Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo17
To determine the prevalence of anxiety, depression and burnout in residents of Gynecology and Obstetrics during COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil and its associated factors.
Cross-sectional study involving all regions of Brazil, through the application of a sociodemographic questionnaire, the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HAD) and the Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI-HSS) instrument. Multivariate analysis was performed after adjusting the Poisson model.
Among the 719 participating medical residents, screening was positive for anxiety in 75.7% and for depression in 49.8% of cases. Burnout syndrome was evidenced in 41.3% of the physicians studied. Those with depression are more likely to have anxiety (OR 0.797; 95%CI 0.687 - 0.925) and burnout syndrome (OR 0.847 95%CI 0.74 - 0.97). Residents with anxiety (OR 0.805; 95%CI 0.699 - 0.928) and burnout (OR 0.841; 95%CI 0.734 - 0.963) are more likely to have depression.
High prevalence of anxiety, depression and burnout were found in residents of Gynecology and Obstetrics in Brazil, in addition to important correlations between anxiety-depression and depression-burnout.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo42
To evaluate the effects of surgical treatment of deep endometriosis on the metabolic profile, quality of life and psychological aspects.
Prospective observational study, carried out with women of reproductive age diagnosed with deep endometriosis, treated in a specialized outpatient clinic, from October/2020 to September/2022, at a University Hospital in Fortaleza - Brazil. Standardized questionnaires were applied to collect data on quality of life and mental health, in addition to laboratory tests to evaluate dyslipidemia and dysglycemia, at two moments, preoperatively and six months after surgery. The results were presented using tables, averages and percentages.
Thirty women with an average age of 38.5 years were evaluated. Seven quality of life domains showed improved scores: pain, control and impotence, well-being, social support, self-image, work life and sexual relations after surgery (ES ≥ 0.80). There was an improvement in mental health status with a significant reduction in anxiety and depression postoperatively. With the metabolic profile, all average levels were lower after surgery: total cholesterol 8.2% lower, LDL 12.8% lower, triglycerides 10.9% lower, and fasting blood glucose 7.3% lower (p < 0.001).
Surgical treatment of deep endometriosis improved the quality of life and psychological aspects of patients. The lipid profile of patients after laparoscopy was favorable when compared to the preoperative lipid profile.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):281-288
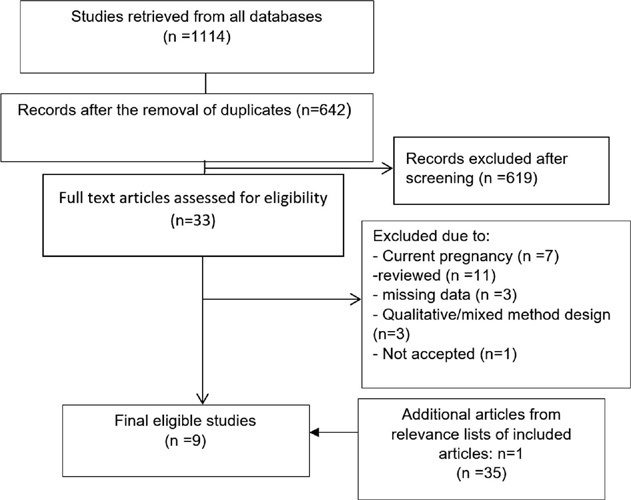
Female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) can affect women’s lives through various physical, psychological, social and even sexual mechanisms. According to the World Health Organization guidelines for managing the health effects of FGM/C, further research into its psychological effects and preventative measures is required. In this study, a comprehensive review of the mental health consequences of circumcised women of reproductive age has been conducted with a special focus on providing preventive solutions.
A comprehensive search of the Web of Science, PubMed(MEDLINE), Proquest ,Scopus and Google scholar was carried outfrom 2000 to 2022. The second stage of search was conducted in grey literature. To facilitate a systematic approach to search the literature, the PECO framework, was adopted.
The result of this narrative review study showed that, the most common mental health disorder in reproductive age circumcised women were depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress disorder. Some studies found a significant relationship between parents’ education level and circumcised girls, so that parents of the circumcised women had a low level of education. Two studies considered religious beliefs, tradition, cleanness, sexual desire control and virginity as the reasons for FGM/C.
All forms of FGM/C may be harmful to one’s health. Women, who have undergone widespread forms of circumcision, are more likely to develop mental disorders. As the psychosocial effects of circumcision can affect the sexual experience of circumcised women, addressing this issue, emphasizing its legal aspects, and providing preventative solutions can improve physical, mental, social, and even sexual health in circumcised women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):149-159
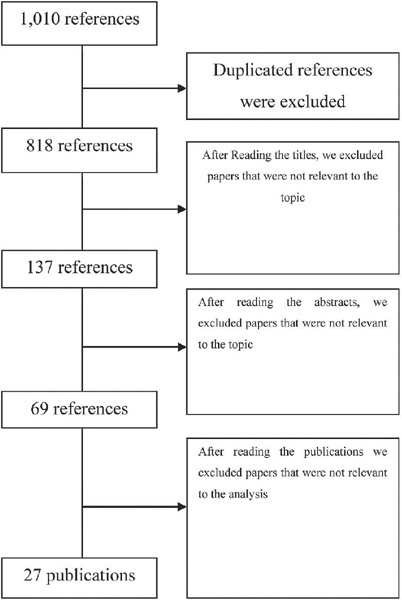
This article aims to review the literature regarding the use of technologies to promote mental health for pregnant women. We seek to: understand the strategies that pregnant women use for mental health care. Also, we investigate the existence of scientific evidence that validates such practices.
This study follows the PRISMA guidelines for systematic reviews. We analyze 27 studies published between 2012 and 2019. We include publications in Portuguese, English, and Spanish.
The results revealed several different possibilities to use technology, including the use of text messages and mobile applications on smartphones. Mobile applications are the most commonly used approaches (22.5%). Regarding the strategies used, cognitive-behavioral approaches, including mood checks, relaxation exercises, and psychoeducation comprised 44.12% of the content.
There is a need for further investigation and research and development efforts in this field to better understand the possibilities of intervention in mental health in the digital age.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):667-677
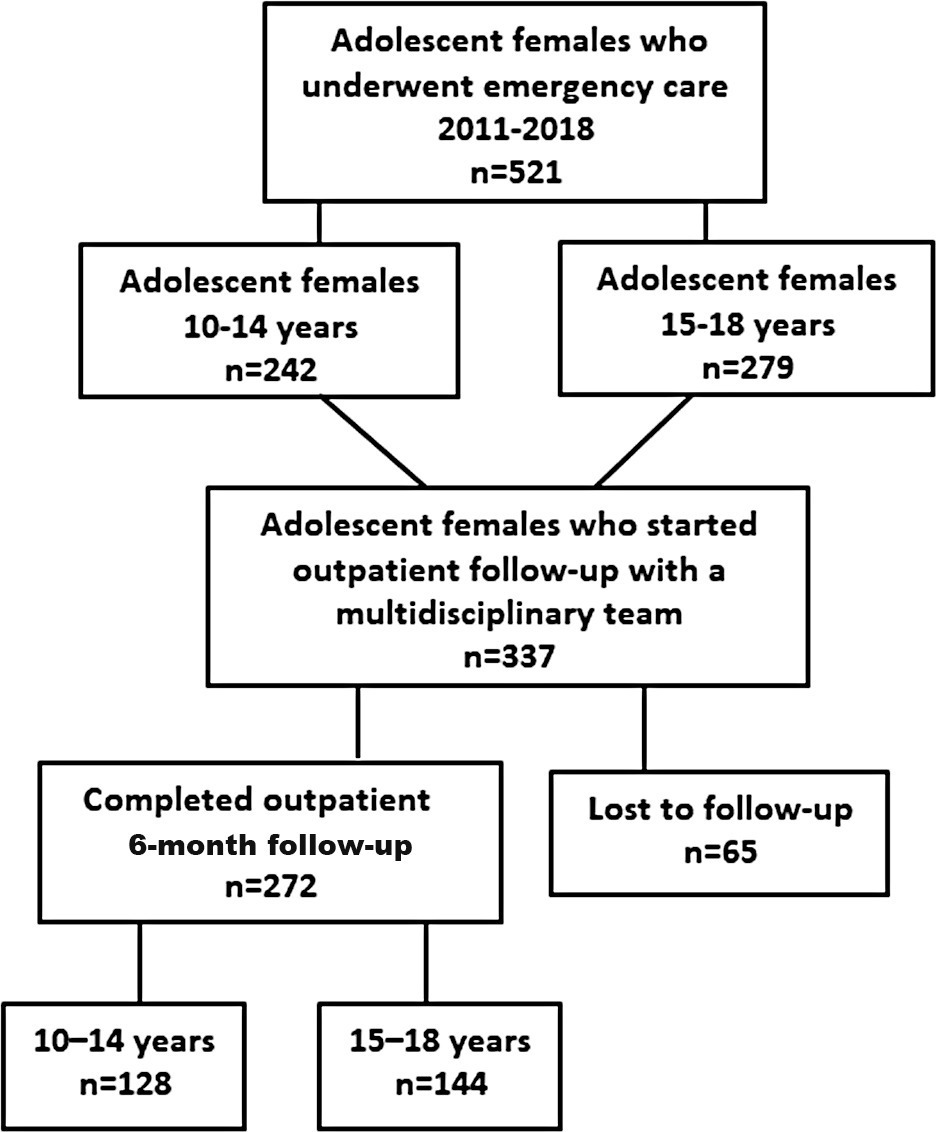
To compare the sexual violence suffered by women in early and late adolescence, the reactions triggered after the aggression, and the care provided.
A retrospective study in which we reviewed the medical records of 521 female adolescents treated by a multidisciplinary team at a reference hospital in the city of Campinas, state of São Paulo, Brazil. We analyzed sociodemographic variables, and those pertainin to the characteristics of the episodes of violence, the emergency care, and the physical and psychological reactions observed during the follow-up. For the analysis, the sample was divided into groups of early (10 to 14 years) and late (15 to 18 years) adolescence. We used the Chi-squared/Fisher Exact, Mann-Whitney, and Kruskal-Wallis tests to compare the groups; the level of significance adopted was 5%.
The early group (n= 242) contained more adolescents who were enrolled in school (p< 0.001), suffered more daytime aggressions (p= 0.031), in their residences (p< 0.001), by an aggressor with whom they were acquainted (p< 0.001), had greater need of legal protection (p= 0.001), and took longer to seek care (p= 0.048). Feelings of guilt, shame, and the perception of violence were similar between the groups. In the late group (n= 279), there was greater consumption of alcohol during the aggression (p= 0,005); they received significantly more prophylaxis treatments; reported more physical symptoms (p= 0.033), sleep disorders (p= 0.003), symptoms of anxiety (p= 0.045), and feelings of anguish (p= 0.011); and had more prescriptions of psychotropics (p= 0.005). Only 52% completed the 6-month follow-up, with no differences between the groups.
The age groups showed differences in the characteristics of the episodes of violence; early adolescents took longer to seek help, and the late group presented more intense symptoms and psychological worsening during the follow-up. Measures of prevention and specific care aimed at this population are needed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):343-351
To evaluate the emotional and clinical aspects observed in women with gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) followed-up in a reference center (RC) by a multidisciplinary team.
Retrospective cohort study of the clinical records of 186 women with GTD and of the emotional aspects (EA) observed in these women by a teamof psychologists and reported by the 389 support groups conducted from 2014 to 2018.
The women were young (mean age: 31.2 years), 47% had no living child, 60% had planned the pregnancy, and 50% participated in two or more SG. Most women (n=137; 73.6%) reached spontaneous remission ofmolar gestation in a median time of 10 weeks and had a total follow-up time of seven months. In the group of 49 women (26.3%) who progressed to gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN), time to remission after chemotherapy was 18 weeks, and total follow-up time was 36 months. EA included different levels of anxiety and depression,more evident in 9.1% of the women; these symptoms tended to occur more frequently in women older than 40 years (p=0.067), less educated (p=0.054), and whose disease progressed to GTN (p=0.018), as well as in those who had to undergo multi-agent chemotherapy (p=0.028) or hysterectomy (p=0.001) adjuvant to clinical treatment.
This study found several EA in association with all types of GTD. It also highlights the importance of specialized care only found in a RC, essential to support the recovery of the mental health of these women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):500-507
The present study was conducted with the objective of investigating the effectiveness of solution-focused group counseling (SFGC) on promoting the mental health of midwifery students.
The present study is an intervention-based study with a pretest, a post-test, and a control group. The statistical population included all of the midwifery students studying in the midwifery department of the Bam University of Medical Sciences, Kerman, Iran, who filled out the General Health Questionnaire (GHQ) in the screening phase. In the second phase, 40 individuals, having a low level of mental health based on the cutoff score of 23, were selected and randomly divided into 2 groups (intervention and control), each group with 20 participants. The intervention group participated in 5 sessions of 75 minutes for SFGC. Then, the post-test was held in both groups and the data analysis was conducted using the Mann-Whitney and the Kruskal-Wallis test with IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 21.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA). The significance level was considered as p < 0.05.
The findings showed that the mean of the post-test mental health scores of the intervention group (14.5 ± 50.35) and of the control group (23.6 ± 35.83) showed a statistically significant difference (p < 0.0001). Moreover, the comparison between the mean scores of the mental health subscales (physical symptoms, stress, social performance, and depression) showed a statistically significant difference in these groups, and SFGC improved physical symptoms, stress, social performance, and depression in the members of the intervention group.
Solution-focused group counseling may improve all levels of mental health. This type of counseling is recommended to be used to solve the psychological problemsand to improve the mental health of students, as well as of the staff of the health system.