Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):27-34
To determine differences in some nutritional aspects of pregnant women assisted at prenatal care services in a country town and in a metropolitan area.
Pregnant women received prenatal care in the city of Belo Horizonte (BH), metropolitan area, and Paula Cândido (PC), a country town. A Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ) containing socioeconomic information and information about eating habits was applied. In addition,weight and height were measured on the occasion of the visits and the women were ask to give their prepregnancy weight for subsequent BMI calculation. Data were analyzed according to region and trimester of pregnancy using the SPSS software version 15.0, the t-test to compare averages and the chi-square test of independence, with the level of significance set at 5%.
240 pregnant women were included, 90 fromthe country town and 150 from themetropolitan area. Of these,most weremarried (BH = 56.6%; PC = 46.6%) and did not work outside the home (BH = 54.0%; PC = 84.4%). They predominantly had 3-4 meals/ day during the 1st and 2nd quarters (BH = 54.0 and 46%; PC = 66.7 and 63.3%, respectively) and had 5-6 meals/day during Q3 in BH (44%). There was significant weight gain only in the 1st quarter (BH: 58,0%; PC: 53.3%). Weight gain versus eating habits was significant for the variables "lunch or dinner away from home" for the 1st quarter in BH (p = 0.006), "How many times they consume milk" in the 1 st quarter in PC (p = 0.03), and "How many times they consume junk food" in the 3rd quarter in BH (p = 0.009).
Pregnant woman showed proper eating habits in both regions despite the prevalence of pregestational overweight in BH and a low level of education and income, especially in the country town, an indicator that may be unfavorable for the nutrition of pregnant women during this period. Studies of association between eating habits and newborn health will provide more information about nutrition during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(7):319-324
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320150005388
To compare body attitudes of pregnant women in various body mass index categories, during different gestational periods and under gestational risk conditions, as well as to analyze the association of the study variables with the body attitudes of pregnant women.
We included 386 pregnant women in all gestational periods, aged 18 to 46 years (mean 29.32±6.04 years ), who attended prenatal care in the public and private sectors of a city in Southeastern Brazil, excluding women with incomplete data. The instruments for assessment were "Body Attitudes Questionnaire", "Critério de Classificação Econômica Brasil", and a sociodemographic questionnaire. In addition, anthropometric and obstetric data were collected. Descriptive, comparative, and correlational statistical analyses were performed.
The body attitudes of pregnant women were similar in all pregnancy trimesters (F=0.39; p=0.9). Negative body attitudes increased gradually among low weight (108.2±12.5), appropriate weight (116.2±16.0), overweight (125.1±14.3), and obese (132.9±16.4) groups, and among pregnancy women with normal (120.0±17.1) and high-risk pregnancies (124.9±16.7). The sociodemographic, economic, and obstetric variables did not influence the variance of body attitudes. The body mass index explained 11.3% of the variance of body attitudes in pregnant women.
Nutritional status and risk conditions showed an association with negative body image and should therefore be evaluated in pregnant women for a better maternal and child health.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(8):386-393
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000800008
PURPOSE: To evaluate sociodemographic, behavioral and reproductive factors and morbidities associated with inadequate weight gain during pregnancy. METHODS: Cohort study conducted from December 2007 to August 2008 with women in the first trimester of pregnancy looking for prenatal care in the Public Health System who lived in the cities of Petrópolis or Queimados, Rio de Janeiro state (Brazil). Women with multiple pregnancy, who had a miscarriage in the index pregnancy or who lacked information for the assessment of pregravid nutritional status or weight gain were excluded. Pregravid nutritional status and weight gain during pregnancy were determined according to the criterion established by the Institute of Medicine (IOM). Statistical analysis was performed using a multinomial logistic regression model. RESULTS: A total of 1,287 women were included in the study; 26.6% of them were overweight or obese while 11% were underweight. Inadequate weight gain during pregnancy was observed in 71.4% of pregnant women; 35.6% of them did not gain enough weight while 35.8% gained more weight than recommended by the IOM. In the multivariate analysis, women with hypertension (OR=2.1; 95%CI 1.4-3.1), pregravid overweight (OR=2.5; 95%CI 1.4-4.5) or obesity (OR=2.7; 95%CI 1.8-3.9) and who had a higher educational level were more likely to gain more weight than recommended, while pregravid underweight (OR=0.6; 95%CI 0.4-0.9) represented a protection against excessive gain. CONCLUSION: Pregravid nutritional diagnosis and weight gain monitoring should be actions effectively instituted in the routine of health professionals.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(4):175-183
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000400007
PURPOSE: To associate the quality of life with the nutritional status of climacteric women. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional study on a sample of 200 climacteric women aged 40 to 65 years who responded to a 24-hour food recall and to questions about socioeconomic factors and current, previous and family medical history. Body mass index (BMI), waist circumference (WC) and waist-hip ratio were used for anthropometric evaluation. To assess the quality of life, we applied the MRS-menopause rating scale. RESULTS: The average BMI and waist circumference were 30.1 kg/m² (obesity grade 1) and 99 cm (very increased risk for cardiovascular disease), respectively. Increased protein consumption and decreased fiber, calcium and vitamin D intake were detected. The most prevalent disease was hypertension, 48.5% of the women studied were taking medication for cardiovascular disease and 23% were taking antidepressant medications. Regarding quality of life, significant results related to BMI as well as blood pressure were found. CONCLUSIONS: A nutritional intervention aiming to correct or improve food consumption and anthropometric profile may result in health benefits for climacteric women. The prevalence of obesity, associated with a poorer quality of life, morbidity and mortality underscores the need for a feeding re-education program during the climacteric.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(3):107-112
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000300003
PURPOSE: To analyze the influence of maternal nutritional status, weight gain and energy consumption on fetal growth in high-risk pregnancies. METHODS: A prospective study from August 2009 to August 2010 with the following inclusion criteria: puerperae up to the 5th postpartum day; high-risk singleton pregnancies (characterized by medical or obstetrical complications during pregnancy); live fetus at labor onset; delivery at the institution; maternal weight measured on the day of delivery, and presence of medical and/or obstetrical complications characterizing pregnancy as high-risk. Nutritional status was assessed by pregestational body mass index and body mass index in late pregnancy, and the patients were classified as: underweight, adequate, overweight and obese. A food frequency questionnaire was applied to evaluate energy consumption. We investigated maternal weight gain, delivery data and perinatal outcomes, as well as fetal growth based on the occurrence of small for gestational age and large for gestational age neonates. RESULTS: We included 374 women who were divided into three study groups according to newborn birth weight: adequate for gestational age (270 cases, 72.2%), small for gestational age (91 cases, 24.3%), and large for gestational age (13 cases, 3.5%). Univaried analysis showed that women with small for gestational age neonates had a significantly lower mean pregestational body mass index (23.5 kg/m², p<0.001), mean index during late pregnancy (27.7 kg/m², p<0.001), and a higher proportion of maternal underweight at the end of pregnancy (25.3%, p<0.001). Women with large for gestational age neonates had a significantly higher mean pregestational body mass index (29.1 kg/m², p<0.001), mean index during late pregnancy (34.3 kg/m², p<0.001), and a higher proportion of overweight (30.8%, p=0.02) and obesity (38.5%, p=0.02) according to pregestational body mass index, and obesity at the end of pregnancy (53.8%, p<0.001). Multivariate analysis revealed the index value during late pregnancy (OR=0.9; CI95% 0.8-0.9, p<0.001) and the presence of hypertension (OR=2.6; 95%CI 1.5-4.5, p<0.001) as independent factors for small for gestational age. Independent predictors of large for gestational age infant were the presence of diabetes mellitus (OR=20.2; 95%CI 5.3-76.8, p<0.001) and obesity according to body mass index during late pregnancy (OR=3.6; 95%CI 1.1-11.7, p=0.04). CONCLUSION: The maternal nutritional status at the end of pregnancy in high-risk pregnancies is independently associated with fetal growth, the body mass index during late pregnancy is a protective factor against small for gestational age neonates, and maternal obesity is a risk factor for large for gestational age neonates.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(8):188-195
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000800004
PURPOSE: To describe the epidemiological profile and nutritional status of pregnant women infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and its effect on the nutritional status of these women during pregnancy. METHODS: A retrospective cohort study was conducted on 121 pregnant women with HIV infection, single fetus pregnancies, who received prenatal care and delivered at a referral unit for HIV-infected pregnant women during the period from 1997 to 2007. Outcomes of the study were the initial and final nutritional status as measured by body mass index, weight gain, anemia (hemoglobin <11 g/dL) and low birth weight. Bivariate analysis investigated the association of these outcomes with socio-demographic, clinical-care and dietary characteristics. We estimated the relative risks (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI). RESULTS: At the beginning of pregnancy, 11.0% of the women were underweight, and in late pregnancy, the prevalence was 29.3%. Low educational level, urinary infection and worm infestation were associated with low gestational weight in late pregnancy. The percentage of insufficient weight gain was 47.5%, with well-nourished pregnant women (RR=3.3 95%CI 1.3-8.1) and women with no companion (RR=1.5 95%CI 1.1-2.2) having a higher risk for this outcome. The prevalences of overweight at the beginning and at the end of pregnancy were 26.8 and 29.4, respectively. There was a significant prevalence of anemia (61.0%). CONCLUSIONS: The high percentage of negative nutritional outcomes identified at this referral service with multidisciplinary care for pregnant women living with HIV reveals the need to establish more effective strategies to deal with the complex context of HIV.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(4):176-181
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000400005
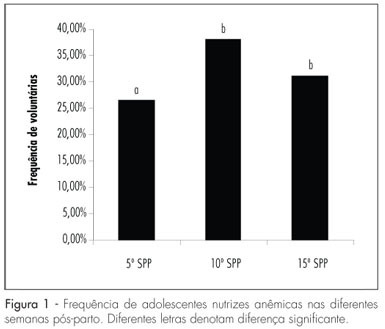
PURPOSE: to evaluate changes in the nutritional status of lactating adolescents in different postpartum weeks. METHOD: this is an analytical, observational, longitudinal study. Lactating adolescents were followed-up from the 5th to the 15th postpartum week (PPW). The nutritional status was evaluated in the 5th, 10th and 15th PPW by the Body Mass Index (BMI/age). A colorimetric method was used to determine hemoglobin level and microcentrifugation to define hematocrit. ANOVA with repeated measures was used to compare means, followed by the Tukey post-test. The level of significance was 5%. RESULTS: modification in nutritional status was observed from the pregestational period to the 15th PPW, with a reduction in the frequency of lactating adolescents with low weight (from 21% to 9%) and a rise in the frequency of overweight (21% to 27%) and eutrophic (58% to 64%) adolescents. Although mean hemoglobin (12.3±1.7 g/dL) and hematocrit (39.0±4.0%) levels were normal, a high frequency of anemia (30%) was observed throughout the study period. CONCLUSION: the present results show that the body weight of lactating adolescents rises during the lactation period and could lead to a higher frequency of obesity among adolescents. Anemia is still a nutritional problem, not only during pregnancy, but also during the postpartum period. It is necessary to prevent and treat probable subclinical nutritional deficiencies at this biological time.
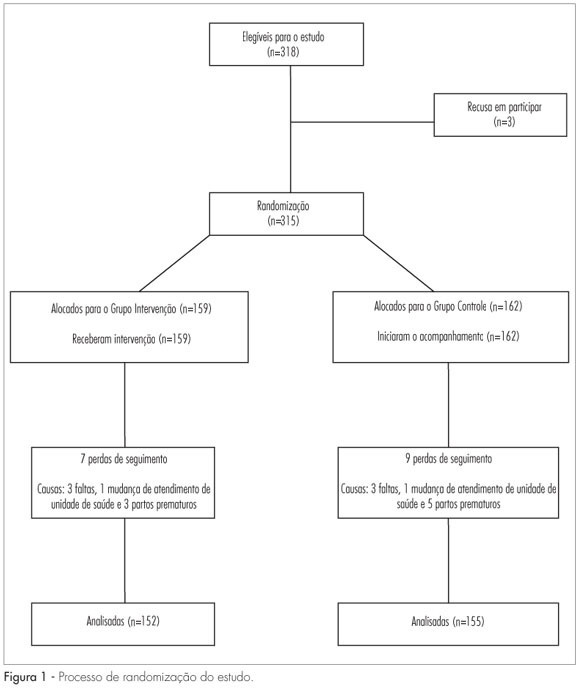
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(1):13-19
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000100002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the impact of dietary counseling on controlling weight gain in pregnant women, who were served in a public health service facility. METHODS: the study was conducted at a known health unit located in the metropolitan region of the city of Porto Alegre, in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Three hundred and fifteen pregnant women between the 10th and 29th week of gestation were randomized to Control and Intervention Groups. The Intervention Group received dietary counseling according to nutritional status, and pregnant women in the Control Group were instructed to follow the routine of the health service facility. Weight and height were measured, and the body mass index (BMI) was calculated. The pre-gestational nutritional status was determined according to the following BMI criteria: low weight (<18.5 kg/m²), eutrophy (18.5 to 24.9 kg/m²), overweight (25.0 to 29.9 kg/m²), and obesity (>30 kg/m²). The nutritional status during pregnancy was determined according to the BMI curve for gestational age adopted by the Health Ministry of Brazil. Data were analyzed by the relative risk and respective 95% confidence interval, and by the Student's t-test and χ2 test. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05. RESULTS: the assessment of nutritional status before pregnancy showed that 28.0% of the women were overweight and 4.1% were underweight. In the first and last interview during pregnancy, the rates of prevalence of excessive weight were 36.2 and 46.0%, respectively. The intervention proved to be effective in reducing the rate of weekly weight gain of pregnant women with excess weight (342.2 versus 420.2; p=0.015) and the prevalence of clinical complications (9.2 versus 24.85; p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: dietary counseling was effective in decreasing the weight gain of pregnant women who were overweight and reducing clinical complications, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, infant low weight, and prematurity in the Intervention Group.