Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):165-171
To describe the obstetric outcomes of patients withmultiple sclerosis (MS) and the impact of pregnancy and the postpartum period on the progression of the disease.
A case series study performed between December 2019 and February 2020, reporting pregnancies occurred between 1996 and 2019. The subjects included were women with MS undergoing follow-up at an MS referral center in Northeastern Brazil, and who had at least one pregnancy after the onset of MS symptoms, or who had their first relapse in the first year after delivery.
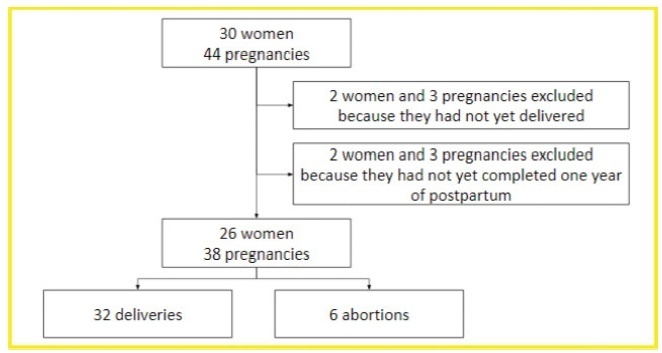
In total, 26 women and 38 pregnancies were analyzed - 32 of them resulted in delivery, and the remaining 6, in miscarriages. There was a significant increase in the prevalence of relapse during the postpartum period when compared with the gestational period. In 16 (42.1%) of the pregnancies, there was exposure to diseasemodifying therapies (DMTs) - 14 (36.8%), to interferon β, and 2 (5.3%), to fingolimod. Higher rates of abortion, prematurity and low birth weight were reported in the group was exposed to DMT when compared with the one who was not.
In the sample of the present study, there was a significant increase in the rate of MS relapse during the postpartum period when compared with the gestational period. Additionally, it seems that exposure to DMTs during pregnancy may affect the obstetric outcomes of the patients.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(12):544-549
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012001200003
PURPOSE: To describe the epidemiological cases and microbiological profile of Streptococcus agalactiae serotypes isolated from infected newborns of a Women's Health Reference Centre of Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil. METHODS: Cross-sectional laboratory survey conducted from January 2007 to December 2011. The newborns' strains, isolated from blood and cerebrospinal fluid samples, were screened by hemolysis on blood ágar plates, Gram stain, catalase test, CAMP test, hippurate hydrolysis or by microbiological automation: Vitek 2 BioMerieux®. They were typed by PCR, successively using specific primers for species and nine serotypes of S. agalactiae. RESULTS: Seven blood samples, one cerebrospinal fluid sample and an ocular sample, were isolated from nine newborns with infections caused by S. agalactiae, including seven cases of early onset and two of late onset. Only one of these cases was positive for paired mother-child samples. Considering that 13,749 deliveries were performed during the study period, the incidence was 0.5 cases of GBS infections of early onset per 1 thousand live births (or 0.6 per 1 thousand, including two cases of late onset) with 1, 3, 2, zero and 3 cases (one early and two late onset cases), respectively, for the years from 2007 to 2011. It was possible to apply PCR to seven of nine samples, two each of serotypes Ia and V and three of serotype III, one from a newborn and the other two from a paired mother-child sample. CONCLUSIONS: Although the sample was limited, the serotypes found are the most prevalent in the literature, but different from the other few Brazilian studies available, except for type Ia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2012;34(5):235-242
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032012000500008
PURPOSE: To evaluate the survival and complications associated with prematurity of infants with less than 32 weeks of gestation. METHODS: It was done a prospective cohort study. All preterm infants with a gestational age between 25 and 31 weeks and 6 days, born alive without congenital anomalies and admitted to the NICU between August 1st, 2009 and October 31st, 2010 were included. Newborns were stratified into three groups: G25, 25 to 27 weeks and 6 days; G28, 28 to 29 weeks and 6 days; G30, 30 to 31 weeks and 6 days, and they were followed up to 28 days. Survival at 28 days and complications associated with prematurity were evaluated. Data were analyzed statistically by c² test, analysis of variance, Kruskal-Wallis test, odds ratio with confidence interval (CI) and multiple logistic regression, with significance set at 5%. RESULTS: The cohort comprised 198 preterm infants (G25=59, G28=43 and G30=96). The risk of death was significantly higher in G25 and G28 compared to G30 (RR=4.14, 95%CI 2.23-7.68 and RR=2.84, 95%CI: 1.41-5.74). Survival was 52.5%, 67.4% and 88.5%, respectively. Survival was greater than 50% in preterm >26 weeks and birth weight >700 g. Neonatal morbidity was inversely proportional to gestational age, except for necrotizing enterocolitis and leukomalacia, which did not differ among groups. Logistic regression showed that pulmonary hemorrhage (OR=3.3, 95%CI 1.4-7.9) and respiratory distress syndrome (OR=2.5, 95%CI 1.1-6.1) were independent risk factors for death. There was a predominance of severe hemorrhagic brain lesions in G25. CONCLUSION: Survival above 50% occurred in infants with a gestational age of more than 26 weeks and >700 g birth weight. Pulmonary hemorrhage and respiratory distress syndrome were independent predictors of neonatal death. It is necessary to identify the best practices to improve the survival of extreme preterm infants.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(10):286-291
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001000003
PURPOSES: To determine the rate of low birth weight and some of the risk factors associated with this event among adolescents. METHODS: A cross-sectional study conducted between October 1994 and December 2009 at a maternity in Campinas, in Brazil, using information generated from the computerized obstetric form. After selection of adolescents who delivered at this hospital, two groups were created, with and without low birth weight, respectively. Relative risk and 95% confidence interval for all independent variables (risk factors) and the Χ2 test for some perinatal results were performed. The level of significance was set at 5%. RESULTS: During the study period, 24,000 births occurred at CAISM. Of these, 2,404 occurred among 2,357 teenagers (10.02%) and the frequency of low birth weight was 15.1%. Adolescent pregnancy recurred in 294 (8.2%). Age less than 15 years-old, anemia, smoking, and hypertension were not significantly associated with low birth weight. Antecedent of miscarriage and association with systemic lupus erythematosus increased the risk of low birth weight. Cesarean section and an Apgar score below seven were more prevalent among adolescents with low birth weight, and 85% of all adolescents had less than six prenatal visits. CONCLUSIONS: The prevalence of low birth weight is higher among adolescents than among adult women, and there was a large number of adolescents with less than six prenatal visits . The antecedent of miscarriage and the presence of systemic lupus erythematosus were risk factors associated with the occurrence of low birth weight among adolescents.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(9):240-245
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000900004
PURPOSE: To determine the accuracy of ultrasound in fetal weight estimation and to evaluate maternal and/or fetal factors that could interfere in the result. METHODS: This was a transverse prospective study, involving 106 patients, with 212 fetal weight evaluations, by two observers, within 24 h to delivery. The following parameters were measured: biparietal diameter, head circumference, abdominal circumference, and femoral length. Fetal weight was estimated using the Hadlock formula and the results were compared to birth weight. The maternal factors examined were: weight, BMI, and skin to uterus distance measured by ultrasound, and the fetal factors were: presentation, position, placental localization and thickness, fetal weight, and amniotic fluid index (AFI). RESULTS: There was good correlation between estimated fetal weight and birth weight (R=0.97). In 79.2% and in 92.4% of cases the estimated fetal weight was within 10% and 15% of birth weight, respectively. The only maternal factor that presented a positive correlation with percent error in the estimate of fetal weight was the skin to uterus distance (R³0.56). Fetal weight showed negative correlation with percent error (R>-0.36; p<0.001), with a significant tendency to overestimate fetal weight in the group of very low weight - <1000 g (p<0.05). The AFI showed a low negative correlation with percent error (R=-0.21; p<0.001) with no difference between AFI groups (p=0.516). CONCLUSION: Ultrasound presented good accuracy in the estimation of fetal weight. The error of weight estimate was directly proportional to the skin to uterus distance and inversely proportional to fetal weight. AFI did not interfere significantly in the ultrasound prediction of fetal weight.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(4):157-163
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000400002
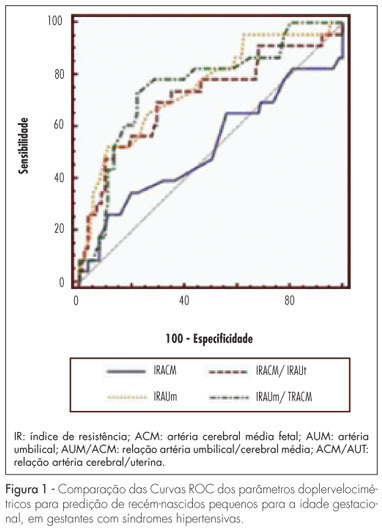
PURPOSE: to determine the best Doppler flow velocimetry index to predict small infants for gestational age (SGAI), in pregnant women with hypertensive syndromes. METHODS: a cross-sectional study was conducted enrolling 129 women with high blood pressure, submitted to dopplervelocimetry up to 15 days before delivery. Women with multiple fetuses, fetal malformations, genital bleeding, placental abruption, premature rupture of fetal membranes, smoking, use of illicit drugs, and chronic diseases were excluded. A receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve for each Doppler variable was constructed to diagnose SGAI and the sensitivity (Se), specificity (Sp), positive (PLR) and negative (NLR) likelihood ratio were calculated. RESULTS: the area under the ROC curve for the middle cerebral artery resistance index was 52% (p=0.79) with Se, Sp, PLR, and NLR of 25.0, 89.1, 2.3 and 0.84% for a resistance index lower than 0.70, respectively. While the area under the ROC curve for the resistance index of the umbilical artery was 74% (p=0.0001), with Se=50.0%, Sp=90.0%, PLR=5.0 and NLR=0.56, for a resistance index higher or equal to 0.70. The area under the ROC curve for the resistance index umbilical artery/middle cerebral artery ratio was 75% (p=0.0001). When it was higher than 0.86, the Se, Sp, PLR and NLR were 70.8, 80.0, 3.4 and 0.36%, respectively. For the resistance index of the middle cerebral artery/uterine artery ratio, the area under the ROC curve was 71% (p=0.0001). We found a Se=52.2%, Sp=85.9%, PLR=3.7 and NLR=0.56, when the ratio was lower than 1.05. When we compared the area under the ROC curve of the four dopplervelocimetry indexes, we observed that only the resistance index umbilical artery/middle cerebral artery, resistance index middle cerebral artery/uterine artery and resistance index umbilical artery ratios seem to be useful for the prediction of SGA. CONCLUSION: in patients with high blood pressure during pregnancy, all dopplervelocimetry parameters, except the middle cerebral artery resistance index, can be used to predict SGAI. The umbilical artery/middle cerebral artery ratio seems to be the most recommended one.