-
Original Article01-11-2023
Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorders – The Impact of the Creation of a Multidisciplinary Team on Maternal Outcomes in Portugal
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):747-753
Abstract
Original ArticlePlacenta Accreta Spectrum Disorders – The Impact of the Creation of a Multidisciplinary Team on Maternal Outcomes in Portugal
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):747-753
Views222See moreAbstract
Objective
To describe a cohort of placenta accreta spectrum (PAS) cases from a tertiary care institution and compare the maternal outcomes before and after the creation of a multidisciplinary team (MDT).
Methods
Retrospective study using hospital databases. Identification of PAS cases with pathological confirmation between 2010 and 2021. Division in two groups: standard care (SC) group – 2010–2014; and MDT group – 2015–2021. Descriptive analysis of their characteristics and maternal outcomes.
Results
During the study period, there were 53 cases of PAS (24 - SC group; 29 - MDT group). Standard care group: 1 placenta increta and 3 percreta; 12.5% (3/24) had antenatal suspicion; 4 cases had a peripartum hysterectomy – one planned due to antenatal suspicion of PAS; 3 due to postpartum hemorrhage. Mean estimated blood loss (EBL) was 2,469 mL; transfusion of packed red blood cells (PRBC) in 25% (6/24) - median 7.5 units. Multidisciplinary team group: 4 cases of placenta increta and 3 percreta. The rate of antenatal suspicion was 24.1% (7/29); 9 hysterectomies were performed, 7 planned due to antenatal suspicion of PAS, 1 after intrapartum diagnosis of PAS and 1 after uterine rupture following a second trimester termination of pregnancy. The mean EBL was 1,250 mL, with transfusion of PRBC in 37.9% (11/29) - median 2 units.
Conclusion
After the creation of the MDT, there was a reduction in the mean EBL and in the median number of PRBC units transfused, despite the higher number of invasive PAS disorders.
-
Review Article02-09-2022
Main Complications during Pregnancy and Recommendations for Adequate Antenatal Care in Sickle Cell Disease: A Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):593-601
Abstract
Review ArticleMain Complications during Pregnancy and Recommendations for Adequate Antenatal Care in Sickle Cell Disease: A Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(6):593-601
Views301See moreAbstract
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is the most common monogenic disease worldwide, with a variable prevalence in each continent. A single nucleotide substitution leads to an amino-acid change in the β-globin chain, altering the normal structure of hemoglobin, which is then called hemoglobin S inherited in homozygosity (HbSS) or double heterozygosity (HbSC, HbSβ), and leads to chronic hemolysis, vaso-occlusion, inflammation, and endothelium activation. Pregnant women with SCD are at a higher risk of developing maternal and perinatal complications. We performed a narrative review of the literature considering SCD and pregnancy, the main clinical and obstetrical complications, the specific antenatal care, and the follow-up for maternal and fetal surveillance. Pregnant women with SCD are at a higher risk of developing clinical and obstetric complications such as pain episodes, pulmonary complications, infections, thromboembolic events, preeclampsia, and maternal death. Their newborns are also at an increased risk of developing neonatal complications: fetal growth restriction, preterm birth, stillbirth. Severe complications can occur in patients of any genotype. We concluded that SCD is a high-risk condition that increases maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. A multidisciplinary approach during pregnancy and the postpartum period is key to adequately diagnose and treat complications.
-
Systematic Review05-24-2021
Vertical Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):207-215
Abstract
Systematic ReviewVertical Transmission of SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):207-215
Views218See moreAbstract
Objective
The evaluation of the available evidence on vertical transmission by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV)-2.
Data Sources
An electronic search was performed on June 13, 2020 on the Embase, PubMed and Scopus databases using the following search terms: (Coronavirus OR COVID-19 OR COVID19 OR SARS-CoV-2 OR SARS-CoV2 OR SARSCoV2) AND (vertical OR pregnancy OR fetal).
Selection of Studies
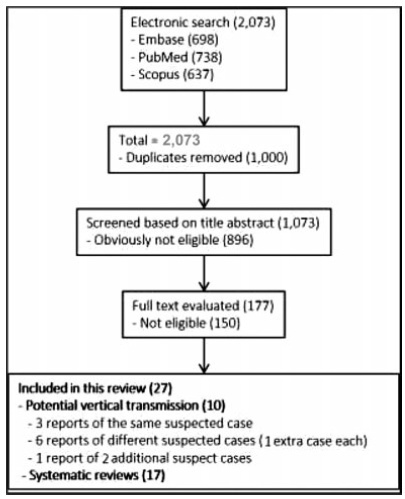
The electronic search resulted in a total of 2,073 records. Titles and abstracts were reviewed by two authors (WPM, IDESB), who checked for duplicates using the pre-established criteria for screening (studies published in English without limitation regarding the date or the status of the publication).
Data Collection
Data extraction was performed in a standardized way, and the final eligibility was assessed by reading the full text of the articles. We retrieved data regarding the delivery of the potential cases of vertical transmission, as well as themain findings and conclusions of systematic reviews.
Data Synthesis
The 2,073 records were reviewed; 1,000 duplicates and 896 clearly not eligible records were excluded. We evaluated the full text of 177 records, and identified only 9 suspected cases of possible vertical transmission. The only case with sufficient evidence of vertical transmission was reported in France.
Conclusion
The risk of vertical transmission by SARS-CoV-2 is probably very low. Despite several thousands of affected pregnant women, we have identified only one case that has fulfilled sufficient criteria to be confirmed as a case of vertical transmission. Well-designed observational studies evaluating large samples are still necessary to determine the risk of vertical transmission depending on the gestational age at infection.
-
Original Article12-21-2020
Is Vaginal Breech Delivery Still a Safe Option?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):712-716
Abstract
Original ArticleIs Vaginal Breech Delivery Still a Safe Option?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):712-716
Views247See moreAbstract
Objective:
To determine whether there was any difference in neonatal and maternal outcomes between breech vaginal delivery and cephalic vaginal delivery.
Methods:
A retrospective, case-control study was conducted between January 2015 and December 2017 in a Portuguese hospital. A total of 26 cases of breech vaginal delivery were considered eligible and 52 pregnant women formed the control group.
Results:
Induced labor was more frequent in the breech vaginal delivery group (46% versus 21%, p = 0.022). Episiotomy was more common in the breech vaginal delivery group (80% versus 52%, p = 0.014), and one woman had a 3rd degree perineal laceration. Newborns in the study group had a lower birthweight (2,805 g versus 3,177 g, p < 0.001). There was no significant difference in the neonatal outcomes.
Conclusion:
The present study showed that breech vaginal delivery at term compared with cephalic presentation was not associated with significant differences in neonatal and maternal morbidity. It also suggests that breech vaginal delivery remains a safe option under strict selection criteria and in the presence of an experienced obstetrician.
-
Original Article12-21-2020
Active Versus Expectant Management for Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes at 34-36 Weeks of Gestation and the Associated Adverse Perinatal Outcomes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):717-725
Abstract
Original ArticleActive Versus Expectant Management for Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes at 34-36 Weeks of Gestation and the Associated Adverse Perinatal Outcomes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):717-725
Views267Abstract
Objective:
To compare the type of management (active versus expectant) for preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM) between 34 and 36 + 6 weeks of gestation and the associated adverse perinatal outcomes in 2 tertiary hospitals in the southeast of Brazil.
Methods:
In the present retrospective cohort study, data were obtained by reviewing the medical records of patients admitted to two tertiary centers with different protocols for PPROM management. The participants were divided into two groups based on PPROM management: group I (active) and group II (expectant). For statistical analysis, the Student t-test, the chi-squared test, and binary logistic regression were used.
Results:
Of the 118 participants included, 78 underwent active (group I) and 40 expectant management (group II). Compared with group II, group I had significantly lower mean amniotic fluid index (5.5 versus 11.3 cm, p = 0.002), polymerase chain reaction at admission (1.5 versus 5.2 mg/dl, p = 0.002), time of prophylactic antibiotics (5.4 versus 18.4 hours, p < 0.001), latency time (20.9 versus 33.6 hours, p = 0.001), and gestational age at delivery (36.5 versus 37.2 weeks, p = 0.025). There were no significant associations between the groups and the presence of adverse perinatal outcomes. Gestational age at diagnosis was the only significant predictor of adverse composite outcome (x2 [1] = 3.1, p = 0.0001, R2 Nagelkerke = 0.138).
Conclusion:
There was no association between active versus expectant management in pregnant women with PPROM between 34 and 36 + 6 weeks of gestation and adverse perinatal outcomes.
Key-words Antibiotic prophylaxisMaternal morbidityneonatal morbiditypreterm premature rupture of membranesSee more -
Original Article06-22-2020
Maternal and Perinatal Outcomes of Pregnancies Complicated by Chronic Hypertension Followed at a Referral Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):248-254
Abstract
Original ArticleMaternal and Perinatal Outcomes of Pregnancies Complicated by Chronic Hypertension Followed at a Referral Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(5):248-254
Views240See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess maternal and perinatal outcomes of pregnancies in women with chronic hypertension (CH). Methods Retrospective cohort of women with CH followed at a referral center for a 5 year period (2012-2017). Data were obtained from medical charts review and described as means and frequencies, and a Poisson regression was performed to identify factors independently associated to the occurrence of superimposed preeclampsia (sPE).
Results
A total of 385 women were included in the present study; the majority were > than 30 years old, multiparous, mostly white and obese before pregnancy. One third had pre-eclampsia (PE) in a previous pregnancy and 17% of them had organ damage associated with hypertension, mainly kidney dysfunction. A total of 85% of the patients used aspirin and calcium carbonate for pre-eclampsia prophylaxis and our frequency of sPE was 40%, with an early onset (32.98 ± 6.14 weeks). Of those, 40% had severe features of PE, including 5 cases of HELLP syndrome; however, no cases of eclampsia or maternal death were reported. C-section incidence was high, gestational age at birth was 36 weeks, and nearly a third (115 cases) of newborns had complications at birth One third of the women remained using antihypertensive drugs after pregnancy.
Conclusion
Chronic hypertension is related with the high occurrence of PE, C-sections, prematurity and neonatal complications. Close surveillance and multidisciplinary care are important for early diagnosis of complications.
-
Original Article04-17-2020
Gestational Outcomes in Patients with Severe Maternal Morbidity Caused by Hypertensive Syndromes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):74-80
Abstract
Original ArticleGestational Outcomes in Patients with Severe Maternal Morbidity Caused by Hypertensive Syndromes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):74-80
Views190See moreAbstract
Purpose
To evaluate the impact of the presence of criteria for severe maternal morbidity and maternal near miss associated with hypertensive disorders on maternal and perinatal outcomes in a maternity school.
Methods
The present is a sub-analysis of a larger study involving 27 centers in Brazil that estimated the prevalence of serious maternal morbidity and near miss. It is an analytical and cross-sectional study with a quantitative approach, involving 928 women who were cared for at Maternidade Escola Assis Chateaubriand (MEAC, in Portuguese), Universidade Federal do Ceará (UFC, in Portuguese), from July 2009 to June 2010. The women were diagnosed with near miss according to the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria. The sample was divided into 2 groups: patients with (n = 827) and without hypertension (n = 101). The results were considered statistically significant when p < 0.05. The Pearson chi-squared and Fisher Exact tests were used for the categorical variables, and the Mann–Whitney U test was used for the continuous variables.
Results
In total, 51 participants with maternal near miss criteria were identified, and 36 of them had hypertensive disorders. Of these, 5 died and were obviously excluded from the near miss final group. In contrast, we observed 867 cases with non-near miss maternal morbidity criteria. During this period, there were 4,617 live births (LBs) in the institution that was studied.
Conclusion
In the severe morbidity/maternal near miss population, the presence of hypertensive complications was prevalent, constituting a risk factor for both the mother and the fetus.
-
Case Report03-27-2020
Delayed-Interval Delivery in Dichorionic Twin Pregnancies: A Case Report of 154 Latency Days
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):61-64
Abstract
Case ReportDelayed-Interval Delivery in Dichorionic Twin Pregnancies: A Case Report of 154 Latency Days
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):61-64
Views160See moreAbstract
Premature delivery often complicates multifetal pregnancies, placing neonates at risk of seriousmorbidity andmortality. In select cases, pretermbirth of one sibling may not require delivery of the remaining fetus(es), which may remain in utero for a delayedinterval delivery, consequently improving neonatalmorbidity andmortality. Currently, there is no consensus on the best protocol for the optimalmanagement of these cases. We report one case of delayed-interval delivery of a dichorionic pregnancy assisted in our center. In this case, prophylactic cerclage, tocolytic therapy and administration of broad-spectrum prophylactic antibiotics enabled delivery at 37 weeks, corresponding to 154 days of latency, which is, to our knowledge, the longest interval described in the literature. The attempt to defer the delivery of the second fetus in peri-viability is an option that should be offered to parents after counseling, providing that the clinical criteria of eligibility are fulfilled. The correct selection of candidates, combined with the correct performance of procedures, as well as fetal and maternal monitoring and early identification of complications increase the probability of success of this type of delivery.


