Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
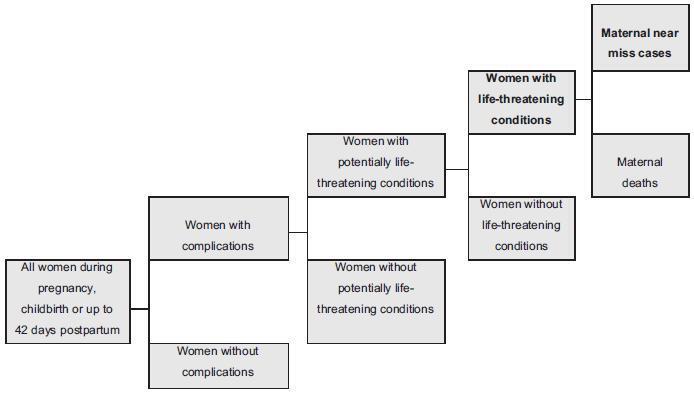
Twin pregnancy accounts for 2 to 4% of total births, with a prevalence ranging from 0.9 to 2.4% in Brazil. It is associated with worse maternal and perinatal outcomes. Many conditions, such as severe maternal morbidity (SMM) (potentially life-threatening conditions and maternal near-miss) and neonatal near-miss (NNM) still have not been properly investigated in the literature. The difficulty in determining the conditions associated with twin pregnancy probably lies in its relatively low occurrence and the need for larger population studies. The use of the whole population and of databases from large multicenter studies, therefore, may provide unprecedented results. Since it is a rare condition, it ismore easily evaluated using vital statistics from birth e-registries. Therefore, we have performed a literature review to identify the characteristics of twin pregnancy in Brazil and worldwide. Twin pregnancy has consistently been associated with SMM, maternal near-miss (MNM) and perinatal morbidity, with still worse results for the second twin, possibly due to some characteristics of the delivery, including safety and availability of appropriate obstetric care to women at a high risk of perinatal complications.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(4):232-237
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000400005
PURPOSE: to identify maternal and perinatal factors related to neonates with birthweight >4,000 g. METHODS: cross-section cohort study with 411 consecutive cases of fetal macrosomia (FM) which occurred from March 1998 to March 2005. Data were compared to 7,349 cases of fetal birthweight >2,500 and <3,999 g which occurred in the same period. Maternal variables (maternal age, parity, diabetes, previous cesarean section, meconium-stained amniotic fluid, cephalopelvic disproportion, main cesarean section indications) and perinatal variables (birth injury, <7 1-min and 5-min Apgar score, fetal and early neonatal mortality range, need of neonatal intensive care unit) were analyzed. For statistical analysis the chi2 test with Yates correction and Student's t test were used with the level of significance set at 5%. RESULTS: FM was significantly associated with older mothers, more parous and <7 1-min Apgar score (p<0.05; OR=1.8; 95% CI: 1,4-2.5) and <7 5-min Apgar score (p<0,05; OR=2.3; 95% CI: 1.3-4,1), diabetes mellitus (p<0.05; OR=4.2; 95% CI: 2.7-6.4), meconium-stained amniotic fluid (p<0.02; OR=1.3; 95% CI: 1.0-1.7), need of neonatal intensive care unit (p<0,05; OR=2.0; 95% CI: 1.5-2.7), early neonatal mortality (p<0,05; OR = 2.7; 95% CI: 1.0-6.7), cesarean section (p < 0.05; OR = 2.03; 95% CI: 1,6-2,5) and cephalopelvic disproportion (p < 0.05;OR = 2.8; 95% CI: 1.6-4,8). There was no statistical difference between birth injury and fetal mortality range. In the FM group the main cesarean section indications were repeat cesarean sections (11.9%) and cephalopelvic disproportion (8.6%); in the normal birthweight group, repeat cesareans (8.3%) and fetal distress during labor (3.9%). CONCLUSIONS: in spite of the characteristic limitations of a retrospective evaluation, the analysis demonstrated which complications were associated with large fetal size, being useful in obstetric handling of patients with a diagnosis of extreme fetal growth. FM remains an obstetric problem of difficult solution, associated with important maternal and perinatal health problems, due to the significant observed rates of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality in developed and developing countries.