Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(6):295-302
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000600006
PURPOSE: To evaluate bone mineral density (BMD) and their risk factors associated with postmenopausal osteoporosis. METHODS: A cross-sectional clinical study was performed on 431 women (aged 40 - 75 years). Inclusion criteria: amenorrhea >12 months and age >45 years or, bilateral oophorectomy >40 years with BMD values (T-score of lumbar spine/femur neck) by DXA of the last 12 months. Risk factors evaluated: age, age and time of menopause, smoking, physical activity (30 min/5 times/week), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), use of corticotherapy and hormone therapy (HT), previous fracture, maternal hip fracture and body mass index (BMI=weight/height²). The χ2 test and the logistic regression method (Odds Ratio - OR) were used to determine osteoporosis risk. RESULTS: According to WHO criteria, 106 (24.6%) women showed osteoporosis (T-score <-2.5 DP), 188 (43.6%) osteopenia (-1.0/-2.4 DP), and 137 (31.8%) were normal (>-1.0 DP). Osteoporosis was detected in 12% of women aged 40 - 49 years, in 21.8% of women aged 50 - 59 years and in 45.7% of women aged >60 years (p<0.001). Osteoporosis occurred in 11.8% of women with a menopause period <5 years, in 29.4% with a menopause period from 6 to 10 years, and in 41% of women with a menopause period >10 years (p<0.001). Of the women with early menopause, 80% showed osteopenia/osteoporosis (p=0.03), and of those with BMI <20 kg/m², 50% were osteoporotic (p<0.001). The risk for osteoporosis detection increased with age (OR=1.1; CI95%=1.0-1.1), time of menopause (OR=1.1; CI95%=1.0-1.1), smoking (OR=1.9; CI95%=1.2-3.2), RA (OR=3.6; CI95%=1.3-9.6) and maternal fracture history (OR=2.1; CI95%=1.1-3.0) (p<0.05). In contrast, HT use (OR=0.3; 95%CI=0.2-0.6) and high BMI (OR=0.9; 95%CI=0.8-0.9) reduced the risk (p<0.05). CONCLUSION: In postmenopausal women, age, time of menopause, smoking and maternal history of fracture were clinical indicators of risk for osteoporosis, whereas HT use and high BMI proved to be protective factors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(2):88-93
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000200007
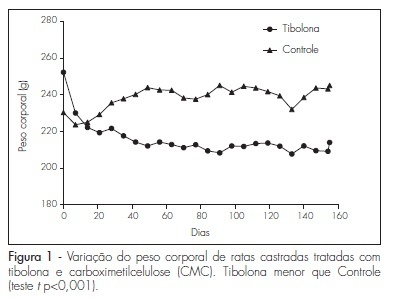
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of the prolonged use of a high dose of tibolone on the body weight variation and lipid profile of oophorectomized female rats. METHODS: 15 Wistar rats weighing 250 g were randomly divided into two groups. The Experimental Group (n=9) received 1 mg/day of oral tibolone. The Control Group (n=6) received daily 0.5 mL of 0.5% carboxymethylcellulose by gavage. Bilateral oophorectomy was performed 30 days before the beginning of the experiment. On day 0 of the experiment, the animals began to receive the respective treatment for 20 weeks. Body weight was controlled every seven days and food consumption was measured every three to four days along the experiment, in order to establish the daily mean consumption per animal. The results were compared by the Student's t-test, with the significance level set at p<0.05. RESULTS: the daily food consumption of the Tibolone Group was significantly lower (12.7±1.2 g, p<0.001) compared to the Control Group (14.5±1.4 g). This difference was also significant when the body weight was compared between the Tibolone and Control Groups (p<0.001), with the Tibolone Group having lower weight along the experiment. At the end of the experiment, the mean body weight was 215.6±9.3 g in the Tibolone Group and 243.6±6.4 g in the Control Group. Regarding the lipid profile, the Tibolone Group had significantly (p<0.001) lower total cholesterol compared to the Control Group (30.3 versus 78.6 mg/dL). The level of HDL-c was also significantly different (p<0.001), with the Tibolone Group showing lower levels than the Control Group (9.0 versus 52.0 mg/dL). No significant difference between the groups was registered in the other biochemical parameters examined (LDL-c, VLDL-c and triglycerides). CONCLUSIONS: tibolone causes a significant reduction of HDL-c and total cholesterol and has a deleterious effect on the body weight of oophorectomized rats, which may be related to the lower food ingestion by these animals.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(5):254-261
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000500009
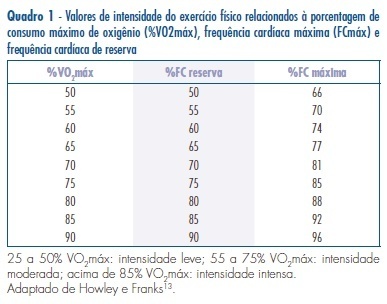
It is believed that estrogen deficiency, lipid profile alterations, body weight gain, and sedentary lifestyle are strongly associated with the increased incidence of arterial hypertension in postmenopausal women. In an attempting to reduce the incidence of arterial hypertension in this population, a variety of approaches has been used, but the results are conflicting and the changing in lifestyle has been proposed and an important preventive action to control the arterial hypertension and associated risk factors in this women age - mainly practice of physical exercise. Continuous exercise has been used as an important approach in management cardiovascular disease and endocrine-metabolic disorders. Continuous exercise prescription is characterized by, at least, 30 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity (60 to 70% of maximum heart rate), three days of the week. Intermittent exercise is characterized by low intensity exercise periods, alternating with high-intensity exercise periods, ranging of 50 to 85% of the maximum heart rate, during ten minutes. Intermittent exercise has been employed as training program in weight loss therapy and personal training because previous studies have shown similar metabolic adaptations and aerobic capacity after continuous or intermittent exercise. This review focused on the relevance of continuous and intermittent exercise on the blood pressure control, discussion of the data found in experimental model of menopause and in women and the relationship between incidence of arterial hypertension and its genesis in postmenopausal women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(4):196-202
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000400007
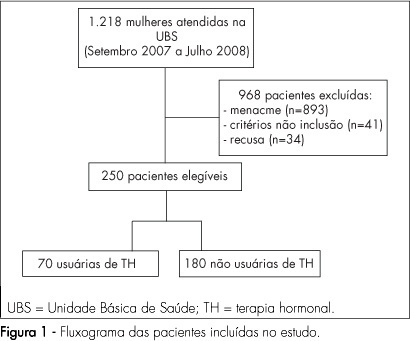
PURPOSE: to evaluate the quality of life of post-menopause women, users and non-users of hormonal therapy (HT), in a Healthcare Unit in Franca, São Paulo, Brazil. METHODS: a clinical transversal study, carried out with 250 post-menopausal women, with ages from 45 to 70 years old, attended to in Healthcare Units, from September 2007 to August 2008. Participants were divided into two groups: HT users (n=70) and non-users (n=180). Women making continuous HT use for at least six months were considered as users. Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics have been evaluated. Blatt-Kupperman's menopausal index has been applied to assess climacteric symptoms, and the Women's Health Questionnaire (WHQ), to assess their quality of life. Fisher's exact test or χ2 and Mann-Whitney and Kruskal-Wallis's tests have been used for the statistical analysis. RESULTS: no significant difference has been found in the comparison of groups, concerning age, menarche, menopause, parity and body mass index. It has been seen that 67.2% of the women were married, 83.2% had attended primary school and 53.2% were housewives, with no difference between the groups. HT users reported lower frequency of climacteric symptoms (BKMI) with moderate and marked intensity, as compared to non-users (p<0.001). Even though HT users presented lower average score in cognitive deficit (p<0.001), vasomotor symptoms (p=0.04), sleeping problems (p<0.001), attractiveness (p=0.02) from the WHQ, there has been no difference in the total score, as compared to non-users. CONCLUSIONS: post-menopausal women, HT users and non-users, admitted at Healthcare Units, have not presented differences in global quality of life.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(3):124-130
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000300004
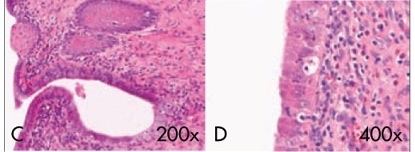
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of long-term use of a high dose of tibolone on the morphology of the endometrium of castrated female rats. METHODS: fifteen female Wistar rats, aged eight weeks and weighting about 250 g were used. All the female rats were submitted to bilateral oophorectomy and 30 days afterwards, vaginal cytology was collected, to verify the menopause status. The female rats were randomly divided in two groups. The Treatment Group (n=9) received 1 mg of tibolone/day orally; the Control Group (n=6) received a solution of carboxymethylcellulose vehicle. After 20 weeks of treatment, all the animals were sedated and sacrificed by cervical dislocation. The uterus was removed and fixated in 10% buffer formaldehyde. Both uterine horns were divided in three regions (proximal, medial and distal) and processed to be included in paraffin. Histological sections, stained with hematoxylin-eosin were submitted to morphological and morphometrical analysis. The following parameters have been analyzed: thickness of the endometrial superficial epithelium, thickness of the endometrium stroma, endometrial area, absolute number of endometrial glands and number of glands/endometrial area. The data obtained were compared by the t-Student test. RESULTS: in the Tibolone Group, the uteri were well developed and there was a significant increase (p<0.01) of all the histomorphometric parameters. In some cases, the cylindrical epithelium became stratified, pavimentous and covered the internal portions of the glands, as well as of the endometrium cavity. Rats from the Control Group presented uterine atrophy. There were few tubular-like glands and scarce intercellular substance. Glands were covered by cubic epithelium which extended itself to the endometrial cavity. CONCLUSIONS: high doses of tibolone, given for long periods of time to castrated female rats, have an estrogenic effect which can be dose-dependent, causing proliferation in the endometrium and causing changes in the cell differentiation (squamous metaplasia), but do not lead to hyperplasia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(3):131-137
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000300005
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effects of tamoxifen on the expression of TGF-β and p27 proteins in polyps and adjacent endometrium of women after menopause. METHODS: prospective study with 30 post-menopausal women with diagnosis of breast cancer, taking tamoxifen (20 mg/day), presenting diagnosis of suspect endometrial polyps through transvaginal ultrasonography, and submitted to diagnostic and surgical hysterectomy to withdraw the polyps and adjacent endometrium. A immunohistochemical study has been done to verify the expression of the TGF-β and p27 proteins in the polyps and adjacent endometrium. These proteins' quantification has been done by morphometry. RESULTS: the patients' average age was 61.7 years old; their average age at the menopause onset was 49.5; and the average of using tamoxifen was 25.3 months. The average concentration of positive cells for TGF-β protein in the glandular and stroma polyp epithelium was 62.6±4.5 cells/mm². For the p27, in the glandular polyp epithelium, it was 24.2±18.6 cells/mm² and for the stroma, 19.2±15.2 cells/mm². There was no significant difference between the expression of TGF-β and p27 in the glandular epithelial form the polyps and the adjacent endometrium. The expression of proteins in the polyp and adjacent endometrium with its respective glandular and stroma epithelium showed a significant difference for the p27 protein (r=0.9, p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: we have concluded that the TGF-β expression is not related to the effect of tamoxifen on the growing of endometrial polyps, but the absence of polyps' malignization by tamoxifen may be explained by the high expression of p27 protein in its glandular epithelium.
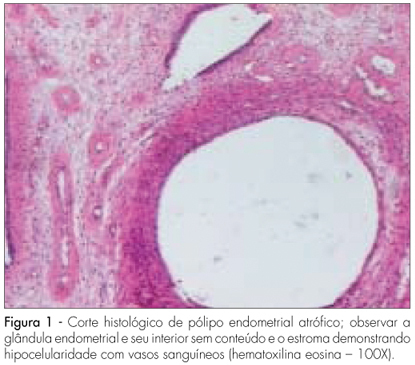
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(1):28-34
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000100006
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of depression and anxiety in climacteric women and the probable factors responsible for its occurrence. METHODS: a transversal study that has selected 93 women attended at a climacteric outpatient clinic, from May 2006 to August 2007. Inclusion criteria were: women from 40 to 65 years old who agreed with participating in the project. Exclusion criteria: patients in hormonal therapy, hormone-therapy by implant, DIUs and depo injections in the preceding six months, endocrinopathies leading to menstrual irregularities, hepatopathies, thrombopathies, use of drugs which interfere in the menstrual cycle, anxiolytics and antidepressants (as their use indicates previous diagnosis of mood disorders), hysterectomy, oophorectomy, cancer or psychiatric disease, and patients who had been submitted to radio or chemotherapy. During the interview, four questionnaires were applied: Anamnesis, containing socio-demographic, clinical and living habits data; Blatt-Kupperman's Menopausal Index for climacteric syndrome diagnosis; Anxiety sub-scale of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression scale (HADS-A) for anxiety diagnosis; and Beck's Depression Inventory for the diagnosis of depression. Descriptive and correlation analysis among the variables, χ2 and Hosmer-Lemeshow tests were performed using the Statistica Software program, version 6. RESULTS: the average depression prevalence among the patients was 36.8%, while that of anxiety was 53.7%. There was no significant difference between the prevalence of depression and anxiety in the three phases of climacterium. There was a significant relationship between the presence of moderate climacteric symptoms and the presence of mood alterations (p<0.001). Depression was more frequent in women with anxiety (OR=4.2) and insomnia (OR=4.9), having a job being a protection factor (OR=0.2). Risk factors related to anxiety were the presence of depression (OR=6.1) and antecedents of pre-menstrual tension (OR=7.0). CONCLUSIONS: the prevalence of depression and anxiety is high in climacterium, being possible to detect risk factors related to their occurrence.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):524-530
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001000008
Detection of endometrial cancer in asymptomatic women has not proved to be a cost-effective procedure. Studies on this matter have shown that ultrasonography as a detecting method presents a high ratio of false-positive results and a negligible effect on the mortality rate. This way, the assistance strategy should be based on earlier diagnosis and appropriate treatment in women who present postmenopause bleeding. Being a non-invasive method, largely available and with high sensitivity, the transvaginal ultrasonography should be the initial investigative method. Though there is no consensus about the echographical endometrial thickness, above which the investigation is to proceed, diagnostic hysteroscopy should be the next step. The risk of neoplasia in endometriums with thickness under or equal to 3 mm is low enough to limit hysteroscopy to exceptional cases. Biopsy must be a necessary part of the hysteroscopy, because the diagnosis, made on visual basis, alone may lead to false results. Outpatient hysteroscopy can be done in more than 95% of the cases, even in menopausal women, rarely with severe complications. The adoption of "non-contact" examination techniques and the progressive reduction of the hysteroscope diameter have decreased the discomfort associated to small outpatient procedures.