Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(9):625-630
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000900002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the nutritional condition of pregnant adolescents using the pregestational body mass index (BMI) and the BMI at the end of pregnancy and to establish a possible association with the type of delivery and weight of the newborn child. METHODS: in a descriptive retrospective observational study 558 pregnant teenagers as well as their newborns were evaluated in the Obstetrics outpatient clinic of the Universidade Federal de São Paulo, Brazil (UNIFESP-EPM), from January 1998 to December 2000. The sample consisted of pregnant girls who were between 10 and 19 years old at the time of the first prenatal examination, excluding the teenagers who had preexistent disease and those with incomplete data in their records. Thus, the sample consisted of 300 pregnant teenagers. Qualitative variables are presented as absolute and relative frequency and quantitative variables as mean, standard deviation and range. The correlation between maternal variables (pre-pregnancy BMI and final BMI) and parameters of the newborn (type of delivery and weight) was determined by the c² test and the differences were identified by partitioning of the c² values, with the level of significance set at p < 0.05 (a = 0.05). RESULTS: nutritional deviation was detected in 34.7% of the girls, at the beginning of pregnancy. Of these adolescents, 27.7% presented malnutrition, 4% were overweight and 3% were obese. By the end of the gestational period, BMI of 54.3% of them was normal, 1.3% correponded to malnutrition, 27% to overweight and 17.3% to obesity. The mother's nutritional condition (malnutrition, normal, overweight and obesity) did not affect the method of delivery, either vaginal (80.3%) or cesarean section (19.7%). The patients who reached end of pregnancy with BMI corresponding to malnutrition had 75% of neonates under 2.500 g. CONCLUSIONS: the mother's nutritional status was not related to the type of delivery. BMI corresponding to malnutrition at the end of pregnancy was significantly related to more cases of newborn babies under 2.500 g.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(8):513-519
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000800003
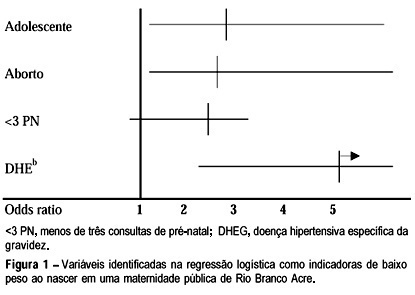
Purpose: to study pregnancy in adolescent women as a possible risk factor for low birth weight. Material and Methods: a cross-wide study was performed on 562 adolescent and non-adolescent mothers who were interviewed during the first 24 h after delivery in the period from January 10,2002, to March 25, 2002, in a public maternity hospital located in Rio Branco, Acre State, Brazil. Those who delivered dead fetuses, whose babies died after being born, or had twins were excluded from the study. Results: among the 562 mothers who were studied, 37.0% (n=208) were teenagers (16±1.6 years), and 63.0% (n=354) were 20 or more years old (22.9±6.3 years). The average weight of the newborns was statistically higher (p<0.010) among the adult mothers (3,158.64±626.50 g) than among the adolescent mothers (3,019.93±587.43 g). When the 32 (5.7%) premature newborn babies (<37 week's pregnancy) were excluded, there was also a significantly greater proportion (p<0.007) of newborns with low weight (<2,500 g) among the adolescent mothers (11.9%) than among the non-adolescent ones (5.5%). The analysis of logistic regression showed an increased risk for newborns with low weight among the adolescent mothers (OR=2.99; 1.47-6.07), as well as for abortion (OR=2.78; 1.23-6.30) and pregnancy - induced hypertensive disorders (OR=5.16; 1.65-16.12). Conclusions: the present study shows that associated with the psychosocial, familial, and economic impact, already reported in the literature, pregnancy in adolescents is associated with deleterious effects on the conceptus, which requires a cohort study to assess the repercussions at both the medium- and long-term.