Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo84
12-04-2024
Included evaluation of the possibility of using the systemic inflammatory indices for preoperative screening for the presence and severity of endometriosis (EM) in comparison to the findings of the exploratory laparoscopy
88 women with clinical manifestations suggestive of EM were evaluated clinically and by US and gave blood samples for estimation of serum cancer antigen-125 (CA125), platelet and total and differential leucocytic counts for calculation of inflammatory indices; the Systemic Immune-Inflammation index, the Systemic Inflammation Response Index (SIRI), the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte ratio (NLR), the Neutrophil-Monocyte ratio, the Neutrophil-Platelet ratio and the Platelet-Lymphocyte ratio. Then, patients were prepared to undergo laparoscopy for diagnosis and staging.
Laparoscopy detected EM lesions in 63 patients; 27 of stage I-II and 36 of stage III-IV. Positive laparoscopy showed significant relation with US grading, high serum CA125 levels, platelet and inflammatory cell counts and indices. Statistical analyses defined high SIRI and NLR as the significant predictors for positive laparoscopy and high serum CA125 and NLR as the most significant predictors for severe EM (stage III-IV) on laparoscopy
The intimate relation between EM and inflammation was reflected systematically as high levels of blood cellular components, but indices related to neutrophil especially NLR and SIRI showed highly significant relation to the presence and severity of EM and might be used as routine, cheap and non-invasive screening test before exploratory laparoscopy to guide the decision-making.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo42
06-27-2024
To evaluate the effects of surgical treatment of deep endometriosis on the metabolic profile, quality of life and psychological aspects.
Prospective observational study, carried out with women of reproductive age diagnosed with deep endometriosis, treated in a specialized outpatient clinic, from October/2020 to September/2022, at a University Hospital in Fortaleza - Brazil. Standardized questionnaires were applied to collect data on quality of life and mental health, in addition to laboratory tests to evaluate dyslipidemia and dysglycemia, at two moments, preoperatively and six months after surgery. The results were presented using tables, averages and percentages.
Thirty women with an average age of 38.5 years were evaluated. Seven quality of life domains showed improved scores: pain, control and impotence, well-being, social support, self-image, work life and sexual relations after surgery (ES ≥ 0.80). There was an improvement in mental health status with a significant reduction in anxiety and depression postoperatively. With the metabolic profile, all average levels were lower after surgery: total cholesterol 8.2% lower, LDL 12.8% lower, triglycerides 10.9% lower, and fasting blood glucose 7.3% lower (p < 0.001).
Surgical treatment of deep endometriosis improved the quality of life and psychological aspects of patients. The lipid profile of patients after laparoscopy was favorable when compared to the preoperative lipid profile.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):780-789
01-11-2023
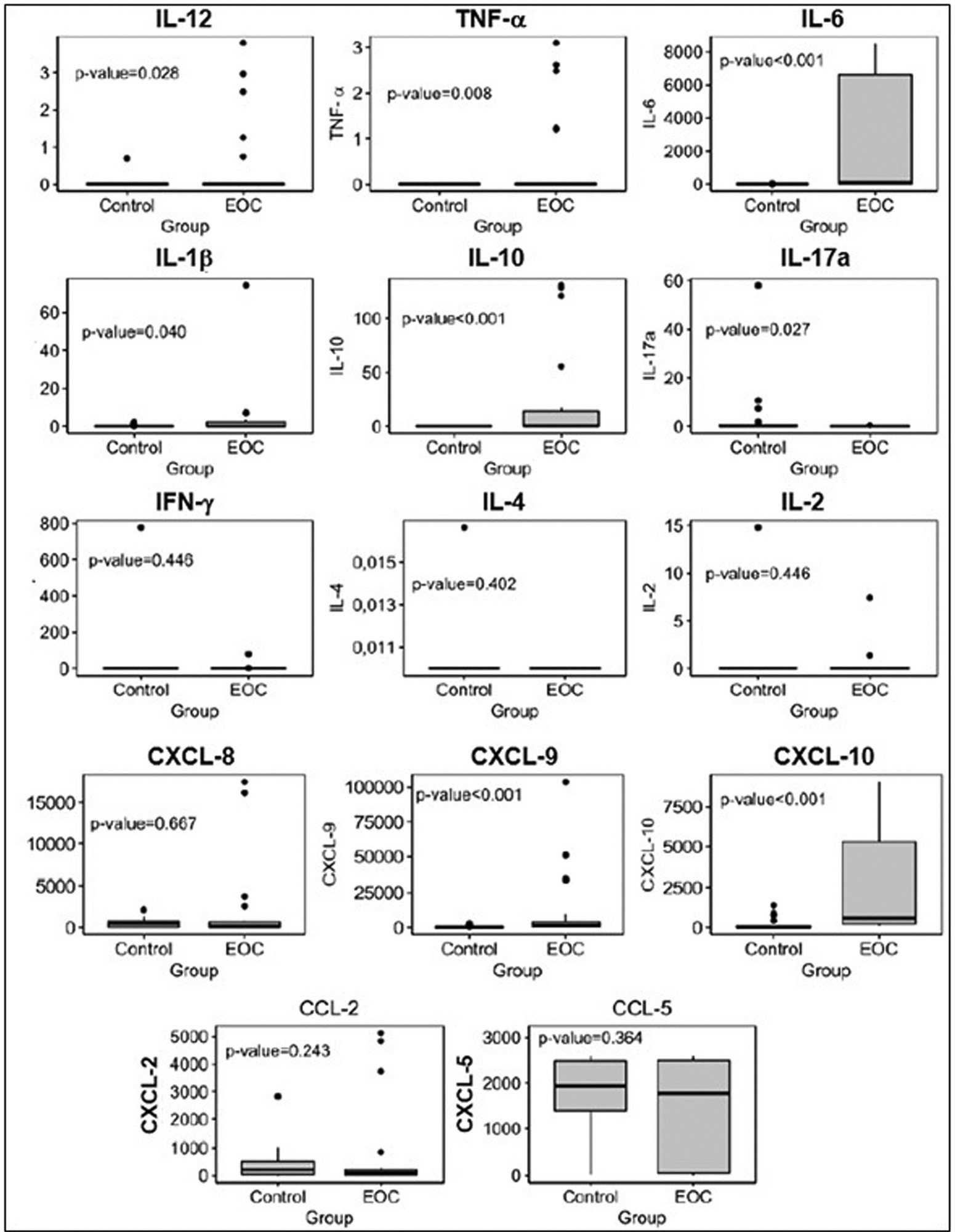
To compare the patterns of systemic inflammatory response in women with epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) or no evidence of malignant disease, as well as to evaluate the profile of systemic inflammatory responses in type-1 and type-2 tumors. This is a non-invasive and indirect way to assess both tumor activity and the role of the inflammatory pattern during pro- and antitumor responses.
We performed a prospective evaluation of 56 patients: 30 women without evidence of malignant disease and 26 women with EOC. The plasma quantification of cytokines, chemokines, and microparticles (MPs) was performed using flow cytometry.
Plasma levels of proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-12 (IL12), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), and interleukin-10 (IL-10), and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9 (CXCL-9) and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL-10) were significantly higher in patients with EOC than in those in the control group. Plasma levels of cytokine interleukin-17A (IL-17A) and MPs derived from endothelial cells were lower in patients with EOC than in the control group. The frequency of leukocytes and MPs derived from endothelial cells was higher in type-2 tumors than in those without malignancy. We observed an expressive number of inflammatory/regulatory cytokines and chemokines in the cases of EOC, as well as negative and positive correlations involving them, which leads to a higher complexity of these networks.
The present study showed that, through the development of networks consisting of cytokines, chemokines, and MPs, there is a greater systemic inflammatory response in patients with EOC and a more complex correlation of these biomarkers in type-2 tumors.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):429-435
06-02-2021
To evaluate serum levels of adiponectin in pregnant adolescents between 30 and 36 weeks of gestation.
A prospective cross-sectional study enrolled 67 normal pregnant women between 30 and 36 weeks of gestation and eutrophic (body mass index [BMI]: 18.5-25 kg/m2), of which 36 were adolescents (< 20 years old) and 31 adults (≥ 20 years old). Serum adiponectin levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The t-student or Mann-Whitney tests were used for intergroup comparison.
Pregnant adolescents showed significantly higher serum adiponectin concentrations comparedwith pregnant adults (p=0.04). No differences were observed in adiponectin levels in younger pregnant adolescents (< 16 years old) compared with older pregnant adolescents (≥ 16 years old). Adiponectin values were divided into 3 subgroups:<3,000 ng/mL, between 3,000 and 5,000 ng/mL, and>5,000 ng/mL. Birthweight was significantly higher in women>5,000 ng/mL when compared with<3,000 ng/mL in the adolescent group. No association between pregestational adiponectin levels and BMI, gestational weight gain, and gestational age was observed; however, there was a positive relation with birthweight (p=0.0239).
Serum adiponectin values in pregnant adolescents between 30 and 36 weeks of gestation were higher compared with pregnant adults; however, no differences between younger and older pregnant adolescents were observed.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(11):602-607
11-01-2017
To investigate the level of anxiety and its relationship with interleukin (IL)- 10 (anti inflammatory cytokine that modulates mood swings) in a group of female soccer players.
Fifty-two eumenorrheic soccer players were evaluated (age 19.8 ± 4.7 years). The presence of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and phases of the menstrual cycle were determined by a daily symptomreport (DSR) kept for 3 consecutivemonths. The concentration of cytokine IL-10 was determined from urine samples collected at four moments: at the follicular and luteal phases of the menstrual cycle, and before (pre) and after (post) the simulated game, and it was quantified by flow cytometry (Luminex xMAP - EMDMillipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The level of anxietywas determined through the BAI anxiety questionnaire answered by all athletes at the same time of the urine collection. The Student t-test, analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Pearson correlation with significance level at 5% were used for data analysis.
We showed that the prevalence of PMS among female soccer players is similar to that reported in the literature. In addition,we showed that the group withPMS has a higher level of anxiety compared with group without PMS (p = 0.002). Interleukin-10 analysis in players without PMS revealed that there was a significant decrease in the level of this cytokine before the game during the luteal phase when compared with the follicular phase (p < 0.05). The correlation analysis between IL-10 and anxiety showed a negative correlation post-game in the luteal phase in the group without PMS (p = 0.02; r = -0.50) and a positive correlation post-game in the luteal phase in PMS group (p = 0.04; r = 0.36).
Our results suggest that IL-10 may contribute to reduce anxiety in the group without PMS. This could be attributed to the fact that no IL-10 variation was observed in the group with PMS, which presented higher anxiety symptoms when compared with the group without PMS.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(7):317-324
07-01-2016
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in post menopausal women, and inflammation is involved in the atherosclerosis process.
to assess whether dietary pattern, metabolic profile, body composition and physical activity are associated with low-grade chronic inflammation according to highsensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) levels in postmenopausal women.
ninety-five postmenopausal participants, with no evidence of clinical disease, underwent anthropometric, metabolic and hormonal assessments. Usual dietary intake was assessed with a validated food frequency questionnaire, habitual physical activity was measured with a digital pedometer, and body composition was estimated by bioelectrical impedance analysis. Patients with hs-CRP ≥ 10 mg/L or using hormone therapy in the last three months before the study were excluded from the analysis. Participants were stratified according to hs-CRP lower or ≥3 mg/L. Sedentary lifestyle was defined as walking fewer than 6 thousand steps a day. Two-tailed Student's t-test, Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney U or Chi-square (x 2) test were used to compare differences between groups. A logistic regression model was used to estimate the odds ratio of variables for high hs-CRP.
participants with hs-CRP ≥ 3 mg/L had higher body mass index (BMI), body fat percentage, waist circumference (WC), triglycerides, glucose, and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) (p = 0.01 for all variables) than women with hs-CRP <3 mg/L. Also, women with hs-CRP ≥3 mg/L had a higher glycemic load diet and lower protein intake. Prevalence of sedentary lifestyle (p < 0.01) and metabolic syndrome (p < 0.01) was higher in women with hs-CRP ≥3 mg/L. After adjustment for age and time since menopause, the odds ratio for hs- CRP ≥3 mg/L was higher for sedentary lifestyle (4.7, 95% confidence interval [95%CI] 1.4-15.5) and carbohydrate intake (2.9, 95%CI 1.1-7.7).
sedentary lifestyle and high-carbohydrate intake were associated with low-grade chronic inflammation and cardiovascular risk in postmenopause.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(12):609-616
04-13-2010
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010001200008
Preeclampsia is a systemic syndrome characterized by inflammatory and antiangiogenic states. The pathogenesis of preeclampsia involves deficient trophoblast invasion that is responsible for altered uterine blood flow and placental oxidative stress. The damaged placenta produces higher concentrations of sFlt-1, a soluble receptor for VEGF and PlGF that is released in the maternal circulation and is involved in endothelial dysfunction. Actually, all processes involved in inflammation, endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress are strongly correlated and act in a synergistic way. Recent data have shown that an increase in serum concentrations of sFlt-1 initiates 5 to 6 weeks before the clinical manifestations of preeclampsia and these alterations correlate with a decrease in serum concentrations of PlGF. Therefore, both sFlt-1 and PlGF have been suggested to be useful for an early-diagnosis of preeclampsia. The knowledge about the role of antiangiogenic factors in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia has raised the possibility of a therapy involving these factors.In this article we revisited the pathogenesis of preeclampsia addressing its antiangiogenic and inflammatory states.In conclusion, we correlated these alterations with the higher risk for cardiovascular diseases presented by these women in future life.