Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):264-271
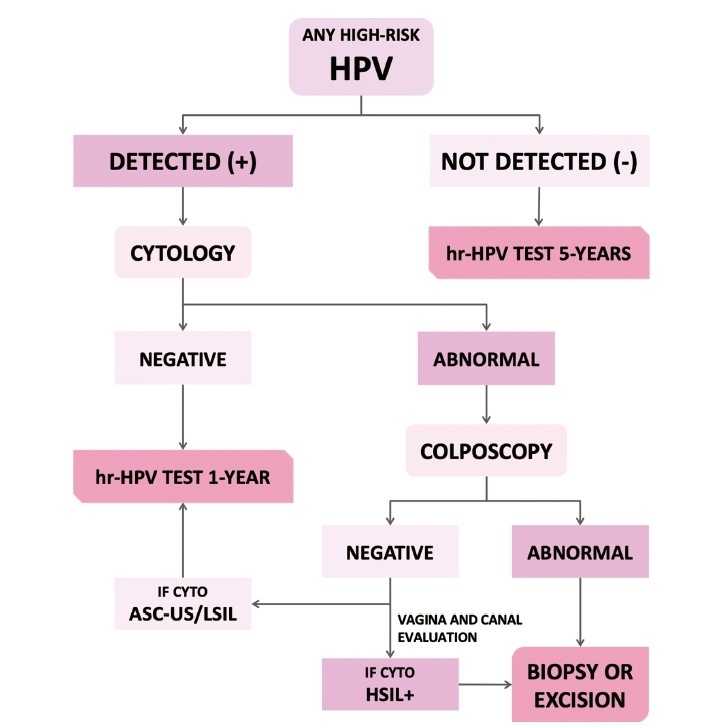
The present update is a reassessment of the 2018 ‘Guidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil’ (Zeferino et al.)9, according to the changes observed in new international guidelines and knowledge updates. The most relevant and recent guidelines were assessed. Questions regarding the clinical practice were formulated, and the answers considered the perspective of the public and private sectors of the Brazilian health system. The review addressed risk-based strategies regarding age to start and stop screening, the use of cytology and colposcopy to support management decisions, treatment, follow-up strategies, and screening in specific groups, including vaccinated women. The update aims to improve the prevention of cervical cancer and to reduce overtreatment and the misuse of HPV testing.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):338-346
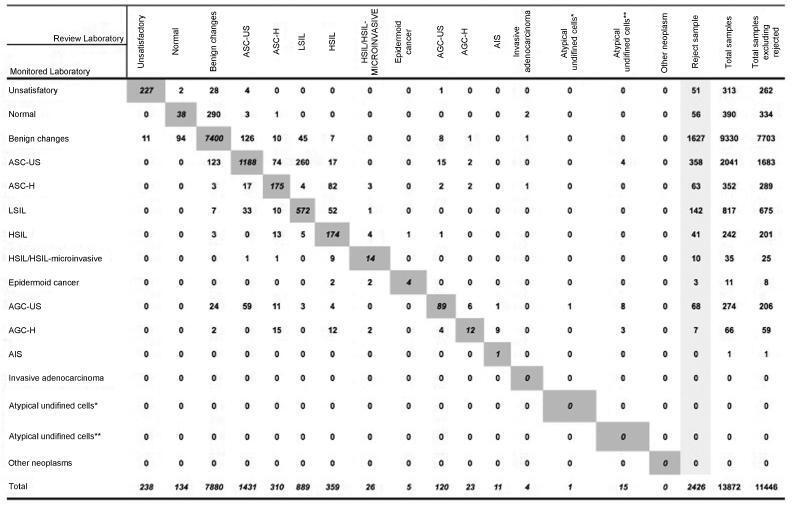
To discuss the implementation and contributions of the External Quality Monitoring in the city of Rio de Janeiro and to analyze the performance of the main providers of cervical cytopathology in this city from September 2013 to March 2017, here referred to as “Alpha laboratory” and “Beta laboratory.”
Observational, cross-sectional, retrospective study using information from the Cervical Cancer Control Information System (SISCOLO, in the Portuguese acronym), municipal coordinationmodule, External QualityMonitoring report. The proportions of false positives, false negatives, unsatisfactory samples and rejected samples were estimated. The agreement among the observers was analyzed through the Kappa index and the reduction of disagreements in the period for each laboratory studied, comparing the results of each cycle.
A total of 19,158 examinations were selected, of which 19,130 (99.85%) were monitored, 16.649 (87, 03%) were reviewed by the External Quality Monitoring Unit, 2,481 (12,97%) were rejected and 441 (2,65%) were considered unsatisfactory. The “Beta laboratory” presented excellent concordance in all cycles; the “Alpha laboratory” had good concordance in the first two cycles (K = 0.76 and 0.79), becoming excellent in the following four cycles. The average Kappa index was 0.85, with median of 0.86. The percentage of diagnostic disagreement was 6.63% of the reviewed exams, of which 5.38% required a change of conduct
External Quality Monitoring is an exercise in diagnostic improvement, and its implementation was fundamental to ensure the reliability of the cytopathological exams in the city of Rio de Janeiro.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):203-208
To evaluate the prevalence of adherence to screening methods for breast and cervical cancer in patients attended at a university hospital and to investigate whether knowing someone with breast cancer, moreover belonging to the patient’s family, affects the adherence to the screening recommendations.
This was a cross-sectional and quantitative study. A structured interview was applied to a sample of 820 women, between 20 and 69 years old, who attended a university hospital in the city of Juiz de for a, MG, Brazil. For the analysis, the chi-square test was used to assess possible associations between the variables, and the significance level was set at p-value ≤ 0.05 for a confidence interval (CI) of 95%.
More than 95.0% of the sample performed mammography and cervical cytology exam; 62.9% reported knowing someone who has or had breast cancer, and this group was more likely to perform breast self-examination (64.9%; odds ratio [OR] 1.5; 95% CI 1.12-2.00), clinical breast examination (91.5%; OR 2.11; 95% CI 1.37-3.36), breast ultrasound (32.9%; OR 1.81, 95% CI 1.30-2.51), and to have had an appointment with a breast specialist (28.5%; OR 1.98, 95% CI 1.38-2.82).Women with family history of breast cancer showed higher propensity to perform breast self-examination (71.0%; OR 1.53 95% CI 1.04-2.26).
There was high adherence to the recommended screening practices; knowing someone with breast cancer might make women more sensitive to this issue as they were more likely to undergo methods which are not recommended for the screening of the general population, such as breast ultrasound and specialist consultation; family history is possibly an additional cause of concern.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(3):147-153
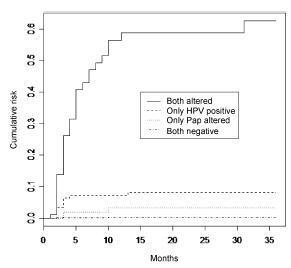
To compare the predictive capability of HPV and Pap smear tests for screening pre-cancerous lesions of the cervix over a three-year follow-up, in a population of users of the Brazilian National Health System (SUS).
This is a retrospective cohort study of 2,032 women with satisfactory results for Pap smear and HPV tests using second-generation hybrid capture,made in a previous study. We followed them for 36 months with data obtained from medical records, the Cervix Cancer Information System (SISCOLO), and the Mortality Information System (SIM). The outcome was a histological diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or more advanced lesions (CIN2ş). We constructed progression curves of the baseline test results for the period, using the Kaplan-Meier method, and estimated sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value, and positive and negative likelihood ratios for each test.
A total of 1,440 women had at least one test during follow-up. Progression curves of the baseline test results indicated differences in capability to detect CIN2ş (p < 0.001) with significantly greater capability when both tests were abnormal, followed by only a positive HPV test. The HPV test was more sensitive than the Pap smear (88.7% and 73.6%, respectively; p < 0.05) and had a better negative likelihood ratio (0.13 and 0.30, respectively). Specificity and positive likelihood ratio of the tests were similar.
These findings corroborate the importance of HPV test as a primary cervical cancer screening.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):192-197
DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050002
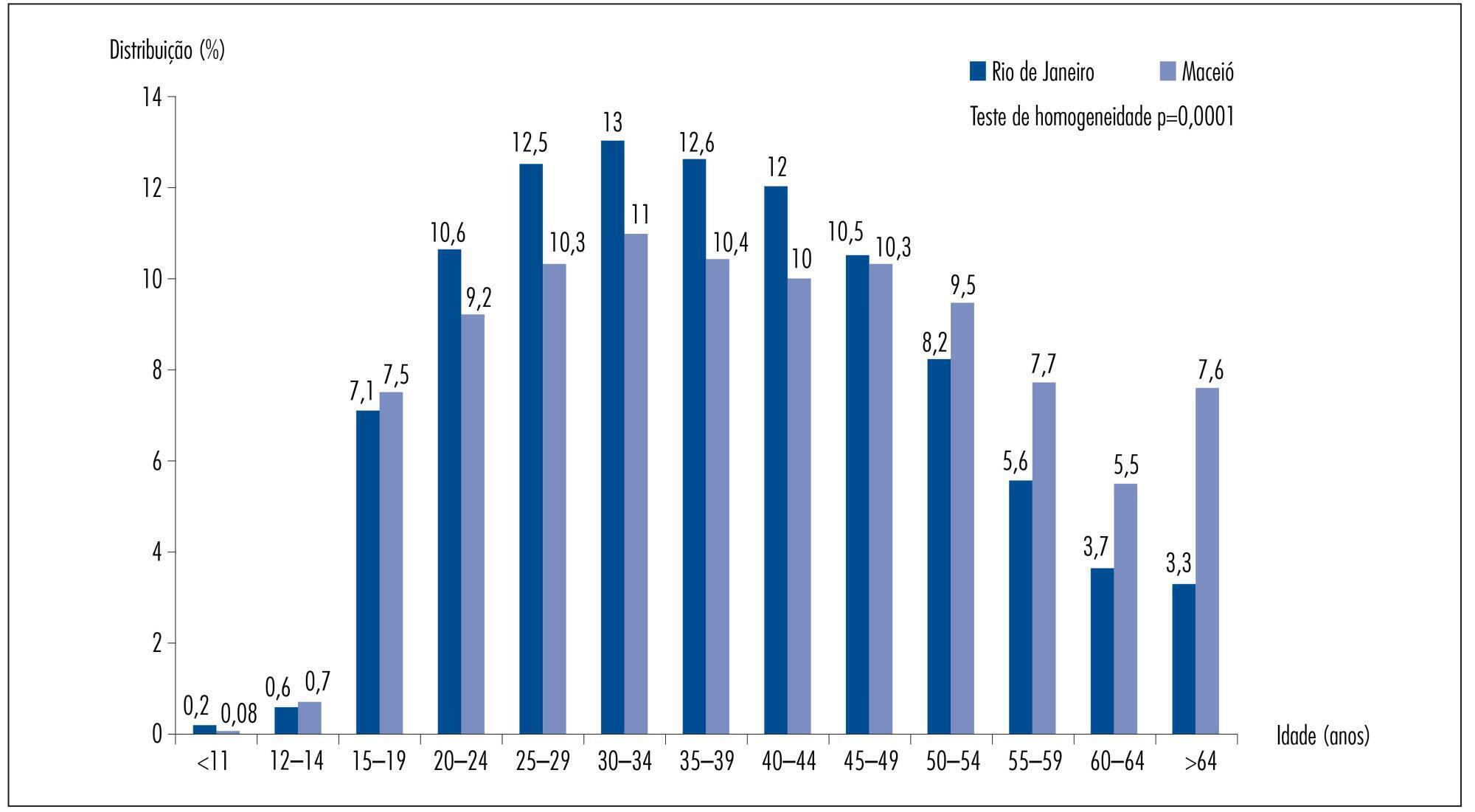
To analyze the prevalence of cervical cytopathological results for the screening of cervical cancer with regard to women's age and time since the last examination in Maceió and Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, among those assisted by the Brazilian Unified Health System.
Cervical cytopathological results available in the Information System of Cervical Cancer Screening for the year 2011 were analyzed, corresponding to 206,550 for Rio de Janeiro and 45,243 for Maceió.
In Rio de Janeiro, examination at one and two year intervals predominated, while in Maceió examination at one and three year intervals had a higher predominance. Women who underwent cervical smear screening in Maceió were older than those in Rio de Janeiro. The prevalence of invasive squamous cell carcinoma was similar for the two cities, but all the other results presented a higher prevalence in Rio de Janeiro: ASCUS (PR=5.32; 95%CI 4.66-6.07); ASCH (PR=4.27; 95%CI 3.15-5.78); atypical glandular cells (PR=10.02; 95%CI 5.66-17.76); low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (PR=6.10; 95%CI 5.27-7.07); high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (PR=8.90; 95%CI 6.50-12.18) and adenocarcinoma (PR=3.00; 95%CI 1.21-7.44). The rate of unsatisfactory cervical samples was two times higher in Maceió and that of rejected samples for analysis was five times higher in Maceió when compared to Rio de Janeiro.
The prevalence rates of altered cervical cytopathological results was significantly higher in Rio de Janeiro than in Maceió. There is no objective information that may justify this difference. One hypothesis is that there may be a difference in the diagnostic performance of the cervical cancer screening, which could be related to the quality of the Pap smear. Thus, these findings suggest that it would be necessary to perform this evaluation at national level, with emphasis on the performance of cervical cancer screening in order to improve the effectiveness of cervical cancer control.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(5):198-204
DOI 10.1590/S0100-7203201400050003
To assess the adherence to a cervical cancer screening program and to identify reported reasons for inadequate screening in women receiving care as part of the Family Health Strategy.
A selective prevalence study on cervical cancer screening in women receiving care as part of the Family Health Strategy in the cities of Duque de Caxias and Nova Iguaçu in the state of Rio de Janeiro, southeastern Brazil, nine years after they participated in a previous study of the Brazilian National Cancer Institute. Only those women who were not diagnosed with CIN II or more severe lesions by histopathology, did not undergo hysterectomy during the study period and still resided in the communities were eligible to participate in the study. Information on exam sites, test results and schedules, sociodemographic characteristics and reported reasons of non-adherence was obtained. Data were collected through interviews and medical record review. The prevalence of adherence to screening was estimated, and the chi-square test was used to compare proportions between the variables studied and their relationship with the reported reasons of non-adherence to screening.
A total of 764 women were interviewed, 70.7% of whom received adequate cervical cancer screening. The reported reasons for inadequate screening included: no risk perception (44.6%), social barriers (26.3%), perceived barriers to action (22.3%) and institutional barriers (21.4%). These reasons were proportionately higher among residents of Nova Iguaçu than among residents of Duque de Caxias (p<0.01), except for institutional barriers (p=0.19).
Although difficulties and barriers were reported, there was good adherence to cervical cancer screening among the women studied. Health providers should receive proper training for complying with the Brazilian Ministry of Health guidelines of regular testing and to facilitate access to screening.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(11):518-523
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001100007
PURPOSE: To determine the prevalence and risk factors associated with failure of voluntary screening for cervical cancer during the gestational period in Rio Grande, Rio Grande do Sul State, Southern Brazil. METHODS: Previously trained interviewers applied a standardized questionnaire in the maternity to all mothers from this municipality who had delivered from January 1st to December 31st 2010 to obtain information about the demographic characteristics of the pregnant women, family socioeconomic status, and prenatal care received. The χ² test was used to compare proportions and Poisson regression with robust adjustment of variance was used in the multivariate analysis. RESULTS: Among the 2,288 respondents, 33% were not submitted to the Pap smear during pregnancy. Two thirds of these women stated that they were not aware of the need to perform it, 18% were not screened out of fear or shame, and the rest for other reasons. After adjustment, the highest prevalence ratios (PR) for noncompliance with the Pap smear occurred among young women (PR=1.5; 95%CI 1.25 - 1.80), with lower educational level (PR=1.5; 95%CI 1.12 - 2.12), who were living without a partner (PR=1.4; 95%CI 1.24 - 1.62), smokers (PR=1.2; 95%CI 1.07 - 1.39), who did not plan the current pregnancy (PR=1.3; 95%CI 1,21 - 1.61), who had attended less than six medical visits during the prenatal period (PR=1.4; 95%CI 1.32 - 1.69) and among users of oral contraceptives (PR=1.2; 95%CI 1.04 - 1.38). CONCLUSIONS: The higher the risk for uterine cervical cancer, the less likely a pregnant woman is to undergo a Pap smear. This definitely contributed to the increased morbidity and mortality from this disease in this setting.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(6):248-253
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000600002
PURPOSE: To verify whether women with atypias of undetermined significance and precursor lesions or invasive cervical outcomes were referred to Medium Complexity Units (MCU) following the guidelines recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. METHODS: Retrospective study based on the cytopathological outcomes of users of the Unified Health System, seen at Basic Health Assistance Units (BHAU) and referred to MCUs in the municipality of Goiânia, state of Goiás, from 2005 to 2006. We assessed 832 records according to the recommendations of the Brazilian Ministry of Health, as established by the Brazilian Nomenclature for Cervical Cytopathologic Outcomes and Recommended Clinical Practice. To check the distribution of variables such as reasons for referral, results of colposcopy and histopathology and clinical procedures we calculated absolute and relative frequencies, mean, minimum and maximum values. RESULTS: We understood 72.7% of the referrals were not in accordance with the recommendations of the Ministry of Health. There were 605 women with test results classified as atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance, possibly non-neoplasms, and squamous intraepithelial lesion of low level which were sent to MCU, and of these 71.8% were submitted to colposcopy, and 64.7% had histopathological examination which results were classified as 31.0% with non-neoplasms and 44.6% as NIC I. Out of 211 women with results classified as more severe squamous lesions, 86.3% were submitted to colposcopy and 68.7% of these had histopathological examinations. CONCLUSIONS: The results of this study revealed high rates of inappropriate referrals to MCU, which required a high percentage of unnecessary procedures. The recommendations of the Ministry of Health were followed by BHAU and the majority of women received counseling/treatment as recommended.