2006. The patients were divided into two groups: adolescents (10 to 19 years old) and adults (20 to 34 years old). The variables studied were: educational level, marital status, number of prenatal visits, gestational age at the onset of prenatal care, duration of gestation, delivery route and birth weight. Statistical analysis was performed using the Epi-Info software, version 3.4.1, and the associations between variables were analyzed by the odds ratio (OR), with a 95% confidence interval (CI). Models of logistic regression were also used. The level of significance adopted was 0.05. RESULTS: The study evaluated 1,978 patients. The frequency of deliveries in adolescents was 25.4%. This group presented low educational level, no mates, low number of prenatal visits, late onset of prenatal care, low birth weight and prematurity. In the analysis of prematurity as the outcome variable, there was a clear association with low number of prenatal visits (OR 3.0; 95%CI 2.2-4.0) and late onset of prenatal care (OR 1.9; 95%CI 1.3-2.6) and low educational level (OR 1.9; 95%CI 1.4-2.5) related to adolescence (OR 1.5; 95%CI 1.1-1.9). The incidence of caesarean delivery was significantly lower among adolescents (33.3%) than among adults (49.4%), with a lower association with pre-eclampsia and cephalo-pelvic disproportion. CONCLUSIONS: Pregnancy in adolescence was associated with late onset of prenatal care and low number of visits, as well as low educational level, low birth weight, prematurity and a lower incidence of cephalo-pelvic disproportion and pre-eclampsia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(8):174-181
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000800002
PURPOSE: To describe the maternal and perinatal outcomes of pregnant women diagnosed with leukemia who were followed up for prenatal care and delivery at a university hospital. METHODS: A retrospective study of the period from 2001 to 2011, which included 16 pregnant women with a diagnosis of leukemia followed by antenatal care specialists in hematological diseases and pregnancy. For acute leukemia diagnosed after the first trimester, the recommendation was to perform chemotherapy despite the current pregnancy. For chronic leukemia, patients who were controlled in hematological terms were maintained without medication during pregnancy, or chemotherapy was introduced after the first trimester. We analyzed the maternal and perinatal outcome. RESULTS: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) was diagnosed in five cases (31.3%), acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in two cases (12.5%) and chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in nine cases (56.3%). Of the cases of acute leukemia, two (28.6%) were diagnosed in the first trimester, two (28.6%) in the second and three (42.9%) in the third. Two patients with ALL diagnosed in the first trimester opted for therapeutic abortion. Four patients with acute leukemia received chemotherapy during pregnancy, with a diagnosis established after the 20th week. In one case of ALL with a late diagnosis (30 weeks), chemotherapy was started after delivery. All pregnant women with acute leukemia developed anemia and thrombocytopenia, and four (57.1%) developed febrile neutropenia. Of nine pregnant women with CML, four were treated with imatinib mesylate when they became pregnant, with treatment being interrupted in the first trimester in three of them and in the second trimester in one. During pregnancy, three patients (33.3%) required no chemotherapy after discontinuation of imatinib, and six (66.7%) were treated with the following drugs: interferon (n=5) and/or hydroxyurea (n=3 ). In the group of pregnant women with CML, anemia occurred in four (44.4%) cases and thrombocytopenia in one (11.1%). The perinatal outcomes of pregnancies complicated by acute leukemia were as follows: mean gestational age at delivery was 32 weeks (standard deviation - SD=4.4) and the mean birth weight was 1476 g (SD=657 g), there were 2 (40.0%) perinatal deaths (a fetal one and a neonatal one). In pregnancies complicated by CML, the mean gestational age at delivery was 37.6 weeks (SD=1.1) and the mean birth weight was 2870 g (SD=516 g). There was no perinatal death and no fetal abnormality was detected. CONCLUSIONS: Maternal and fetal morbidity is high in pregnancies complicated by acute leukemia. Whereas, in pregnancies complicated by CML, the maternal and fetal prognosis appears to be more favorable, with greater ease in management of complications.