-
Original Article03-18-2025
Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor: a promising new biomarker to identify cervical precursor lesions and cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo4
Abstract
Original ArticleGastrin-releasing peptide receptor: a promising new biomarker to identify cervical precursor lesions and cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo4
Views157Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to verify the relation between gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR), oncogenic Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and cervical lesions severity.
Methods:
GRPR mRNA levels were evaluated in cervical cancer-derived cell lines and in primary keratinocytes expressing HPV16 oncogenes by RT-PCR. GRPR protein expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry in organotypic cell cultures derived from keratinocytes transduced with HPV16 oncogenes and in 208 cervical samples, including 59 non-neoplastic tissue, 28 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 (CIN3), 44 squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) and 77 adenocarcinomas (ADC). Generic primers (GP5+/GP6+) were used to identify HPV infection in tissue samples. Experiments involving cell lines were analyzed through non-parametric tests (Kruskal Wallis), and Fisher's Exact Test for human tissues samples. All statistical tests were considered significant at p <0.05. Immunohistochemical evaluation was conducted independently and blindly by two observers (AD- LO). Any discordant findings were resolved through discussion to reach a consensus score.
Results:
GRPR mRNA levels were not increased in cells expressing HPV16 or HPV18 oncogenes. However, at the protein level, GRPR was upregulated in organotypic cell cultures containing HPV oncogenes. Besides, it was identified an association between GRPR expression and cervical lesion severity (p < 0.0001). The detection rate of high-risk HPV DNA was directly correlated with cervical disease. Nonetheless, HPV infection was not directly associated with GRPR in cervical samples.
Conclusion:
GRPR expression is highly predictive of cervical lesion severity, irrespective of HPV infection and might contribute to improving patient's therapeutic management as well as being used a marker of disease progression.
Key-words AdenocarcinomaCarcinoma, squamous cellGastrin-releasing peptide receptorHuman papillomavirusOncogenesPapillomavirus infectionsUterine cervical dysplasiaUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more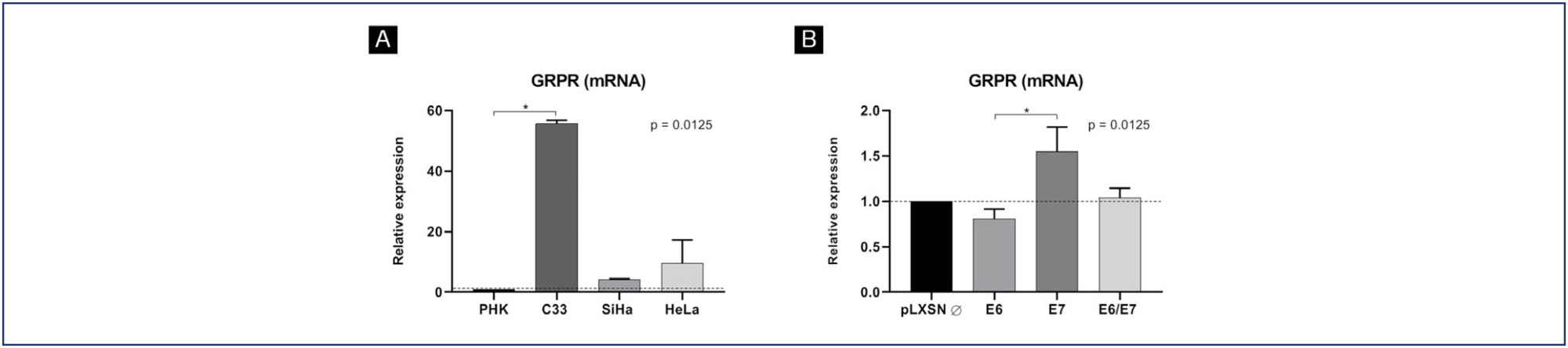
-
Original Article03-14-1999
Frequency of mutations at codon 12 of the K–ras gene in invasive ductal breast cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(3):127-131
Abstract
Original ArticleFrequency of mutations at codon 12 of the K–ras gene in invasive ductal breast cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(3):127-131
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000300002
Views117See morePurpose: the frequency of point mutation at codon 12 of the K¾ras gene was determined in paraffin blocks of surgical specimens from patients who had ductal invasive breast cancer. Material and Methods: Fifty surgical specimens blocked in paraffin from patients with ductal invasive breast cancer, with histological degree II and III, were used. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used for amplification of DNA fragments studied. The material cleavage was obtained with restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP). The electrophoresis in agarose gel, with Ladder 123 (GIBCO-BRL) marker, was employed to verify if some mutation had occurred. The results were shown using ultraviolet beam and recorded by photos. Results: mutations at codon 12 of K-ras gene were found in five samples (10%) and all of them were polymorphic for this caracter. The five patients whose tumors expressed mutation were in the postmenopausal period. Four patientes had tumors of histological degree II and one, III.
-
Original Article08-28-2006
Association of p53 protein expression and degree of differentiation in infiltrating ductal breast carcinomas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):298-303
Abstract
Original ArticleAssociation of p53 protein expression and degree of differentiation in infiltrating ductal breast carcinomas
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(5):298-303
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000500006
Views74See morePURPOSE: to assess p53 protein expression in infiltrating ductal breast carcinoma and to analyze its association with histological and nuclear grade. METHODS: sixty-five consecutive females who were diagnosed with primary infiltrating ductal breast tumor from July 1999 to July 2001 were included in the present study. Mean patient age at diagnosis was 69.2 years (range 41 - 90). All patients were first treated with surgical therapy, conservative surgery or mastectomy. None of the patients received any preoperative adjuvant therapy. Resected breast tumor specimens were fixed in 10% formalin, paraffin embedded, and conserved for immunohistochemical analysis. p53 protein expression was evaluated. Primary monoclonal anti-human p53 antibody DO-7 (DAKO) was used. Frequency distributions were tested by the chi2 test. A level of p<0,05 was considered significant. RESULTS: p53 expression was detected in 24 (36,9%) of 65 carcinomas. Of the cases with protein expression, 13 (54,2%) were high or histological grade III, 8 (33,3%), were grade II, 3 (12,5%) were grade I. On nuclear grade analysis, of the cases with protein expression, 13 (4,2%) were nuclear grade III, 9 (37,5%) were grade II and 2 (8,3%) were grade I. p53 expression was frequent in carcinomas with high histological and nuclear grades. CONCLUSIONS: p53 expression was significantly associated with the histological grade. On the other hand, nuclear grade was not significantly related to p53 expression.
-
Original Article08-29-2005
Association between p53 and Ki-67 expression and clinicopathologic features in patients with carcinoma of the cervix
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(5):243-247
Abstract
Original ArticleAssociation between p53 and Ki-67 expression and clinicopathologic features in patients with carcinoma of the cervix
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(5):243-247
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000500003
Views128See morePURPOSE: to evaluate the association between p53 and Ki-67 expression in the tumor and clinicopathological features in patients with carcinoma of the cervix. METHODS: samples were taken from the tumor of 36 patients with stage IB (FIGO) cervical carcinoma submitted to radical hysterectomy. Tissue samples were taken from the tumor, fixed in formalin and embedded in paraffin. The specimens were analyzed by histopathology (hematoxylin and eosin) and immunohistochemically evaluated using monoclonal antibodies for p53 and Ki-67. Data were analyzed statistically by the chi2 test to evaluate eventual differences between the groups. RESULTS: the age of the patients ranged from 27 to 73 years (48.7±10.4 years). Clinical stage (FIGO) was IB1 in 27 cases (75%) and IB2 in 9 cases (25%). A positive tumoral expression of the p53 protein was found in half of the cases. In relation to the Ki-67 expression, a high cell proliferation index was shown in 73.3% of the cases. There was no association between tumoral p53 and Ki-67 expression with age (p=0.091 and 0.900), clinical stage (p=0.054 and 0.667), histological classification (p=0.674 and 0.674), grade of differentiation (p=0.070 and 0.282), presence of lymphatic vascular space invasion (p=0.248 and 0.667), parametrial involvement (p=0.729 and 0.763) and pelvic lymph node metastasis (p=0.729 and 0.636, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: tumoral expression of p53 and Ki-67 was not associated with the clinicopathological features in patients with stage IB carcinoma of the cervix.
-
Original Article06-19-2002
p53 Protein Overexpression as a Prognostic Marker for Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia III Recurrence/Progression
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):51-57
Abstract
Original Articlep53 Protein Overexpression as a Prognostic Marker for Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia III Recurrence/Progression
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(1):51-57
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000100008
Views165See morePurpose: to evaluate p53 overexpression value in vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) III recurrence/progression. Methods: twenty patients with undifferentiated VIN III were selected and followed up every six months for four years and divided into two groups: fourteen without and six with recurrence/progression lesion. The recurrence/progression cases were distributed as follows: in three patients recurrence occurred only once; in two, twice, and only one progressed to squamous cancer. In both groups the site of vulvar lesion and p53 overexpression and immunostaining pattern were analyzed. A similar study was performed in recurrence/progression cases, besides the analysis of the time interval to occur the arise of recurrence/progression. Results: recurrence was observed in 25% of the cases and, in 5%, progression to carcinoma. The mean time interval for recurrence was 24.5 months. Multifocal location of the initial lesion was the predominant form (50%) in both groups. In the majority of the cases (87.5%) recurrence/progression occurred at the same site of the initial vulvar lesion. p53 overexpression was observed in 50% of the VIN III primary lesions and in 75% of the recurrence/progression cases. Conclusions: p53 overexpression seems to play an important role in VIN III pathogenesis and may predict the clinical course of the lesions. VIN III recurrence/progression has a tendency to occur in the same area of the initial lesion, suggesting the presence of molecular disturbance.


