-
Original Article03-11-2022
Exercise and Physical Activity Levels and Associated Factors Among High-Risk Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):360-368
Abstract
Original ArticleExercise and Physical Activity Levels and Associated Factors Among High-Risk Pregnant Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):360-368
Views260See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the levels of physical activity and exercise practice, and examine the associated maternal characteristics; as well as the anxiety levels of high-risk pregnant women.
Methods
A cross-sectional study conducted with pregnant women at a High-risk Prenatal Clinic (HRPC) in a tertiary maternity. Pregnant women of 18 to 40-years-old, with a single fetus, and with gestational age up to 38 weeks were included. The level of physical activity and exercise practice of the study’s participants were investigated using the Pregnancy Physical Activity Questionnaire (PPAQ). Maternal sociodemographic, anthropometric, and medical data were investigated using a specific form. For anxiety levels, the short version of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) was applied. We used the Student t-test, chi-square test, odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) and multiple logistic regression. The significance level was 5%.
Results
Among the 109 pregnant women included, 82 (75.2%) were classified as sedentary/little active. The higher energy expenditure were for domestic activities (133.81±81.84 METs), followed by work-related activities (40.77±84.71 METs). Only 19.3% women exercised during pregnancy (4.76±12.47 METs), with slow walking being the most reported exercise. A higher level of education was the most important factor associated with women being moderately or vigorously active (OR=29.8; 95% CI 4.9-117.8). Nulliparity (OR=3.1; 95% CI 1.0-9.1), low levels of anxiety (OR=3.6; 95% CI 1.2-10.7), and unemployment (OR=4.8; 95% CI 1.1-19.6) were associated with the practice of exercise during pregnancy.
Conclusion
Most women with high-risk pregnancies exhibited a sedentary pattern, with low prevalence of physical exercise practice. Recognizing factors that hinder the adoption of a more physically active lifestyle is essential for an individualized guidance regarding exercise during pregnancy.
-
Original Article10-03-2014
Changes in motor behavior during pregnancy in rats: the basis for a possible animal model of restless legs syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):436-441
Abstract
Original ArticleChanges in motor behavior during pregnancy in rats: the basis for a possible animal model of restless legs syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(10):436-441
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005105
Views79See morePURPOSE:
Pregnant women have a 2-3 fold higher probability of developing restless legs syndrome (RLS – sleep-related movement disorders) than general population. This study aims to evaluate the behavior and locomotion of rats during pregnancy in order to verify if part of these animals exhibit some RLS-like features.
METHODS:
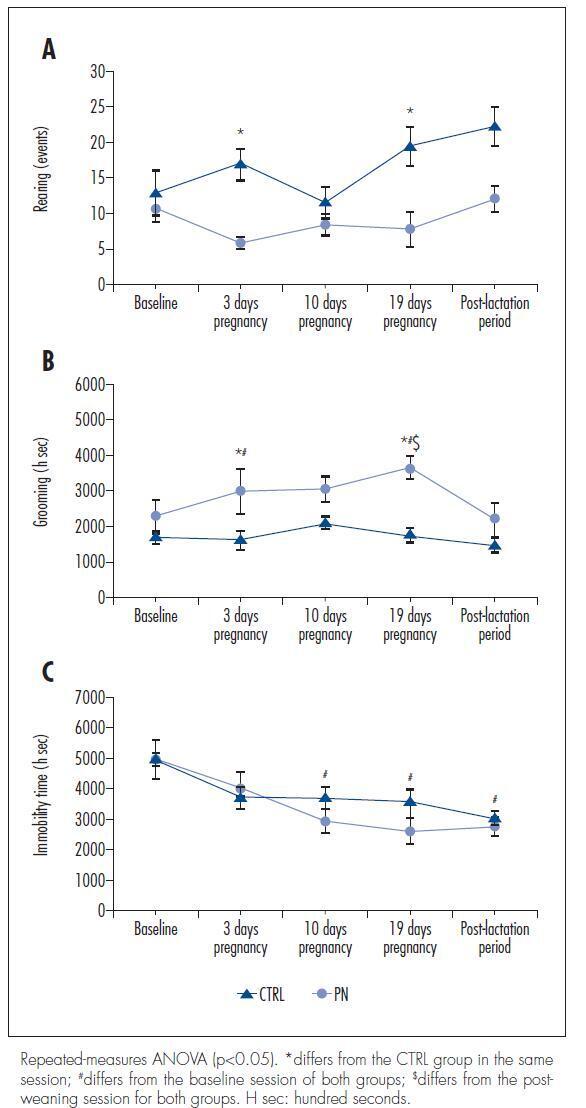
We used 14 female 80-day-old Wistar rats that weighed between 200 and 250 g. The rats were distributed into control (CTRL) and pregnant (PN) groups. After a baseline evaluation of their behavior and locomotor activity in an open-field environment, the PN group was inducted into pregnancy, and their behavior and locomotor activity were evaluated on days 3, 10 and 19 of pregnancy and in the post-lactation period in parallel with the CTRL group. The serum iron and transferrin levels in the CTRL and PN groups were analyzed in blood collected after euthanasia by decapitation.
RESULTS:
There were no significant differences in the total ambulation, grooming events, fecal boli or urine pools between the CTRL and PN groups. However, the PN group exhibited fewer rearing events, increased grooming time and reduced immobilization time than the CTRL group (ANOVA, p<0.05).
CONCLUSION:
These results suggest that pregnant rats show behavioral and locomotor alterations similar to those observed in animal models of RLS, demonstrating to be a possible animal model of this sleep disorder.
-
Original Article07-05-2013
Relationship between the level of physical activity and premenstrual syndrome incidence
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):210-214
Abstract
Original ArticleRelationship between the level of physical activity and premenstrual syndrome incidence
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(5):210-214
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000500004
Views69See morePURPOSE: To determine the relationship between the level of physical activity and the incidence of premenstrual syndrome. METHODS: A cross-sectional design was conducted on 71 apparently healthy university students (24.4±4.8 yrs; 61.5±8.7 kg; 1.63±0.06 m). The level of physical activity was determined with a questionnaire and the presence of premenstrual syndrome was verified based on daily symptoms self-reported in a diary during two consecutive menstrual cycles. 17 premenstrual symptoms are considered in the diary, which should be scored on a 5-point scale (0-4) according to their occurrence, so that a score can be calculated in each cycle. The occurrence of premenstrual syndrome was considered if three or more symptoms were reported up to six days before menstruation (premenstrual period) and were absent up to six days after menstruation (postmenstrual period). RESULTS: The Spearman correlation coefficient showed a significant and negative relationship between the level of physical activity and premenstrual syndrome score (r=-0.506; 95%CI -0.335 to -0.678; p<0.001). When the participants were divided into a group with a positive diagnosis of premenstrual syndrome (n=31) and a healthy group (n=40), the Mann-Whitney test showed higher habitual physical activity in the healthy group than in the premenstrual syndrome group (7.96±1.17 and 6.63±1.20, respectively) (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: There is a negative relationship between the level of physical activity and the incidence of premenstrual syndrome, with women with a positive diagnosis of premenstrual syndrome having a lower level of physical activity than healthy women.
-
Original Article06-06-2013
Physical activity and body composition in menopausal women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(4):153-158
Abstract
Original ArticlePhysical activity and body composition in menopausal women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(4):153-158
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000400004
Views150See morePURPOSE: To analyze the relationship between physical activity and body composition in menopausal women. METHODS: The study included 62 menopausal women aged 50 years or more (61.2±7.6). The practice of physical activity was assessed with an accelerometer and is reported as minutes per week of low physical activity and moderate plus vigorous physical activity, and total physical activity in counts. Lean mass and total fat mass were assessed by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, and are reported as percentages. The relation between body composition variables and physical activity was evaluated by Spearman and Pearson correlation. Comparisons between groups were performed using the independent t test and Mann-Whitney test. RESULTS: The age group 59 years or older had higher mean values of total physical activity in counts (1,307.081 versus 2,843.840) and of minutes per week of moderate-vigorous physical activity (273 versus 156 minutes). Women who completed 150 minutes or more of moderate-vigorous physical activity had significantly lower total fat mass (43.8 versus 47.2 kg), higher lean mass (53.8 versus 49.6 kg) and lower BMI (27.7 versus 30.5 kg/m²) when compared to those with less than 150 minutes of physical activity per week. Only time spent in moderate activities showed a significant negative correlation with the percentage of total fat (r=-0.26, p<0.05), whereas total physical activity in counts correlated with the percentage of lean body mass (r=0,30), percentage of total fat (r=-0.32), trunk fat (r=-0.29), and BMI (r=-0.32); all correlations were statistically significant at p<0.05. CONCLUSION: menopausal women aged 50 years or more who spent more minutes in moderate and vigorous activity and higher total physical activity counts showed lower fat mass and higher lean mass.
-
Original Article03-30-2010
Immediate breast reconstruction effects on quality of life of women with mastectomy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(12):602-608
Abstract
Original ArticleImmediate breast reconstruction effects on quality of life of women with mastectomy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(12):602-608
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001200007
Views97See morePURPOSE: to prospectively evaluate the effects of immediate breast reconstruction on the quality of life of women who underwent mastectomy. METHODS: 76 women that underwent mastectomy at Centro de Atenção Integral à Saúde da Mulher da Universidade Estadual de Campinas, in Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil, from August 2007 to December 2008, were included. Two groups were formed: 41 women who underwent mastectomy combined with immediate breast reconstruction (M+RI) and 35 that were subjected to mastectomy alone (M). The quality of life evaluation was assessed with the World Health Organization's questionnaire - Quality of Life (WHOQOL-100). The questionnaire was administered on three occasions: at the time of admission, one month after surgery, and again six months after surgery. The WHOQOL-100 scores were calculated according to analysis' guidelines by the World Health Organization. For comparison of the scores between groups, it was used the Student's t-test, Fisher exact test, chi-square test, and Mann-Whitney test. For the analysis of repeated measures over time, ANOVA and ANOVA for repeated measures were used. RESULTS: at all time points evaluated, beginning with the preoperative assessment, the average quality of life scores of the M+IR Group were higher than those of the M Group, primarily in the "physical", "psychological", "level of independence" and "social relationships" domains of the questionnaire. Of the six areas covered by the questionnaire, three ("physical", "social relations", "environment") showed no significant differences between groups. The M+IR Group had a better score (15.5 to 14.9 for the M+IR and 14.3 to 14.2 for M; p=0.04) in the psychological domain. There was a significant reduction in the level of independence in the first month after surgery in both groups, with a significant recovery after six months. CONCLUSIONS: the present results suggest that immediate breast reconstruction is significantly beneficial regarding the psychological aspects of quality of life, without affecting the patient's physical functionality.
-
Review Article07-29-2009
Physical exercise and menopause
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(5):254-261
Abstract
Review ArticlePhysical exercise and menopause
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(5):254-261
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000500009
Views59See moreIt is believed that estrogen deficiency, lipid profile alterations, body weight gain, and sedentary lifestyle are strongly associated with the increased incidence of arterial hypertension in postmenopausal women. In an attempting to reduce the incidence of arterial hypertension in this population, a variety of approaches has been used, but the results are conflicting and the changing in lifestyle has been proposed and an important preventive action to control the arterial hypertension and associated risk factors in this women age - mainly practice of physical exercise. Continuous exercise has been used as an important approach in management cardiovascular disease and endocrine-metabolic disorders. Continuous exercise prescription is characterized by, at least, 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity (60 to 70% of maximum heart rate), three days of the week. Intermittent exercise is characterized by low intensity exercise periods, alternating with high-intensity exercise periods, ranging of 50 to 85% of the maximum heart rate, during ten minutes. Intermittent exercise has been employed as training program in weight loss therapy and personal training because previous studies have shown similar metabolic adaptations and aerobic capacity after continuous or intermittent exercise. This review focused on the relevance of continuous and intermittent exercise on the blood pressure control, discussion of the data found in experimental model of menopause and in women and the relationship between incidence of arterial hypertension and its genesis in postmenopausal women.


