-
Systematic Review12-01-2017
Is Pethidine Safe during Labor? Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):686-691
Abstract
Systematic ReviewIs Pethidine Safe during Labor? Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(12):686-691
Views142See moreAbstract
Purpose
To verify if pethidine is safe for the conceptus when used during labor.
Methods
Systematic review in the Capes Periodicals/PubMed and MEDLINE/Virtual Health Library (BVS, in the Portuguese acronym) databases.
Results
A total of 17 studies published from January 1st, 2000, to September 2nd, 2016, with a total of 1,688 participants involved were included in the present review. There was no record of conceptus vitality decrease associated with low doses of pethidine being administered to mothers during labor.
Conclusions
Intramuscular (IM) or intravenous (IV) pethidine at low doses, of up to 50 mg, is safe to administer during labor.
-
Original Article05-01-2017
Assistance to Normal Delivery in Two Public Maternities: Perception of the Health Professionals
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):202-208
Abstract
Original ArticleAssistance to Normal Delivery in Two Public Maternities: Perception of the Health Professionals
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):202-208
Views142See moreAbstract
Purpose
To evaluate the perception of health professionals involved in the labor process and theassistanceto normal delivery, comparing two hospitals in the cityof Goiânia, Brazil, regarding the perception of theseprofessionals when they are performing the routines and practices recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Methods
This is an analytical comparative study with a quantitative approach, performed in two public hospitals in the city of Goiânia, in the state of Goiás, Brazil. The study included 86 professionals working in assistance to immediate labor in two hospitals. A questionnaire containing 40 questions was applied. The questionnaire related to the Program for the Humanization of Prenatal and Childbirth Care (PHPN, in the Portuguese acronym) of the Brazilian Ministry of Health, the presence of a companion, and the procedures performed. For the data analysis, we used the chisquare and Fisher’s exact tests.
Results
Most of the professionals claimed to know about the PHPN proposed by Brazilian Ministry of Health in the two hospitals. With regard to good practices, most professionals said that they are performed in maternity ward 2, while on maternity 1, although many of them are present, there are still many unnecessary interventions.
Conclusion
When comparing the two maternity hospitals, maternity 2, which was created as a routine humanization model, manages to better adhere to the WHO recommendations. In maternity 1, there was a series of interventions considered by the WHO as ineffective, or used in an inappropriate manner.
-
Original Article11-01-2016
Analysis of the Construct Validity and Internal Consistency of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) State-Anxiety (S-Anxiety) Scale for Pregnant Women during Labor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(11):531-537
Abstract
Original ArticleAnalysis of the Construct Validity and Internal Consistency of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) State-Anxiety (S-Anxiety) Scale for Pregnant Women during Labor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(11):531-537
Views208See moreAbstract
Purpose
To analyze the internal consistency and the construct validity of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI) State-Anxiety (S-Anxiety) scale for pregnant women during labor.
Method
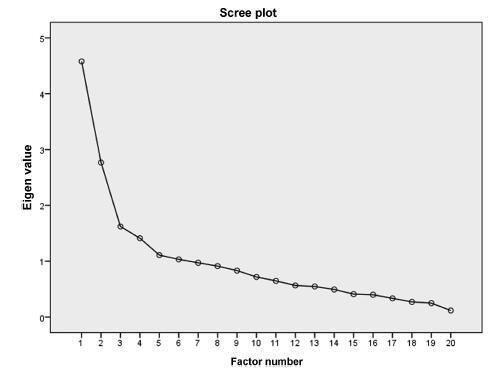
A study of measurement property including 150 pregnant women aged between 15 and 45 years old, during the first period of labor and with term pregnancies. The questionnaire used was the STAI S-Anxiety scale. In order to assess the internal consistency, Cronbach’s α was calculated through an exploratory factor analysis. The correlation between the factors was calculated using the Pearson coefficient. The state of significance used for this analysis was 0.05.
Results
The STAI S-Anxiety scale used in the context of labor showed two factors represented as the absence (factor 1) and the presence of anxiety (factor 2); item 4 (“I regret it”) did not show a representative value. Both factors showed high indications of Cronbach’s α, varying from 0.830 for factor 1, and 0.723 for factor 2. In the results of the Pearson coefficient between the two factors, a significant but weak correlation was observed (r = -0.188; p = 0.021).
Conclusion
The STAI S-Anxiety scale used in pregnant women during labor presented appropriate values of internal consistency; however, item 3 did not show a significant factorial value. Therefore, this questionnaire must be applied cautiously and carefully without the use of the item 4 in the clinical practice and in researches about labor.
-
Original Article01-01-2016
Estimation of Fetal Weight during Labor: Still a Challenge
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):04-08
Abstract
Original ArticleEstimation of Fetal Weight during Labor: Still a Challenge
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):04-08
Views180See moreObjective
To evaluate the accuracy of fetal weight prediction by ultrasonography labor employing a formula including the linear measurements of femur length (FL) and mid-thigh soft-tissue thickness (STT).
Methods
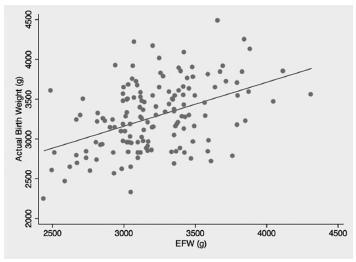
We conducted a prospective study involving singleton uncomplicated term pregnancies within 48 hours of delivery. Only pregnancies with a cephalic fetus admitted in the labor ward for elective cesarean section, induction of labor or spontaneous labor were included. We excluded all non-Caucasian women, the ones previously diagnosed with gestational diabetes and the ones with evidence of ruptured membranes. Fetal weight estimates were calculated using a previously proposed formula [estimated fetal weight = [1] 1687.47 + (54.1 x FL) + (76.68 x STT). The relationship between actual birth weight and estimated fetal weight was analyzed using Pearson's correlation. The formula's performance was assessed by calculating the signed and absolute errors. Mean weight difference and signed percentage error were calculated for birth weight divided into three subgroups: < 3000 g; 3000-4000g; and > 4000 g.
Results
We included for analysis 145 cases and found a significant, yet low, linear relationship between birth weight and estimated fetal weight (p < 0.001; R2 = 0.197) with an absolute mean error of 10.6%. The lowest mean percentage error (0.3%) corresponded to the subgroup with birth weight between 3000 g and 4000 g.
Conclusions
This study demonstrates a poor correlation between actual birth weight and the estimated fetal weight using a formula based on femur length and mid-thigh soft-tissue thickness, both linear parameters. Although avoidance of circumferential ultrasound measurements might prove to be beneficial, it is still yet to be found a fetal estimation formula that can be both accurate and simple to perform.
-
Original Article08-02-2013
Preference in the process of parturition: a comparison between primiparous and nulliparous women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(6):281-285
Abstract
Original ArticlePreference in the process of parturition: a comparison between primiparous and nulliparous women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(6):281-285
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000600008
Views124See morePURPOSE: It was to describe and compare the preference of nulliparous and primiparous women for a particular mode of delivery and to determine whether the previous experience of childbirth influences the delivery process. METHODS: We conducted a prospective cross-sectional study. One-hundred interviews were held with 56 nulliparous and 44 primiparous women using previously prepared questionnaires. The quantitative and categorical data were evaluated by the chi-square or Fisher's Exact Test. RESULTS: 60.7% of nulliparous women and 70.5% of primiparous women reported to prefer vaginal delivery. When analyzing the answers about receiving sufficient information about the type of delivery, the presence or absence of influence on the choice of route of delivery and the preferred route of delivery by the partner, there were no statistically significant differences between the two groups. The level of significance used for the tests was 0.05. CONCLUSIONS: This study permitted us to conclude that the previous experience of delivery does not influence the expectation of the delivery process or the choice for a specific mode of delivery. When choosing the route of delivery, women seek to ensure the health of mother and neonate, as well as to avoid the process of pain and suffering.
-
Original Article01-06-2011
Evaluation of the quality of care for normal delivery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(10):297-304
Abstract
Original ArticleEvaluation of the quality of care for normal delivery
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(10):297-304
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001000005
Views82PURPOSE: To evaluate the quality of health care assistance during childbirth in the hospitals of Goiânia, in Brazil. METHODS: Thirteen hospitals were appraised from April to December 2007, and a random sample of 404 normal births was studied. Data were obtained from interviews with mothers after delivery and by consulting their medical records. The quality of assistance at birth was evaluated by using the Bologna score and by comparing the procedures used in those hospitals to standard recommended practices. RESULTS: The Bologna score presented an average value of 1.04 (95%CI=0.9-1.1). The elective caesarian rate was 30%, the emergency caesarian rate was 10%, and the rate of induced childbirth was 1.6% The percentage of childbirths attended by health care professionals was 100%, but pediatricians in the delivery room were present only in 30% of the time. During labor, half of the women had no evaluation of the uterine dynamics and 29% had no auscultation fetal monitoring. The partogram was used for only 28.5% of the women, whereas the use of oxytocin was 45.8%. CONCLUSIONS: The results indicate a poor quality of childbirth care with low values of the Bologna score, high elective and emergency caesarians rates, a high number of unnecessary and potentially harmful interventions, and an insufficient frequency of beneficial interventions.
Key-words Cross-sectional studiesDelivery of health careHealth services evaluationLaborNatural childbirthobstetricSee more -
Original Article04-10-1998
Obstetrical management of fetal death
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):145-149
Abstract
Original ArticleObstetrical management of fetal death
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):145-149
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300004
Views183See moreAlthough 80 to 90% of all dead fetuses may be spontaneously eliminated after two to three weeks from death, labor induction has been the mostly used management. The purpose of the current study was to evaluate the results of labor induction for pregnancies with fetal death and gestation age above 20 weeks. It was a descriptive clinical study which was performed at the Hospital e Maternidade Leonor Mendes de Barros in São Paulo, Brazil. One hundred and twenty-two pregnancies with fetal death were evaluated regarding their social and demographic characteristics, causes of fetal death, previous pregnancies history and delivery (induction, route, complications). The statistical procedures used were estimation of mean and standard deviation and chi². The main causes of fetal death were hypertension and infections. The mostly used drug for labor induction was misoprostol (37.7%) followed by oxytocin (19.7%), while 27% of cases had spontaneous onset of labor. The mean time of induction was 3 hours. The majority of women had vaginal delivery and cesarean section was performed in 9.1% of them. It is concluded that labor induction for fetal death is safe and efficient, irrespective of the method used. Misoprostol when used in the vagina is specially useful for cases with an unripe cervix because of the modifying effect of the drug on the cervix.
-
Original Article08-07-1999
Amnioinfusion during labor with meconium-stained amniotic fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):389-392
Abstract
Original ArticleAmnioinfusion during labor with meconium-stained amniotic fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1999;21(7):389-392
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031999000700004
Views73See morePurpose: to report the personal experience with the use of the amnioinfusion technique in patients in labor presenting meconial amniotic fluid, and the incidence of complications, the meconium aspiration syndrome and of cesarean sections. Method: twenty patients at term and in labor with meconial amniotic fluid were evaluated retrospectively, at the delivery ward at two public institutions of Rio Grande do Sul. An initial infusion of 1.000 ml of normal saline solution at room temperature, at an infusion rate of 20-30 ml per minute was initiated and then reduced to 3 ml per minute. The liquid was drained by elevating the cephalic pole. Results: the procedure was feasible when a nasogastric catheter was used. None of the patients presented major complications related to the procedure. None of the neonates presented meconium below their vocal cords. The cesarean section rate was 3/20 (15%). Conclusion: the amnioinfusion is a low-cost and feasible technique that did not show any complication in this study.


