Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 12-17-2021;43(10):736-742
Thyroid diseases are the second most common endocrine disorders in the reproductive period of women. They can be associated with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), preterm delivery, low Apgar score, low birthweight (LBW) or fetal death. The aim of the present study is to explore thyroid dysfunction and its relationship with some poor perinatal outcomes (Apgar Score, low birthweight, and preterm delivery).
Dried blood spot samples from 358 healthy pregnant women were analyzed for thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), total thyroxine (TT4), and thyroglobulin (Tg). Neonatal data were collected upon delivery. Four groups were formed based on thyroid function tests (TFTs).
Of the 358 tested women, 218 (60.72%) were euthyroid. Isolated hypo thyroxinemia was present in 132 women (36.76%), subclinical hyperthyroidism in 7 women (1.94%), and overt hypothyroidism in 1 (0.28%). The perinatal outcomes IUGR (p = 0.028) and Apgar score 1 minute (p = 0.015) were significantly different between thyroid function test [TFT]-distinct groups. In the multiple regression analysis, TT4 showed a statistically significant inverse predictive impact on LBW (p < 0.0001), but a positive impact of Tg on LBW (p = 0.0351).
Thyroid hormones alone do not have a direct impact on neonatal outcomes, but the percentage of their participation in the total process cannot be neglected. Based on the regression analysis, we can conclude that TT4 and Tg can be used as predictors of neonatal outcome, expressed through birthweight and Apgar score. The present study aims to contribute to determine whether a test for thyroid status should become routine screening during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 06-18-2021;43(4):256-263
To investigate the association between prenatal care (PNC) adequacy indexes and the low birth weigth (LBW) outcome.
A total of 368,093 live term singleton births in the state of Rio de Janeiro (Brazil) from 2015 to 2016 were investigated using data from the Brazilian Live Birth Information System (Sistema de Informações sobre Nascidos Vivos, SINASC, in Portuguese). Seven PNC adequacy indexes were evaluated: four developed by Brazilian authors (Ciari Jr. et al., Coutinho et al., Takeda, and an index developed and used by the Brazilian Ministry of Health - MS) and three by authors from other countries (Kessner et al., the Adequacy of Prenatal Care Utilization index - APNCU, and the Graduated Prenatal Care Utilization Index - GINDEX). Adjusted odds ratios were estimated for the PNC adequacy indexes by means of multivariate logistic regression models using maternal, gestational and newborn characteristics as covariates.
When the PNC is classified as “inadequate”, the adjusted odds ratios to the LBWoutcome increase between 42% and 132%, depending on which adequacy index is evaluated. Younger (15 to 17 years old) and older (35 to 45 years old) mothers, those not married, of black or brown ethnicity, with low schooling (who did not finish Elementary School), primiparous, with preterm births, as well as female newborns had increasing odds for LBW. The models presented areas under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve between 80.4% and 81.0%, and sensitivity and specificity that varied, respectively, between 57.7% and 58.6% and 94.3% and 94.5%.
Considering all PNC adequacy indexes evaluated, the APNCU had the best discriminatory power and the best ability to predict the LBW outcome.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 12-01-2018;40(12):749-756
To describe caffeine consumption during pregnancy and its association with low birth weight (LBW) and preterm birth in the birth cohort of Ribeirão Preto, state of São Paulo, Brazil, in 2010.
Cohort study, with descriptive and analytical approach. Data included 7,607 women and their newborns in Ribeirão Preto, state of São Paulo, Brazil. The women answered standardized questionnaires about reproductive health, prenatal care, life habits, sociodemographic conditions, and information about coffee intake. The independent variable was high caffeine consumption (≥300 mg/day) from coffee during pregnancy, and the dependent variables were LBW (birth weight < 2,500 g) and preterm birth (< 37 weeks of gestational age). Four adjusted polytomous logistic regression models, relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were fitted: biological and sociodemographic conditions; obstetric history; current gestational conditions; and all variables included in the previous models.
A total of 4,908 (64.5%) mothers consumed caffeine, 143 (2.9%) of whom reported high consumption. High caffeine intake was significantly associated with reduced education and with the occupation of the head of the family, nonwhite skin color, not having a partner, higher parity, previous abortion and preterm birth, urinary tract infection, threatened abortion, alcohol consumption and smoking. No association was found between high caffeine consumption and LBW or preterm birth in both
In this cohort, high caffeine intake was lower than in other studies and no association with LBW or preterm birth was found.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 08-01-2018;40(8):444-449
To identify maternal factors associated with the presence of low birth weight in term neonates.
Matched hospital-based case-controlled study performed in a high complexity institution located in the city of Neiva, Colombia. The study included women with term gestation and singleton live fetuses. Patients with prior diseases, coming from other regions, with pregnancy resulting from assisted reproduction, or with a diagnosis of fetal abnormality or aneuploidy were excluded. Low birth weight was the dependent variable, and the independent variables that were analyzed were maternal sociodemographic and clinical characteristics. Adjusted and non-adjusted odds ratios (aOR and OR) together with the 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were reported.
The study included 270 participants (90 cases and 180 controls). Controlling for maternal age, educational level, socioeconomic and civil status, social security and the presence of maternal disease during gestation, it was found that weight gain (aOR 0.77, 95% CI 0.70-0.85) and the absence of prenatal care (aOR 8.20, 95% CI 3.22-20.87) were among the factors associated with low birth weight.
The absence of weight gain and of prenatal care are factors associated with the presence of low birth weight in term neonates and should be considered in clinical practice.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 04-01-2016;38(4):189-195
Previous studies have shown that low birth weight (LBW) is associated with cardiovascular risk in late adulthood. Recent studies in adolescents suggest that modifiable factors may have greater influence on increased cardiovascular risk. This study aims to investigate the association between LBW and changes in anthropometric and biochemical risk factors during adolescence in a population with low average socioeconomic status.
In a retrospective double cohort, data of birth weight were extracted from hospital records of children born on the same day between 1992 and 2002. According to the World Health Organization, we classified the children as having LBW or normal birth weight. A total of 172 subjects among children, adolescents and adults were researched. We measured anthropometric and clinical data, lipid profile and glucose after an overnight fasting. The low and normal weight groups were compared using Mann-Whitney U, Fischer exact, Chi-square (2) and Student's t tests.
Pregnant women with preeclampsia delivered more newborns with LBW (p< 0.001). Anthropometric and clinical parameters were similar between groups. No differences were found in the family history of cardiovascular diseases (p= 0.1), family incomes (p= 0.8) and maternal school education (p= 0.8) between groups.
In this study, LBW did not increase cardiovascular disease risk factors in adolescents. We observed absence of association between low birth weight and poor health outcomes among adolescents with low socioeconomic status from an urban city in the Brazilian northeast.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 01-01-2016;38(1):04-08
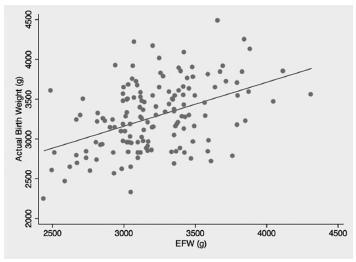
To evaluate the accuracy of fetal weight prediction by ultrasonography labor employing a formula including the linear measurements of femur length (FL) and mid-thigh soft-tissue thickness (STT).
We conducted a prospective study involving singleton uncomplicated term pregnancies within 48 hours of delivery. Only pregnancies with a cephalic fetus admitted in the labor ward for elective cesarean section, induction of labor or spontaneous labor were included. We excluded all non-Caucasian women, the ones previously diagnosed with gestational diabetes and the ones with evidence of ruptured membranes. Fetal weight estimates were calculated using a previously proposed formula [estimated fetal weight = [1] 1687.47 + (54.1 x FL) + (76.68 x STT). The relationship between actual birth weight and estimated fetal weight was analyzed using Pearson's correlation. The formula's performance was assessed by calculating the signed and absolute errors. Mean weight difference and signed percentage error were calculated for birth weight divided into three subgroups: < 3000 g; 3000-4000g; and > 4000 g.
We included for analysis 145 cases and found a significant, yet low, linear relationship between birth weight and estimated fetal weight (p < 0.001; R2 = 0.197) with an absolute mean error of 10.6%. The lowest mean percentage error (0.3%) corresponded to the subgroup with birth weight between 3000 g and 4000 g.
This study demonstrates a poor correlation between actual birth weight and the estimated fetal weight using a formula based on femur length and mid-thigh soft-tissue thickness, both linear parameters. Although avoidance of circumferential ultrasound measurements might prove to be beneficial, it is still yet to be found a fetal estimation formula that can be both accurate and simple to perform.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 01-06-2012;33(10):286-291
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001000003
PURPOSES: To determine the rate of low birth weight and some of the risk factors associated with this event among adolescents. METHODS: A cross-sectional study conducted between October 1994 and December 2009 at a maternity in Campinas, in Brazil, using information generated from the computerized obstetric form. After selection of adolescents who delivered at this hospital, two groups were created, with and without low birth weight, respectively. Relative risk and 95% confidence interval for all independent variables (risk factors) and the Χ2 test for some perinatal results were performed. The level of significance was set at 5%. RESULTS: During the study period, 24,000 births occurred at CAISM. Of these, 2,404 occurred among 2,357 teenagers (10.02%) and the frequency of low birth weight was 15.1%. Adolescent pregnancy recurred in 294 (8.2%). Age less than 15 years-old, anemia, smoking, and hypertension were not significantly associated with low birth weight. Antecedent of miscarriage and association with systemic lupus erythematosus increased the risk of low birth weight. Cesarean section and an Apgar score below seven were more prevalent among adolescents with low birth weight, and 85% of all adolescents had less than six prenatal visits. CONCLUSIONS: The prevalence of low birth weight is higher among adolescents than among adult women, and there was a large number of adolescents with less than six prenatal visits . The antecedent of miscarriage and the presence of systemic lupus erythematosus were risk factors associated with the occurrence of low birth weight among adolescents.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 07-05-2004;26(3):177-184
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000300002
PURPOSE: to assess the use of antenatal corticosteroid (AC) by mothers and its repercussion on the birth conditions of preterm babies at the eight university neonatal units belonging to the Brazilian Network of Neonatal Research. METHODS: an observational prospective cohort study. All 463 pregnant women with a gestational age (GA) of 23 to 34 weeks and their 514 newborn babies were evaluated during the period from August 1 to December 31, 2001. The data were obtained by maternal interview, by the analysis of the medical records and by the follow-up of the newborn infants, and analyzed statistically using chi2, Mann-Whitney and ANOVA tests and multiple logistic regression, with the level of significance set at 0.05. RESULTS: 60.1% (282/463) of the pregnant women (a variation from 12.5 to 87.3% among units) received at least one AC dose. The AC use was directly associated with the number of prenatal visits, with maternal hypertension and with the antenatal use of tocolytic agents. Babies from treated pregnant women presented higher birth weight (1,379±421 vs 1,244±543 g), longer gestational age (30.9±2.0 vs 29.5±3.5 weeks), better Apgar scores at the 1st and 5th minute, and a reduced need for intervention in the delivery room. The use of AC, the GA and a baby small for GA independently improved the birth conditions. CONCLUSIONS: at most centers, AC was administered at frequencies below the desired ones, and in 50% of cases in an inadequate manner. Treatment was applied more to mothers who received appropriate prenatal care and was associated with better birth conditions.
